— —
CAUTION 1
|
ТемпеÑаÑÑÑа a |
ТемпеÑаÑÑÑа завиÑÐ¸Ñ Ð¾Ñ ÑÑепени Ð¸Ñ Ð¸Ð·Ð¼ÐµÐ»ÑÑениÑ.
a
|
Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ¼ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð . a |
ТемпеÑаÑÑÑа Ð · Ð ²ðñðμμññ²²² ññðððððÐñðñññððððððñððððððððððð² Ð Ð ñоñññð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μñ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðððñððμ Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐñÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ¸Ñ. Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ñ ñ ñ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð »ÐµÑода.
a
ТемпеÑаÑÑÑа, Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μl
a
slingshot Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ел Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ññññððð Ð ² иñññðð - Ð ² Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð 'Ð Ð Ð Ð »Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ñ ñ ñ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð »ÐµÑода.
a
100% Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð δÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð δÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð ² Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ññð ° ° °ñ
a
100% Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð 'Ð Ð Ð Ð' Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð CAUTION.
a
|
Ð ²Ðððð¸Ð¼ÐμÐμÐμÐðÐ °Ð²Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ðññ a |
rпÑеделение slingshot Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ² »Ñное вÑемÑ.
a
|
| Ð ¢ ÐμмпÐμÑÐ ° ÑÑÑÑ, С, ÑÐ ° монР° гÑÐμвР° Ð½Ð¸Ñ Ð¸ ÑÐ »ÐμÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ð½ÐμкоÑоÑÑÑ ÑвÐμÑÐ'ÑÑ Ð²ÐμÑÐμÑÑв и оÑÐμвÑÐ¸Ñ Ð¿Ñл Ðμй (Ð ° ÑÑогÐμÐ »Ðμй. a |
Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ½ ¸ðμμðккÐμвÐðÐðввввР°Ð °Ð²Ð²ÐðÐ °ðÐ °Ð °ÐðÐððÐ'ððñððð¸¸ððð¾ñññμ¹¹¹¹¹ ТемпеÑаÑÑÑа Ð · Ð Ð ²ÐððÐμÐ Ð Ð Ел фор Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ñ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ² ² Ð Ð Ð Ð
a
Lock Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ñð¸ððμμðððμ¼¿ºÐºðÐμ²ñÐμÐðÐ °Ð²²Ð²ÐðÐ °ÐðвÐðÐμÐðÐ °Ð °Ðμððð'''ðñññññ¸'ððð¾ñññμμμ¹¹¹¹ ТемпеÑаÑÑÑа Ð · Ð ²ÐððμμÐ Ð Ð Ð ²ÐðÐμÐ Ð Ð ²ñosððð¾¾''¸ññðððððÐðÐμñððð𲲸 μμð½μμ𲸸 Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ²
a
Ð ÐμРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРг ÐÑÐµÐ´ÐµÐ»Ð°Ñ 350 - 700 С. ТемпеÑаÑÑÑа Ð · Ð ²ðñðμμññ²²² ññðððððÐñðñññððððððñððððððððððð² Ð Ð ñоñññð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μñ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μμñððμ ° ° Ð ÐμйÐñ ° Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ñ ñ ñ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ð РРРРРРв нем ÑглеÑода.
a
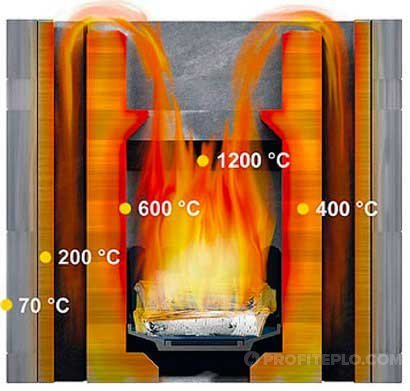
Factors affecting the combustion temperature of firewood
There are several factors that contribute to combustion:
- The type of wood used for burning.
- material moisture.
- The volume of air entering the furnace.
These are the main indicators that you need to pay special attention to, since the efficiency of burning wood, and the temperature that can rise during the combustion process, will depend on them.
Humidity level
The moisture content of wood plays a key role in kindling, so this important point requires separate consideration. Any tree that has just been cut down has a certain moisture content. In most cases, this figure is 50%. But in some cases it increases to 65%. And this suggests that this type of material will dry for a very long time under the influence of high temperature before igniting.
