Notes
- Mikhail Gelfand. . Elements.ru.
- Coal reserves of the countries of the world / Zheleznova N. G., Kuznetsov Yu. Ya., Matveev A. K., Cherepovsky V. F., M .: Nedra, 1983. - P. 128
- Prigorovsky M. M. Fossil coals of the USSR // Science and life: journal. - 1935. - January (No. 1). - S. 24.
- Understanding Energy and Energy, Timothy F. Braun and Lisa M. Glidden 2014
- Dremov, Alexei V. Substantiation of rational parameters of dedusting in a combine tunneling face: dissertation of a candidate of technical sciences: 05.26.01; . - Moscow, 2010. - 148 p.
- Kuzmichev A. S. red. "Handbook on dust control in the mining industry" M.: Nedra, 1982. - 240p.
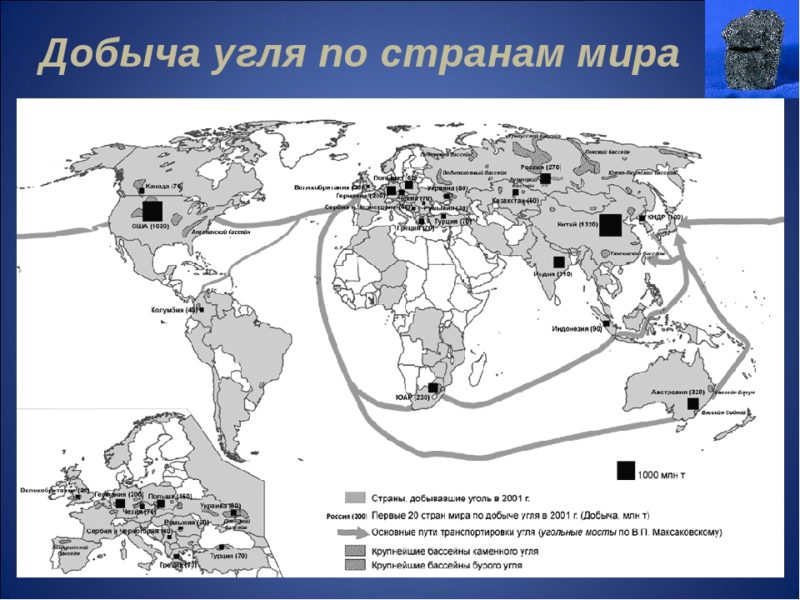
Coal mining areas in Russia
The range of its use is very wide. Coal is used to generate electricity, as an industrial raw material (coke), for the production of graphite, for the production of liquid fuels by hydrogenation.
Russia has vast reserves of coal deposits and coal basins.
A coal basin is an area (often over 10 thousand square kilometers) of coal-bearing deposits, formed under certain conditions over a certain period of time. The coal deposit has a smaller area and is a separate tectonic structure.
On the territory of Russia there are platform, folded and transitional basins.
The largest amount of coal deposits was found on the territory of Western and Eastern Siberia.
60% of Russian coal reserves are humic coals, including coking coal (Karaganda, South Yakutsk, Kuznetsk basin). There are also brown coals (Urals, Eastern Siberia, Moscow region).
Coal reserves are dispersed over 25 coal basins and 650 individual deposits.
Coal mining is carried out in a closed or open way. Closed mining is carried out in mines, open - in quarries (sections).
The life of the mine is on average 40-50 years. Each layer of coal is removed from the mine for about 10 years, followed by the development of a deeper layer through reconstruction. Reconstruction of mine horizons is a prerequisite for preserving the environment and ensuring the safety of workers.
In the cuts, the extraction of coal is carried out in successive strips.
For the period of 2010, coal in Russia was mined in 91 mines and 137 cuts. The total annual capacity was 380 million tons.
After coal is mined in mines or cuts, it goes directly to the consumer or is sent to coal enrichment enterprises.
At special factories, pieces of coal are sorted by size and then enriched.
The enrichment process is the purification of fuel from waste rock and impurities.
Today, coal in Russia is mined mainly in the territory and 10 main basins. The largest deposit of hard and coking coal is the Kuznetsk basin (Kemerovo region), brown coal is mined in the Kansk-Achinsk basin (Krasnoyarsk Territory, Eastern Siberia), Anthracites - in the Gorlovsky basin and in the Donbass.
The coal in these basins is of the highest quality.
Other well-known coal basins in Russia include the Pechora basin (Arctic), the Irkutsk-Cheremkhovo basin in the Irkutsk region, and the South Yakutsk basin in the Far East.
