Required thickness
In each climatic zone, it is important to choose the right foam thickness for wall insulation from the outside, since such positioning allows you to protect the masonry from freezing and extend the life of wall structures. It will be necessary to apply a finishing non-ventilated coating on the front side, which will protect the polymer from the effects of outdoor air.
It will be necessary to apply a finishing non-ventilated coating on the front side, which will protect the polymer from the effects of outside air.
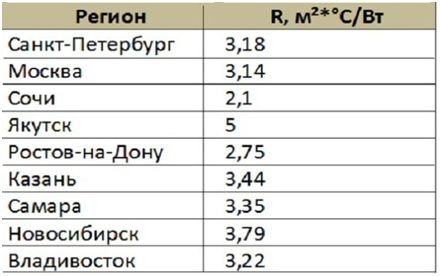
The value of the thermal resistance of the wall is recommended by SNiPs for each region. In an abbreviated version, the SNiP 23-02-2003 table looks like this:
The specified resistance value is collected by the sum of the indicators of all materials used, including finishing coatings.
Payment
As an example, we can take a Moscow wall with a thickness of 1.5 bricks, which will be 0.38 m. .38:0.5=0.76). The remaining resistance value (3.14-0.76 = 2.38 m² × ° C / W) is provided by insulation and finishing materials. If we multiply the thermal conductivity of the foam 0.028 W / m² × ° С, we get the required thickness of 6.6 cm. Taking into account the external plaster and interior decoration, it is permissible to choose plates with a thickness of 5 cm.
The practice of performing work has shown that when using standard sheets of extruded polystyrene foam, the insulating layer is on average made of the following thickness:
- for internal insulation of premises, plates with an end face up to 4 cm are sufficient;
- for external arrangement in a temperate climate put 5 cm;
- in cold zones 10 cm and conditions of the far north 15 - 20 cm. For more information on calculating the thickness of insulation for walls, see this video:
Before working with this material, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the technology of wall insulation with foam plastic.
Types of foam
Penoplex is produced in the form of 5 main varieties that differ in the purpose of the types of work.
- Fundamental. Mounted on the basement (underground) part of the building, used as a fixed formwork. Protect the base of the building from freezing.
- Wall. Needed for outdoor work on thermal and sound insulation.
- "Roof". It is installed on attic floors and roof slopes, attic rooms. Traps the heat and sound of rain.
- "Comfort". It is intended for internal works (walls, floors, ceilings, balconies).
- Road. The most dense grade of this material is labeled "Penoplex-45".
Installation work on the outer part of the wall does not differ in composition from the implementation of internal insulation.
One of the thinnest insulation
The advantages of insulation with expanded polystyrene are difficult to overestimate. However, one of the most significant of them is its thickness. This means that the product has practically the lowest thermal conductivity.
The only material that foam is inferior to is penoizol, which is a multicomponent liquid material. However, it can only be used for insulation of non-residential buildings.
The reason for this is the high toxicity of the material. In addition, only professional builders can work with penoizol, and with the help of foam plastic, each person can complete the finish on their own.
Do-it-yourself foam insulation technology for external walls
It is within the power of a master who is familiar with the basics of finishing work to insulate the walls.
Let us consider in detail the method of insulation, called the "wet facade".
Tools

- level, plumb line, hammer, tape measure, pencil, hacksaw (knife), trowel and spatula;
- a bucket for mixing glue and plaster;
- hammer drill or impact drill with bits or drills for concrete;
- whisk nozzles on a drill for preparing solutions.
From consumables get:
- glue for polystyrene on a cement or synthetic basis;
- dowels with a rod length of 4-5 cm more than the thickness of the foam;
- mounting foam or adhesive foam;
- foam gun.
Work progress step by step
Wall insulation begins with preparatory work:
calculation of the amount of insulation and its purchase;
- preparing and testing instruments;
- purchase of consumables;
- installation of scaffolding (if necessary).
- The surface of the walls is being prepared, which is cleaned of dust and dirt.
- The voids in the seams (if any) are sealed with cement mortar or foam.
- The surface is leveled with plaster so that the irregularities do not exceed 1.5 - 2 cm. This will facilitate the fitting of the sheets, reduce the amount of expensive glue during further finishing.
- At a level of 50 cm from the ground, a support bar is fixed strictly horizontally, if the foam is not placed to the ground, and finishing with other material is provided.
