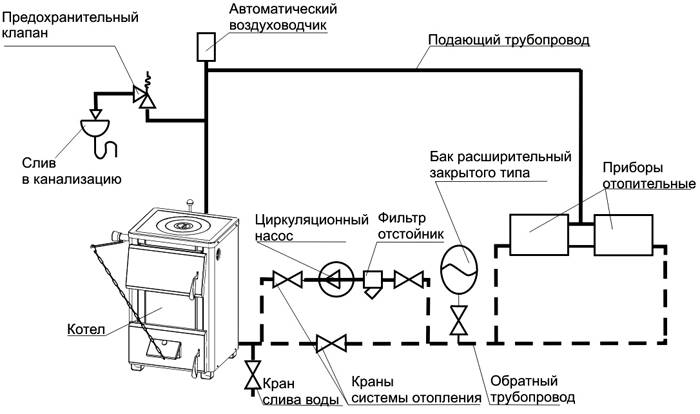
Expansion tank installation
When installing an expansion tank, two circumstances must be considered:
- When the container is filled with liquid, its weight will increase significantly, so the mount must be designed for loads.
- The unit must be freely accessible for maintenance (especially in open systems, where water will need to be added periodically).
The method of installation will depend on the materials used. This can be welding, flanges or plastic connection with a special soldering iron.
A fairly common mistake when using sealing materials that are not suitable for mounting heating elements.
For example, a sealant for plastic windows - it is not designed to work with high temperatures, so after a while it will leak.
Tips for installing an expansion tank for a heating system:
- The works are planned during the warm period, at positive temperatures;
- Be sure to install a safety valve;
- The latest models of gas boilers have a small tank in their design; you should not rely only on it if the length of the pipeline is considerable. It is necessary to recalculate everything and, if necessary, install an additional expander.
- If a tap is installed in a short section between the tank and the heating pipes, this will allow, if necessary, to dismantle the unit without disturbing the operation of the entire system.
Organizing a warm floor system is most difficult in the bathroom, because you need to make everything airtight so that the system does not interact with moisture. - device options and installation steps.
Tanks with a balloon-type membrane.
In this case, the air chamber is located along the perimeter of the entire tank and surrounds the rubber chamber for the coolant. When it arrives, the latter begins to expand like an inflated balloon. Thanks to this tank device, it is possible to more accurately control the pressure in the system.
It should be noted that balloon membranes can be replaced as they wear out, while diaphragm membranes cannot be replaced. The material from which the membrane is made is very important. It must have thermal stability and at the same time high elasticity. When choosing a tank, you should be familiar with such membrane characteristics as durability, operating temperature, water resistance and compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards.
Scheme of the expansion tank
Principle of operation
From the course of physics it is known that the liquid is incompressible.
In the heating circuit, water is used as a heat carrier.
In the temperature range from 20 to 90 degrees, it changes volume, expanding as it heats up.
If we imagine the heating network as a vessel of complex configuration, then heating the contents will cause the walls to break due to the expansion of the liquid.
To compensate for this phenomenon, an expansion tank is used, which serves as an additional volume for placing excess coolant.
Having expanded, the water enters the tank, and when cooled (approximate prices for a heating cable for water supply) goes back into the system.
It is simply impossible to remove excess water, because when it cools, the void will be occupied by air, and the circuit will cease to function.
Do you know what to do if water flows from the tank into the toilet. Read the useful article for tips and advice from master plumbers on troubleshooting.
About the scope of asbestos-cement pipes with a size of 150 mm is written on this page.
Thus, the expansion tank protects the heating system from both excess and shortage of coolant, compensating for all movements in its volume.
