Heat meters
Let us recall once again that the heat supply network of an apartment building is equipped with heat energy metering units that record both the consumed gigacalories and the cubic capacity of water passed through the house line.
In order not to be surprised by bills containing unrealistic amounts for heat at temperatures in the apartment below the norm, before the start of the heating season, check with the management company whether the meter is in working order, whether the verification schedule has been violated.
Many manufacturers of boiler equipment require that at the inlet to the boiler there be water not lower than a certain temperature, since the cold return has a bad effect on the boiler:
-
- the efficiency of the boiler is reduced,
- condensation on the heat exchanger increases, which leads to boiler corrosion,
- due to the large temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the heat exchanger, its metal expands in different ways - hence the stress and possible cracking of the boiler body.
The first method is ideal, but expensive.
Esbe
offers a ready-made module for adding to the boiler return and controlling the load of the heat accumulator (relevant for solid fuel boilers) - the LTC 100 device is an analogue of the popular Laddomat unit (Laddomat).
Phase 1. The beginning of the combustion process. The mixing device allows you to quickly increase the temperature of the boiler, thus starting the circulation of water only in the boiler circuit.
Phase 2: Start loading the storage tank. The thermostat, opening the connection from the storage tank, sets the temperature, which depends on the version of the product. High, guaranteed return temperature to the boiler, maintained through the entire combustion cycle
Phase 3: The storage tank is in the process of being loaded. Good management ensures efficient loading of the storage tank and proper stratification in it.
Phase 4: The storage tank is fully loaded. Even at the end of the combustion cycle, the high quality of the regulation ensures good control of the return temperature to the boiler while simultaneously fully loading the storage tank
Phase 5: End of the combustion process. By completely closing the top opening, the flow is directed directly to the storage tank, using the heat in the boiler
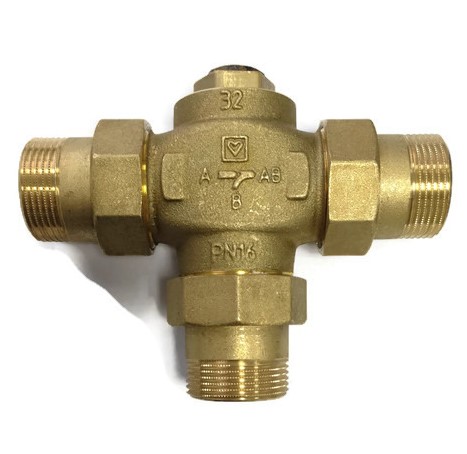
The second method is simpler, using a high quality three-way thermal mixing valve.
For example valves from ESBE or or VTC300. These valves differ depending on the capacity of the boiler used. VTC300 is used with boiler power up to 30 kW, VTC511 and VTC531 - with more powerful boilers from 30 to 150 kW
The valve is mounted on the bypass line between the boiler supply and return.
The built-in thermostat opens input "A" when the temperature at the output "AB" is equal to the thermostat setting (50, 55, 60, 65, 70 or 75°C). Inlet "B" closes completely when the temperature at inlet "A" exceeds the nominal opening temperature by 10°C.
When the temperature of the coolant at the outlet of the valve "AB" is less than 61°C, the inlet "A" is closed, hot water flows through the inlet "B" from the boiler supply to the return. If the temperature of the coolant at the outlet "AB" exceeds 63°C, the bypass inlet "B" is blocked and the coolant from the return of the system through the inlet "A" enters the return of the boiler. Bypass outlet "B" reopens when the temperature at outlet "AB" drops to 55°C
When the coolant passes through outlet “AB” with a temperature of less than 61°C, inlet “A” from the return of the system is closed, and hot coolant is supplied to outlet “AB” from bypass “B”. When the outlet “AB” reaches a temperature of more than 63°C, the inlet “A” opens, and the water from the return is mixed with the water from the bypass “B”. To equalize the bypass (so that the boiler does not work constantly on a small circle of circulation), a balancing valve must be installed in front of the input "B" on the bypass.
