Welding difficulties

Gaseous zinc is a substance harmful to humans. Once in the respiratory tract, it leads to suffocation. Therefore, welding indoors without the organization of well-functioning ventilation is prohibited. In addition, for safety reasons, the welder must wear a respirator under the mask.
At high temperatures, zinc begins to evaporate rapidly, which leads to the formation of cavities and pores inside the steel. And this is a decrease in the quality of the junction and the strength of the joint of two galvanized pipes.
Overhead welding
Welding takes place in several stages, the first of which is the welding of the root of the seam.
seam root
Use an electrode with a diameter of 3 mm and current in the minimum or medium range.
Depending on the conditions, welding can be performed in several ways:
If sampling and welding on the reverse side is possible, then when welding, attention should be paid to the formation of a bead from the underside. There should be no overhangs and undercuts .. It is best to perform such a seam with oscillatory movements from edge to edge, with a delay on them
Thus, additional sampling is not required, and after cleaning the joint from welding, it will be possible to apply a second roller (read more Plastic ceilings: installation features)
It is best to perform such a seam with oscillatory movements from edge to edge, with a delay on them. Thus, no additional sampling is required, and after cleaning the joint from welding, it will be possible to apply a second roller (read more Plastic ceilings: installation features).
Ceiling weld
- If there is a need to form a bead on the reverse side, it is necessary to make constant translational movements of the electrode inside the gap on the shortest possible arc. Make sure that the arc burns from the back side, then the metal will solidify in the shape of an umbrella (read more Baikal Ceiling Plate).
The main attention in such welding should be focused on the back bead. If possible, maintain the welding speed depending on the lower bead so that there is no strong bulge
If, nevertheless, the inner roller turned out to be too protruding, then sampling to bare metal is necessary.
Seam root on the reverse side
Filling the cut
Welding of 2 and 3 rollers takes place with a 3 mm electrode. at the average maximum current, or 4 mm. on average. The choice depends on the width of the first roller. In order not to form a bulge, you should linger at the edges, then slightly shift the arc along the edge and go over the ladder to the other edge.
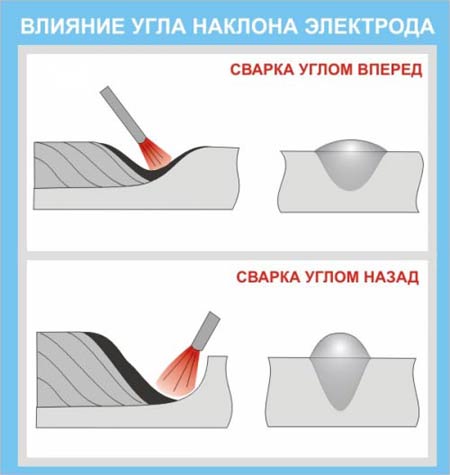
If it is necessary to change the shape of the bead during welding, change the speed, tilt the electrode at a different angle, increase the step size.
Influence of the angle of the electrode on the shape of the seam
Layers 4 and 5 depend on the width of the previous rollers - full width, or 2 rollers. The next layers are made in the form of surfacing without oscillatory movements. When approaching the edge, it is necessary to leave a distance with the diameter of the coated electrode, between the penultimate roller and the edge.
How to cook a ceiling seam - diagram
face layer
The front layer is boiled into a recess of 0.5-2 mm.
Depending on the thickness of the metal and the width of the last layer, several passes may be required.
When welding in 1 pass and deepening the penultimate layer by 0.5-1 mm. it is necessary to perform welding using the “arc forward” method. Choose a step depending on the formation of the roller.
If the recess is from 1 to 2 mm, use the "ladder" method.
When welding in several passes, the side beads passing at the edge are in each case welded in different ways: with or without manipulation, ladder or arc forward. The last roller in the center is cooked so as to evenly connect the 2 side ones.
A detailed diagram is shown in the picture above.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=0-WoYkM3wRc
In conclusion, it is worth adding that you should not engage in ceiling welding without experience. This is a rather difficult task, requiring certain knowledge and skills that come with time. Start welding with simpler types of connections.
TIG welding
This technology is usually called argon-arc. The name comes from the fact that argon gas is most often used as a shielding gas, but not always. Typically, a tungsten rod is used to weld steel products, and the welding itself is performed with direct polarity.
For connection, you can use a filler wire, or you can do without it. It all depends on the wall thickness of the workpieces to be joined. But most often a combined technology is used. That is, the root weld is welded without an additive, and the surface layers are welded using a wire. By the way, pipes made of steel 10 and 20 are always welded without filler wire.
If gas pipes with a wall thickness of less than 5 mm are joined together, then welding must be carried out from top to bottom, in other cases from bottom to top. In general, overhead and vertical welding should be avoided, so it will be better if the connection of pipe structures is carried out in rotary rollers, and the welding process itself is carried out in the lower position.
- All preparatory processes are exactly the same as in the first two cases.
- When connecting pipelines of large diameter (more than 80 mm), it is necessary to observe exact centering and tacking. In this case, after applying the first horse layer, the tacks must be remelted.
- It is necessary to extinguish and ignite the arc only on the edge or on the molten metal of the weld. At the same time, welding on the seam must be completed at a distance of 20-30 mm from the end of the seam.
- It is necessary to finish the supply of protective gas after the break of the electric arc after 5-10 seconds.
- If the gas pipeline is formed from pipes of high-alloy corrosion-resistant steel, then before welding, shielding gas is supplied inside the pipeline, or a protective flux is used in the process, for example, FP8-2 paste.
- Thick-walled pipes (thickness more than 10 mm) with a diameter of more than 100 mm, made of low-alloy and low-carbon steels, are welded without backing rings. In this case, the process itself must be carried out by the reverse step method, welding sections no longer than 20 cm long. The thickness of the seam should not be less than 3 mm, and a smooth transition to the pipe surface itself is necessarily ensured.
Gas supply of cities and towns is a planned event. Therefore, the process of welding gas pipelines belongs to the category of responsible ones. But in different cases, different methods of welding are used, a lot depends on the conditions for conducting welded processes, on the parameters of the pipes being installed, on the capabilities of the company that is engaged in the installation of the pipeline. But in any case, once again it must be recalled that the connection of pipe structures for gas should be carried out only by highly qualified welders.
Orbital welding of stainless pipes
This method is based on the argon-arc method, but the welding head moves around the circumference of the pipe, along the joint, creating a continuous seam. Hence the name. The process is fully automated and controlled by the processor. The length of the arc is set by attaching the head to the rails in the desired position.
The program embedded in the processor changes the process parameters depending on the position of the head during its orbital movement. To do this, the joint along the length is divided into horizontal, vertical and sections at an angle.When the head passes through any of them, the values of the parameters automatically change:
- head speed;
- the value of the welding current;
- filler wire feed rate;
- argon consumption.
Since welding conditions are optimal in all parts of the orbit, a uniform, high-quality weld is formed. To connect pipes with a diameter of 8 - 275 mm, an open type head is used. On pipelines of larger cross section, pre-filled with inert gas, a closed design is used. Docking of stainless steel pipes with thick walls is carried out in several passes with a change in the angle of inclination of the head. The duration of the process increases, therefore, a forced cooling unit is included in the equipment set.
It doesn't matter how stainless steel pipes are welded. The main quality of the seam, on which the reliability and service life of pipelines depends
You can manually achieve good results, but it is better to get a semi-automatic argon arc welding (TIG). It is universal and allows you to weld various metals with a thickness of 1 mm.