Laying technology
The built-up roof keeps within in dry, calm weather at a temperature above 5 degrees. When the ambient temperature is less than this indicator, the melting of the lower layer becomes more difficult, and the gas consumption increases. Work is performed in the following order:
- First, fillets are equipped - sides with a slope of 45 degrees, located at the junction of the roofing material with vertical surfaces. They are necessary to prevent abrasion of the roofing material in the seams.
- The vertical surfaces where the waterproofing coating will be applied are sanded to improve adhesion.
- Then the lining layer of the coating is glued. To do this, the roll is rolled out, its edge is fixed, and the loan, melting the lower layer of material with a gas burner, presses the waterproofing coating with a rolling roller.
- The second strip of coating is glued with an overlap of 10-15 cm to protect the seam from moisture penetration.
- Check the quality of gluing the first layer. The material in the area of the seams should not move away or bubble.
- Subsequent layers of the deposited coating are glued in the same way. However, they are fixed with an offset so that the seams between the stripes do not match.
Laying technology
Junctions with vertical surfaces
Functions of vapor barrier materials
The roofing device is called a roofing pie and consists of alternating layers of vapor barrier, insulation, waterproofing and external coating, fixed to the truss system. Small ventilated gaps are left between the layers, providing air circulation and removal of excess moisture.
The vapor barrier coating is fixed on the inner surface of the ceiling or slope. Its main task is to prevent the ingress of water vapor into the roof structure and the formation of condensate in the inner layers of insulation and waterproofing. A small part of the moisture still penetrates through the cracks and pores in the materials, however, it evaporates in the inner walls and is carried out.
GESN 12-01-015-01
Vapor barrier device: gluing in one layer
LOCAL RESOURCE STATEMENT GESN 12-01-015-01
| Name | unit of measurement |
| Vapor barrier device: gluing in one layer | 100 m2 of insulated surface |
| Scope of work | |
| 01. Device for pasting insulation from rolled roofing materials. 02. Preparation of the primer. |
PRICE VALUES
The price lists the direct costs of the work for the period March 2014 for the city of Moscow, which are calculated on the basis of standards 2014 with additions 1 by applying indexes to the prices of the resources used. Indices applied to federal prices 2000.
The following indexes and hourly rates from the "Union of Estimators" were used:
Index to the cost of materials: 7,485
Index to the cost of cars: 11,643
Used hourly rates:
In parentheses are the wages per month at a given hourly rate.
Hourly rate of the 1st category: 130.23 rubles. at one o'clock (22 920) rub. per month.
Hourly rate 2 categories: 141.21 rubles. at one o'clock (24 853) rub. per month.
Hourly rate 3 categories: 154.46 rubles. at one o'clock (27 185) rub. per month.
Hourly rate 4 categories: 174.34 rubles. at one o'clock (30 684) rub. per month.
Hourly rate of the 5th category: 200.84 rubles. at one o'clock (35 348) rub. per month.
Hourly rate of the 6th category: 233.96 rubles. at one o'clock (41 177) rub. per month.
By clicking on this link, you can see this standard calculated in 2000 prices.
The basis for the use of the composition and consumption of materials, machines and labor costs are GESN-2001
LABOR
| № | Name | Unit Change | Labor costs |
| 1 | Labor costs of construction workers Category 3.8 | man-hour | 17,51 |
| 2 | Labor costs of machinists (for reference, included in the cost of EM) | man-hour | 0,18 |
| Total labor costs of workers | man-hour | 17,51 | |
| Wages of workers = 17.51 x 170.36 | Rub. | 2 983,07 | |
| Salary of machinists = 41.8 (for the calculation of invoices and profits) | Rub. | 41,80 |
How to quickly make an estimate for the repair of an apartment, knowing the area of \u200b\u200bfinishing.