Part of the heat will go only to remove excess moisture by evaporation. For this reason, the temperature will not reach the maximum value. Heat transfer under this condition will decrease.
For maximum benefit, there are a few basic options to use:
- Drying is the best option. To do this, the tree is cut into small pieces, and then folded into a dry place in a barn or shed. Under natural conditions, the drying process will take approximately 1 year. And if the firewood is stored longer and lies for two summers, then their humidity will be 20%. This is already the best indicator.
- The second option is less preferable - to burn what is, not paying attention to humidity. But in this situation, you will have to spend twice as much firewood to form the desired temperature. In addition, you should be prepared to clean the chimney from soot.
The better the wood dries, the higher the combustion temperature can be taught. And it depends on the release of heat. Heat will not work with wet wood.
Warming up process
Warming up is the heating of a separate section of a wooden material to a temperature sufficient to ignite the entire surface.

After that, the process will continue when coal is formed. When heated to 250-350 degrees, the selected material will begin to decompose into components. Then smoldering begins, but the flame does not appear yet. At this point, smoke formation can be observed. When the temperature continues to rise, the level of pyrolysis gases increases - a flash occurs. Firewood will burn completely.
Flammability of materials
Flammability is directly affected by the percentage of moisture contained in the selected rock. An important role is played by the power of the heating source, as well as the cross-section of the wood and the speed of the air flow.
To make the flame flare up faster, it is desirable to use light wood, which has a large porosity. Wet wood will ignite very slowly, because it will dry out before an open fire forms.
Burning also depends on the shape of the tree - it is advisable to use a rectangle, since the circle will flare up much longer. To speed up the process, it is necessary to select a material with a small cross section and sharp edges
It is important to ensure that the required amount of oxygen is supplied to the heated area.
The combustion temperature of firewood and flammability are also greatly influenced by the design of a home stove. It can be made from different materials and this directly affects the combustion temperature of the materials put inside. If the stove is massive, then the firewood in it will burn out almost completely, but this process will take a very long time.
Great care must be taken when using. Failure to comply with safety measures can lead to a fire in a wood-burning bath at a high burning temperature of the stove

A potbelly stove made of steel sheet cools quickly, while heat is distributed throughout the surrounding space, but first it will pass from the combustion zone to the walls, and only then into the room.
combustion process
By observing the functioning of the furnace, one can think about why the supplied air does not affect the color of the resulting flame. Oxygen must have a chemical effect and give the soot a bright color, which may even turn white. But this phenomenon can be easily explained, because the particle size also affects the temperature. The smaller it is, the lower the temperature will be. Therefore, small hot particles form the same temperature as the gas that surrounds them. It should also be noted that each type of wood has a certain heat transfer. To find out these figures, you can study the table, which shows all the thermal conductivity indicators for each type of material.
Thermal characteristics of wood
Wood species differ in density, structure, quantity and composition of resins. All these factors affect the calorific value of wood, the temperature at which it burns, and the characteristics of the flame.
Poplar wood is porous, such firewood burns brightly, but the maximum temperature indicator reaches only 500 degrees. Dense wood species (beech, ash, hornbeam), burning, emit over 1000 degrees of heat. Birch indicators are somewhat lower - about 800 degrees. Larch and oak flare up hotter, giving out up to 900 degrees of heat. Pine and spruce firewood burns at 620-630 degrees.
The quality of firewood and how to choose the right one
Birch firewood has the best ratio of heat efficiency and cost - it is not economically profitable to heat with more expensive species with high combustion temperatures.
Spruce, fir and pine are suitable for making fires - these softwoods provide relatively moderate heat. But it is not recommended to use such firewood in a solid fuel boiler, in a stove or fireplace - they do not emit enough heat to effectively heat the home and cook food, they burn out with the formation of a large amount of soot.
Fuel from aspen, linden, poplar, willow and alder is considered low-quality firewood - porous wood emits little heat during combustion. Alder and some other types of wood "shoot" embers in the process of burning, which can lead to a fire if firewood is used to fire an open fireplace.
When choosing, you should also pay attention to the degree of moisture content of the wood - raw firewood burns worse and leaves more ash
Factors affecting the combustion temperature
The temperature of burning wood in a stove depends not only on the type of wood. Significant factors are also the moisture content of firewood and the traction force, which is due to the design of the thermal unit.
