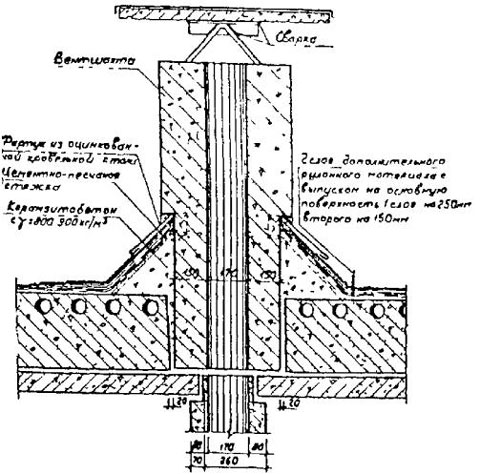
Ventilation shaft device
The structure, as a rule, looks like a cylindrical trunk. It is located strictly vertically and contains three parts:
- one large one - about 300x600 mm;
- two small ones - about 150 mm.
It is the large part that is the trunk, which crosses all the floors of the building, from the basement to the attic.
The design may be non-standard. Increased dimensions must be taken into account when selecting fans.
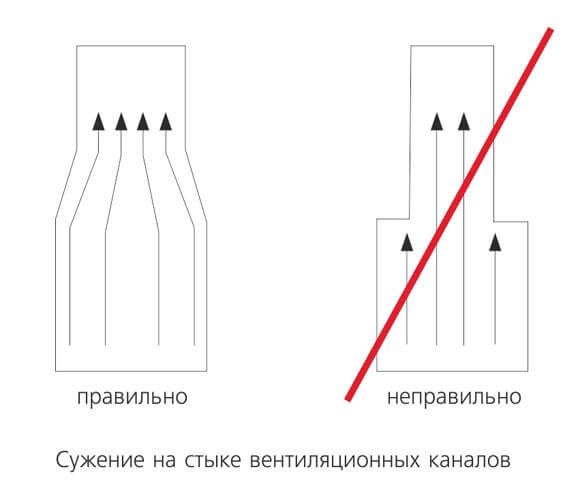
Through special windows located in rooms such as a kitchen or a bathroom, polluted air enters not very large channels and, rising through them to a height of about three meters, ends up in a common shaft. Thanks to such a device, the distribution of used air through the duct from one room to another, for example, from the kitchen to the bathroom, and then to the rooms, is practically excluded.
In outbuildings, say, farms or poultry farms, the ventilation shaft near the ridge is considered an ideal design option that provides air circulation. They run the entire length of the roof of the building in the direction of the ridge.
To close access to raindrops of rain, an umbrella is mounted above the outlet of the box. As a rule, in natural air exchange structures, a deflector is mounted directly on the wellhead. With gusts of wind, a rarefaction is created here, which contributes to increased traction. But first of all, of course, the deflector does not allow the air flow to “tip over” in the box
When calculating the system, the vacuum created by the wind is not taken into account.
Variants with artificial air exchange, which contribute to the removal of aggressive air impurities of the first and second classes, work somewhat differently: polluted air is thrown out to a fairly significant height. Such an emission is also called a flare.
Height
When placing an exhaust duct on the roof of a building, the smallest allowable distance between it and the air intake of the supply system must be taken into account. According to SNiP:
- horizontally it is equal to ten meters,
- vertically, respectively, six.
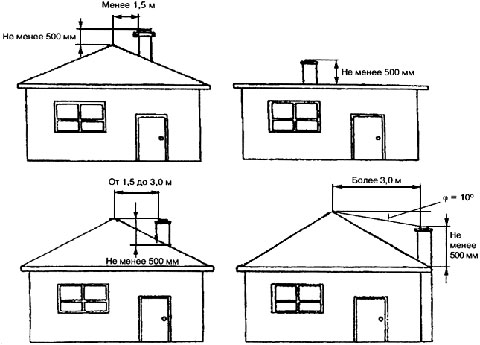
The height of the ventilation shaft above the roof is determined by the following conditions:
- when it is located near the ridge, the mouth, that is, the hood opening must be at least half a meter higher than the ridge;
- when located at a distance of one and a half to three meters from the ridge, the hole is flush with the ridge;
- for distances over three meters, the hole is led out along the side of the angle of 10⁰ to the horizon with the top on the ridge.