OPERATION OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS
| № | Cipher | Name | Unit Change | Consumption | St-st unit Rub. | TotalRUB. |
| 1 | 020129 | Tower cranes when working on other types of construction 8 t | mash.-h | 0,11 | 1005,96 | 110,66 |
| 2 | 021141 | Truck-mounted cranes when working on other types of construction 10 t | mash.-h | 0,07 | 1303,9 | 91,27 |
| 3 | 121011 | Mobile bitumen boilers 400 l | mash.-h | 1,81 | 349,29 | 632,21 |
| 4 | 400001 | Cars onboard, carrying capacity up to 5 tons | mash.-h | 0,1 | 1014,92 | 101,49 |
| Total | Rub. | 935,64 |
CONSUMPTION OF MATERIALS
| № | Cipher | Name | Unit Change | Consumption | St-st unit Rub. | TotalRUB. |
| 1 | 101-0078 | Bitumen oil building roofing grades BNK-45/190, BNK-45/180 | T | 0,025 | 11452,05 | 286,30 |
| 2 | 101-0322 | Kerosene for technical purposes grades KT-1, KT-2 | T | 0,06 | 19512,65 | 1 170,76 |
| 3 | 101-0594 | Mastic bituminous roofing hot | T | 0,196 | 25374,15 | 4 973,33 |
| 4 | 101-0856 | Roofing ruberoid with powdered dressing grade RKP-350b | m2 | 110 | 46,41 | 5 105,10 |
| Total | Rub. | 11 535,49 |
TOTAL RESOURCES: RUB 12,471.13
TOTAL PRICED: RUB 15,454.20
You can see this standard calculated in 2000 prices. by following this link
The price was compiled according to the standards of GESN-2001 edition 2014 with additions 1 in prices March 2014.To determine the intermediate and final values of the price, the DefSmeta program was used
Estimate for the construction of a house, for the repair and decoration of apartments - the program DefSmeta
Program rentalThe program provides an assistant who will turn the budgeting into a game.
Built-up roof device
The built-up roof will serve for a long time if its layers are laid according to all the rules. There are quite a lot of works, they are located in the article in order of priority.
Foundation preparation.
In places where roofs adjoin vertical surfaces, install welded roofing materials to a height of at least 10-15 cm (unless there are special recommendations). At the junction of the built-up roof to the walls of the heated premises (including chimney pipes and ventilation ducts), the entrance to the vertical wall must be at least 25 cm. This is necessary so that condensation does not form in the roofing pie.
Vapor barrier installation
Bituminous weldable vapor barrier material can be installed using the fusing method, or it can be laid freely, but all joints must be fused.
thermal insulation layer
Thermal insulation is laid on the finished vapor barrier layer. The surface must be absolutely dry and clean. The rules are:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=QfErp0fSttQ
Screed device
A screed is poured over the insulation. When using rigid slabs of mineral wool (compressive rigidity of at least 0.06 MPa), the built-up roof can be made directly on the insulation, without a screed device. But for greater reliability, it is better not to skip this stage. The order of work is as follows:
The screed is left to gain strength. This takes an average of 28 days. To maintain the required level of humidity, immediately after laying, the screed is covered with plastic wrap, tarpaulin, burlap. During the first week, the surface is periodically wetted: at a high temperature several times a day, at a low temperature - once.
Adjacency to vertical surfaces: arrangement of sides, overlaps
In places where the roof adjoins vertical surfaces, to ensure tightness, it is recommended to make a side with an angle of 45 °. You can make it:
- using a cement-sand mortar (grade M 150, dimensions 100 * 100 mm)
- by installing special fillets, which are produced by the same companies that produce materials for built-up roofing.
Fillets are installed on bituminous mastic, the side of the solution after setting the cement is coated with a primer.
The device of the sides on the built-up roof
The sides are covered with an additional layer of lining carpet of the Technoelast EPP type. A strip of such a width is cut from the roll so that at least 100 mm of material remains on the base of the roof and at least 25 mm is wound onto a vertical surface.Lateral overlap of strips - not less than 80 mm. The material of the additional carpet laid out along the perimeter is welded onto the sides over the entire width.
Processing corners of built-up roofing - external and internal
When laying the next layers (underlay and roofing), the lining layer is also first fused, then the main carpet is laid and fused, bringing it 80 mm higher than the side. The stripe width of the additional carpet depends on the layer.
Adjacency of the built-up roof to vertical surfaces
Endova and horse
If a pitched built-up roof is being installed, an additional lining layer is laid on the ridge at the bend of the roof. Its width is 250 mm on each side. On complex roofs in the places of valleys, the lining layer must be at least 500 mm on both sides of the bend.
Laying material in the valley (an additional layer is still laid from below
When laying on a ridge, the joints of the sheets are placed against the direction of the prevailing winds. The overlap of the panels is at least 80 mm, the joints must be fused. In the valley, if possible, the underlayment is laid in a single piece. If the length of the roll is not enough, rolling starts from the bottom, moving up. The junction is also necessarily melted.
Device
Vapor barrier is the lowest layer of the roofing pie. When applied to the rafter system of pitched roofs, the rafters or the lathing stuffed to them from below are hemmed with material, forming the bottom of the sections into which the insulation is laid.
