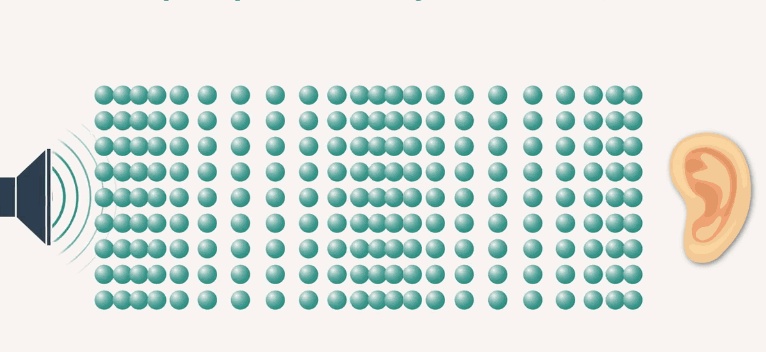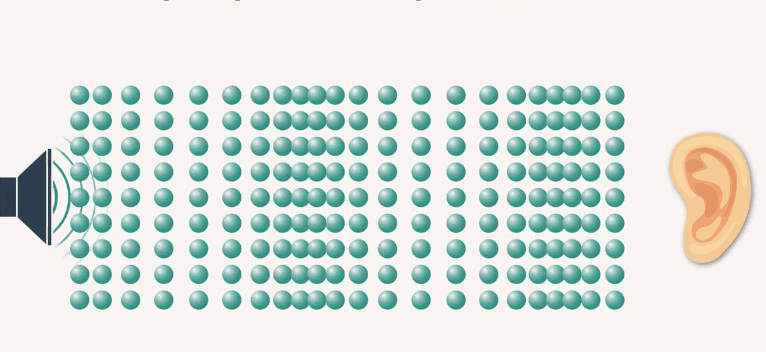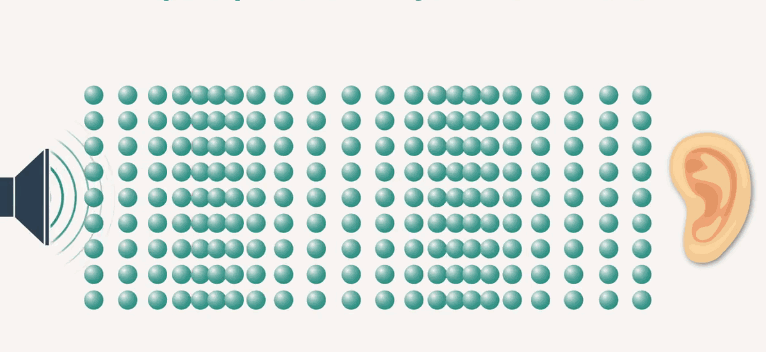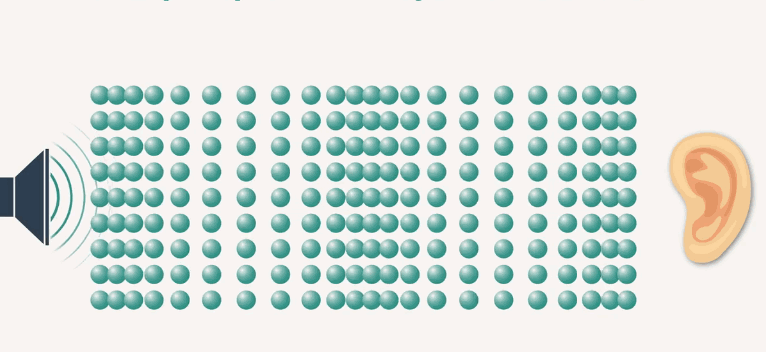Music waves. Noise
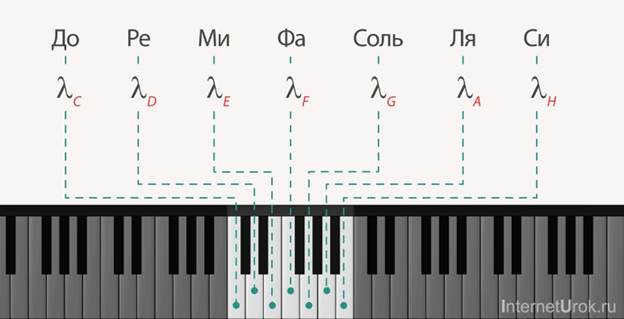
The most interesting sound waves are musical sounds and noises. What objects can create sound waves? If we take a wave source and an elastic medium, if we make the sound source vibrate harmonically, then we will have a wonderful sound wave, which will be called musical sound. These sources of sound waves can be, for example, the strings of a guitar or a piano. This may be a sound wave that is created in the gap of the air pipe (organ or pipe). From music lessons you know the notes: do, re, mi, fa, salt, la, si. In acoustics they are called tones (Fig. 7).
