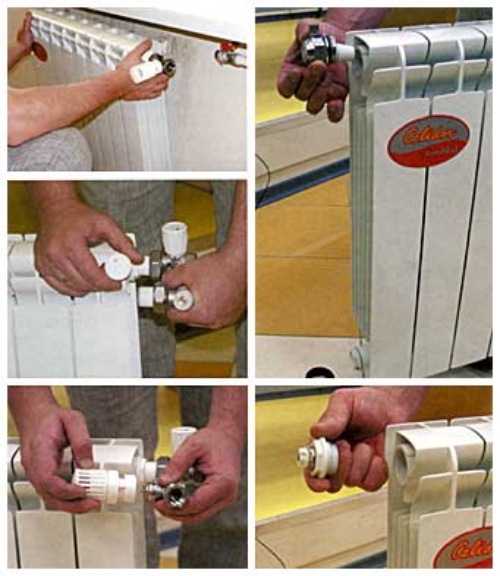
Installing the battery in the system
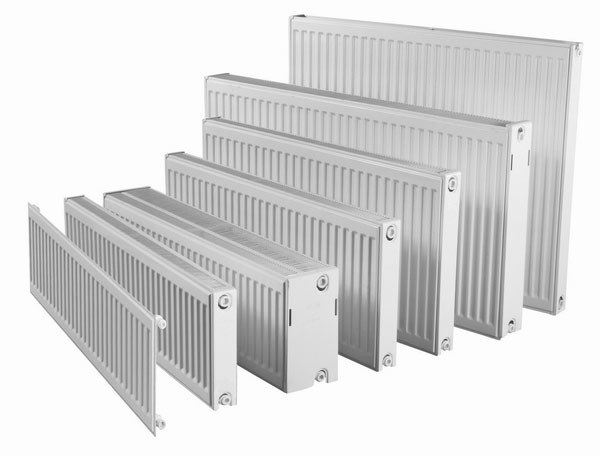
When choosing one or another type of low radiator, it is necessary to determine its parameters, based on the size of the window and the required heat transfer. The length of the heat exchanger must be equal to the width of the opening or exceed it by 200-300 mm.
Having the skill of owning the necessary tool, it is not difficult to connect the radiator to the system with your own hands.
The following guide will help you with this:
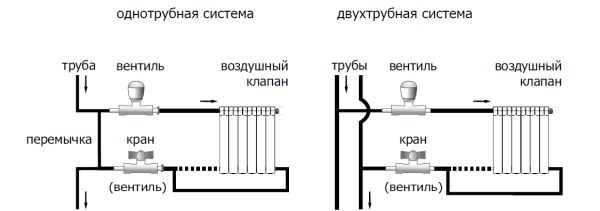
- determine the type of system - one- or two-pipe;
- determine the most optimal connection scheme - diagonal, one-sided or lower;
Inconspicuous element of the interior
- then we install taps on the inlet and outlet pipes. allowing to shut off the coolant supply in case of an emergency;
- in the remaining holes we screw in the Mayevsky crane (top) and the plug (bottom).
- pre-assembly can be carried out dry, the final connection is made using linen winding and sanitary paste;
- it is possible to attach batteries from various metals to heating systems made of metal, metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes.
Picture montage
Tall radiators
When radiator sizing is limited due to lack of space for a standard appliance, tall and narrow coils are preferred as these models have limited width.
Cast iron radiators. Unlike domestic cast iron products of standard dimensions, among foreign products you can find designer appliances, the height of which is unusual for Russian consumers. For example, the Demrad Retro line of cast-iron radiators.
Their sizes are as follows:
- the height of the section with a width of 76 millimeters varies between 661 - 954 millimeters;
- depth - 203 mm.
Working pressure - 10 atmospheres, they are tested at 13 atmospheres.