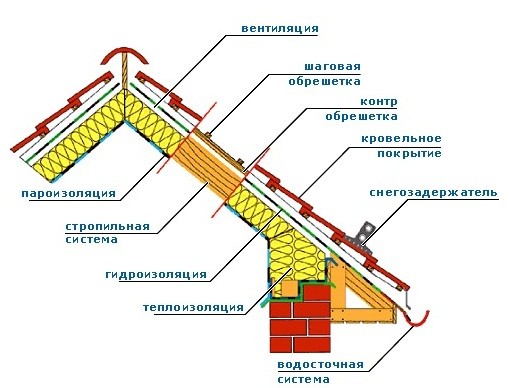
Depending on the general procedure for arranging the roof, the moment is chosen when the vapor barrier is mounted:
- If the roof of a house under construction is being erected or a complete restoration is being carried out, there are only rafters and nothing else, then the vapor barrier is attached before laying the thermal insulation.
- If the roof is insulated with an already laid roof, but ecowool or polyurethane foam is used as a heater, then the vapor barrier is fixed first, and then the niches are filled with a heat insulator through the provided gaps. The gaps are hermetically sealed at the end of the work.
- With the roof already installed and the use of mineral wool or other similar material, the vapor barrier is attached last from the inside of the attic, sewing the insulation along the rafters or crate.
The procedure is as follows:
The vapor barrier rolls out in strips along the roof visor
It is important to observe the correct orientation, on the inside and outside, which is clearly indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging and in the instructions.
Fastening is carried out from the bottom up with an overlap of strips of at least 5 cm along the entire length. The vapor barrier is attached to the rafters and the lower crate with a construction stapler
On adjacent fences or structures suitable for the roof slope, at least 15 cm is started and securely fixed to the base with adhesives or adhesive tape.
The joints between the strips are glued with adhesive or adhesive tape. All staples from the stapler are closed with adhesive tape or special flight tape.
Along the lower edge of the slope and along the ridge, the vapor barrier either joins with the insulation of the adjacent surface, or is inserted into the end of the ventilation gap.
The main task is to ensure the continuity and tightness of the vapor barrier layer. The quality of work and the reliability of the selected material directly affects the durability of the roof.
Materials from technonikol
Not so long ago, construction stores received material under the Technonikol brand. All developers were skeptical about this phenomenon, because they already had a good product called roofing material. The old bituminous material could serve as both a waterproofing layer and a vapor barrier. The problem was that with intensive protection, he could not cope with the pressure of moisture and, under its influence, collapsed in just a few years.At the end of this period, residents of private houses had to change the coverage.

It cannot be said that technonicol has completely ousted roofing material from the market. Most developers continue to use the old roll product, but modern material has a number of advantages.
- Increased strength indicators
- Great elasticity
- Improved waterproof performance
- The surface of the material does not undergo the process of decay and does not breed microorganisms
- Meets all fire safety requirements
- Resistant to high mechanical stress
This list can be continued for quite some time, in short, technonicol is good in everything compared to roofing material. The most popular vapor barrier material today is considered a three-layer membrane. This coating is designed specifically for flat roofs.
If we divide it into components and consider them separately, then each film will perform the following tasks:
- Do not allow moisture that has fallen on the roof in the form of precipitation
- Block access to moist air coming from inside living quarters
It is worth noting that such a product is a good protection with a thickness of only 1.2 millimeters. If we compare the vapor barrier produced by this company and other brands, then it is their surface that copes with mechanical loads much better than the others.
The insulating material is laid directly on the base, regardless of its material. Due to its structural features, there is no need for its thorough preparation. For laying, it is enough to clean the surface and repair large defects.
If you are going to force the roof plane with elements of a large mass, then it is best to purchase a reinforced vapor barrier material. Its structure is not much different from the previous type, but includes durable polyethylene strips. A laminated surface is applied over the already known layers to give the material greater protection.
It should not be assumed that technonicol production materials are used only in the arrangement of flat roofs, they can be used on absolutely any structures. The versatility of this material allows it to be laid anywhere, even to insulate walls and floors.
Additional layers significantly increase the mass of the material, so when laying it, this factor should always be taken into account. In addition to weight, the price per square meter also increases, so developers prefer to reduce their needs and arrange a simple three-layer membrane.
Often, for the arrangement of a flat roof, developers use reinforced vapor barrier of the Technonikol brand. This type of material has a similar structure to the previous type. It contains the usual layers, but in the middle of them a mesh is laid, consisting of durable strips of polyethylene. They are the reinforcing component. On top of them, the product is laminated on both sides, which gives it higher performance.

If you compare such products with roofing material, then laying them will cost you significantly more, but after 10 years you will pay for everything. When erecting a temporary structure, it is best to use old rolled material, so you will save quite a tangible amount.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=iz0CACHiams
But if you are going to arrange a high-quality roofing pie for a residential building, then by all means buy material under the Technonikol brand.