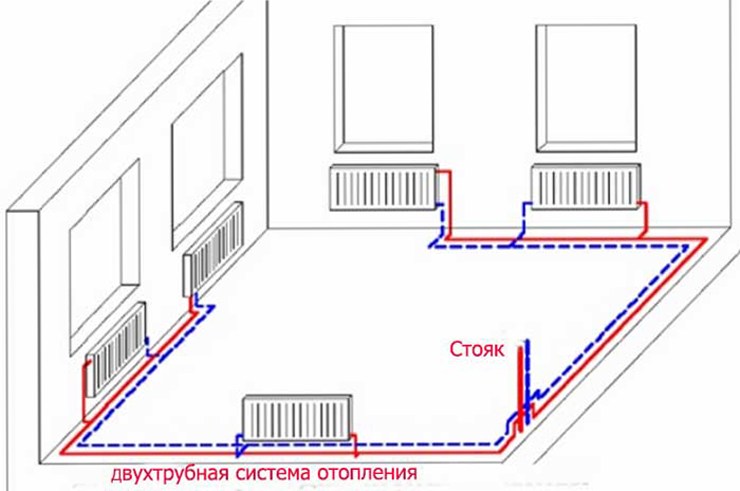
Briefly about the return and supply in the heating system
The water heating system, using the supply from the boiler, supplies the heated coolant to the batteries, which are located inside the building. This makes it possible to distribute heat throughout the house. Then the coolant, that is, water or antifreeze, after passing through all available radiators, loses its temperature and is fed back for heating.
The simplest heating structure is a heater, two lines, an expansion tank and a set of radiators. The conduit through which the heated water from the heater moves to the batteries is called the supply. And the conduit, which is located at the bottom of the radiators, where the water loses its original temperature, returns back, and will be called the return. Since, when heated, the water expands, the system provides a special tank. It solves two problems: a supply of water to saturate the system; accepts excess water, which is obtained during expansion. Water, as a heat carrier, is directed from the boiler to the radiators and back. Its flow is provided by a pump, or natural circulation.
Supply and return is present in one and two tubular heating systems. But in the first there is no clear division into the supply and return pipes, and the entire pipe line is conditionally divided in half. The column that leaves the boiler is called the supply, and the column that leaves the last radiator is called the return.
In a single-pipe line, heated water from the boiler flows sequentially from one battery to another, losing its temperature. Therefore, at the very end, the batteries themselves will be cold. This is the main and probably the only disadvantage of such a system.
But the single-pipe option will gain more pluses: lower costs for the purchase of materials are required compared to the 2-pipe; the diagram is more attractive. The pipe is easier to hide, and it is also possible to lay pipes under doorways. Two-pipe is more efficient - two fittings (supply and return) are installed in parallel in the system.
Such a system is considered by experts to be more optimal. After all, her work fluctuates in the supply of hot water through one pipe, and the chilled water is diverted in the opposite direction through another pipe. Radiators in this case are connected in parallel, which ensures uniformity of their heating. Which one establishes the approach should be individual, while taking into account many different parameters.
Just a few general tips to follow:
- The entire line must be completely filled with water, air is a hindrance, if the pipes are airy, the heating quality is poor.
- A sufficiently high fluid circulation rate must be maintained.
- The difference between the supply and return temperatures should be about 30 degrees.
Optimal values in an individual heating system
Autonomous heating helps to avoid many problems that arise with a centralized network, and the optimal temperature of the coolant can be adjusted according to the season. In the case of individual heating, the concept of norms includes the heat transfer of a heating device per unit area of the room where this device is located. The thermal regime in this situation is provided by the design features of the heating devices.
It is important to ensure that the heat carrier in the network does not cool below 70 ° C. 80 °C is considered optimal
It is easier to control heating with a gas boiler, because manufacturers limit the possibility of heating the coolant to 90 ° C. Using sensors to adjust the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be controlled.
A little more difficult with solid fuel devices, they do not regulate the heating of the liquid, and can easily turn it into steam. And it is impossible to reduce the heat from coal or wood by turning the knob in such a situation. At the same time, the control of heating of the coolant is rather conditional with high errors and is performed by rotary thermostats and mechanical dampers.
Electric boilers allow you to smoothly adjust the heating of the coolant from 30 to 90 ° C. They are equipped with an excellent overheating protection system.