- With the help of a level and a plumb line, markup is made.
- A sheet is applied according to the marking and through it (so that there are no mistakes) a hole is drilled in the wall for the dowel.
- Starting from the central hole, fix the sheet on the wall.
- The second and subsequent sheets are placed with an offset (staggered).
- The seams are sealed with mounting foam. Remove excess sealant after complete curing, usually after 12 hours and up to a day.
- With a special toothed roller or other improvised means, punctures are made up to 0.5 - 1 cm deep on the foam surface for better adhesion to the layer of glue-plaster.
- A 1-2 mm layer of specialized glue for expanded polystyrene is applied to the foam plastic, which is leveled with a spatula.
- A fiberglass mesh is applied to the glue and “heated”. The joints are overlapped, overlapping by 10 cm. The seams between the sheets and the edges of the grids should not match.
- Smooth out the adhesive with a spatula. By adding portions of glue in the right places, the final leveling of the surface is carried out, working as when using putty.
Finishing
 After the composition has dried, the surface is primed with means for outdoor work.
After the composition has dried, the surface is primed with means for outdoor work.
The final finishing is carried out with facade paint or bark beetle plaster is used. The latter option is preferable, as it hides inaccuracies and irregularities, which are especially clearly visible in side lighting.
With frame insulation, there are no tricks. The foam is fixed with dowels with wide caps between the frame rails. The remaining voids are filled with mounting foam or glue-foam. Then, without fail, a waterproofing membrane is nailed to the frame. It is convenient to do this with bars of a counter-lattice, the thickness of which is 1-1.5 cm. After installing siding or of another material, there will be a gap between it and the foam, which will reduce the likelihood of materials dampening - the facade will become “ventilated”.
Styrofoam for wall insulation
Styrofoam is an economically advantageous material. The economic benefit is manifested not only at the construction stage, but also at the stage of subsequent operation. This is achieved due to high rates of heat retention for insulating walls and other structural elements, as well as a reliable level of fire resistance.
During installation, the standards for the thickness of the plates must be observed. For external walls, this figure is 50 mm, and for internal 30 mm. Density - 25.
With the use of this material, it is possible to carry out work on external and external wall insulation. Outside, the installation process takes place using cement mortars, various mounting devices, glue and other things. The inner side when installing the foam will have a good level of noise protection. Gypsum boards must be used. You can use an alternative option - plaster.
The plates that are involved in the fastening process for the outer part must correspond to a thickness of 50 mm.The inner side will require from 30 mm. The wall, which is located on the outside of the room, must first be treated with cement mortar. Its application takes place using a special metal mesh. After completion of the work, we can assume that the foam has been successfully installed.
Density. Indicator
When working on wall insulation, expanded polystyrene has a density index of 25. An external wall with a sheet of 50 mm will have high heat retention rates, as well as additional sound insulation.
Styrofoam with a density of 25 looks quite advantageous against the background of its counterpart, the density of which is 15. The main differences are in quality. You can feel a big difference in the quality of foam with a density of 25 and 15 without even starting to operate them.
The grades of extruded polystyrene presented earlier in the article have the following density indicators:
- 31C (from 28.5 to 30.5 kg).
- 31 (from 28 to 34 kg).
- 45 (from 38.1 to 45 kg).
Vapor permeability properties
The vapor permeability index directly affects the efficiency of air exchange that occurs between the inside of the premises and the outside. This happens because the air outside has a lower temperature index than the inside.
When air is exchanged from the inside to the outside, the level of permeability should increase. In terms of vapor permeability, traditional foam outperforms extruded foam.
- Traditional foam has 0.063 mg/(m*h*Pa).
- The extruded foam has 0.013 Mg/(m*h*Pa).
Why is it so? If you use extruded polystyrene foam for external insulation, this will lead to undesirable consequences. Its low vapor permeability has a high level of insulation, which will lead to the accumulation of moisture that will not allow the materials to dry out and ventilate.