Influence of humidity
In freshly cut wood, the moisture index reaches from 45 to 65%, on average - about 55%. The combustion temperature of such firewood will not rise to the maximum values, since the thermal energy will be spent on the evaporation of moisture.In accordance with this, the heat transfer of the fuel is reduced.
In order for the required amount of heat to be released during the combustion of wood, three ways are used
:
- almost twice as much freshly cut firewood is used for space heating and cooking (this translates into higher fuel costs and the need for frequent maintenance of the chimney and gas ducts, in which a large amount of soot will settle);
- freshly cut firewood is pre-dried (the logs are sawn, split into logs, which are stacked under a canopy - it takes 1-1.5 years for natural drying to 20% humidity);
- dry firewood is purchased (financial costs are offset by the high heat transfer of the fuel).
The calorific value of birch firewood from freshly cut wood is quite high. Freshly cut ash, hornbeam and other hardwood fuels are also suitable for use.
Influence of air supply
By limiting the supply of oxygen to the furnace, we lower the combustion temperature of the wood and reduce the heat transfer of the fuel. The duration of combustion of the fuel load can be increased by closing the damper of the boiler unit or stove, but fuel savings result in low combustion efficiency due to suboptimal conditions. To the wood burning in an open-type fireplace, air enters freely from the room, and the intensity of draft depends mainly on the characteristics of the chimney.
The simplified formula for the ideal combustion of wood is
:
C + 2H2 + 2O2 = CO2 + 2H2O + Q (heat)
Carbon and hydrogen are burned when oxygen is supplied (left side of the equation), resulting in heat, water and carbon dioxide (right side of the equation).
In order for dry wood to burn at maximum temperature, the volume of air that enters the combustion chamber must reach 130% of the volume required for the combustion process. When the air flow is blocked by dampers, a large amount of carbon monoxide is formed, and the reason for this is the lack of oxygen. Carbon monoxide (unburnt carbon) goes into the chimney, while the temperature in the combustion chamber drops and the heat transfer of firewood decreases.
An economical approach when using a solid fuel wood-fired boiler is to install a heat accumulator that will store excess heat generated during fuel combustion in the optimal mode, with good traction.
With wood-burning stoves, you won’t be able to save fuel like that, since they directly heat the air. The body of a massive brick oven is capable of accumulating a relatively small part of the thermal energy, while for metal stoves, excess heat goes directly into the chimney.
If you open the blower and increase the draft in the furnace, the combustion intensity and heat transfer of the fuel will increase, but the heat loss will also increase. With the slow combustion of firewood, the amount of carbon monoxide increases and heat transfer decreases.
What is the combustion process
Combustion is a process at the turn of physics and chemistry, which consists in the transformation of a substance into a residual product. At the same time, thermal energy is released in large quantities. The combustion process is usually accompanied by the emission of light, which is called a flame. Also, during the combustion process, carbon dioxide is released - CO 2, an excess of which in an unventilated room can lead to headaches, suffocation and even death.
For the normal course of the process, a number of mandatory conditions must be met.
First, combustion is possible only in the presence of air. Impossible in a vacuum.
Secondly, if the area in which combustion occurs is not heated to the ignition temperature of the material, then the combustion process will stop. For example, the flame will go out if a large log is immediately thrown into a freshly fired oven, preventing it from warming up on small wood.
Thirdly, if the subjects of combustion are damp and emit liquid vapors, and the combustion rate is still low, the process will also stop.

Flammability
The flammability of a tree species is greatly influenced by its volumetric weight and the percentage of moisture contained in the species.
An important role for the appearance of fire is played by the power of the heating source, the cross-section of wood, the speed of the air flow and the density of the material. Light wood with high porosity can cause the earliest appearance of a flame.
As for wet wood, it ignites more slowly, since it must dry before an open fire appears.
Expert advice:
for storing firewood, choose dry places, away from moisture. Otherwise, they will dry for a long time in the oven.
Also, combustion will depend on the shape of the logs, since the round forms of the tree will not burn as well as the rectangular logs, which have a small section, sharp ribs and a developed side surface. Unplaned wood species of birch logs are more likely to ignite than smooth wood.