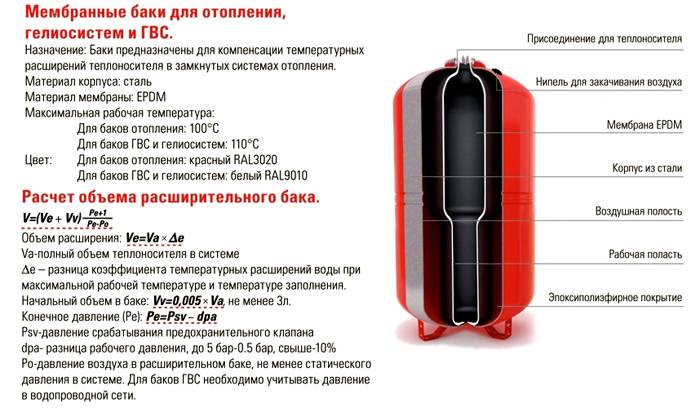
Expansion tank design
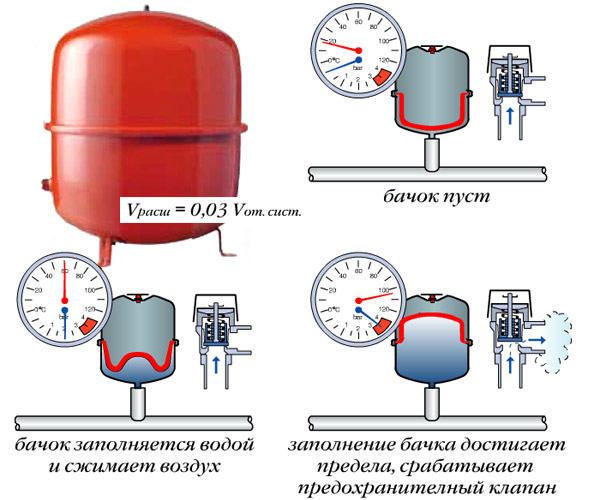
The expansion tank is a carbon steel body with a powder coated red, gray or white coating, inside which is a rubber membrane in the form of a diaphragm or in the form of a cylinder. The first is mainly used in small containers, the second - in large ones. Tanks in the factory are sometimes equipped with a safety valve that protects the system from exceeding the allowable pressure. If this happens, the valve opens, releasing excess water. Better to play it safe and make sure your product has it. If not, buy and mount next to the tank.
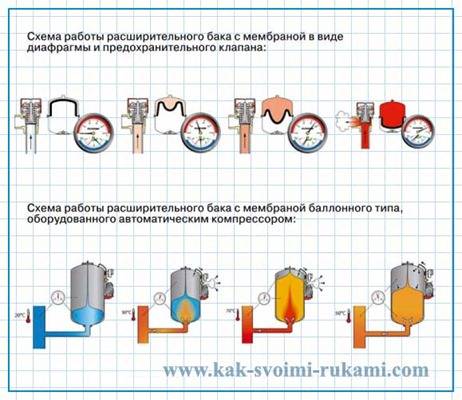
Expansion tank with a membrane in the form of a diaphragm. Such a device is more like a barrel, divided in two by a movable rubber partition. In production, air is pumped into the upper part of the tank, which creates an initial pressure. After connecting the tank, the coolant from the network begins to flow into its lower chamber. At that moment, when the elastic membrane becomes in a zero-calm position and, as it were, lies on the surface of the coolant, the heating system is considered to be completely filled and ready to start. When the temperature of the coolant rises, its volume increases, and the excess is discharged into the expansion tank. By compressing the air, the membrane is moved into the air chamber, due to which the internal space of the tank becomes larger, and an excess of coolant enters there. As soon as the coolant cools down and returns to its original volume, the effect on the membrane stops and the air in the upper chamber, without resistance, brings the membrane to its original, calm position, thereby automatically adjusting the pressure in the system.
Features of choosing an expansion tank for a heating system, a few nuances
When choosing an expansion tank, you need to pay attention to the following criteria:
- installation location;
- type of heating system (with natural and forced circulation);
- operating parameters of the system, including pressure (it is necessary to perform pressure calculations for the tank, coolant, heat exchanger);
- the volume of the expansion tank (cannot be less than 10% of the total volume of water in the system);
- the need for automated control;
- features of the tank operation (autonomous non-volatile, with forced circulation and connection to the electrical network)
One of the criteria for choosing equipment is the calculation of water and its pressure. In such calculations of the heating system, the following are taken into account:
- the volume of water in the boiler unit (it is indicated in the passport for the boiler);
- the volume of water for radiators (it is necessary to calculate separately for each radiator and summarize the obtained values);
- the volume of coolant in the pipes of the system (calculated for all circuits using the formula Vtot = π × D2 × L/4, where D is the pipe diameter, L is the pipe length).
This calculation calculates how much volume the tank should have. Usually, when designing, it is laid down that the volume of the expansion tank cannot be less than 10-15%. This value will be sufficient to remove air from the heating circuit and protect the equipment from ruptures or leaks during thermal expansion.