Rice. 7. Musical tones
All items that can emit tones will have features. How do they differ? They differ in wavelength and frequency. If these sound waves are not created by harmonically sounding bodies or are not connected into a common orchestral piece, then such a number of sounds will be called noise.
Noise – random fluctuations of various physical nature, characterized by the complexity of the temporal and spectral structure. The concept of noise is everyday and is physical, they are very similar, and therefore we introduce it as a separate important object of consideration.
Noise classification
Tinnitus can have different types, their classification can help in the correct diagnosis. Types of noise and extraneous sounds:
- Pulsating beat. Most often, such a sound occurs during an aneurysm of the ear vessels, with otitis media, with Meniere's pathology, eustachitis and the presence of a cyst in the ear cavity.
- Clicky sound. Clicking can provoke unexpected contraction of the soft palate and middle ear. This phenomenon becomes the norm for people disposed to convulsions.
- Simple noise. This type is expressed by buzzing, hissing and clicking.
- Difficult. A strong ringing, squeaking, human voices and music are heard.
Otitis externa diffuse: causes, symptoms and treatment
Each type individually has its own degree of damage, treatment is carried out on an individual basis.
What causes noise in the right ear
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of this condition, only after the diagnosis. It is impossible to treat any ear pain on your own, especially to establish a diagnosis for yourself. Sometimes a pulsating knock or ringing can signal the development of a serious pathology; it is dangerous to delay treatment in this case. The person stops sleeping at night, becomes depressed and irritable.
The most well-known reasons are:
-
Atherosclerosis is a common disease that affects the elderly, although middle-aged people have also recently begun to get sick. The pathology is expressed by the deposition of a fatty layer on the membrane of the vessels, cholesterol plaques are formed. Ultimately, a blockage occurs in the cervical vessels, blood circulation in the cerebral vessels is disturbed, the nutrition of the brain section is suspended and a pulsation appears in the ears, sometimes only on the right side.
- Another reason is the arterial syndrome of the spine. During such a pathology, there is a violation of the flow of blood flow to the areas of the vertebral region. The first symptom of this disease is the presence of tinnitus. In addition, the patient will complain of headache and numbness of the facial region.
- Postotitis period. If a person has had otitis media, this is an inflammatory process of the inner and middle ear. If this disease has become chronic, then noises will be present quite often and cause constant discomfort to a person. There will be no pain, however, it is likely that the patient will hear and navigate poorly, during his own conversation he will hear an echo in his head.
- Ear plug.If you do not clean the ear canal correctly or for a long time, a sulfur plug will form. After the usual washing, the hearing returns to normal, the noise stops.
- Tumor of the brain and neck. Oncology can sometimes be expressed by extraneous sounds in the right ear, this is due to the fact that the neoplasm begins to affect the auditory nerve. If the tumor reaches a large size, the person may become deaf.
There are harmless reasons, but there are also serious ones. The sooner the diagnosis is established, the sooner the recovery will come!
Causes of tinnitus
There are many etiological factors leading to the occurrence of tinnitus: direct pathologies of the hearing organs, taking certain medications, general diseases, aging of the body, etc.
Pathologies of the outer ear:
- foreign body in the auricle;
- otitis externa;
- sulfur plug.
Pathologies of the middle ear:
- tumor formation, trauma or other damage to the eardrum, for example, listening to loud music through headphones or prolonged exposure to sounds from a working tractor or chainsaw;
- exudative otitis;
- otosclerosis.
Pathologies of the inner ear:
- sensorineural hearing loss;
- Meniere's disease;
- tumor of the auditory nerve;
- complications of SARS, influenza;
- acoustic neuritis;
- ototoxic effects of drugs or other substances:
- aminoglycoside antibiotics - amikacin, gentamicin, kanamycin;
- macrolides - azithromycin;
- drugs acting on the central nervous system - haloperidol, caffeine, aminophylline;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - diclofenac, indomethacin;
- loop diuretics - furosemide, uregit and others;
- cardiovascular drugs - digitalis;
- organic solvents - benzene, methyl alcohol.
- labyrinthitis;
- presbycusia - senile hearing loss due to age-related changes in auditory cells.
Systemic diseases accompanied by tinnitus:
- metabolic diseases - diabetes, thyrotoxicosis, thyroiditis, hypoglycemia;
- malignant and benign tumor processes - acoustic neuroma, tumor of the eardrum or brain stem, meningioma;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- osteochondrosis, developing in the cervical spine;
- stenosis of the jugular veins or carotid arteries.
Other reasons:
- poisoning with industrial poisons;
- hepatitis;
- fluid in the ear
- fistula of perilymph;
- stress;
- head injury.
Therapeutic measures
How to get rid of tinnitus can only be said by a qualified specialist, after conducting a thorough and comprehensive diagnosis
It is important to understand that noise is only a symptom. The task of the doctor is to eliminate the disease that provoked him.