In the largest sections, the thermal power reaches 270 watts. At the same time, narrow heating radiators can have height dimensions of 2400 millimeters. Working pressure is limited to 6 atmospheres. The high height contributes to the solid heat transfer of the heating radiator. at a delta of temperatures equal to 70 degrees, it reaches even more than 433 watts.
Aluminum radiators. Usually, for tall aluminum radiators, the piping is placed at the bottom to make the pipes invisible.
Bimetal radiators. Basically, the models of tall and narrow bimetallic radiators are original design designs, and, accordingly, all their sizes are non-standard. Basically, these products are rarely sectional - they are usually monolithic.
An example of such heaters is the Sira RS-800 BIMETALL model radiator, which has the following parameters:
- section height 880 mm;
- depth 95 millimeters;
- length 80 millimeters.
Before calculating the size of a heating radiator, it is necessary to determine the model of a particular heater for a room of a certain purpose and area. It should be remembered that heat transfer is not affected by the size, but by the power of individual sections that are assembled into one battery. The choice, given the size of heating radiators, details on the video:
How to choose the right low battery
In modern stores you can find a wide variety of models of low batteries, both domestically produced and from well-known brands from manufacturers in other countries. In order not to waste money on purchasing a battery with unused properties, it is recommended to rely on the following:
- Rooms with panoramic windows are best heated with batteries made of aluminum or two or more different materials.
- In private houses that are not connected to the central heating mains, but use their own boiler, steel or aluminum radiators should be installed.
- The radiator should create an effective thermal curtain when placed in a window opening. To do this, its length must be greater than the width of the window.
Tubular radiators for residential heating Bimetal heating radiators Flat heating radiators Heating radiators for a private house
Common types of low batteries
Since radiators are very simple, the differences between them are based on the geometry of the case, what material it is made of, what kind and size the radiator fins have.
The minimum dimensions of a low radiator are usually 0.2 meters high, 0.5 meters long and 0.1 meters deep. The maximum dimensions can be 0.5 meters high, 6 meters long and 0.23 meters deep.
The design of low batteries is determined primarily by materials such as:
Batteries are sections obtained by casting. For heat transfer, each section contains a number of ribs determined by the design.
The properties of cast iron determine both the disadvantages and advantages of such a radiator. Cast iron is brittle and like an eggshell, which, due to its bulge, is strong on the outside, but easily breaks on the inside. Therefore, the force of water pressure inside such a radiator should be less than 9-11 atmospheres. And since the surface of the cast iron after casting turns out to be rough and uneven, debris settles on it inside the radiator over time and creates a layer that weakens the transfer of heat from the water to the cast iron of the radiator. But with the mentioned shortcomings, the cast-iron radiator holds heat well and is not subject to destruction from prolonged contact with water.
By casting, steel does not allow obtaining the ribbed shape necessary for the radiator. For this reason, steel low steel batteries are made from individual plates and often combined with pipes. A low stack based on a pipe framed by plates that serve to increase convection has heat losses due to gaps that occur at the point where the plates are attached to the pipe.
If the radiator is made of steel plates, which form cavities for filling them with hot water, the heat transfer is much greater than that of a pipe-based radiator, but the resistance to hydraulic shocks decreases due to the presence of seams connecting the plates, which is one of the disadvantages of such radiators. .
Another disadvantage of steel radiators is rust, which appears inside when it comes into contact with atmospheric oxygen in a humid environment. In addition to the drawbacks mentioned, steel radiators are very expensive due to the laborious manufacturing and the need to use corrosion-resistant steel. According to their heat transfer properties, they are close to cast-iron radiators.
Aluminum batteries can be obtained either by casting or extrusion, or made from plates. Their main advantage is their weight, which is significantly less than that of cast iron and steel.
In terms of their ability to withstand water pressure, aluminum radiators are almost one and a half times better than cast iron ones. But the convection properties of aluminum are worse than those of cast iron and steel.
In addition, aluminum is less durable than cast iron and steel, so water hammer can quickly cause water to leak through cracks in the hull. For this reason, the service life of such radiators is less than that of cast iron and steel.