Open and closed heating systems
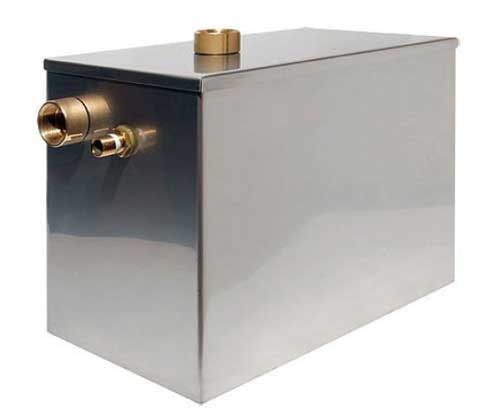
Open tanks are used for heating systems where the coolant circulates by gravity. The tank is usually cylindrical or rectangular with an open top and is connected to the heating system through an outlet at the bottom.
There are many more disadvantages of using open tanks:
- need regular maintenance;
- heat losses in the system are quite high;
- the inner walls of the tank are subject to corrosion;
- during installation, additional piping is required;
- installation is carried out in the attic, which requires additional reinforcement of the floors due to the large weight of the tank.
An example of an open expansion tank made of stainless steel
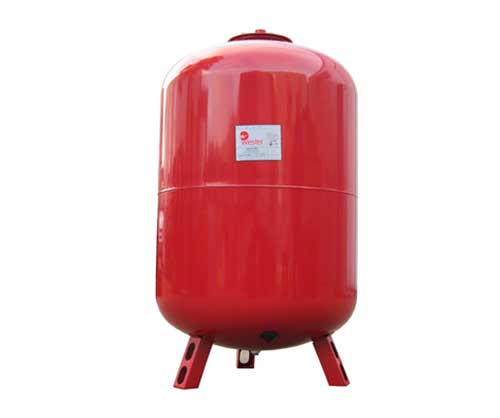
Closed tanks can be used for any heating system, but they are usually required for forced heating. The tank is closed, that is, contact between the coolant and the surrounding air is excluded. In addition, sealed tanks can be equipped with automatic or manual valves, pressure gauges to measure the pressure in the system.
The advantages of such equipment are many:
- the tank can be mounted in the boiler room, it does not require frost protection;
- the pressure level in the system can be quite high;
- the tank is more protected from corrosion, its service life is long;
- the coolant does not evaporate;
- there are no heat losses;
- maintenance of the system is simpler, there is no need to monitor the pressure, water level.
Expansion tank closed type WESTER
Closed membrane tank
For the membrane system, a sealed tank is used, the operation of which is similar to a conventional closed one. The principle of operation is very simple - when heated, the coolant expands, "excess" water enters one compartment of the tank, putting pressure on the elastic membrane. When cooling, the pressure decreases, the air from the second tank pushes cool water back into the system, that is, it circulates.
The membrane can be removable or non-removable, it does not come into contact with the internal walls of the device. If the membrane is damaged, it must be replaced, as the tank ceases to function.
Among the advantages of using such equipment, it should be noted:
- compact tank dimensions;
- the coolant does not evaporate;
- system heat losses are minimal;
- the system is protected from corrosion;
- it is possible to work with high pressure without fear of damage to the system.
Diaphragm expansion tank
Expansion tank of an open heating system calculation and installation rules
Expansion tanks are used in all schemes of individual heating systems. The main purpose of the expansion tank is to compensate for the volume of the heating system caused by the thermal expansion of the coolant.
Features of an open heating tank
The fact is that the volume of the coolant increases with increasing pressure, and if no additional capacity is provided where the excess volume could fit, then the pressure in the heating system can increase so much that a breakthrough occurs. An expansion tank is used to eliminate excess pressure in the system.
In addition, the expansion tank of an open heating system differs from tanks designed for closed systems. In closed systems, tanks are used that do not communicate with the atmosphere. In an open system, the use of such a tank is impossible, since excess pressure in the tank will create a large resistance to the circulation of the coolant. Therefore, open tanks are used for open heating systems.
Hence, there is a big disadvantage of open heating systems - this is the evaporation of the coolant from the tank. As a result, it is periodically necessary to control the level of coolant in the tank and, if necessary, make up for losses.