The Taimyr, Lena and Tunguska basins in Eastern Siberia are being actively developed, as well as deposits in the Trans-Baikal Territory, Primorye, Novosibirsk Region.
admin
The largest branch (in terms of the number of workers and the cost of production fixed assets) of the fuel industry is coal mining in Russia.
The coal industry extracts, processes (enriches) coal, lignite and anthracites.
Kuznetsk basin
Balance sheet
coal reserves of Kuzbass category
A + B + C1 are estimated at 57 billion tons, which
makes up 58.8% of coals in Russia.
At the same time, coking coal reserves
account for 30.1 billion tons, or 73% of all reserves
country.
V
Kuzbass produces almost all
range of coal grades. Bosom
Kuzbass are rich in other useful e
fossils are manganese, iron,
phosphorite, nepheline ores, combustible
slates and other minerals.
Kuznetsk
coals are of high quality:
ash content 8-22%, sulfur content - 0.3 -0.6%,
specific heat of combustion – 6000 – 8500
kcal/kg.
Average development depth
underground method reaches 315m.
Near
40% of the mined coal is consumed in the
Kemerovo region and 60% is exported to
other regions of Russia and for export.
V
structure of coal exports from Russia to
Kuzbass accounts for over 70% of its physical
volume.
Here lies the coal
high quality, including coking.
Nearly 12% of mining is carried out by open pit
way.
Belovsky district is
one of the oldest mining areas
coal price Kuzbass |
Balance reserves
coal of the Belovsky district
are more than 10 billion. tons.
Development
Kuznetsk coal basin began
in 1851 with more or less regular
fuel extraction at the Bachat mine for
Guryevsky metallurgical plant.
The Bachat mine was six
miles northeast of the village
Bachats. Now at this place are
mines "Chertinskaya - Koksovaya", "Novaya-2"
and the Novobochatsky section.
firstborn
coal industry Belova
is considered the Pioneer mine, in 1933.
Here the first ton of coal was mined. V
currently Belovsky district is
largest coal mining area in
Kuzbass.
Belovsky district
the geographic center is
Kemerovo region.
main centers
are Novokuznetsk, Kemerovo,
Prokopyevsk, Anzhero-Sudzhensk, Belovo,
Leninsk-Kuznetsky.
Kansko-Achinsk
swimming pool situated
in the south of Eastern Siberia in Krasnoyarsk
region along the Trans-Siberian Railway
and gives 12% of coal production in Russia. Brown
the coal of this basin is the most
cheap in the country, since mining
carried out in an open manner. Because of
poor quality coal is not transportable
and therefore on the basis of the largest cuts
(Irsha-Borodinsky, Nazarovsky,
Berezovsky) powerful thermal
power plants.
Pechorsky
swimming pool is an
largest in the European part and gives
4% of coal production in the country. He is removed from
major industrial centers and
located in the Arctic, mining is underway
mine only. In the northern
parts of the basin (Vorkuta, Vorgashor
deposits) produce coking
coals, in the south (Inta deposit)
- predominantly energetic.
The main consumers of Pechora
coal are Cherepovets Metallurgical
plant, enterprises of the North-West, Center
and the Central Black Earth.
Donetsk
swimming pool v
Rostov region is eastern
part of the coal basin,
located in Ukraine. This is one of
the oldest coal mining areas. Mine
the method of extraction determined the high
cost of coal. Coal mining with each
decreases year by year and in 2007 the pool gave
only 2.4% of the total Russian production.
Irkutsk-Cheremkhovsky
swimming pool v
Irkutsk region provides low
the cost of coal, since mining
performed in an open manner and
provides 3.4% of the country's coal. Due to the big
remoteness from large consumers
used in local power plants.
South Yakutsk
swimming pool (3,9%
of all-Russian production) is located on
Far East. Has significant
reserves of energy and technological
fuel, and all production is carried out
open way.
TO
promising coal basins
include Lensky, Tunguska and
Taimyr, located beyond the Yenisei
north of the 60th parallel. They take
vast areas in underdeveloped
and sparsely populated areas of Eastern Siberia
and the Far East.
Parallel
with the creation of coal bases of interdistrict
importance, there was a wide development of local
coal basins, which made it possible
to bring coal mining closer to its regions
consumption. However, in the western regions
Russia's coal production is declining
(Podmoskovny basin), and in the eastern -
increases sharply (fields
Novosibirsk region, Zabaikalsky
edge, Primorye.