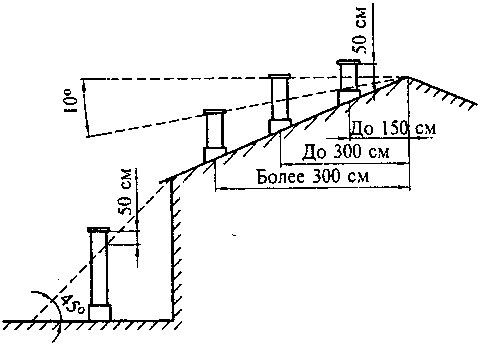
The height of the mouth above the roof for a standard design is usually chosen to be 1 m, in the case of a flare, at least 2 m above the highest point of the roof. For emergency - the mine is raised to a height of at least 3 m from the ground.
Material
In residential and public buildings with a system of combined exhaust ducts, lightweight concrete, brick, boards, upholstered with galvanized inside are most often used. The trunk of the passage from the inside is preliminarily covered with felt, which is dipped in a clay solution and plastered on the outside. In industrial buildings, the exhaust structure is mainly made of sheet steel.
fire safety
When organizing the ventilation of a building, all rooms and floors are connected to each other by a network of channels and air ducts, which in itself is dangerous from the point of view of fire safety. Therefore, these elements themselves and the gaskets between them are made of materials that meet the SNiP, according to which explosion and fire safety is ensured.In particular, the shaft is separated from the air duct by a partition made of non-combustible and moisture-resistant material.
What does traction depend on?
When the air temperature is low outside and high inside, there is a certain difference. The larger it is, the stronger the air from the interior rises, that is, the amount of exhaust air increases. When it becomes warm outside, the difference decreases and the efficiency of the exhaust ventilation decreases.
Device of ventilation ducts
Choice of length and section:
- pipes for a stainless steel fireplace are selected in such a way that the chimney pipe has a channel cross section of at least 16 sq.cm.
- The side of the channel must be at least 10 cm. Often pipes are selected according to the standard 14 * 14 cm, while the length of such a channel can be 3 m.
- With a larger section (14x27 cm), the length of the channel should be less (2 m).
All calculations and nuances of the ventilation system must be carried out in advance. Since in the process of work it is almost impossible to make changes to the “project”. Practice has shown that the length of the ventilation ducts of different rooms located on the same level should be almost equal. If the channels have a large difference in length, then this can seriously impair the efficiency of ventilation. Therefore, it should be remembered that a long fan pipe on the roof will have a large traction force, and if the air flow drops, the exhaust force will significantly decrease in a shorter channel. This situation can often occur in the ducts of houses with limited outside air intake (read: "Chimneys and ventilation ducts, operating rules").
Features of ventilation installation
The technology of laying air ducts is a sequence of certain operations and depends on the type of ventilation system. However, the installation of an engineering network is preceded by its calculation, the selection of pipes and the marking of their location.
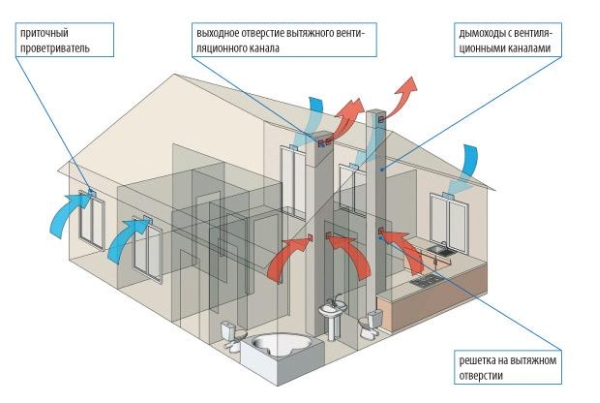
Installation of natural ventilation
The system is laid down during the construction of the house or mounted in channels specially provided for this. Installation of natural ventilation consists of the following steps:
- fixing air ducts;
- installation of gratings and deflectors;
- ensuring air flow due to supply valves;
- installation of hoods in the kitchen;
- installation of fans in bathrooms in the grilles of ventilation ducts working for blowing.
In this case, it should be borne in mind that the ventilation round pipe will provide better draft, and the air change will be more efficient.
Scheme of natural ventilation of a private house
If, during natural ventilation in the premises, the air is dry and there is a musty smell, then it is necessary to provide air flow through an additional valve or an ajar window. The reason for the increased humidity and the appearance of mold is insufficient outflow. It is quite difficult to eliminate this defect after construction is completed, and the easiest way is forced ventilation.
