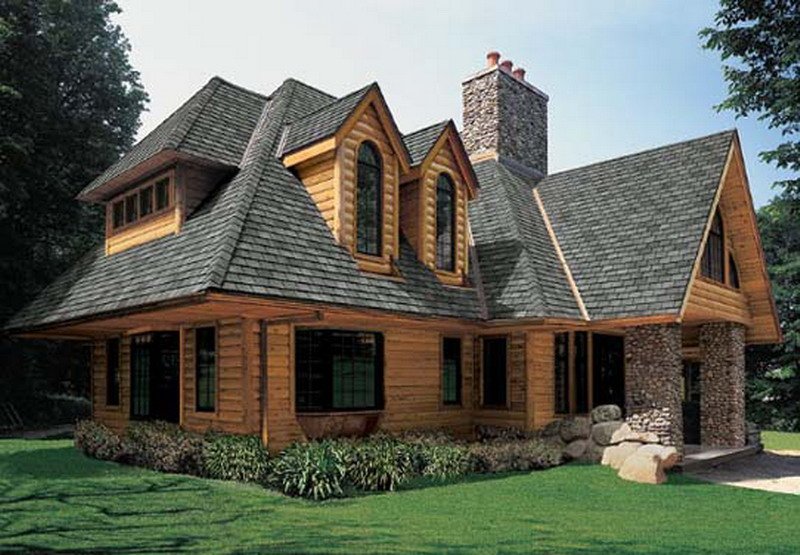
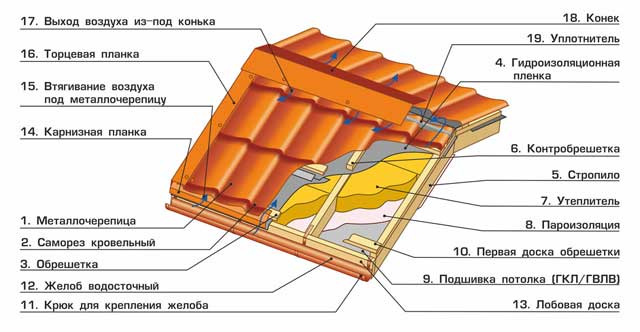
Roof insulation with polystyrene foam
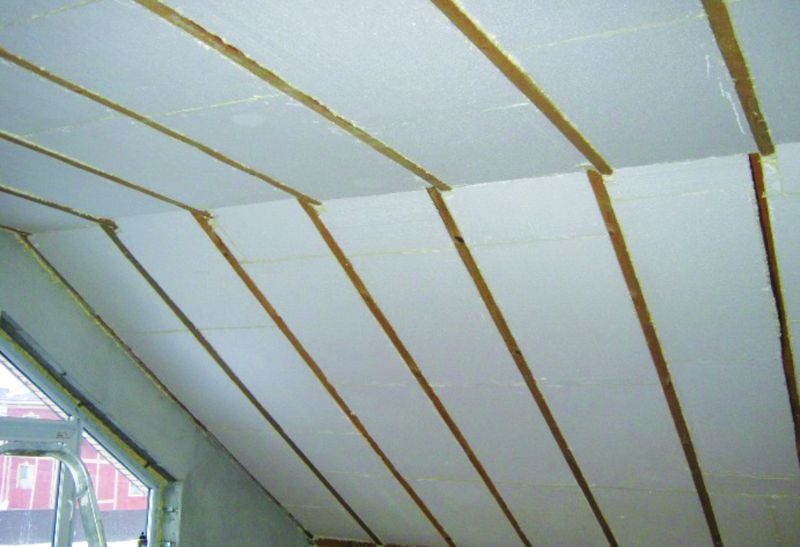
Mineral wool is not the only possible material for thermal modernization of the attic floor. Styrofoam continues to be quite popular.
Its main advantage over mineral wool is its low price. It is quite difficult to insulate slopes with this material; this requires skills and special care.
The slabs must be perfectly cut to fit the space between the rafters. For profiled slabs, the comb will have to be cut off. The rafters themselves should also be even, which is very difficult to achieve.
Rigid polystyrene foam, even sized, can slip over time, so during installation it is necessary to provide for a method of reliable fastening (brackets, dowels, glue).
If gaps remain between the rafters and polystyrene foam, they will subsequently become cold bridges through which warm air will leave the premises, so it is customary to fill them with sealant.