In addition, for open heating systems, it is important not only that the tank can communicate with the atmosphere, but also the correct calculation of the tank volume and proper installation and connection to the heating system
Calculation of the volume of an open expansion tank
Traditionally, the volume of the expansion tank is defined as 5% of the volume of the entire heating system. This is due to the fact that with an increase in water temperature to 80 degrees, its volume increases by approximately 4%. Adding to this a small space so that the water does not overflow over the edges of the tank by another 1%, in total we get the volume of the expansion tank as a percentage of the volume of the entire heating system.
If another coolant is used in an open system, then the volume of the tank should be adjusted based on the thermal expansion of the coolant used.
Most of the difficulties arise with the calculation of the volume of coolant in the heating system. To calculate the volume of the system, it is necessary to sum up the internal volume of all elements of the pipe system of radiators, heating and the boiler. Also, the volume of the system can be determined indirectly by the power of the boiler, based on the fact that 1 kW of boiler power is needed to heat 15 liters of coolant.
Installation and connection of an open expansion tank
Unlike a closed expansion tank, there are certain rules for an open one.
The most important rule is that the tank must be located above the entire heating system. Otherwise, according to the principle of communicating vessels, water will flow out of it.
This circumstance often leads to the rejection of an open-type heating system, because. it is not always possible to conveniently install an expansion tank.
The second important feature is that the tank must be connected to the return line. The fact is that the return temperature of the water is lower, and, therefore, the water will evaporate more slowly.
In addition, given the low return water temperature, the expansion tank can be connected to the system using a transparent hose, which will make it easier to control the amount of water in the system.
Additionally, the expansion tank can be provided with special pipes to prevent overflow and control the water level in the tank.
Device selection according to the calculation
Before proceeding with the calculation of the membrane, you need to know that the larger the volume of the heating system and the higher the maximum temperature index of the coolant, the larger the tank itself should be.
There are several ways in which the calculation is carried out: contacting specialists at the design bureau, performing calculations on their own using a special formula, or calculating using an online calculator.
The calculation formula looks like this: V = (VL x E) / D, where:
- VL - the volume of all main parts, including the boiler and other heating devices;
- E is the coefficient of expansion of the coolant (in percent);
- D is an indicator of membrane efficiency.
Volume determination
The easiest way to determine the average volume of the heating system is by heating boiler capacity based on 15 l/kW. That is, with a boiler power of 44 kW, the volume of all highways of the system will be equal to 660 liters (15x44).
The expansion coefficient for a water system is approximately 4% (at a heating medium temperature of 95 °C).
If antifreeze is poured into the pipes, then they resort to the following calculation:
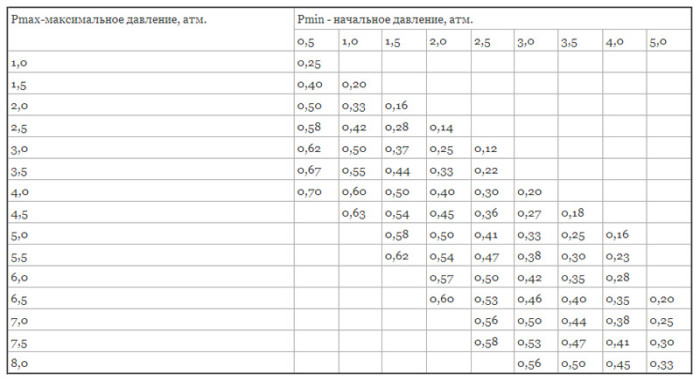
The efficiency rating (D) is based on the initial and highest pressure in the system, as well as the starting air pressure in the chamber. The safety valve is always set to maximum pressure. To find the value of the performance indicator, you need to carry out the following calculation: D = (PV - PS) / (PV + 1), where:
- PV - the maximum pressure mark in the system, for individual heating, the indicator is 2.5 bar;
- PS - the membrane charging pressure is usually 0.5 bar.
Now it remains to collect all the indicators in the formula and get the final calculation:
The resulting number can be rounded up and opt for an expansion tank model starting from 46 liters. If water is used as a heat carrier, then the volume of the tank will be at least 15% of the capacity of the entire system. For antifreeze, this figure is 20%. It is worth noting that the volume of the device may be slightly larger than the calculated number, but in no case, not less.
