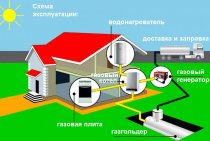
APPENDIX Reference
TERMS AND DEFINITIONS OF GENERAL CONCEPTS RELATED TO THE WORKING PROCESS OF BURNERS ON GAS AND LIQUID FUELS
|
Term |
Definition |
|
1. Lower calorific value of fuel |
The amount of heat released during the complete combustion of a unit mass (volume) of fuel, provided that the water formed during combustion will be in a vapor state Note. The net calorific value of a fuel refers to a unit volume of fuel, and the net calorific value of a fuel refers to a unit mass of fuel |
|
2. Higher calorific value of fuel |
The amount of heat released during the complete combustion of a unit mass (volume) of fuel, provided that the water formed during combustion is in a liquid state |
|
3. Relative density of gaseous fuel |
Density ratio of gaseous fuel to air density |
|
4. Lowest Wobbe number of gaseous fuel |
The ratio of the volumetric net calorific value to the square root of the relative density of gaseous fuel |
|
5. Stoichiometric volume of combustion air |
The amount of air required for the complete combustion of a unit volume or mass of fuel, calculated from the chemical composition of the fuel |
|
6. Actual combustion air volume |
The amount of air actually used to burn a unit volume or mass of fuel |
|
7. Combustion air ratio |
Ratio of actual volume of combustion air to stoichiometric |
|
8. Minimum excess air ratio for combustion |
The smallest value of the excess air coefficient, which ensures the combustion of fuel with a chemical incompleteness of combustion that does not exceed the norm |
|
9. Fuel ignition temperature |
The minimum temperature at which, under given conditions, a combustible mixture ignites while maintaining the minimum thermal gradient over its volume |
|
10. Fuel flammability limits |
The minimum or maximum volumetric concentration of fuel in a stationary mixture with air (oxygen), sufficient to ignite it from an ignition source |
|
11. Torch root zone |
The set of flame points that are the least distant from the burner outlets |
|
12. Flame front |
The layer in which the combustion chain reaction is currently taking place |
|
13. Flame stability |
A steady state in which the flame is in a fixed position with respect to the burner outlets |
|
14. Flashback |
Movement of the root zone of the torch towards the outflowing mixture |
|
15. Flame out |
Movement of the flame root zone from the burner outlets in the direction of fuel or combustible mixture flow |
|
16. Partial flame separation |
Movement of the flame root zone from the burner outlets in the direction of fuel or combustible mixture flow, which does not appear over the entire cross section |
|
17. Flameout |
Movement of the flame root zone from the burner outlets in the direction of fuel or combustible mixture flow, accompanied by its extinction |
|
18. Extinction of the flame |
Cessation of fire for any reason |
|
19. Pulsing flame |
Alternating change in the parameters of the torch and the localization of its root zone |
|
20. Thermostat |
A device that controls the operation of the burner depending on the temperature of the controlled medium |
|
21. Pressure switch |
A device that controls the operation of the burner depending on the pressure of the controlled medium |
|
22. Soot number |
Bacharach number indicating unburned carbon in combustion products |
|
23. Degree of shielding |
The ratio of the cooled area of the heat-receiving surface to the entire area of the heat-receiving surface of the combustion chamber |
|
24. The degree of restriction of the torch |
The ratio of the area of the outlet section of the burner to the cross-sectional area of the combustion chamber |
|
25. Fuel-using installation |
A device that is designed to use fuel in order to obtain thermal energy when it is burned using a burner. Note. Fuel plants include: - devices with combustion chambers (boilers, furnaces, dryers, heat generators, etc.); - devices without combustion chambers (devices for welding and out-of-furnace heating) |
(Revised edition, Rev. No. 1).
INFORMATION DATA
1. DEVELOPED AND INTRODUCED by the Ministry of Gas Industry of the USSR
2. APPROVED AND INTRODUCED BY Decree of the USSR State Committee for Product Quality Management and Standards dated 05.12.89 No. 3575
3. The standard fully complies with ST SEV 1706-88. The standard complies with the international standards ISO 3544-78 and ISO 5063-78 in terms of terminology
4. REPLACE GOST 17356-71
5. RE-ISSUE
Industrial burners
Industrial gas burners Lanemark HC, equipped with pressure draft, are high-quality, reliable and versatile equipment with a Thermimax matrix head, which ensures optimal mixing of fuel with air. Thermimax die heads provide clean and efficient gas combustion in a wide range of applications.
Industrial gas burners are indispensable for industrial enterprises in which natural gas plays the role of a fuel cell. The burner allows oxygen to mix with the fuel, and also ensures the combustion of the mixture in the device. The device provides an uninterrupted combustion process to achieve the highest possible performance and significant fuel savings. The gas burner is arranged quite simply: in it, the gas is mixed with oxygen in the right proportion, and the diffuse mixture, passing through a special hole, forms an ignition. Industrial burners operate with process, coke oven and synthetic gases, as well as degassing gases. They are developed according to special drawings, taking into account the specifics of use.