Such a radiator is made of several parts. the material of each of which is selected with the best fit to the task being performed. In such a battery, water passes through a pipe made of copper alloy or other material. The pipe is able to withstand water pressure of several tens of atmospheres and is not subject to destruction from prolonged contact with water. Therefore, its service life will be comparable to a cast-iron battery.
To increase the surface area of contact with air, aluminum or non-ferrous metal alloy plates are placed on the pipe. Such a radiator may have small dimensions, but due to heat loss at the place where the plates are attached to the pipe, its efficiency will be less than that of aluminum batteries.
The complexity of manufacturing and the use of non-ferrous metals makes such a battery more expensive than aluminum.
Main materials used for production
Currently, the main criterion that separates all models of low radiators available on the market is the material from which they are made. Along with the traditional ones, which were used in the last century, new types appear that have better performance properties.
Cast iron radiators
The elements made of cast iron stand out with the longest history of use. They are distinguished by high heat transfer, prolonged cooling and heating, large mass and their low resistance to shock loads.
The increased roughness of the inner surface of the cast sections of the cast-iron battery contributes to the accumulation of dirt and rust deposits on its walls, which significantly reduces heat transfer over time.
Note! Despite the fluidity of cast irons, the manufacturer manufactures heat exchangers with a height of at least 390 mm. This is due to the disadvantages mentioned above.
There are batteries made at a sufficient artistic level, which allows you to decorate the interior of rooms.
Here is a decoration you can install at home
Steel heat exchangers
Products from this iron-carbon alloy may be smaller than cast iron. They are a lamellar structure, the basis of which are metal pipelines. This aspect significantly reduces the required amount of coolant in the system and, as a result, increases its output.
In the photo - steel panel batteries
Heat exchangers made of steel have a number of positive and negative aspects. Their mass is much lower than cast iron, they are more compact and have a greater heat transfer. The disadvantages include susceptibility to corrosion and poor resistance to water hammer.
Steel heating radiators, low in height, have poor maintainability. If one of the sections is damaged in a cast-iron battery, it is easy to replace or eliminate it.
The steel product will have to be replaced entirely, which will lead to additional costs. The price of such units is one of the most significant in the segment.
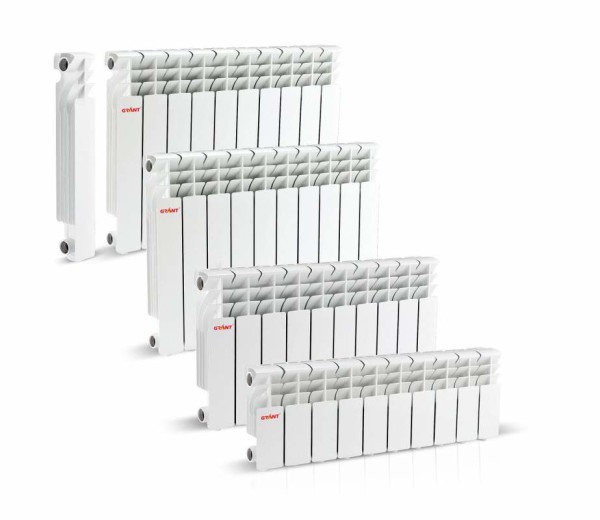
Aluminum radiators
Low aluminum heating radiators have a set of advantages over their competitors.
- the minimum mass of all such products;
- good heat dissipation;
- and the plasticity of the metal makes it possible to obtain products of elegant shapes.
The size of the devices does not affect their characteristics.
Note! Aluminum does not have high strength characteristics, which can lead to leakage due to water hammer in the system, formed during filling or draining. The average service life of such products does not exceed 12-15 years
The cost of radiators made of aluminum is low.
Bimetallic batteries
One of the last types of heating devices recommended for use in individual heating systems of private houses are the so-called bimetallic batteries. They are made on the basis of steel or copper pipelines equipped with aluminum plates.