Coal reserves in Russia
See also: Minerals of Russia
5.5% of the world's coal reserves are concentrated in Russia, which is more than 200 billion tons. Such a difference with the percentage of proven coal reserves for 2006 is due to the fact that most of it is not suitable for development, as it is located in Siberia in the permafrost region. 70% falls on brown coal reserves.
The largest promising deposits
Elga field in the south-east of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), 415 km east of the city of Neryungri. Belongs to OAO Mechel. The most promising object for open development.
The area of the deposit is 246 km², it is a gentle brachysyncline asymmetric fold. The main coal seams are confined to the deposits of the Neryungri (6 seams, 0.7-17 m thick) and Undyktan (18 seams, also 0.7-17 m thick) formations.
Most of the coal resources are concentrated in four layers y4, y5, n15, n16, usually of a complex structure. The coals are mostly semi-shiny lenticular-banded with a very high content of the most valuable component -
vitrinitis (78-98%). According to the degree of metamorphism, coals belong to the III (fat) stage. Coal grade Zh, group 2Zh. Coals are medium- and high-ash (15–24%), low-sulfur (0.2%), low-phosphorus (0.01%), good sintering (Y = 28–37 mm), with high calorific value (28 MJ/kg).
Elga coal can be enriched to the highest world standards and receive high quality export coking coal. The deposit is represented by thick (up to 17 meters) flat seams with overburden deposits of small thickness (overburden ratio is about 3 m³ per ton of raw coal), which is very beneficial for organizing open-pit mining.
(Tyva) has reserves of about 1 billion tons of coking coal of a scarce brand "Zh" (the total reserves are estimated at 20 billion tons). 80% of the reserves are located in one layer 6.4 m thick (the best mines in Kuzbass work in layers 2-3 m thick, in Vorkuta coal is mined from layers thinner than 1 m). After reaching the design capacity by 2012, Elegest is expected to produce 12 million tons of coal annually.
The license for the development of Elegest coal belongs to the Yenisei Industrial Company, which is part of the United Industrial Corporation (OPK). On March 22, 2007, the Government Commission for Investment Projects of the Russian Federation approved the implementation of projects for the construction of the Kyzyl-Kuragino railway line in conjunction with the development of the mineral resource base of the Republic of Tuva.
- History of coal mining in Russia
- Coal mining
- Coal reserves in Russia
- Notes
- Literature
- Links
What about in Russia
Russia is one of the largest exporters of coal in the world. Moreover, in 2017, for the first time, the volume of export deliveries exceeded the volume of deliveries to the domestic market. And in the same year, for the first time in the modern history of Russia, coal production exceeded 400 million tons of coal per year.
And this is far from the limit. According to the current strategy, by 2030 in our country it is necessary to increase production to 410 million tons of coal (and in an optimistic scenario - up to 480 million tons).
However, the actions of Europe have a serious impact on the coal industry in Russia. The decrease in demand for coal caused a drop in its cost in the European market - up to $47 per 1 ton (prices are at the level of mid-2016).
Meanwhile, transportation costs have increased: for example, the cost of transporting Kuzbass enterprises (Russia's largest exporters) in April 2019 alone amounted to about 70% of the cost of fuel. Thus, deliveries for companies simply become a "losing event".
Against the backdrop of gloomy prospects, some companies began to cut production plans (this, in particular, was stated by representatives of the Kuzbass Fuel Company, Mechel and PAO Raspadskaya).
Some of the coal miners, with the support of the Ministry of Energy, made a request to Russian Railways to reduce tariffs for the supply of coal to Europe in order to somehow recoup the costs. The transport company agreed and in mid-July announced the temporary cancellation of the "export surcharge".
Related reference materials
Save the article to social networks:
COAL (a. black, bitouminous, mineral coal; n. Steinkohle; f. houille, charbon mineral; and. hulla, carbon de piedra) is a solid combustible mineral of plant origin - a type of fossil coal, intermediate between brown coal and anthracite.
Coal is a dense black rock, sometimes cepo-black, giving a black line on a porcelain plate. Organic matter contains 75-92% carbon, 2.5-5.7% hydrogen, 1.5-15% oxygen.
The higher calorific value in terms of dry ashless state is 30.5-36.8 MJ/kg. Most hard coals are humoliths; sapropelites and humitosapropelites are present in the form of lenses or small layers.