But even with all the precautions, polystyrene foam does not allow you to create a sealed warm attic contour. But when performing thermal insulation of reinforced concrete attic floors, it will become the most practical solution - in this case there is no need to use complex engineering solutions
But when performing thermal insulation of reinforced concrete attic floors, it will become the most practical solution - in this case there is no need to use complex engineering solutions.
The correct scheme of the roofing pie
The roof pie is a multi-layer structure, which includes such components as:
- interior decoration of the under-roof space;
- air ventilation gap;
- vapor barrier film;
- insulation;
- waterproofing;
- crate;
- roofing material.
It also includes gutters, an anti-icing system, fences, snow retainers and decorative roof elements. That is, we can say that the roofing pie is nothing more than the entire roof structure, with the exception of the truss system.
The presence of all these components is optional, the structure of the pie may vary depending on the type of roof, on the roofing used.
For example, a flat roof pie does not include snow retainers and decorative elements; for attic rooms for technical purposes, there is no need for vapor and thermal insulation of the roof.
The device of a roofing pie for metal tiles, corrugated board, for soft roofs or other materials also has some differences.
scheme of a roofing pie for a soft roof made of bituminous tiles
- For soft rolls - a special waterproofing lining made of polypropylene is required.
- For roofs made of metal tiles or profiled sheets, sound insulation is additionally required, otherwise the noise from the rain will create discomfort in the room.
On a note
As you can see, some layers in the roofing cake may be absent, and some, on the contrary, are “dictated” by the features of a particular structure.
Garage slabs
Typically, slabs are used in the construction of a stone garage. They are laid directly on the masonry walls, on a previously laid out layer of cement mortar.
Since the slab is fed by a crane and held by it on weight, it can be easily corrected and put in place as best as possible using crowbars or metal pipes, using them as levers.
After laying the plates in their places, they begin to seal the joints and places of the mounting loops with cement or concrete mortar.
The design of the plates itself is designed in such a way that longitudinal voids are located inside it, which play the role of thermal insulation.But if the roof structure is with an attic space, then the plates should still be covered with a layer of insulating material.
As in the previous case, roofing material, roofing felt or bituminous mastic is laid down in order to protect the insulation material from the penetration of condensate and water vapor.
Any building ends with a roof, which is its highest point. The roof protects the building from atmospheric precipitation, sunlight, winds and frost, in other words, it provides much-needed comfort inside the building. This means that the roof must be stable and strong in order to successfully withstand gusts of wind and rain, protect from the effects of solar radiation, retain heat and be impervious to moisture. Thus, the roof protects buildings from the destruction that occurs as a result of atmospheric action: moisture, freezing and thawing.
Roof knots
In order for the roofing cake to be reliably protected from external influences, special attention should be paid to the places where it adjoins building structures - parapets, walls, pipes, external parts of ventilation systems, etc. There are various flat roof nodes, first of all, this node:
- adjoining;
- overhang;
- passage through the roof.
The nodes are installed on a reinforced concrete base in places where the roofing pie adjoins the vertical structure with a cut. Manufacturers of roofing materials often develop their own systems, which may have certain design features.
The node must ensure the tightness of the joint and its thermal protection, therefore, the installation of the nodes should be taken very carefully.
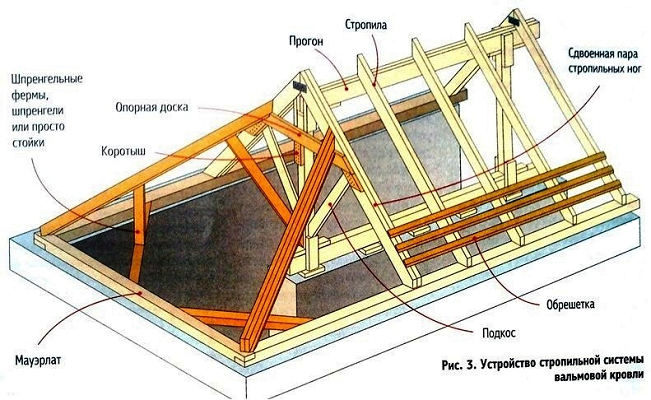
Features of building a hip roof
The design allows you to withstand any wind load, but subject to strict adherence to the geometry of the connection of the four main diagonal rafters.
The accuracy of the connection and geometry of the rafters
All efforts can be in vain if the optimal angles of inclination of the hip rafters to the ceiling and the angle between themselves are violated. The best option is considered to be a scheme in which the corner hip rafters are connected to each other at an angle of 90 °.