Reliable strength of two metals in bimetallic devices
Their advantages include the following:
- sufficient corrosion resistance;
- significant (up to 100 atm.) working pressure that they are able to withstand;
- low volume of coolant required for heating.
Such structures also have disadvantages:
- lower heat transfer compared to aluminum products;
- the highest cost among all low radiators.
Panel heating systems
In the event that you decide to get your home's heating system completely devoid of visible elements, panel heaters can come to the rescue. These are really low horizontal heating radiators. Their height from the floor does not exceed 20 cm with a thickness of 30 mm.
Such products are located along the walls and are closed with decorative overlays (panels). Using this option, you can get a heating system with a height of 100 mm, working as a standard with high batteries. Significant disadvantages of this heating option are high cost and complete unsuitability for repair.
What should be the dimensions
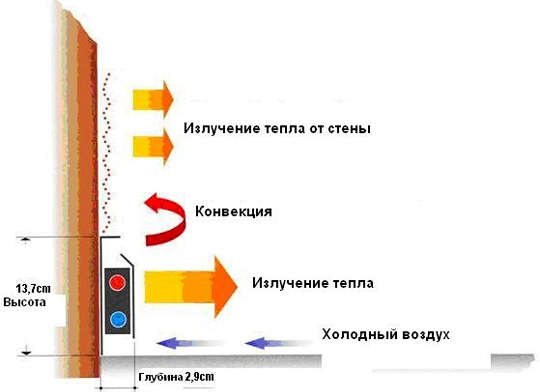
In order for the heating radiator to give off maximum heat (in this case, we are not talking about its thermal power, but about the efficiency of its work), the dimensions should be as follows:
- The length should be more than 70-75% of the width of the window opening.
- The height should be such that between the floor and the battery was 8-12 cm, and at the same time between the window sill and it was 6-12 cm.
If the recommendations are not followed, then the operation of the aluminum radiator will be accompanied by heat loss. Therefore, even if he can issue the necessary for a room with an area of 20 square meters. m 200 watts of heat, then due to incorrect dimensions in the room there will be insufficient heat. After all, part of it can be lost under the windowsill or go to floor heating.
When the length is less than 70% of the width of the window opening, the battery will not be able to create a thermal curtain that can block the movement of cold air entering through the window. The consequence of this situation will be the appearance of cold and warm zones in the room. Also, the windows will be constantly covered with steam. And even the power of the heating radiator, which is greater than the need, cannot become a lifesaver.
Therefore, if the window has a width of 2 m, then the length of the battery must be at least 1.4 m
Of course, in order to select a device with such a length, it will be necessary to take into account sections of different heights and their heat transfer. The calculation can take a long time, but it's worth it
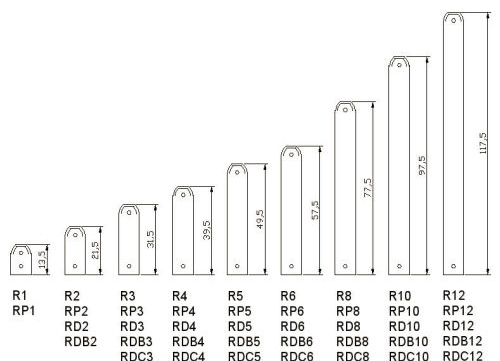
Main dimensions
Dimension means:
The center distance (it is also called inter-nipple or center-to-center) should not be confused with the height of the radiator. The first indicator indicates how many centimeters are between the upper and lower collectors (holes). The height is the distance between the lowest and highest point of the section.