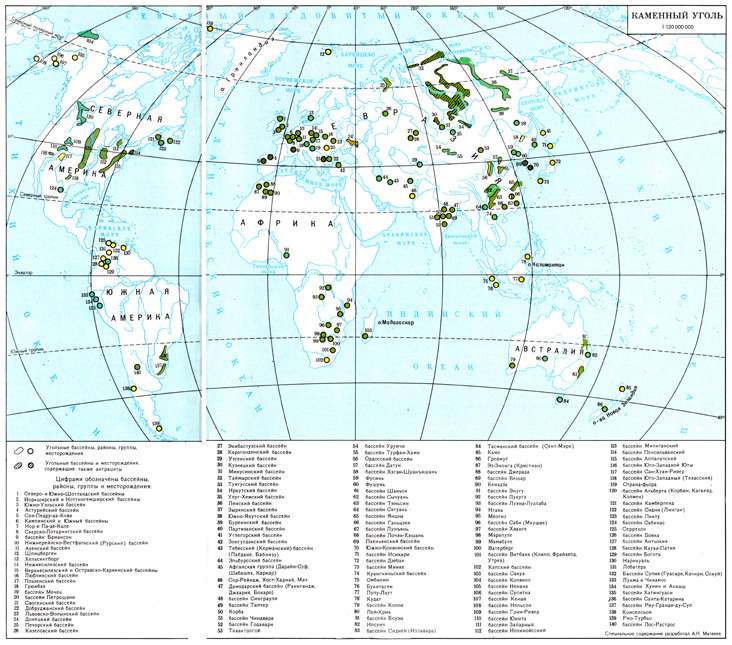
Bituminous coals occur in the form of seams and lenticular deposits of various thicknesses (from fractions of meters to several tens and hundreds of meters) at different depths (from outcrops to 2500 m and deeper). Coals are formed from the decomposition products of organic remains of higher plants that have undergone changes (metamorphism) under the pressure of the surrounding rocks of the earth's crust and relatively high temperatures.
Coal is characterized by a neutral composition of the organic mass. They do not react with weak alkalis either under normal conditions or under pressure. Their bitumens, in contrast to brown coals, are mainly represented by compounds of aromatic structure. Fatty acids and esters were not found in them, compounds with the structure of paraffins are of little importance.
Hard coals are divided into shiny, semi-shiny, semi-matte, matte. Depending on the predominance of certain petrographic components, vitren, claren, dureno-claren, clarene-durene, durene and fuse coals are distinguished.
Seams of coal can be composed of one of the indicated lithotypes, more often their alternation (the so-called banded coals). As a rule, shiny varieties of coal are low-ash due to the insignificant content of mineral impurities.
Among the structures of the predominant substance of coals (coal-forming microcomponents), 4 types (thelinitic, post-thelinitic, precollinite and collinite) are distinguished, which are successive stages of a single process of decomposition of lignin-cellulosic tissues and reflect the general patterns of formation of coal-bearing formations.
The main units of classification of coals are genetic groups established by the structure of the substance of coal-forming microcomponents, which, in addition to the four types mentioned, also includes leuptinite coals. Thus, 5 genetic groups have been identified.
Each of them is divided into corresponding classes according to the type of substance of coal-forming microcomponents.
Boom alternatives
It all started in April 2016, when 195 countries (including Russia) signed the Paris Climate Agreement. The document obligated the world community to reduce greenhouse emissions into the environment in order to keep the increase in global average temperatures by 2100.
Undoubtedly, one of the main sources of emissions is coal, which is burned in large quantities in power plants. It accounts for about 39% of CO2 emissions. In order to fulfill the main tenet of the agreement, some states decided to gradually abandon the consumption of coal.
In Europe, they approached the matter seriously and the first thing they began to close the mines. France closed the last mine in 2014, the UK in 2015, and Germany in 2018.
And in early May 2019, the UK decided on a large-scale experiment and stopped the operation of coal-fired power plants for a whole week.
At the same time, European states have embarked on the development of alternative energy. The substitution program has already paid off: in 2017, the amount of energy generated by renewable energy sources in the EU countries for the first time in history exceeded the amount of energy from coal-fired power plants.
Germany and the United Kingdom were the most notable: by the end of 2018, they had provided a 56% increase in renewable electricity for the entire European Union.