The optimal angle between the hip beams is an important but insufficient condition for the strength of the hip roof frame. If you look at the roof frame in profile, both hip planes must have exactly the same size and the same angle of inclination.
Otherwise, the structure will be overloaded on one of the sides, and this is the first step towards deformation and destruction. If you look at the frame from above, you can see that with an ideal assembly, the opposite corner hip rafters should be parallel.
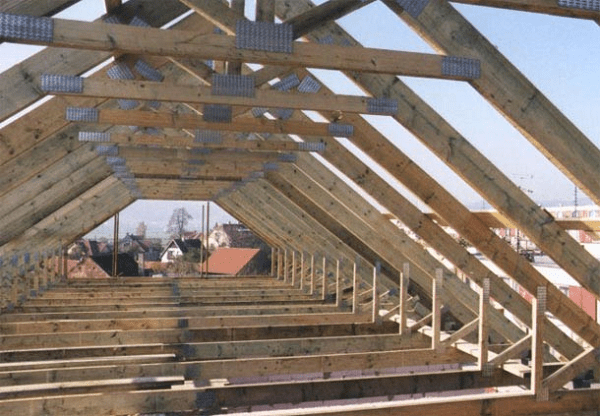
Methods for connecting beams and hip roof rafters
Despite the efforts made to unload part of the structure, it is difficult to make the frame absolutely ideal in terms of the arrangement of beams and load-bearing elements. Therefore, in all main power beams and rafters, metal overlay plates and wooden overhead elements are used when fastening and fixing on walls.
Most often, beams and rafters at the setup stage are “drafted” together, the easiest way to do this is with the help of self-tapping screws and clamps. After adjusting the dimensions of all joints, it is necessary to check the position of the beams and rafters, then all the fasteners are finally connected, it is easier to do this with nails, hammering them in pairs at different angles.
The first to fix the ligaments of the diagonal hips on the ridge run, while the withdrawal from the calculated place of the opposite beams must be verified
This is the most responsible and difficult stage of the assembly of the structure, and it is important to do this procedure slowly and very efficiently. The qualification of a hip roof builder is manifested precisely at this stage, all subsequent work is quite capable of being done by an ordinary carpenter who has a general idea of \u200b\u200bthe device of diagonal rafters and hips
The load on the diagonals of hip roofs exceeds the force on an ordinary rafter by more than one and a half times. Therefore, the adjusted and fixed corner hips are first knocked out with struts and stops. Each of the retaining elements is adjusted individually and is also fastened with reinforcement of the connection.
At the next stage, it is important to correctly install the sprigs and ordinary rafters; upon completion, you need to tighten the fastening of the rafter legs on the Mauerlat or floor beams
Before laying the vapor barrier, it is imperative to treat with preservative solutions. It's easier and safer, you can use the most popular Tikkurila formulations in an organic solvent.
Wooden roof
Wooden roofing belongs to the category of elite. Although it has a century-old history, in our time it can often be found in suburban areas.
A wooden roof has all the main properties of an elite structure: environmental friendliness, a high degree of thermal and sound insulation, a stylish and unique appearance and compliance with the traditions of Russian architecture
Then why the elite? First of all, thanks to the rare properties:
- a wooden roof reliably protects the house from any negative atmospheric phenomena;
- it is environmentally friendly, light, breathable and durable - service life up to 100 years, depending on weather conditions;
- has good sound insulation, frost and wind resistance;
- perfectly retains heat;
- quite strong, wear-resistant, able to withstand significant loads;
-
has an expressive texture, which gives the buildings an exquisite style and exclusivity, a unique color and charm.
And most importantly, the soul of the master lives in it - in every block, plank, carved fragment, from the old Russian shingles to the elegant European Holzschindeln (wooden shindel). The most capricious types of wood submit to the hands of masters. They come to life, turning into products of amazing beauty.
The tree in the hands of a real master seems to come to life, with its help, creations of amazing beauty are created.
But along with its uniqueness, wood roofing also has disadvantages:
- increased risk of fire;
- laboriousness of production and, as a result, high price.
Therefore, not every developer, unfortunately, has the opportunity to build such a beautiful and environmentally friendly roof.
New technologies and an original design approach allow you to experiment and find the most daring solutions for arranging wooden roofs, but not everyone can pay for such beauty.