Formula for calculating the volume of the expansion tank
KE - the total volume of the entire heating system. This indicator is calculated based on the fact that I kW of heating equipment power is equal to 15 liters of coolant volume. If the boiler power is 40 kW, then the total volume of the system will be KE \u003d 15 x 40 \u003d 600 l;
Z is the value of the temperature coefficient of the coolant.As already noted, for water this is about 4%, and for antifreeze of different concentrations, for example 10-20% ethylene glycol, from 4.4 to 4.8%;
N is the efficiency value of the membrane tank, which depends on the initial and maximum pressure in the system, the initial air pressure in the chamber. Often this parameter is specified by the manufacturer, but if it is not there, you can perform the calculation yourself using the formula:
DV - the highest allowable pressure in the network. As a rule, it is equal to the allowable pressure of the safety valve and rarely exceeds 2.5-3 atm for ordinary domestic heating systems;
DS is the pressure value of the initial charge of the membrane tank based on a constant value of 0.5 atm. for 5 m of the length of the heating system.
N = (2.5-0.5)/
So, from the data obtained, we can derive the volume of the expansion tank with a boiler power of 40 kW:
K \u003d 600 x 0.04 / 0.57 \u003d 42.1 liters.
A 50 l tank with an initial pressure of 0.5 atm is recommended. since the final indicators for choosing a product should be slightly higher than the calculated ones. A slight excess of the volume of the tank is not as bad as the insufficiency of its volume. In addition, when using antifreeze in the system, experts advise choosing a tank with a volume of 50% more than the calculated one.
Calculator for calculating the volume of an expansion tank for a heating system
What you need to know when making calculations
When installing a heating system, it is not always possible to save usable space, which is so important in small rooms. But at the same time, you can find out the exact volume of the desired device.
When calculating, the following formula is used:
Vb (tank volume) = Vt (heat transfer fluid volume) * Kt ( heat expansion factor) / F (membrane tank capacity factor)
To determine the volume of the coolant, the following methods are used:
- the time of trial filling of the entire structure is recorded. This can be done with a water meter;
- add up all the volumes of the mechanisms present - pipes, batteries and heat sources;
- a correspondence of 15 liters of coolant fluid per kilowatt of equipment power is applied.
Calculation of volume on a separate example
The coefficient that takes into account the thermal expansion of the coolant used depends on the presence of antifreeze additives. It varies depending on the percentage of these additives, and can also change under the influence of temperature. There are special tables where you can see the data from the calculation of the heating of the coolant. This information is entered into the calculator. If water is used, then this is necessarily displayed in the program.
Antifreeze liquids as a heat carrier are especially relevant if it is necessary to turn off the heating in the cold season.
Be sure to take into account the efficiency factor of the membrane expansion tank. It can be determined by this formula:
F= (Pm-Pb)/(P1+1)
In this case, Pm stands for the maximum pressure that can lead to emergency activation of a special safety valve. This value must be indicated in the product data sheet.
The diagram shows the installation option of the device
Pb is the pressure for pumping the air chamber of the device. If the design has already been pumped up, then the parameter is indicated in the technical specifications. This value can be changed independently. For example, to resume pumping with a car pump or to remove excess air using a built-in nipple. For autonomous systems, the recommended indicator is 1-1.5 atmospheres.
Related article:
Tank in an open heating system
In such a system, the coolant - plain water - moves according to the laws of physics in a natural way due to the different densities of cold and hot water. The slope of the pipes also contributes to this. The coolant, heated to a high temperature, tends upward at the outlet of the boiler, pushed out by cold water coming from the return pipeline from below. This is how natural circulation occurs, as a result of which the radiators heat up. It is problematic to use antifreeze in a self-flowing system due to the fact that in the expansion tank the coolant is in the open state and quickly evaporates, which is why only water acts in this capacity.When heated, it increases in volume, and its excess enters the tank, and when cooled, it returns to the system. The tank is located at the highest point of the contour, usually in the attic. So that the water in it does not freeze, it is insulated with insulating materials and connected to the return pipeline to avoid boiling. In case of overfilling the tank, water is discharged into the sewer.
The expansion tank is not closed with a lid, hence the name of the heating system - open. The water level in the tank must be controlled so that there are no air pockets in the pipeline, leading to inefficient operation of the radiators. The tank is connected to the network through an expansion pipe, and a circulation pipe is provided to ensure the movement of water. As the system fills up, water reaches the signal pipe, on which
tap. An overflow pipe is used to control the expansion of water. It is responsible for the free movement of air inside the container. To calculate the volume of an open tank, you need to know the volume of water in the system.