Minerals
During the Carboniferous period, deposits of various minerals were formed, the most important of which were coals. Carboniferous coal deposits account for about 25% of the world's total fossil coal reserves. Coal basins and carbon deposits are widely represented in Europe and North America, where more than 80% of the total geological reserves of coals of this age are concentrated. The main coal basins in the European part of Russia are near Moscow, in Ukraine - Donetsk and Lvov-Volyn. Of the coal basins of the Carboniferous period in the Asian part of Russia, the most important are the Kuznetsk and Tunguska, in Kazakhstan - the Karaganda and Ekibastuz. Numerous coal basins, predominantly of Middle and Late Carboniferous age, are known in foreign Europe and Asia, North America and on the southern continents. The largest basins in Europe are associated with carbon deposits: South Wales, Lancashire, Northumberland, Kent in Great Britain, Asturian in Spain, Valenciennes in France, Liege and Campin in Belgium, Lower Rhine-Westphalian (Ruhr) in Germany, Upper Silesian in Poland, Ostrava in Czech Republic. The coal content of the coal system in Asia is less developed than in Europe. The main coal basins are known in northeast China, in Turkey (Zonguldak), Mongolia, Indonesia, etc. In North America, the largest coal accumulation is associated with the Pennsylvanian strata (Appalachian, Illinois, Pennsylvania, Michigan, Texas basins). Of the fossil fuels, in addition to coal, the coal system contains deposits of oil and natural gas. In Russia, the commercial oil and gas potential of the Carboniferous is typical for the east of the East European Platform (Volga-Ural oil and gas province), where oil and gas deposits are present in the lower and middle sections. Oil and gas deposits are also found in the Dnieper-Donetsk depression. Here, oil and gas deposits are confined to the Visean, Serpukhovian and Bashkirian deposits, and the main gas reserves lie in the upper Carboniferous. Large oil and gas fields of the Mississippian (Early Carboniferous) age are known in the central and eastern states of the USA (Midcontinent). Numerous deposits of various ores of sedimentary and magmatic origin are subordinated to deposits of the Carboniferous system. Sedimentary ores include brown iron ore (East European platform, Urals), bauxites (Podmoskovny basin, Central Asia). Deposits of refractory clays are connected in places with deposits of the Carboniferous system; with intrusions - the largest (now mostly depleted) deposits of iron ore in the Urals and less rich in the Sayano-Altai and other folded regions, as well as deposits of ores of polymetals. Carboniferous limestones are widely used as cement raw materials, building and facing stone, etc.
Coal deposits
The Elga deposit in Sakha is considered the most promising for open development. Its area is 246 km2. Coal deposits of this type are a gentle asymmetric fold. The deposits of the Lower Cretaceous and Upper Jurassic will be coal-bearing.The key coal seams of this coal deposit are laid down in the deposits of the Neryungri and Undyktan suites. The coals there are mostly semi-shiny and with a fairly high content of the most valuable component - vitrinite. Elga coal can be enriched with the help of special equipment, which makes it possible to obtain products with a higher quality.
Strong flat seams of such coal are covered by deposits of small thickness, which is extremely important when extracting a fossil in an open way.
The Elegest deposit in Tuva has reserves of approximately 20 billion tons. And this is confirmed by interesting facts about coal.
A huge part of the reserves is located in one layer with a thickness of 6.4 m. The development of this field continues today.
The Minusinsk coal basin is located in the Republic of Khakassia. Coal mining began there in 1904. The largest deposits include Chernogorskoye and Izykhskoye. According to geologists' estimates, the coal reserves in that area amount to 2.7 billion tons. Stone long-flame coals with a high calorific value predominate in the basin. Coal of this type is classified as medium ash. The maximum ash content is typical for the coals of the Izykh deposit, and the minimum for the coals of the Beyskoye deposit. Both cuts and mines help to extract minerals there.
The Kuznetsk coal basin is one of the largest coal deposits in the world. Kuzbass is located in the southern part of Western Siberia in a shallow basin between the mountains of Alatau, Gornaya Shoria and the Salair Ridge. This territory belongs to the Kemerovo region. The abbreviation "Kuzbass" is the second name of the region. Coal is mined there by different methods. There are 58 mines and more than 30 cuts on the territory of this basin. In terms of quality, Kuzbass fuel is diverse and is classified as one of the best coals. The thickness of the coal seams that prevails there is from 1.3 to 4.0 meters, but there are also thicker seams of 9-15 and even 20 meters, and in some places up to 30 meters. The maximum depth of such coal mines does not exceed 500 meters. The average thickness of the developed coal seams is 2.1 m, but up to 25% of mine coal production falls on seams over 6.5 m.
China ranks third in coal production. The large deposits of this state are those located in the Shanxing coal basin, in the Great Plain of China, in Datong and in the Yangtze.
A large amount of coal is also mined in Australia - in the states of New South Wales and Queensland.