Scheme of application of various brands
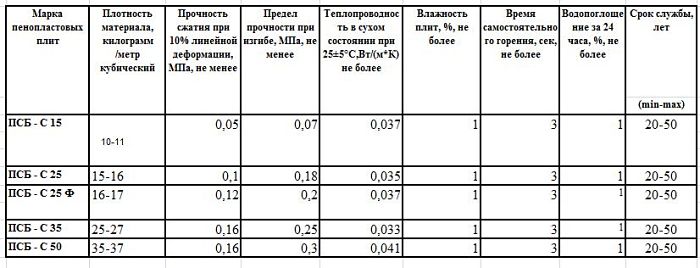
The following key types of expanded polystyrene are produced, which have differences in density and other characteristics:
- PSB-S-15, the density of this brand of foam is up to 15 kg/cu.m.
- PSB-S-25, from 15 kg/cu.m. up to 25 kg/cu.m.
- PSB-S-35, from 25 kg/cu.m. up to 35 kg/cu.m.
- PSB-S-50, from 35 kg/cu.m. up to 50 kg/cu.m.
The thermal conductivity component of the foam, expressed in numerical terms, refers to the range 0.037 W/mK - 0.043 W/mK. The specified value can be correlated with the thermal conductivity of air, which is equal to 0.027 W/mK.
The use of polystyrene PSB-S-15
Polyfoam PSB-S-15 can be used to insulate the facades of houses. This type of insulation is practically not used in construction. It is used in structures that are attached to structures. It can be open balconies or verandas that perform a decorative function. By means of foam plastic PSB-S-15, figures for facades are formed, and this allows:
- frame the corners of the house, windows;
- to separate floors through the creation of cornices.
What is PSB-S-25 suitable for?

Plates having a density of 25 are used to insulate the facades of the house. Styrofoam is considered the standard, the thickness of which is 5 cm. This type of insulation is used for many purposes. Its thickness can be changed - it will depend on the preferences of the consumer.
Styrofoam of maximum thickness can be used to insulate walls that are exposed to atmospheric masses. They can also isolate walls, since such material perfectly prevents the appearance of fungus.
Based on the designation of the material, it is used in various building structures, and this does not impair its quality characteristics.
Application of foam plastic PSB-S-35

Before choosing a heater of the required thickness, it is recommended to find out in advance what is the amount of gas pipe stock, because in no case should it be closed, as this may violate the aesthetics of the appearance of the building. In this case, it is desirable to prefer all the same material PSB-S-35 with a thickness of 5 cm than a material with a density of 25 and a thickness of 10 cm, especially since their prices practically do not differ.
Insulation, the density of which is 35, can be used to isolate the slopes of windows and doors, the facades of buildings. It costs, as a rule, twice as much as the same material made of polystyrene with a density of 25. With a thickness of 5 cm, they can insulate non-residential structures and garages. With a thickness of a similar insulation of 7 centimeters, it can be used for thermal insulation of residential premises.
Due to the normal level of density, it is possible to use a heat insulator with a minimum thickness, which does not imply a deterioration in the quality of insulation. If the polystyrene foam heat insulator is harder, then it can be used to perfectly insulate the walls of basements and foundations.
Warming technology
After it has been decided what material is required to perform the work, it is important to familiarize yourself with the nuances of the work technology. When fastening, it is necessary to take into account such features of thermal insulation as:
- low strength;
- destruction when exposed to moisture and cold (high-quality waterproofing and vapor barrier will be required);
- instability to fire;
- low vapor permeability, creating a greenhouse effect in the house (a forced ventilation device is required).
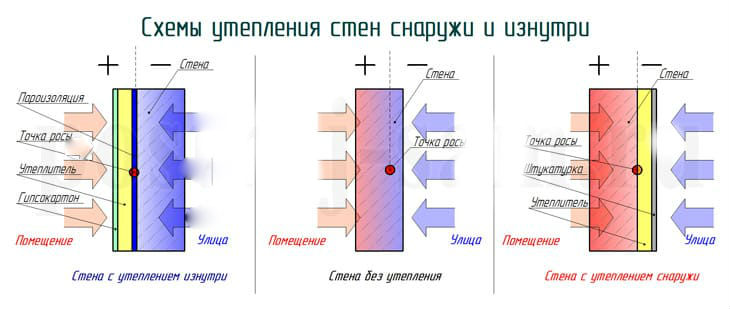
The material can be fastened from the cold air side or from the inside. Styrofoam insulation from the outside will be more competent. Insulation of walls with foam plastic from the inside can be performed only if there are justifications (it is not possible to disassemble the decoration of the house, the insulation of one apartment in an apartment building).