Drainage from flat roofs
According to the method of organizing drainage, flat roofs can be:
- with an external drain (water discharge along the roof contour)
- with internal drain
The latter is much more difficult, requires calculation and accuracy.
Flat roof with internal drainage
The slope must be perfect, without errors. Sealing of all joints of the roof and outlets of pipes, chimneys, ventilation ducts must be of high quality.

Particular attention should be paid to the tightness of the junctions of the waterproofing carpet to the drain funnels in the center of the roof. Any mistakes will lead to a violation of the integral protection of the waterproofing carpet and leaks.

In practice, when constructing a flat roof of a private house, the old win-win method of checking the slope after installing the carpet is used - water will show no worse than a level. By pouring a bucket of water onto the roof, you can make sure that the slope has the desired degree and direction. If everything is correct, then the water will quickly and unhindered go into the drain funnels.

Flat roof with outdoor drain
The device of an external drain is less costly and technologically simpler. But this option is less popular, as it complicates the operation of flat roofs in winter and autumn - a suspended gutter is more difficult to clean from leaves and debris than a funnel in the center of the roof.In addition, outdoor drainpipes freeze over in winter, and so do roof overhangs. This problem is solved by heating with heating cables, but these are additional costs, including for electricity. Unlike the outer one, the inner drain pipe in the building does not freeze, and there will be no icicles on the overhangs.

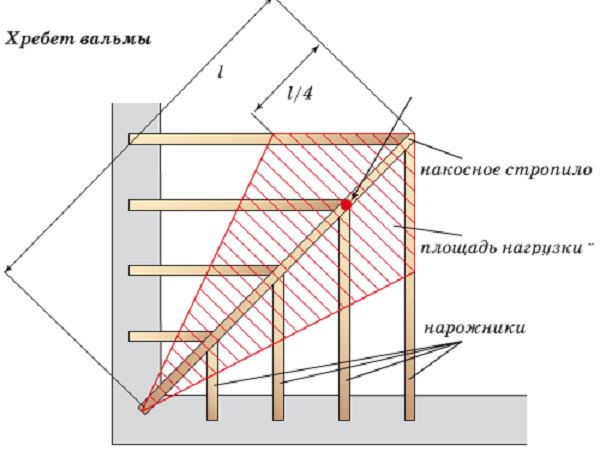
Hip roof supported by floors
Unlike conventional gable roofs, in which the angle of inclination of the flooring can be from 30 - 65 °, hip schemes have an optimal angle of 45 °. Almost all constructions and calculations are performed based on the specified angle of inclination of the main frame elements - diagonal rafters. This option provides maximum structural strength.
The use of layered schemes and supports on the beam ceiling
Most often, such a roof is supported by the lower part of the rafters on a Mauerlat made of timber or thick board, fixed to the upper end of the brick or concrete walls of the future house. Together with the foundation, the walls form a rigid semi-closed system capable of withstanding vertical and horizontal loads from the rafters. Installing a floor from a log, beam or board in such schemes is necessary to form the ceiling and attic floor. The overlap itself does not bear in holding the roof or individual elements of the hip structure.
In the layered construction of truss supports, there is also usually a variant of a ceiling made of wooden beams. With a small size of the house, the specific strength of the floor is enough to partially take on the load from the ridge run and rafters. If the length of the beam increases by more than 5 m, the strength of such an overlap to hold the roof is clearly not enough. Therefore, supporting columns or even part of the walls are built in the central part, on which the central part of the floor beam rests. The load from the ridge run is transmitted through the vertical supports to one powerful central beam, called the bed. Sometimes the force from the weight of the structure is transmitted through the bed directly to the stone supports, without the participation of the ceiling itself.
Thanks to this load redistribution scheme, the rafters can be thinner and lighter, and the pressure on the walls of the house is reduced by 30-40%.
Using joist to hold rafters
Often in the construction of a house, the ability of the main walls to hold the vertical load from the weight of the roof and frame is not always the decisive factor. A similar situation often arises in the construction of panel houses, in buildings with lightweight walls, or when using blocks with low rigidity as the main material for walls, for example, arbolite stone.
In these cases, even partial unloading and transfer of most of the pressure from the weight of the hip roof from the perimeter of the outer walls to the inner stone walls and supports does not solve the problem. The rigidity and strength of the main box of the building is not enough to securely hold even a hip roof, not to mention a gable scheme. The problem of additional rigidity can be solved by making a special overlap of a wooden beam at the base of the roof, with a section of 20x20 cm or 20x15 cm. The beams are laid on top of the finished Mauerlat, with a projection beyond the walls by 60-70 cm, in increments of half a meter. The overlap of the beam must be supported by one of the internal walls.