A major producer of such a mineral is India, and the deposits there are located in the northeastern part of the country.
In the deposits of Saxony and Saar, Rhine-Westphalia and Brandenburg in Germany, lignite and hard coal have been mined for 150 years.
In Ukraine, there are also 3 coal basins: Donetsk, Dnieper and Lvov-Volyn. Anthracites, coking and gas coal are mined there.
Sufficiently large-scale coal deposits are those located in Canada, Uzbekistan, Colombia, Turkey, North Korea, Thailand, Kazakhstan, Poland, the Czech Republic and South Africa.
Uranus
Main article: Uranium mining in Russia
In Russia, the main uranium-ore region is Transbaikalia. About 93% of Russian uranium is mined at the deposit in the Chita region (near the city of Krasnokamensk). Mining is carried out by the Priargunsky Industrial Mining and Chemical Association (PIMCU), which is part of JSC Atomredmetzoloto (Uranium Holding), using the mine method. The remaining 7% is obtained by in-situ leaching from ZAO Dalur (Kurgan Region) and OAO Khiagda (Buryatia).
The resulting ores and uranium concentrate are processed at the Chepetsk Mechanical Plant.
In terms of annual production of uranium (about 3.3 thousand tons), Russia ranks 4th after Kazakhstan.The annual consumption of uranium in Russia is 16 thousand tons and consists of expenses for its own nuclear power plants in the amount of 5.2 thousand tons, as well as for the export of fuels (5.5 thousand tons) and low-enriched uranium (6 thousand tons) .
Tectonics and magmatism
The main structural elements of the earth's crust during the Carboniferous period experienced significant rearrangements caused by the manifestation of Hercynian folding. Their result was the transformation of a significant part of the geosynclinal regions into folded mountain structures - hercynides. The first phase of the Hercynian tectogenesis, which manifested itself at the turn of the Devonian and Carboniferous, caused the growth of geoanticlinal uplifts in geosynclinal areas. Uplifts soon gave way over vast areas to subsidence of the earth's crust and the development of marine transgressions, which reached a maximum in the Visean. The manifestation of the Hercynian folding at the end of the Early Carboniferous was more intense. These movements took place in a number of geosynclinal regions, within which the folded structures of the Hercynides arose. Folding was especially intense in the West European geosynclinal region and the Ural-Mongolian geosynclinal belt. The folded structures that appeared here in the Middle Carboniferous entered the orogenic stage of development. Along with the formation of intermountain depressions, marginal or foothill troughs were formed at the border of uplifted mountain structures and platforms. Thick clastic strata accumulated in depressions and troughs, with which the largest coal basins and deposits are associated. In the platform areas, the tectonic movements of the end of the Early - beginning of the Middle Carboniferous were manifested by uplifts that caused regressions of the sea. In the Middle Carboniferous, new transgressions arose in places. At the turn of the Middle and Late Carboniferous epochs, a new phase of Hercynian folding occurred, which complicated the previously formed Hercynides. In the Late Carboniferous, the movements of the earth's crust became more and more differentiated. Along with the predominance of regressions, there were limited transgressions. Fold-forming movements in geosynclines continued in the Late Carboniferous. Throughout the Carboniferous period, magmatism manifested itself in geosynclinal belts. It is assumed that in the Carboniferous, the platforms of the Southern Hemisphere and the equatorial region formed a single giant supercontinent - Gondwana. In the Northern Hemisphere, the existence of a hypothetical continent of Angaria, located on the site of modern North Asia, is allowed. The geological development of the earth's crust in the Carboniferous predetermined on a planetary scale the predominance of marine deposits in the Lower Carboniferous and the widespread development of continental facies in the middle and upper sections.
Coal mining
Coal mining methods depend on the depth of its occurrence. The development is carried out in an open way in coal mines, if the depth of the coal seam does not exceed one hundred meters. There are also frequent cases when, with an ever-increasing deepening of a coal pit, it is further advantageous to develop a coal deposit by an underground method. Mines are used to extract coal from great depths. The deepest mines in the Russian Federation extract coal from a level of just over one thousand two hundred meters.
In conventional mine production, about 40% of the coal is not extracted. The use of new methods of mining - longwall - allows you to extract more coal.
Along with coal, coal-bearing deposits contain many types of georesources that have consumer significance. These include host rocks as raw materials for the construction industry, groundwater, coal-bed methane, rare and trace elements, including valuable metals and their compounds. For example, some coals are enriched with germanium.
peaked at 8254.9 million tons in 2013.