The design of an industrial gas burner: • Housing; • Igniter in which ignition and combustion occurs; • Fan; • Shut-off valves; • Air and gas flow control device; • Sensors that determine pressure and operating temperature; );• An electronic block designed for preliminary optional planning of tasks.
Depending on the principles of operation and design, industrial burners are divided into: • Injection burners. Air is sucked into the device with a gas jet, oxygen is mixed with the working medium in the device. Depending on the required concentration of the substance, gas burners of partial and full mixing are also distinguished; • Pressurized. Oxygen enters the device using a fan built into the chamber. Mixing takes place in the burner, while the waste product enters the furnace. Such devices work, as a rule, very noisily, but privately at enterprises they suppress sounds with the help of special devices. • Diffuse. Air enters the combustion site through a natural diffusion process.
The use of a burner of this type allows you to maintain a stable temperature in the medium, which is extremely important for its processing in some industries.
Since 1981, Lanemark International has been a market leader in heaters for the refinery, petrochemical and similar industries. The manufacturer skillfully combines scientific developments and practical experience in the manufacture of its equipment. This makes it safe and efficient to use.
LLC "KronDe Group" is the official representative of Lanemark International in Russia and has a permit from Rostekhnadzor, which confirms that the equipment used is safe to operate in the production process and is reliable in operation, as well as a certificate of compliance with the GOST-R technical regulations for the HC burner line.
PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Features of the new patented design: • Multi-fuel system in a single head • Combustion air temperature up to 500°C • Wide fuel and air pressure range • High fuel efficiency • Low noise and gas exhaust • Adjustable flame circuits, Absolute flame stability under all operating conditions • Direct spark or pilot flame ignition - portable or stationary • Robust design with no moving parts • Suction draft models available.
Technical characteristics: • compatibility with many combustible gases; • power - 50 kW - 7.5 mW; • gas supply pressure - 10 mbar - 4 bar i.d.; • flue air pressure drop - 2 mbar - 60 mbar; • excessive air - 0.5% - 500%; • flue air temperature - from atmospheric to 500°C; • nitrogen oxide emissions • CO emissions • noise (sound pressure level) • burner load range with modulated air supply - up to 10:1; • burner load range at fixed air supply – up to 4:1.
All the information you are interested in about industrial burners can be obtained from our specialists on multi-channel telephones in St. Petersburg: (812) 612-05-56, (812) 612-05-57.
Industrial gas burners. General technical requirements
| Designation: | GOST 21204-97 |
|---|---|
| Status: | current |
| A type: | GOST |
| Russian name: | Industrial gas burners. General technical requirements |
| English name: | industrial gas burners. General technical requirements |
| Text update date: | 06.04.2015 |
| Description update date: | 01.06.2019 |
| Publication date: | 01.01.2002 |
| Date of entry into force: | 30.06.1998 |
| Last Modified Date: | 12.09.2018 |
| Reissue: | revised edition |
| Scope and conditions of application: | This standard applies to gas industrial burners operating on gaseous fuels combusted with air or with a mixture of air and recirculation flue gases, as well as the gas part of combined burners used in steam and hot water boilers, heat generators and gas-using installations. The standard does not apply to burners in which additional means are used to intensify the combustion process (electrical or acoustic energy, oxygen); radiation pipes; burners, during which combustion products are formed, used as a controlled atmosphere; infrared burners; burners that are an integral part of gas-using equipment for use in everyday life and catering establishments; burners of open-hearth furnaces, bath regenerative glass furnaces; burners of flare installations for combustion of waste gases |
| Instead: | GOST 21204-83 |
| List of changes: | No. 0 from (reg.) "Introduction date postponed" No. 1 from (reg.) “Text change; Reference ND changed" No. 2 from (reg.) “Text change; Reference ND changed" |
| Located in: |
All-Russian classifier of standards → Energy and heat engineering → Burners. Boilers → Gas burners Classifier of state standards → Machinery, equipment and tools → Machinery and equipment for heavy industry → Classification, nomenclature and general norms All-Russian classifier of products → Products of chemical and petroleum engineering → Other equipment → Gas consuming industrial equipment → General purpose gas burners Technical regulations of the Russian Federation → Technical regulations 'On the safety of machinery and equipment' → 31 1000 Energy equipment → 36 9000 Other equipment → 39 6000 Furnace burners → Technical regulation on the safety of apparatus operating on gaseous fuels → 1. Gas-using equipment intended for cooking, heating and hot water supply → 1. 1 Gas burners for special purposes - OKP code 369620 → 1. 2 Radiant gas radiators closed - OKP code 369640 → 1.3 Gas recuperative and mixing industrial air heaters, including air heaters with block air burners, air conditioners with built-in gas air heaters, gas heat generators for livestock buildings -… → 1.10 Gas heating boilers, including boilers with block air burners - OKP code 493110, 493120 Technical regulations of the Customs Union → On the safety of gaseous fueled vehicles → List of standards for the technical regulations of the Customs Union → List of standards, as a result of which, on a voluntary basis, compliance with the requirements of the Technical Regulations of the Customs Union "On the safety of gaseous fueled vehicles" → Gas-using equipment for cooking, heating and hot water supply |
| Application #0: | |
| Application #1: | |
| Appendix #2: |