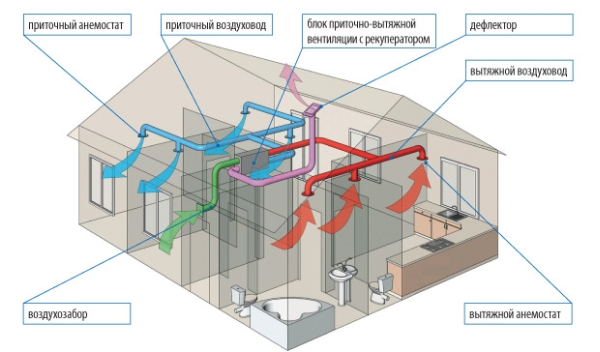
Installation of forced ventilation
This type is indispensable in a country house with a large number of isolated rooms and rooms with high humidity. Installation of forced ventilation is carried out as follows:
- install a supply and exhaust ventilation unit, placing it in an insulated attic;
- connect air ducts to it;
- an air intake is mounted on the outer wall so that the distance to the sewer risers and chimneys is at least 10 m;
- if the air ducts were not installed during the construction of the house, then during the installation of the system they are fixed according to the markup, while the ventilation supply pipe should be closer to the windows or on the opposite side from the door;
- connect the air ducts to the unit using corrugated pipes;
- conduct insulation of ventilation pipes;
- gratings are installed at the ends of the air ducts, and anemostat sockets are installed on the supply air ducts.
Scheme of forced ventilation of a private house
The optimal choice of ventilation pipes, compliance with the technology of their installation and regular maintenance of the system will ensure the supply of fresh air to the premises of a private house and will create a comfortable microclimate for its inhabitants.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=SAwNykjmiyw
The benefits of insulation
- heat transfer decreases;
- the formation of condensate, which causes corrosion, the formation of mold on the surface of the structure is prevented;
- the risk of fire is reduced;
- vibration and noise that occur during the operation of the air exchange system is weakened;
- heat transfer to the environment is reduced.
The thickness of the thermal insulation layer depends on such parameters as:
- the presence of a dew point,
- shape, dimensions of the air outlet,
- thermal conductivity of the heater,
- temperature difference between the ventilation system and the room.
The optimal solution is a technical insulation, which has a high vapor permeability and low thermal conductivity.
In systems with natural air exchange, as well as with forced ventilation for a certain category of buildings, the presence of insulation is mandatory.
For brick ventilation shafts, unlike metal ones, the problem of condensate formation is not, therefore, the issue of thermal insulation loses its relevance.
As for industrial buildings, forced air exchange shafts are made of structural steel, which heats up quite quickly. Since a sufficiently large volume of air passes through them, when cooled, the structure does not have time to reach the dew point, that is, the problem of water vapor condensation in this case is not worth it. The only possibility of condensate formation occurs when the ventilating equipment is stopped, therefore, for such systems, they organize the removal of condensate that may form during this period.
How to insulate
Thermal insulation is performed according to two methods: internal insulation and external.
The second is today considered the most economical and efficient. Soundproofing and fire issues are solved in this case much easier. For example, silencers are installed directly into the sound source. The likelihood of fire spreading is practically reduced to a minimum. Another valuable advantage of this technology is the ability to periodically take measures that prevent the formation of bacteria and microbes, which lead to the delamination of heat-insulating materials, and, therefore, to the loss of their performance.
For the insulation of ventilation ducts and cylindrical shafts, gypsum-slag or facade mineral wool boards are most often used. The process of thermal insulation device, say, for miniplates is carried out in the following sequence:
- prepare the surface, in particular, remove weak areas of the base, prime the surface;
- minplates are laid on glue, blotches and edging are also made from it;
- after waiting for the final drying, install the facade dowels;
- lay a reinforcing layer containing a mesh of fiberglass and glue;
- after complete drying, the surface is primed and covered with decorative plaster.
2019 stylekrov.ru
Principles for choosing a ventilation pipe
Air ducts for ventilation installation must ensure the passage of air flow in accordance with the indicators specified in the design documents. In addition, they need to be different:
- tightness;
- resistance to fire;
- minimum dimensions;
- compliance with sanitary and hygienic standards, including the level of noise produced.
Types of air ducts and features of use
Depending on the various characteristics of pipes for ventilation, they are classified according to the following criteria:
- section shape;
- materials used.