Features of laying vapor barrier of various types
The technology of laying the vapor barrier layer provides for the installation of the canvas on the rafters or the prepared crate on a flat roof. The canvas should completely cover the surface and go onto the plane of another slope, gables and the floor around the entire perimeter by 10-15 cm.
Consider how to properly join strips of material:
- for vapor barrier films, vapor barrier, membrane materials, the overlap is 10-12 cm, the seams are glued with construction tape (can be reinforced) or special glue;
- foil material is laid end-to-end, the seam is closed with aluminum tape.
The vapor barrier sheet is attached to the wooden elements of the truss system or battens with staples (a construction stapler is used) or stainless steel galvanized studs with wide caps. The vapor barrier is fixed to the metal profile using self-tapping screws for metal or double-sided adhesive tape.

The canvas must be stretched, not sag. It is required to provide a ventilation gap between the finishing skin and the vapor barrier. It is needed to evaporate moisture, otherwise water vapor will damage the finish. To do this, counter rails are stuffed over the rafters over the vapor barrier layer.
When choosing a vapor barrier, it is important to know the installation features, which depend on the functional characteristics of the material:
- Polyethylene film can be laid on either side of the insulation.
- A vapor barrier with an anti-condensate layer is laid with a smooth side towards the insulation and a rough side towards the room.
- Membrane types of vapor barrier are divided into one-sided and two-sided. In the first case, the perforation is made in such a way that the steam is able to move only in one direction, in the second case - in both. If a double-sided membrane is chosen as the roof vapor barrier material, it can be mounted on either side. Single-sided material is laid in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
The structure of materials for built-up roofing
Materials for built-up roofing have a multilayer structure. A binder is applied to the base from both sides, and a protective coating is applied to it. All these layers have several options. Their combinations give different properties and characteristics.
The structure of materials for built-up roofing
Base types
A significant part of the properties of the material is set by the base on which the binder is applied. If it can stretch, then the material for the built-up roof can also change its dimensions to a certain extent, if it does not tolerate deformations, then the material is torn. There are the following basics for built-up roofing:
The most durable materials are made on the basis of polyester. Manufacturers say that these materials retain their properties for 25-30 years. So much built-up roofs can be operated without repair, however, with proper installation. The disadvantage of polyester-based weld materials is the high price at the time of the device. But you can save on repairs and replacements.
Types of binder
The binder also determines the set of properties of the material for the built-up roof, but no longer affects the strength, but the waterproofing properties and resistance to weathering. Also, this layer is responsible for the degree of adhesion (adhesion) with the base or underlying layer. There are the following types of binders:
The best characteristics of rubber-bitumen and bitumen-polymer compounds. They have a wide temperature range in which they can be used.
When choosing materials for built-up roofing, be sure to pay attention to this parameter, because some of them tolerate high temperatures (up to +150 ° C), and some - low temperatures (up to -50 ° C). And you can't mix them up
Purpose
The built-up roof, as a rule, is multi-layered, and the materials for different layers must have different characteristics. Those at the bottom should provide waterproofing, sound absorption, and, if possible, have thermal insulation properties. These materials are called lining and when labeled, they are indicated by the letter "P" in the third position in the label.
The welded materials for the top layer of the roof must additionally have a high resistance of the surface to mechanical damage and weather influences. These materials are called "roofing" and in the abbreviation are denoted by the letter "K" in the third position.
Protective layers
Since the binder in the welded materials is sticky, it must be covered with something. This is done using stone chips of various sizes or plastic wrap. Sometimes foil (Folgoizol) is used as a protective layer. Such materials are used in countries with a hot climate. You need foil to lower the temperature - the lower layers heat up 15-20 ° C less than with conventional materials.
Stone chips (powdering) happens:
Since the type of protective coating has a significant impact on the characteristics and scope of materials (fine-grained and dust-like are applied to lining materials on both sides), their designation is also in the marking - this is the second letter.
This is a summary of all the characteristics that you need to know when choosing a weld material. Before buying, be sure to read the description, study the scope and specifications.
The technology of laying a soft roof without fusing is described here.
Built-up roofing material laying rules
First of all, you need to decide on the direction in which the rolls will roll out. On flat roofs, this is done along the long side of the roof. On sloping roofs, the direction depends on the magnitude of the angle:
- less than 15 ° - rolls across the slope (along the slope);
- more than 15 ° - along the slope.
If there are several layers, the longitudinal seams of the layers are displaced by at least 300 mm. When laying, standard overlaps are also provided: side - 80-100 mm, end 150 mm.