We also recommend that you read the instructions for floor insulation with foam plastic. Insulation of ceilings with this material also has its own nuances. To ensure reliable protection from the cold, it is better to place the heat insulator on the cold air side.
Fastening to the wall is carried out with glue, and after the solution has dried, the material is additionally fixed with dowels-fungi. Before proceeding with fixing with dowels, it is better to wait about 3 days. If the heat engineering calculation was performed correctly, and the technology was not violated during installation, the foam will be durable and reliable.
Specification overview
There are different brands of foam, each of which has its own set of properties and parameters. Based on this information, a choice should be made.
Thermal conductivity index
Closed cells represent the structure of the foam, due to which the insulation of this type acquires the ability to retain heat in the room. The thermal conductivity coefficient is: from 0.033 to 0.037 W / (m * K).
Insulation is considered effective, the value of this parameter is not more than 0.05 W / (m * K). There are more effective materials, however, the average characteristics of the foam allow it to be successfully used so far.
Sound insulation qualities, wind protection
The best for protection against extraneous noise is a material that has the following technical characteristics: low thermal conductivity and at the same time the ability to pass air. Porous foam fits these criteria. This means that this type of insulation does an excellent job of protecting the object from noise.
Moreover, the greater the thickness of the sheet, the better the soundproofing qualities of the material. If you need to protect the object from the wind, then the foam will successfully solve this problem, as it consists of many closed cells.
moisture absorption
The ability of this type of insulation to absorb water is quite low, which allows us to consider it non-hygroscopic. The indicator of moisture absorption at constant contact with water during the day corresponds to 1%.

This is somewhat more than that of penoplex (0.4%), but also less than that of most of some other analogues, for example, mineral wool. Due to the low hygroscopicity, the life of the foam is significantly extended, as the risk of mold or mildew is reduced.
Temperature regime
The considered insulation does not change its properties with a significant increase in temperature (up to 90 degrees). Low values also do not have a detrimental effect on this type of material, so it is used, in particular, for thermal insulation of external walls. But during laying with the use of an adhesive, it is recommended to observe the temperature regime: not lower than +5 and not more than +30 degrees.
Influence of external factors
These include: temperature changes, wind load, rain, snow and any mechanical source of pressure. The strength of the foam sheet is low under the influence of the last of the factors considered.
 Due to its heat-insulating characteristics, foam has become widespread in the insulation of walls, roofs, ceilings, balconies.
Due to its heat-insulating characteristics, foam has become widespread in the insulation of walls, roofs, ceilings, balconies.
This is due to the low weight and large-cell structure. Moreover, the thickness of the material practically does not change the situation. If we compare it with penoplex, this option has high strength characteristics.
Degree of resistance to chemicals and microorganisms
Upon contact with a number of substances, the properties of the foam do not change, these include: salt solutions, alkali, acid, gypsum, lime, bitumen, cement mortar, some types of paints and varnishes (based on silicones and water-soluble compounds). It is necessary to avoid contact of polystyrene-based insulation with such substances: solvents, acetone, turpentine, gasoline, kerosene, fuel oil.
fire safety
The insulation belongs to flammable materials (combustibility category G3 and G4), however, its burning time, provided that the source of ignition is removed, does not exceed 3 seconds.

It would be a delusion to consider such a material to be completely safe, but nevertheless it is often used, due to the release of less energy during combustion, as well as spontaneous extinction.
The main brands of foam
After polystyrene foaming, raw materials for finished products are loaded into a container. Steam is injected into it under pressure. The granules foam and are saturated with air. At the next stage, the finished granules are dried from moisture, for this hot air is used.

During drying, the granules are periodically shaken. Finished granules are placed in hoppers, which are calibrated according to the grades of foam. Forming takes place under pressure. During molding, the following types of foam are obtained, which differ in density:
The last number in the marking determines the density of the foam for insulation. Many developers do not know what the specific gravity of the foam is. Density (specific gravity) is the mass of a product in its volume. The density of polystyrene grade PSB-S-15 is 15 kg/m³. Accordingly, one cubic meter of PSB-S-15 polystyrene plates weighs 15 kg.
The question arises of how to independently determine the density of the foam without special equipment. This is easy to do: you need to calculate the cubic capacity of the finished product and weigh it on a scale. To make claims, the store must have an act of state verification of scales in hand. Weighing can be carried out directly in the store or at the construction warehouse of the material supplier. Such a technical calculation of the foam density will be the most optimal.