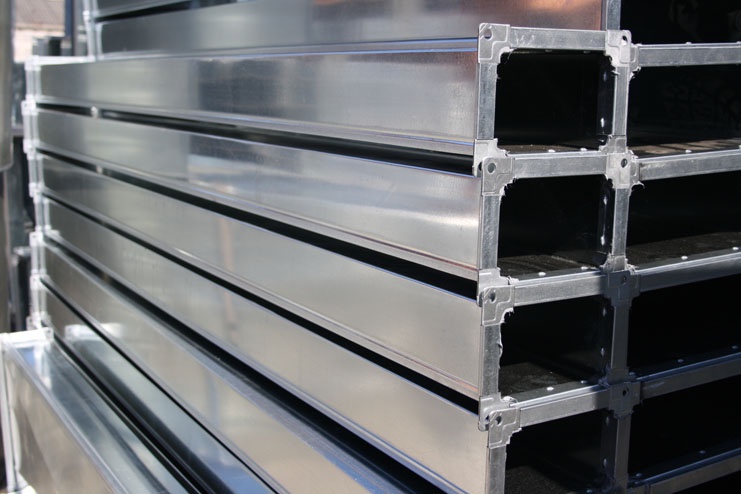
The most popular are air ducts with a cross section of a round or square shape. Round tubes are easier to manufacture, require less material and have good aerodynamic performance. Square and rectangular air ducts are more difficult to manufacture, weigh more and are characterized by an increased noise level. But they take up less space and easily fit into a room with false ceilings. Typically, a rectangular ventilation pipe is used for installation in office buildings, apartments in multi-storey buildings and country cottages. Round ducts are more in demand in industrial premises, where functionality is more important than aesthetic characteristics.
Circular air ducts
As raw materials for the manufacture of ventilation pipes use:
- Galvanized steel. It is resistant to corrosion, retains its characteristics in temperate climates and can be used in rooms with high humidity.
- Stainless steel. It is used for the manufacture of air ducts that provide the transfer of air flows at temperatures up to + 500 ⁰C. Ventilation pipes made of heat-resistant steel are used in aggressive environments - in heavy industry plants.
Rectangular stainless steel ventilation pipes
- Metal-plastic. Air ducts of this type are produced by connecting two layers of metal with foamed plastic. They are distinguished by good strength, low weight, do not require additional thermal insulation and have an aesthetic appearance. However, the high cost limits the use of metal-plastic ventilation pipes.
-
Plastic. Air ducts made of polymers are indispensable for the transfer of aggressive air masses in the chemical, food and pharmaceutical industries. The main material for their production is PVC, which is resistant to moisture, alkali and acid fumes. The smooth surface of the polymer pipes ensures minimal pressure loss of the air flow during movement, and the tightness of the connections of individual elements prevents the transported masses from entering the environment. In supply ventilation systems, polyethylene pipes are in demand, and their fiberglass counterparts are used for joining air distributors and fans.
In addition, air ducts can vary in design and rigidity. Depending on the production method, they are straight-seam, spiral-wound and spiral-welded, and in terms of rigidity - flexible and rigid.
The most popular are ventilation pipes of a rigid type, round or square. They are used for the construction of systems with high requirements for strength and are characterized by ease of operation and installation, but require reliable fastening, as they have significant weight.
Flexible ducts
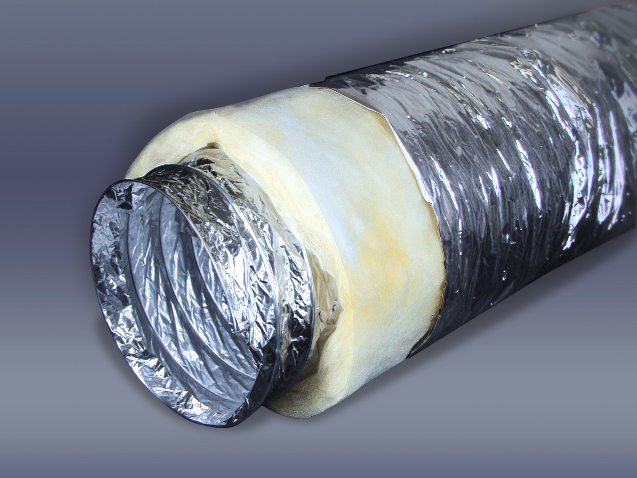
Flexible air ducts are a corrugated sleeve, the basis of which is steel reinforcement made of wire, and metallized polyester is used for the manufacture of walls. They are lightweight, easy to install and maintain. The disadvantages of corrugated ducts include low sound insulation and a corrugated surface, which reduces the speed of air flow when it moves. Which pipes for ventilation should be chosen is determined, taking into account these characteristics.
Flexible duct with thermal insulation
To fasten air ducts during the installation of a ventilation system in a private house, a flanged or flangeless connection is used. In the second case, a band made of thin sheet steel and metal slats serve as a fixing element. With a flanged connection, the air ducts are fastened together by flanges, and seals are used for tightness.