The ends of the beam protruding beyond the walls are used to fasten the lower parts of the rafter legs, and in the central part of the ceiling a frame with supports supporting the ridge run and the upper part of the rafters is installed. The main part of the structure - diagonal rafters are installed at the corners of the floor and connected at one point on the ridge run.
Hip roofs with supports on floor slabs
Constructions with hip triangles have long become an obligatory attribute of two or three-story brick and stone cottages built according to classical technology with reinforced concrete slab ceilings. Due to the high strength of slabs and brick walls, the problem of providing the required rigidity of the supporting surface for the frame is not worth it.
To hold the weight of the frame, the same scheme is used as in the layered version. A frame with vertical struts and struts, which takes the force from the ridge beam and rafters, rests on a bed fixed on a concrete floor slab.
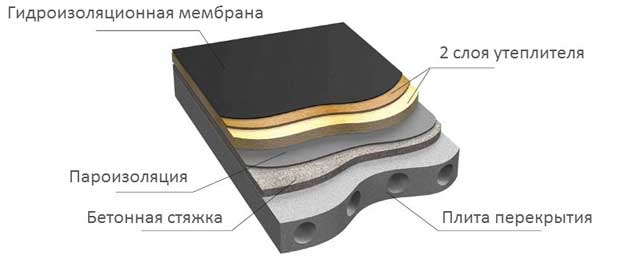
Flat roof insulation technology and basic materials for thermal insulation
Flat roof insulation is considered a complex technological process, one of the important components of which is the use of high-quality modern materials.
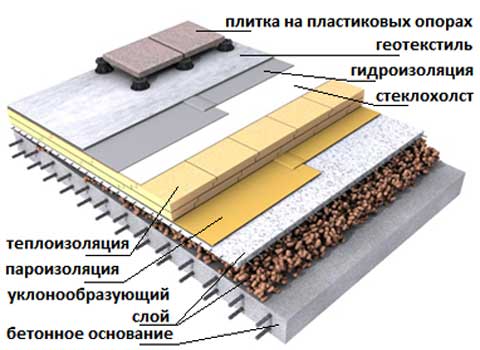
The approximate composition of the heat-insulating "pie" for a flat roof looks like this:
- Floor slab made of profiled sheet or reinforced concrete.
- Vapor barrier coating.
- Thermal insulation layer. As a rule, mineral wool boards or expanded polystyrene are used, which are laid in one, possibly several layers.
- In the case of an exploited roof, a concrete screed is made.
- Sloped waterproofing.
The materials used for thermal insulation of a flat roof must meet the requirements of high vapor permeability, reduced thermal conductivity and water absorption, and fire safety.
Flat roof insulation with mineral wool

Flat roof insulation with polystyrene foam

The density of expanded polystyrene during roof insulation should be at least 35 kg / m2. A layer of waterproofing is mounted under the polystyrene foam plates, and fiberglass is laid on top. The resulting cake is covered with a layer of fine gravel, then paving slabs or asphalt concrete mixture (thickness 5 cm) is laid on the cement mortar.
Expanded polystyrene is also often covered with foam concrete (25 cm), after which a foam-fiber-reinforced concrete screed 3 cm thick is mounted on top of the foam concrete. And only at the end a welded or PVC membrane coating is laid on top.
2019 stylekrov.ru
Materials for insulation
Due to the abundance of thermal insulation materials, the question of choosing the most suitable insulation can be confusing at first. On closer examination, the whole variety of thermal insulation that can be used in this case comes down to three groups:
- mineral wool slabs;
- extruded polystyrene foam (EPS);
- loose mineral heaters.
The roof can be insulated with thick, rigid mineral wool slabs. The density value of the boards should be in the range of 170-230 kg/m3.
The advantages of mineral wool include its incombustibility, the stability of physical and chemical characteristics over time. The light weight, which distinguishes the material, will not play much importance, because.concrete slabs have a very high bearing capacity.
The main disadvantage of mineral wool is its strong water absorption and, as a result, a sharp decrease in thermal insulation characteristics. The insulation layer must be covered with an insulating barrier. Moreover, the roof, insulated with mineral wool, must be protected both from atmospheric precipitation and from moisture rising from the side of the room.