Displacement of panels during the installation of built-up roofing
Laying order
Start the installation of materials of the built-up roof from the lowest place. The roll is preliminarily rolled out, providing access to vertical surfaces (parapets, pipes, etc.). It is necessary to roll out without waves. So that the material does not move, when rolling, one side is pressed with something heavy (you can put an assistant). On the laid roll, mark the length, cut off the excess.
Pre-rolls "try on"
On flat roofs, the roll is rolled from the edges to the center. For convenience, you can use an iron pipe. With a slope of more than 8%, this option does not work. In this case, welding starts from the top, moving down. A piece 1.5-2 meters long is left unwelded. It is processed after the whole piece is glued.
In order to have fewer waves when rolling out the rolls, a couple of days before the start of installation, they are placed “upright”. So they take a round shape, the material then lies flat.
Fusion technology
Regardless of how the material is rolled, it is welded by rolling it “on itself”. So you can control the degree of heating of the bitumen layer: the whole picture is in front of your eyes. If you push the roll "from yourself", the quality of the roofing will be very low and the roof will quickly leak.
You need to roll "on yourself"
The movements of the burner are smooth and uniform. When laying the overlapping areas are heated additionally. In this case, the burner moves along a path in the form of the letter "G". The burner is positioned so that both the base of the roof and the binder on the surface of the roll are heated at the same time. With proper heating, a small roll of molten bitumen forms in front of the roll.
When welding, it is necessary to ensure that the bitumen melts evenly, there are no “cold” zones or zones of local overheating. Some manufacturers (TechnoNIKOL) apply a pattern to the underside of the deposited roofing materials. It is easier to control the degree of heating of bitumen using it - as soon as the pattern "floats", you can roll out the roll and move on.If the bitumen is heated correctly, it flows out along the edges of the roll, leaving a strip of about 25 mm in size. That is, an even seam of dark color is obtained along the edge.
How to control the degree of heating of the welded roofing material
When laying the built-up roof in low areas, the corners of the rolls at the joints are cut by 45 °. This sets the right direction for the movement of water.
Laying of welded material in low areas (valleys)
Sometimes, when laying the finishing layer of a built-up roof, it becomes necessary to weld the material over a coarse-grained or scaly topping. If you simply heat the material and stick it on the sprinkle, there is a high probability of leakage. In this case, it is necessary to preheat the surface of the material with dressing, drown it with a spatula in bitumen. After that, you can already reheat and glue.
Fused roofing is attached to the base by melting its lower bituminous layer with a torch or blowtorch, or cold with a solvent. This group of roofing materials is popular due to the speed and simple installation technology and reasonable price. How is the roofing installation carried out?
Destructive properties of water vapor
The air in the room is saturated with moisture due to people's breathing and body fumes, steam from cooking food, from things that dry after washing, from plants that require regular watering, etc. Most building materials, with the exception of metal and glass, let steam through to some extent, allowing it to escape.
Consider why you need a vapor barrier. Due to the difference in temperatures inside and outside the house, the dew point (moisture condensation) is located inside the wall structures or roofing cake, where the temperature front passes. If you allow the penetration of vapors into the heat insulator, in the cold season, it is in the warming layer that moisture will condense. In winter, it turns into ice and breaks the fibers, worsening the structure of the material, and melts when it gets warmer. A fibrous heat insulator that has absorbed moisture sharply increases the coefficient of thermal conductivity, and it cannot perform its functions - an insulated wall, roof, floor or ceiling will freeze.
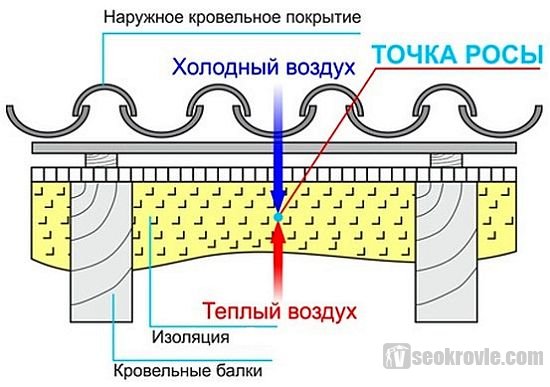
The vapor barrier for the roof protects the insulation from moisture coming from the room, and the waterproofing, together with the roofing, from the effects of precipitation. It should be borne in mind that wet insulation is the optimal environment for the development of mold that damages the truss system, wooden and metal structures of the floor, walls and ceilings. The purpose of the vapor barrier is, among other things, to extend the operational life of the building and ensure a healthy microclimate in the house.