Aluminum heating radiators have the following dimensions:
- The center distance ranges from 150 to 2,000 mm. Very tall radiators are rare. The most popular are radiators with an inter-nipple distance of 500 mm. This is because the existing heating network pipe system was created for cast-iron batteries, which have the same center-to-center distance. Since many owners did not have and do not have the desire to digest pipes, they simply selected / selected a suitable radiator and, thereby, raised the popularity of a battery with a center distance of 0.5 cm. This indicator is very important, and therefore manufacturers indicate it in the name of the battery (RAP-500, Rococo 790, Magica 400, etc.).
- The height is in the range of 245-2000 mm. According to this criterion, batteries can be divided into low, medium and high. Features of each type will be discussed below.
- The depth of the section is from 52 to 180 mm. Some models may have greater depth, however, this is rare.
- The width of the section is 40-80 mm.
What are the types of low heat exchangers
Devices are distinguished based on the following criteria: the type of material from which they are made, the design features of the main components - sections, plates and height. They are produced with a height of 200 to 450 mm, a length of 500 to 6,000 and a depth of 10 to 230. The following types are distinguished:
1. Pig-iron sectional, ribbed. The advantages are good thermal inertia and corrosion resistance.Disadvantages: low operating pressure up to 10 atmospheres, brittleness, susceptibility to accumulation of dirt and plaque inside the channels, which eventually reduces heat transfer. Compact cast iron batteries are models MS 140M-300 (height 388 mm).
2. Steel panel radiators are one or more heating plates enclosed in a ribbed shell. They have excellent thermal conductivity and low inertia, consume a minimum amount of coolant. For example, a steel radiator measuring 100 mm deep, 300 mm high and 1,000 mm long can create an effective thermal curtain at a window with a glazing area of up to 4 m2.
Disadvantages: unstable to water hammer, when draining water, corrosion can form on the walls of the panels, the convection method of heat transfer contributes to the formation of fine dust particles in the room. Of all the compact heaters, they have the highest cost. For example, the price of a Kermi radiator with a height of 300 mm, depending on the length and depth, is 1,260 - 5,100 rubles.

3. Aluminum, injection molding and extrusion sections are characterized by light weight, good heat dissipation and elegant design. The technical characteristics of the low aluminum radiator allow it to withstand operating pressures up to 16 atmospheres. Disadvantages: low convection, service life (10-15 years), instability to water hammer and, as a result, possible leaks between sections. You can buy a 200 mm aluminum battery for 340 - 1,250 rubles.
4. Bimetal consists of 2 parts: a core made of steel or copper pipes and an aluminum shell. The advantages are: the ability to withstand high (up to 100 atmospheres) pressure, low water consumption and good corrosion resistance. The sectional low bimetal radiator Rifar Base 200 has a closed rear surface, which allows it to be mounted in close proximity to glass surfaces. Some models are supplied with feet for installation on the floor. However, in terms of heat transfer, bimetallic batteries are inferior to aluminum products, and their cost is 10-15% higher.
5. The lowest are convector-type plate batteries. Such linear or plinth radiators have a height of 200 to 400 mm and can be attached to the wall and floor, if necessary, covered with decorative grilles. They are characterized by good heat dissipation, the ability to withstand operating pressures up to 20 atmospheres. They are produced in the form of solid products of a certain length. When leaking, they require a complete replacement, which causes some inconvenience.
What to consider when buying
The modern market for heating appliances is saturated with products of Russian and world brands that differ in technical characteristics, quality, and price. In order to avoid unnecessary costs and not miscalculate with quality, experts recommend considering the following factors:
1. For centralized heating systems, which are equipped with residential multi-storey buildings, cast-iron radiators are suitable. For buildings with panoramic windows, it is better to use bimetallic or aluminum windows.
Tricky meter that saves electricity. It pays off in 2 months! Everyone needs to know this in order to save money!
For closed heating systems that are installed in private homes, steel or aluminum batteries are recommended.
2. The length of the radiator must match the dimensions of the window opening or be 10-20 cm longer. Otherwise, it will not be possible to create an effective thermal curtain, which will lead to uneven heating of the air in the room.
Specifications and cost of the most popular models