The device of the heating system what is the return
The heating system consists of an expansion tank, batteries, and a heating boiler. All components are interconnected in a circuit. A fluid is poured into the system - a coolant. The fluid used is water or antifreeze. If the installation is done correctly, the liquid is heated in the boiler and begins to rise through the pipes. When heated, the liquid increases in volume, the excess enters the expansion tank.
Since the heating system is completely filled with liquid, the hot coolant displaces the cold one, which returns to the boiler, where it heats up. Gradually, the temperature of the coolant increases to the required temperature, heating the radiators. The circulation of the liquid can be natural, called gravity, and forced - with the help of a pump.
The return is a coolant that, having passed through all the heating devices included in the circuit, gives off its heat and, cooled, enters the boiler again for the next heating.
Batteries can be connected in three ways:
- 1. Bottom connection.
- 2. Diagonal connection.
- 3. Side connection.
In the first method, the coolant is supplied and the return is removed at the bottom of the battery. This method is advisable to use when the pipeline is located under the floor or baseboards. With a diagonal connection, the coolant is supplied from above, the return is discharged from the opposite side from below. This connection is best used for batteries with a large number of sections. The most popular way is side connection. Hot liquid is connected from above, the return flow is carried out from the bottom of the radiator on the same side where the coolant is supplied.
Heating systems differ in the way pipes are laid. They can be laid in one-pipe and two-pipe way. The most popular is the single-pipe wiring diagram. Most often it is installed in multi-storey buildings. It has the following advantages:
- a small number of pipes;
- low cost;
- ease of installation;
- serial connection of radiators does not require the organization of a separate riser for draining liquid.
The disadvantages include the inability to adjust the intensity and heating for a separate radiator, the decrease in the temperature of the coolant as it moves away from the heating boiler. To increase the efficiency of single-pipe wiring, circular pumps are installed.
For the organization of individual heating, a two-pipe piping scheme is used. Hot feed is carried out through one pipe. On the second, the cooled water or antifreeze is returned to the boiler. This scheme makes it possible to connect radiators in parallel, ensuring uniform heating of all devices. In addition, the two-pipe circuit allows you to adjust the heating temperature of each heater separately. The disadvantage is the complexity of installation and the high consumption of materials.
Central heating
How the elevator assembly works
At the entrance of the elevator there are valves that cut it off from the heating main. On their closest flanges to the wall of the house, there is a division of areas of responsibility between residents and heat suppliers. The second pair of valves cuts off the elevator from the house.
The supply pipeline is always at the top, the return line is at the bottom. The heart of the elevator assembly is the mixing assembly, in which the nozzle is located. A jet of hotter water from the supply pipeline flows into the water from the return, involving it in a repeated circulation cycle through the heating circuit.
By adjusting the diameter of the hole in the nozzle, you can change the temperature of the mixture entering the .
Strictly speaking, the elevator is not a room with pipes, but this node. In it, water from the supply is mixed with water from the return pipeline.
What is the difference between the supply and return pipelines of the route
In normal operation, it is about 2-2.5 atmospheres. Typically, 6-7 kgf / cm2 enters the house at the supply and 3.5-4.5 at the return.
What is the difference in the heating system
The difference on the highway and the difference in the heating system are two completely different things. If the return pressure before and after the elevator does not differ, then instead of supplying the house, a mixture enters, the pressure of which exceeds the readings of the pressure gauge on the return line by only 0.2-0.3 kgf / cm2. This corresponds to a height difference of 2-3 meters.
This difference is spent on overcoming the hydraulic resistance of spills, risers and heaters. The resistance is determined by the diameter of the channels through which the water moves.
What diameter should be risers, fillings and connections to radiators in an apartment building
The exact values are determined by hydraulic calculation.
In most modern houses, the following sections are used:
- Heating spills are made from pipes DU50 - DU80.
- For risers, a pipe DN20 - DU25 is used.
- The connection to the radiator is made either equal to the diameter of the riser, or one step thinner.

In the photo - a more sensible solution. The diameter of the eyeliner is not underestimated.
What to do if the return temperature is too low
In such cases:
-
Reaming nozzle
. Its new diameter is agreed with the heat supplier. The increased diameter will not only raise the temperature of the mixture, it will also increase the drop. The circulation through the heating circuit will be accelerated. - In case of a catastrophic lack of heat, the elevator is disassembled, the nozzle is removed, and the suction (pipe connecting the supply to the return) is suppressed
.