A very important condition for the combustion of any type of wood is a normal flow of oxygen. In some respects, the combustion of wood even surpasses
Complete and incomplete combustion what is released during the combustion of wood
Not only wood can burn, but also its products (chipboard, fiberboard, MDF), as well as metal. However, the combustion temperature of all products is different. For example: the combustion temperature of steel is 2000 degrees, aluminum foil - 350, and wood begins to ignite already at 120 - 150.

If 1 kg of wood burned out, then the products of combustion in the gaseous state will stand out somewhere around 7.5 - 8.0 cubic meters. In the future, they are no longer able to burn, except for carbon monoxide.
Wood combustion products:
- Nitrogen;
- Carbon monoxide;
- Carbon dioxide;
- Water vapor;
- Sulphur dioxide.
Burning by nature can be complete or incomplete. But both of them occur with the formation of smoke. With incomplete combustion, some combustion products can still burn in the future (soot, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons). But if complete combustion occurred, then the products that were formed later are not capable of burning (sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide, water vapor).
Burning wood. Being a material of organic origin, wood is subject to the damaging effects of high temperatures: when air enters, it burns out, forming carbon dioxide and water vapor, in the absence of oxygen, the tree collapses, turning into charcoal and releasing combustible gases.
Wood is a product of photosynthesis and does not disturb the CO2 balance when burned, making it an attractive alternative energy source, especially given the ever-increasing prices of conventional fuels.
One of the main advantages of most solid fuel boilers is that they can be used to create a completely autonomous system. Therefore, more often such boilers are used in areas where there are problems with the supply of natural gas or for a country house. The advantage of solid fuel boilers is also the availability and low cost of fuel. The disadvantage of most representatives of boilers of this class is also obvious - they cannot operate in a fully automatic mode, as they require regular fuel loading.
As a material of organic origin, tree
exposed to the destructive effects of high temperatures: when air enters, it burns out, forming carbon dioxide and water vapor, in the absence of oxygen, the tree collapses, turning into charcoal and releasing combustible gases.
The flammability of wooden elements and structures depends on the hardness of the wood, its moisture content, the nature of the surface treatment, and the location in the room. Thus, hardwoods and smooth-planed surfaces have a lower degree of flame retardancy; the presence of a "fireplace effect" (thrust) and a wooden structure contributes to the rapid development of a fire
At a temperature of 275 ° in the open air, wood burning begins, that is, its combination with atmospheric oxygen, accompanied by a luminous flame. At the same time, in thick pieces, wood does not warm up due to low thermal conductivity; the combustion that has begun turns into smoldering and stops altogether. Therefore, practically the ignition point of wood can be considered (for pine) 300-330 °.
wood pyrolysis
. When wood is exposed to temperatures above 100 ° without air access, chemical changes begin to occur in it, characterized by the release of gaseous and vaporous products of wood decomposition. This process is called wood pyrolysis. upholstered furniture repair
When the temperature rises to 170 °, water is released from the wood, at a temperature of 170 to 270 ° the decomposition of wood begins, and at 270-280 ° there is an energetic charring of the wood with a rapid release of heat. From 280 to 380° there is the main period of dry distillation with the release of the largest amount of acetic acid, methyl alcohol and light resin. The distillation practically ends at a temperature of 430 ° with the formation of black coal (approximately in the amount of 19% of ).
Complete and incomplete combustion what is released during the combustion of wood
Not only wood can burn, but also its products (chipboard, fiberboard, MDF), as well as metal. However, the combustion temperature of all products is different. For example: the combustion temperature of steel is 2000 degrees, aluminum foil - 350, and wood begins to ignite already at 120 - 150.

If 1 kg of wood burned out, then the products of combustion in the gaseous state will stand out somewhere around 7.5 - 8.0 cubic meters. In the future, they are no longer able to burn, except for carbon monoxide.
Wood combustion products:
- Nitrogen;
- Carbon monoxide;
- Carbon dioxide;
- Water vapor;
- Sulphur dioxide.
Burning by nature can be complete or incomplete. But both of them occur with the formation of smoke. With incomplete combustion, some combustion products can still burn in the future (soot, carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons). But if complete combustion occurred, then the products that were formed later are not capable of burning (sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide, water vapor).