More preferably, the use of extruded polystyrene foam boards. They have great rigidity and are able to withstand mechanical loads, which allows you to create a garage with an exploitable roof. The density of XPS used for flat roofing must be at least 30 kg/m3. You should also give preference to low-combustible grades of material.
The folds made along the perimeter of the plates provide a tight connection of adjacent sheets. The garage is almost completely covered with monolithic thermal insulation.
A very big plus is the structure of the EPS. Closed sealed cells with air, which make up the material, practically do not absorb water. The water absorption coefficient is extremely low. This makes it possible to perform less severe waterproofing than that required for mineral wool.
Concrete slabs, which act as floors, have a very large bearing capacity. The roof is able to withstand significant loads, and restrictions on the weight of the insulation are removed. It becomes possible to use a material such as expanded clay.
Of the advantages of the heater, it is worth mentioning its cheapness and ease of operation. Expanded clay is also afraid of moisture and it is necessary to take appropriate measures to prevent it from getting wet. The backfill layer is leveled, then it needs to be covered with a cement screed, on top of which, after hardening, a carpet of rolled waterproofing materials is applied.
If the roof has a large area, then it is desirable to lay a reinforcing mesh inside the expanded clay layer, it will stiffen the backfill layer and prevent cracking of the cement screed.
The base of the exploited flat roof
In this type of construction, the load is carried by the base, which may consist of concrete slabs, a monolithic structure or profiled metal sheets. The arrangement of the base requires careful design and verification of the angle of inclination, if any. Modern experts recommend providing for a flat roof slope ranging from 2% to 2.5%. Such a slope will ensure the proper flow of water from the roof. This parameter should be taken into account when constructing a roof base.
Vapor barrier layer

A vapor barrier layer is laid on the base, which will protect the roofing pie from the effects of steam generated in the inside of the structure. The layer can be made of polymer-bitumen or bituminous material. When arranging this part of the roofing pie, care must be taken to seal the layers and seams.
The vapor barrier layer can be made using one of two types of materials - film and built-up. In the first case, a film of polypropylene or polyethylene is used, and in the second case, bitumen. Fused vapor barrier is considered a more reliable option, as it has a greater thickness. When laying a film vapor barrier, it should be remembered that this material is less durable, therefore it can break at the places where seams are formed.
Basic requirements for vapor barrier material:
- High resistance to steam penetration. This indicator directly depends on the density of the material.
- The degree of incombustibility. For the vapor barrier device, it is recommended to use absolutely non-combustible materials.
Thermal insulation layer

To insulate an exploited flat roof, only heat-insulating materials in the form of plates are used.Fastening of heat-insulating materials can be performed in the following ways: mechanical, adhesive. For mechanical fastening of the insulation, specially designed dowels are used, for adhesive fastening - bitumen. The adhesive method is used only if the base is made of concrete slabs.
Construction and safety
When installing such a roof, in addition to ensuring the competent design of the roofing pie, careful selection is also required by the materials used when laying all its layers.
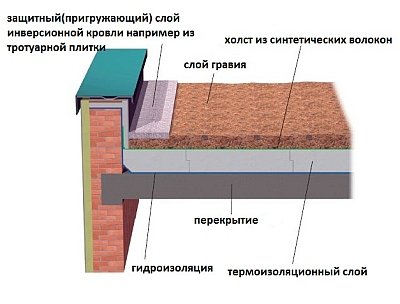
Soil layer and paving slabs. To improve the upper layer of the roof, green spaces, lawns and flower beds are used, and for the pedestrian zone - paving slabs. All this creates an additional load on the building, so it is necessary to ensure maximum strength of the supporting structures.
We recommend reading the article on how to build a frame house with a flat roof.
drainage layer. It is sometimes called the "heart", and is responsible for eliminating stagnant water in the upper layers of the cake and the lower parts of the soil layer. Crushed stone or gravel (20-40 mm) is used as drainage, as well as a geotextile drainage coating.
Thermal insulation layer. Thermal insulation is calculated based on the type of building, number of storeys. The thickness of the insulation is chosen in the range of 5–30 cm - such restrictions are necessary to avoid unnecessary stress on the waterproofing.
waterproofing layer. As a waterproofing, a more elastic and durable material is used, EPDM, TPO, PVC membranes or bitumen rolls, which allows you to cope with all the loads from the top layers of the pie.