A product with a low density has a lower compressive strength. It is not able to withstand shock and static loads. The facade can be spoiled when cleaning snow or foliage. Subsequent restoration of the coating and painting work will require additional costs. However, the low density of the foam guarantees a lower cost for the same thermal insulation properties. The choice of density is based on the scope of each brand of product.
PSB-S -15
This brand has the lowest compressive strength with a linear deformation of 10% (not less than 0.04 MPa). The tensile strength of PSB-S-15 foam plastic in bending should not be lower than 0.07 MPa.
Plates PSB-S-15 provide good thermal insulation. Styrofoam, the density of which is not more than 15 kg / m³, has a thermal conductivity of 0.036 W / (m.k.). This type of insulation is used to isolate unloaded structures and planes, such as building facades, roofs, ceilings, gables.
PSB-25
Styrofoam grades with a bulk weight of 25 kg/m³ are the most popular among private developers. Plates of medium density combine an acceptable price, good thermal insulation characteristics. This type is versatile and has proven itself well in the insulation of various structures.
The volumetric weight of the foam is in the range of 15-25 kg/m³. The thermal conductivity of foam with a bulk density of 25 kg/m³ must be less than 0.033 W/(m.k.). The linear deformation index should not be lower than 0.15 MPa. Bending strength - 0.32 MPa.
PSB-S-35
Plates PSB-S-35 have a fairly large scope. The density of expanded polystyrene PSB-S-35 should be in the range of 25-35 kg / m³. Such a heater will last up to 40 years. It is less fragile than PSB-S-15 and PSB-S-25. Strength and durability are achieved due to the closer bonding of the styrene molecules.
The thermal conductivity of polystyrene with a bulk density of 35 kg/m³ must be less than 0.033 W/(m.k.). Bending strength - 0.38 MPa, linear deformation index - 0.26 MPa. It is a hard and durable material.
PSB-S-50
PSB-S-50 is a dense foam that is able to withstand mechanical and shock loads. It is used for thermal insulation:
- foundations;
- pile foundations;
- floors of industrial enterprises;
- heated roads, car parks and parking lots;
- plating of ships and floating craft.
Expanded polystyrene with a density of 45-50 kg / m³ is supplied on request due to low demand and high cost.
The thermal conductivity of such a material should be less than 0.033 W / (m.k.). The linear deformation index approaches 0.38 MPa. Bending strength - 0.42 MPa. This is the hardest material.
What is extruded polystyrene. Differences between EPP and ordinary polystyrene and polystyrene
EPP, Styrofoam and Styrofoam are categorized as synthetic polymers. The technology of their production provides high quality characteristics. Styrofoam is made from a polymer composition. The resulting granules reach 3-5 mm in diameter. After that, they are pressed together using an adhesive composition.
Considering what expanded polystyrene is, it should be noted that this is a material that has a uniform structure, including granular cells no more than 0.1-0.2 mm. To obtain the material, polystyrene granules are mixed with special foaming agents (they can be carbon dioxide or a mixture of freons). After that, sheets are formed under pressure. After drying, they can be used in construction.
Styrofoam and polystyrene have a lot in common with extruded polystyrene foam, but the latter has a more complex production technology. In the manufacture of the material, the granules are first melted to a state of homogeneous mass. After that, special additives and additional components are introduced into the composition, due to which the substance acquires a viscous-fluid state.This results in a material with inextricable intermolecular bonds.
There are no pores in the finished slabs, and the cells present in this material are filled with gas. Due to this structure, the vapor permeability of the material is extremely low. The density of extruded polystyrene foam is much greater than that of polystyrene foam and polystyrene, so it has better performance characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages
XPS boards have a lot of advantages, but this material also has some disadvantages. The pluses include:
- low thermal conductivity;
- water resistance;
- ability to withstand deformation loads;
- increased rigidity;
- resistance to temperature changes;
- long period of use;
- light weight;
- environmental friendliness.
This insulation is quite rigid, so rodents rarely damage it. At the same time, mice can make moves in the slabs. The water resistance of EPP boards in some cases can be a big minus. When using material to insulate the walls of a wooden house, mold can occur under the formed cake.
Vapor trapping near walls can contribute to dampness and musty smells. In addition, stoves, when heated to temperatures above 75°C, can release substances that can adversely affect human health.