When heated to 130-150 ° wood begins to self-heat. If you create the conditions necessary for the accumulation of heat, then the wood ignites spontaneously.
At the temperatures of industrial premises, wood does not pose a risk of spontaneous combustion. This danger appears only when it is heated to a temperature above 130 °. Spontaneous combustion of wood
in open wooden structures or stacks does not occur due to the lack of appropriate conditions for heat accumulation. Usually, spontaneous combustion of wood occurs in hidden wooden structures or in accumulated wood waste that has been heated for a long time.
Heating wood up to 110 ° is safe and quite acceptable in the process of drying or processing it. At this temperature, drying of wood and partial release of volatile substances occur. The decomposition of wood does not occur, and its chemical composition remains unchanged. At a temperature of 150°, the decomposition of unstable wood compounds is observed. Its color becomes yellow. At a temperature of 230°, its decomposition intensifies, and processes begin to take place with the release of gaseous products. Moreover, a large percentage is occupied by H 2 O and CO 2. The wood turns brown with surface charring. As a result of this process, the chemical composition of wood changes, i.e., there is an increase in the percentage of carbon and a decrease in hydrogen and oxygen. The volumetric weight of wood decreases, but its volume remains constant. The porosity of wood increases, therefore, its surface of contact with air also increases. At a temperature of 230-270 ° in wood, pyrophoric coal is formed, which is able to vigorously absorb (adsorb) oxygen.The latter, by oxidizing the coal, raises the temperature so much that the coal ignites and the wood begins to burn. Spontaneous combustion of wood can occur at lower temperatures for another reason.
The process of wood decomposition is exothermic and under certain conditions can cause its spontaneous combustion. But for this it is necessary that the amount of heat released due to the reaction of wood decomposition would exceed the heat transfer to the environment. Such conditions can be created when wood waste in the dryer accumulates on the heater or the beam is laid in brickwork walls next to a heat source. Another process takes place in sawdust or other wood waste piled in a pile. In practice, there have been cases of heating of sawdust and their spontaneous combustion. Some authors (prof. B. G. Tideman and engineer P. G. Demidov) believe that biological processes are the main cause of spontaneous combustion of sawdust. Microorganisms are born in wet sawdust, which multiply rapidly when the heat is concentrated. Microorganisms decompose fiber. Fermentation of the resulting products occurs. This whole process is accompanied by the release of heat, which heats the sawdust to 60-70 °. In this case, coal is formed that can absorb vapors and gases. The absorption of vapors and gases by coal causes an oxidative process, which leads to further heating of the mass. Due to the heat of adsorption, the temperature rises and reaches 100-130°. Then porous carbon is formed, which also absorbs vapors and gases and raises the temperature of the sawdust. Upon reaching a temperature of 200 ° begins to decompose fiber, which is part of the sawdust. Decomposing, the fiber forms coal, which can be intensively oxidized. Due to the oxidation of coal, the temperature rises to 250-300 °, and the sawdust ignites spontaneously.
Heat output of firewood table of main species
Considering different types of wood, in the end, you can notice some differences: some of them burn very brightly and perfectly, while there is a strong warmth, while others just barely smolder, leaving behind almost no heat. The point here is not at all in their dryness or humidity, but in their structure and composition, as well as the structure of the tree.
Oak, beech, birch, larch or hornbeam have the highest heat output, but these species are the most unprofitable and expensive. Therefore, they are used very rarely, and then in the form of chips or sawdust. The lowest heat transfer is in poplar, alder and aspen. There is a table that lists the main breeds and their heat output.
Table of some basic rocks and their heat output:
- Ash, beech - 87%;
- Hornbeam - 85%;
- Oak - 75, 70%;
- Larch - 72%;
- Birch - 68%;
- Fir - 63%;
- Linden - 55%;
- Pine - 52%;
- Aspen - 51%;
- Poplar - 39%.
Conifers have a low combustion temperature, so they are best used for igniting an open fire (bonfire). However, pine wood catches fire very quickly and can smolder for a long time, since it contains a huge amount of resins, so this breed is able to retain heat for a long time. But still, it is better not to use softwood for heating, since during its combustion a lot of flue gases are formed, which settle in the form of soot on the chimney and have to be cleaned, as it quickly becomes clogged.