Drainage system. It ensures the drainage of atmospheric precipitation from the roof plane, the normal functioning of the drainage system. The drain funnel must be two-level and heated.
Characteristics of insulation and load on a flat roof
Any element of the roof structure is under the influence of several loads, so it must meet fairly stringent requirements. In particular, the thermal insulation of a flat roof is directly under the following loads:
- snow,
- operational,
- wind,
- mounting.
Particular attention should be paid to the mass of snow in regions characterized by heavy rainfall in winter. The mass of wet snow accumulated on the roof can reach several tens of tons. Therefore, a flat roof insulation must be reliable, with excellent physical and chemical properties. Since the possibility of moisture getting inside the ceiling cannot be excluded, the thermal insulation must also be moisture resistant.
An important characteristic of roof insulation is its compressive strength. Thermal insulation of the roof, based on the technology of the device of a flat roof, actually performs the functions of the roofing material of its base, therefore, its compressive strength and density must be quite high
Any deformation during operation or installation can damage the waterproofing layer.
The thermal insulation material in a single-layer insulation structure or the top layer in a multi-layer one must have a high density, about 200 kg / m3, which provides the material with special strength (you can safely walk on it).
Flat Roof Pie
An exploited flat roof (roof) initially assumes that it will not only protect against bad weather, heat and cold, but also withstand certain loads associated with its operation.
It is rational to make a flat roof (for example, the roof of a garage or the floor of a balcony that is a bay window roof) exploitable, because in this case an additional outdoor area appears, which can be used in accordance with your needs.
The most common example of an exploited flat roof is an open attic or balcony, which serves as a resting place.
Balcony waterproofing begins with leveling the base, degreasing the surface, directly installing the waterproofing and finishing coating. The best balcony waterproofing is reinforced, polyurethane mastic, and ceramic tiles can be the top coat.
Another example is the exploited flat roofs of some hypermarkets and car dealerships, where car parking is located. In this case, the entire roofing pie is selected based on the planned loads.
This solution makes it possible to maximize the use of the available area of the building, saving on the construction of traditional parking spaces in the form of underground parking or street parking. Another promising direction in the construction of operated flat roofs are the so-called green roofs. They are called green because the surface of such a roof consists of vegetation: lawn, trees, alpine slides, flower beds, etc. It looks fresh and beautiful, unlike industrial flat roofs, whose main task is protection from precipitation and temperature changes with minimal aesthetic requirements.
Types of operated flat roofs. Roof structure.
1. Classic flat roof
The estimated cost for the manufacture of such a roof is 1020 rubles / m 2. Cost includes labor and material costs. Namely: screeding device, laying a composite membrane.
Ballast inverted roofs
The estimated cost for the manufacture of such a roof is 2100 rubles / m 2. Cost includes labor and material costs. Cost includes labor and material costs. Namely: preparation of the base, laying the 1st layer of geotextile, laying the EPDM membrane, laying the 2nd layer of geotextile, laying thermal insulation from extruded polystyrene foam, laying the 3rd layer of geotextile, laying paving slabs on cross plastic supports.
Flat Roof Pie The operated flat roof (roof) initially assumes that it will not
Foundation preparation procedure
In the section, the device of a flat roof consists of a bearing coating and a base, on which layers of hydro-, steam- and thermal insulation are laid in a certain order. Most often, the bearing coating is a reinforced concrete slab, steel profiled sheet, much less often a coating of wood materials is used.
If the reinforced concrete base has defects, a cement-sand screed is made, after which the surface becomes even.
Depending on the material on top of which the screed is made, its thickness differs:
- if it is concrete, then the layer is from 10 to 15 millimeters;
- when rigid insulation boards are used - 15-25 millimeters;
- in the presence of non-rigid heat-insulating materials - 25-30 millimeters.
When a flat roof device provides for a slope of no more than 15 percent, the screed is performed primarily on the grooves, and then only on the slopes. If the slope exceeds 15 percent, the procedure for creating a screed is reversed - first the slopes are leveled, and only then they are engaged in the arrangement of valleys and grooves.
On the flat roofs of modern houses there are always protruding elements - chimney pipes, parapet walls, ventilation shafts, etc. They should be plastered at least 25 cm high. To the upper edge of the plastered surface, slats are mounted for fastening the rolled carpet. In order to improve adhesion between the carpet and the base, the screed is cleaned of debris, dried and primed with roofing mastics.