Physical properties of foam
The main characteristics of porous polystyrene include:
- strength - the foam does not have outstanding strength characteristics and is able to crumble and break even with a weak mechanical impact. It can be easily damaged with sharp objects or by simply hitting the surface. To reduce the likelihood of destruction, the foam is covered with layers of a harder material that evenly distributes external loads;
- flexibility - expanded polystyrene is weakly amenable to bending influences and can break under them at any time. For the same reason, foam boards are installed only permanently, avoiding any torsional loads;
- thermal conductivity - the presence of gases (natural heat insulators) in hollow capsules provides the material with a low heat transfer coefficient. This is also facilitated by the absence of convection inside the pores due to their small diameter. It will take a long time to completely warm up a piece of foam to a given temperature;
- Tendency to shrink - free-standing EPS boards are susceptible to slight shrinkage caused by gravity. The shrinkage is 1.5-3 mm within six months. At the end of this period, the natural compaction of the material stops;
- thermal expansion - with increasing temperature, the linear dimensions of the plate increase (the process is reversible). Numerical indicators of expansion correspond to approximately 1 mm per 1 m of foam plastic plate with a temperature change of 15-20 ° C;
- vapor absorption - foam plastic is less resistant to diffusion penetration of moisture than to liquid water, therefore, in especially humid rooms, its surface is additionally covered with a layer of metal foil. In its absence, part of the water vapor can penetrate through the layer of material and condense when the temperature drops, which adversely affects the entire thermal insulation system.
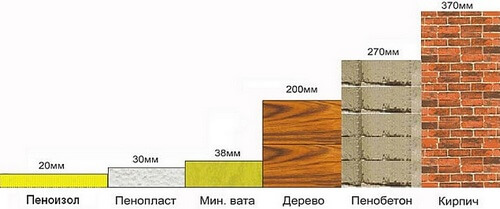
Styrofoam Thickness Guidelines
When choosing a thickness, it must be taken into account that the sheets must have sufficient strength and, during installation or operation, not crack and break under their own weight or as a result of minor mechanical influences.
Therefore, it is recommended to use the following thickness selection rules:
- sheets of 20-50 mm should be used to insulate the internal walls of rooms or loggias;
- in order to insulate the facade, the thickness of the foam sheets must be more than 50 mm;
- insulation of the frame house should be carried out with 50 mm plates;
- thermal insulation of the strip foundation of a house with a strip foundation must be made with slabs with a thickness of more than 100 mm;
- to insulate the attic, you need foam plastic with a sheet thickness of 50 mm for walls and 25 mm for the ceiling;
- for thermal insulation of floors it is better to use plates with a thickness of 100 mm or more.
The standard thickness of foam sheets is from 30 to 100 mm. It happens that it is required to insulate the external walls of the house with plates with a greater thickness, then in such cases it is gained by laying several insulating layers.
What characteristics of foam should I pay attention to?
Since the foam, in addition to thermal insulation properties, must also have optimal strength, the choice of its density is one of the most important selection criteria.
Professionals recommend doing the following:
- for wall insulation outside the house, a heater with a density of 25 kg / m 3 should be used;
- for thermal insulation of floors, the optimum density is 35 kg / m 3;
- for insulation of ceilings inside the house, attic and loggia, foam plastic with a density of 15 kg / m 3 is suitable.
The second criterion for choosing foam is the size of the sheets. They must be selected in such a way that the amount of insulation waste is minimal, therefore it is recommended to measure insulated surfaces in advance and perform appropriate calculations. The standard sizes of foam sheets are as follows: 0.5x1 m, 1x1 m, 2x1 m.
When buying insulation sheets, it is important to include a small margin in the cost estimate, which should average about 10-15% of the total. It is necessary to insulate various parts of the house structures with foam plastic with a competent choice of the dimensions of the insulating material based on the calculations, taking into account all the technical installation conditions and the climatic features of the region
In addition, it is necessary to evaluate the convenience of working with insulation and, if necessary, use denser sheets to prevent damage.
It is necessary to insulate various parts of the house structures with foam plastic with a competent choice of the dimensions of the insulating material based on the calculations, taking into account all the technical installation conditions and the climatic features of the region. In addition, it is necessary to evaluate the convenience of working with insulation and, if necessary, use denser sheets to prevent damage.