The heating system receives water from the supply pipeline directly. The temperature and pressure drop increase sharply.
What to do if the return temperature is too high
- The standard measure is to weld the nozzle and drill it again, with a smaller diameter.
-
When an urgent solution is needed without stopping the heating, the differential at the elevator inlet is reduced with the help of shutoff valves. This can be done with an inlet valve on the return, controlling the process with a pressure gauge. This solution has three disadvantages:
- The pressure in the heating system will increase. We're limiting the outflow of water; the lower pressure in the system will become closer to the supply pressure.
- The wear of the cheeks and the valve stem will accelerate sharply: they will be in a turbulent flow of hot water with suspensions.
- There is always a chance of falling worn cheeks. If they completely shut off the water, the heating (primarily the access one) will be defrosted within two to three hours.
Why do you need a lot of pressure in the track
Indeed, in private houses with autonomous heating systems, an overpressure of only 1.5 atmospheres is used. And, of course, more pressure means more money for stronger pipes and more power for the boost pumps.
The need for more pressure is associated with the number of storeys of apartment buildings. Yes, a minimum drop is needed for circulation; but after all, the water must be raised to the level of the jumper between the risers. Each atmosphere of excess pressure corresponds to a water column of 10 meters.
Knowing the pressure in the line, it is easy to calculate the maximum height of the house, which can be heated without the use of additional pumps. The calculation instruction is simple: 10 meters are multiplied by the return pressure. The pressure of the return pipeline of 4.5 kgf / cm2 corresponds to a water column of 45 meters, which, with a height of one floor of 3 meters, will give us 15 floors.
By the way, hot water is supplied in apartment buildings from the same elevator - from the supply (at a water temperature not higher than 90 C) or the return. With a lack of pressure, the upper floors will remain without water.
How to make radiators hot looking for solutions
If it is found that the return is too cold, a series of troubleshooting steps should be taken. First of all, you need to check the correct connection.If the connection is not made correctly, the downpipe will be hot, but should be slightly warm. Pipes should be connected according to the diagram.
In order to avoid air locks that impede the advancement of the coolant, it is necessary to provide for the installation of a Mayevsky crane or a bleeder for air removal. Before venting, turn off the supply, open the tap and let the air out. Then the tap is closed, and the heating valves open.
Often the reason for the cold return is the control valve: the cross section is narrowed. In this case, the crane must be dismantled and the cross section increased using a special tool. But it is better to buy a new faucet and replace it.
The reason may be clogged pipes. It is necessary to check them for patency, remove dirt, deposits, clean well. If patency cannot be restored, clogged areas should be replaced with new ones.
If the speed of the coolant is insufficient, it is necessary to check whether there is a circulation pump and whether it meets the power requirements. If it is missing, it is advisable to install it, and if there is a lack of power, replace or upgrade it.
Knowing the reasons why heating may not work effectively, you can independently identify and eliminate malfunctions. The comfort in the house during the cold season depends on the quality of heating. If you do the installation work yourself, you can save on hiring third-party labor.
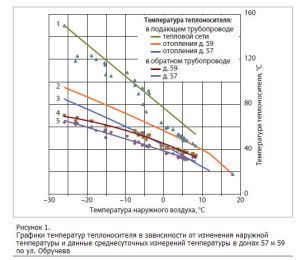
When autumn confidently walks across the country, snow flies beyond the Arctic Circle, and in the Urals night temperatures stay below 8 degrees, then the word form “heating season” sounds appropriate. People recall past winters and try to understand the normal temperature of the coolant in the heating system.
Prudent owners of individual buildings carefully revise the valves and nozzles of boilers. By October 1, tenants of an apartment building are waiting, like Santa Claus, a plumber from a management company. The ruler of valves and valves brings warmth, and with it - joy, fun and confidence in the future.
What is the difference between supply and return heating
And so, to sum up, what is the difference between supply and return in heating:
- Feed - the coolant that goes through the water conduits from the heat source. This can be an individual boiler or central heating of the house.
- The return is water that, having passed through all the radiators, goes back to the heat source. Therefore, at the input of the system - supply, at the output - return.
- It also differs in temperature. The supply is hotter than the return.
- Installation method. The conduit that is attached to the top of the battery is the supply; the one that connects to the bottom is the return line.
With a large temperature difference between the supply and return of the boiler, the temperature on the walls of the combustion chamber of the boiler approaches the temperature of the "dew point" and condensation may occur. It is known that during the combustion of fuel, various gases are released, including CO 2, if this gas combines with the “dew” that has fallen on the walls of the boiler, an acid is formed that corrodes the “water jacket” of the boiler furnace. As a result, the boiler can be quickly disabled. To prevent dew, it is necessary to design the heating system in such a way that the temperature difference between the supply and return is not too large. This is usually achieved by heating the return coolant and / or including a hot water boiler in the heating system with soft priority.
To heat the coolant between the return and supply of the boiler, a bypass is made and a circulation pump is installed on it. The power of the recirculation pump is usually chosen as 1/3 of the power of the main circulation pump (sum of pumps) (Fig. 41). In order to prevent the main circulation pump from "pushing through" the recirculation circuit in the opposite direction, a check valve is installed behind the recirculation pump.
Rice. 41. Return heating
Another way to heat the return is to install a hot water boiler in the immediate vicinity of the boiler. The boiler is “planted” on a short heating ring and positioned in such a way that hot water from the boiler after the main distribution manifold immediately enters the boiler, and from it returns back to the boiler. However, if the need for hot water is small, then both a recirculation ring with a pump and a heating ring with a boiler are installed in the heating system. With proper calculation, the recirculation pumping ring can be replaced with a system with three- or four-way mixers (Fig. 42).
Rice. 42. Return heating with three- or four-way mixers
Almost all technically significant devices and engineering solutions that are present in classical heating schemes were listed on the pages "Heating systems control equipment". When designing heating systems at real construction sites, they should be fully or partially included in the heating systems project, but this does not mean that exactly the heating fittings that are indicated on these pages of the site should be included in a specific project. For example, shut-off valves with built-in check valves can be installed at the make-up unit, or these devices can be installed separately. Instead of mesh filters, you can install mud filters. An air separator can be installed on the supply pipelines, or you can not install it, but instead mount automatic air vents in all problem areas. On the return line, you can install a dirt separator, or you can simply equip the collectors with drains. Adjustment of the temperature of the heat carrier for the circuits of "warm floors" can be done with a qualitative adjustment of three- and four-way mixers, and you can make a quantitative adjustment by installing a two-way valve with a thermostatic head. Circulation pumps can be installed on a common supply pipe or vice versa, on the return. The number of pumps and their location may also vary.
When autumn confidently walks across the country, snow flies beyond the Arctic Circle, and in the Urals night temperatures stay below 8 degrees, then the word form “heating season” sounds appropriate. People recall past winters and try to understand the normal temperature of the coolant in the heating system.
Prudent owners of individual buildings carefully revise the valves and nozzles of boilers. By October 1, tenants of an apartment building are waiting, like Santa Claus, a plumber from a management company. The ruler of valves and valves brings warmth, and with it - joy, fun and confidence in the future.
Calculation of the temperature regime of heating
When calculating the heat supply, the properties of all components must be taken into account. This is especially true for radiators. What is the optimal temperature in the radiators - + 70 ° C or + 95 ° C? It all depends on the thermal calculation, which is performed at the design stage.
An example of drawing up a heating temperature schedule
First you need to determine the heat loss in the building. Based on the data obtained, a boiler with the appropriate power is selected. Then comes the most difficult design stage - determining the parameters of heat supply batteries.
They must have a certain level of heat transfer, which will affect the temperature curve of the water in the heating system. Manufacturers indicate this parameter, but only for a certain mode of operation of the system.
If you need to spend 2 kW of thermal energy to maintain a comfortable level of air heating in a room, then the radiators must have no less heat transfer.
To determine this, you need to know the following quantities:
- The maximum water temperature in the heating system is allowed -t1.It depends on the power of the boiler, the temperature limit of exposure to pipes (especially polymer pipes);
- The optimum temperature that should be in the heating return pipes is t This is determined by the type of mains wiring (one-pipe or two-pipe) and the total length of the system;
- Required degree of air heating in the room –t.
With this data, you can calculate the temperature difference of the battery using the following formula:
Next, to determine the power of the radiator, you should use the following formula:
Where k is the heat transfer coefficient of the heating device. This parameter must be specified in the passport; F is the radiator area; Tnap - thermal pressure.
By varying the various indicators of the maximum and minimum water temperatures in the heating system, you can determine the optimal mode of operation of the system
It is important to correctly initially calculate the required power of the heater. Most often, the indicator of low temperature in heating batteries is associated with heating design errors.
Experts recommend adding a small margin to the obtained value of the radiator power - about 5%. This will be needed in case of a critical decrease in the temperature outside in the winter.
Most manufacturers indicate the heat output of radiators according to the accepted standards EN 442 for mode 75/65/20. This corresponds to the norm of the heating temperature in the apartment.
Ways to reduce heat loss
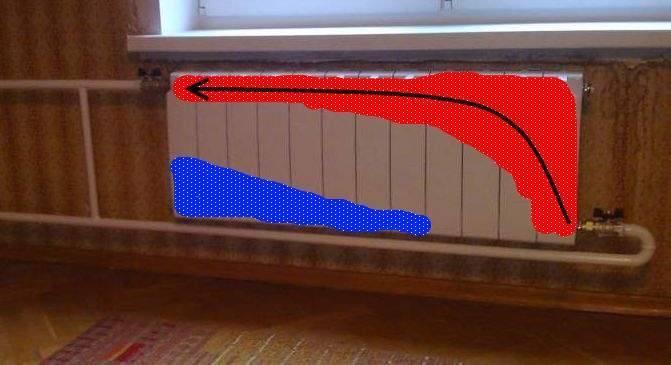
But it is important to remember that the temperature in the room is affected not only by the temperature of the coolant, outdoor air and wind strength. The degree of insulation of the facade, doors and windows in the house should also be taken into account.
To reduce the heat loss of housing, you need to worry about its maximum thermal insulation. Insulated walls, sealed doors, metal-plastic windows will help reduce heat leakage. It will also reduce heating costs.
Let's start with a simple diagram:
In the diagram we see a boiler, two pipes, an expansion tank and a group of heating radiators. The red pipe through which hot water goes from the boiler to the radiators is called DIRECT.
And the lower (blue) pipe, through which colder water returns, is called REVERSE.
Knowing that when heated, all bodies expand (including water), an expansion tank is installed in our system. It performs two functions at once: it is a supply of water for
make-up of the system and excess water goes into it when it expands from heating. Water in this system is the heat carrier and
therefore, it must circulate from the boiler to the radiators and vice versa. Either a pump or, under certain conditions, the force of the earth's gravity can make it circulate.
If everything is clear with the pump, then with gravity, many may have difficulties and questions. We devoted a separate topic to them.
For a deeper understanding of the process, let's turn to the numbers. For example, the heat loss of a house is 10 kW. The operating mode of the heating system is stable, that is, the system neither warms up nor cools down.
In the house, the temperature does not rise or fall. This means that the boiler generates 10 kW and the radiators dissipate 10 kW.
From a school physics course, we know that we need 4.19 kJ of heat to heat 1 kg of water by 1 degree
If we heat 1 kg of water by 1 degree every second, then we need power
G=Q/(4.19*dT)=10/(4.19*10)=0.24 kg/sec.
Can the water in the well freeze? No, the water will not freeze, because. in both sandy and artesian wells, water is below the freezing point of the soil. Is it possible to install a pipe with a diameter greater than 133 mm (I have a pump for a large pipe) in a sandy well of a water supply system? sand well productivity is low.The Malysh pump is specially designed for such wells. Can a steel pipe in a water well rust? Slowly enough. Since during the arrangement of a well for suburban water supply, it is sealed, there is no access to oxygen in the well and the oxidation process is very slow. What are the pipe diameters for an individual well? What is the productivity of the well with different pipe diameters? Pipe diameters for arranging a well for water: 114 - 133 (mm) - well productivity 1 - 3 cubic meters / hour; 127 - 159 (mm) - well productivity 1 - 5 cubic meters ./hour; 168 (mm) - well productivity 3 - 10 cubic meters / hour; REMEMBER! It is necessary that…
Type