Tinnitus is usually treated with conservative methods.
if the cause lies in progressive osteochondrosis, then the treatment plan includes anticonvulsant, anti-inflammatory, non-narcotic analgesics and muscle relaxants
They can be prescribed both in the form of tablets and in the form of injections;
the sulfur plug is removed from the ear canal only by washing it with saline, which is supplied through Janet's syringe (this must be done carefully so as not to damage the eardrum). In this case, neither injections nor tablets are effective;
if there are pathologies of the cerebral vessels, nootropics (usually in the form of tablets) must be included in the therapy, and pharmaceuticals are also prescribed that improve blood circulation in the organ;
if tinnitus was provoked by taking pills that adversely affect hearing function, then the first thing to do is to completely remove these drugs and replace them with others.
In addition to pills and injections, with tinnitus, the patient is also shown physiotherapy. The following is usually given:
- electrophonophoresis;
- hardware treatment;
- magnetotherapy;
- laser therapy.
It is important to remember that doing something in the presence of tinnitus on your own, without consulting a doctor, is undesirable, since you can only worsen your condition. And then neither pills nor physiotherapy will help.
Moreover, it is worth abandoning the therapy of folk remedies.
Diagnostics
If such a symptom manifests itself suddenly, does not go away for a long time, and is also combined with other symptoms, such as headache, dizziness, then it is important to immediately go to an appointment with a qualified otorhinolaryngologist. The first thing the doctor will do is conduct a physical examination, as well as a questioning
Based on the information received, he will be able to guess why a person hears extraneous sounds. To clarify the preliminary diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods can be prescribed.
Instrumental:
- skull x-ray. It is done if there is a suspicion that it was the head injury that provoked the appearance of tinnitus and other unpleasant symptoms, such as dizziness, headache;
- Weber test;
- tone threshold audiometry;
- x-ray of the spinal column;
- CT scan of the skull using a special contrast agent;
- dopplerography of cerebral vessels is performed if atherosclerosis or ischemia is suspected (especially if one of the leading symptoms is dizziness);
- MRI.
Laboratory:
- blood test;
- serological blood test;
- blood biochemistry;
- analysis to determine the level of hormones produced by the thyroid gland.
How to diagnose pathology
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, in addition to a general examination, it is necessary to carry out many research manipulations. Since we are talking not only about hearing, but also about the brain, the diagnosis is extensive.
The doctor writes out referrals for the following procedures:
- Palpation examination. With the help of a thin metal rod, an internal examination of the ear is performed. There must be a curve at the end of the rod.
- Otoscopy. A special metal ring is put on the patient's head. A mirror is attached to the ring from the inside, through which the light beam is directed to the deepest part of the auditory region. Thanks to this method, it is possible to study the state of the eardrum without touching it. If the drug has a fiberoptic wand, then an examination of the external auditory department is carried out.
- Audiometry. Thanks to an audiometer or a tuning fork, the doctor determines the patient's hearing acuity.
-
Vestibulometry. The presence of dizziness, the cause of headache, is studied and determined. The vestibular apparatus and the blood supply to the auditory nerve and brain are examined. A finger test is performed. A person should, when closing both eyes, touch the tip of his nose with his finger.
- Gas testing. This research method allows you to confirm Meniere's disease. The essence of the procedure: the patient inhales the mixture, which was previously saturated with carbon dioxide, in order to expand his blood vessels. Next, some drugs are taken to reduce the level of water in the body.
- CT, MRI and X-rays - diseases of the brain and inner ear are studied.
- Dopplerography. The degree of audibility and patency of ear vessels is considered with the help of special waves.
- Angiography is an x-ray examination. Thanks to the contrast medium, the blood supply to the inner ear and brain activity is determined. A blood flow blockage is being looked for.
- Blood test. The study in the laboratory of the sedimentation rate of erythrocytes, leukocytes and bacteria in the patient's blood.
- microbiological diagnosis. Ear secretions or wax are taken to detect an infection or pathogen.
Maxillary sinus cyst: treatment, precautions
This whole set of studies will help to accurately determine the cause of the noise. Accurate diagnosis is the key to further recovery.
What is tinnitus like?
Noise types:
- Objective. In addition to the patient, the doctor hears such a noise. This type is rare in practice.
- Subjective. Only the patient hears different types of noise.
- Vibrating. Sounds produced by the organ of hearing itself or by the structures surrounding it. It is these mechanical noises that both the patient and the doctor can hear.
- Non-vibrating. Only the patient hears various sounds. They arise from pathological excitation or irritation of the nerve endings of the auditory pathways, the inner ear.
Non-vibration noise gradation:
- central - noises are felt in the center of the head;
- peripheral - a sound heard in one ear.
- Constant. It is observed after surgery for the intersection of the vestibulocochlear nerve or with severe atherosclerosis of the vessels.
- Periodic. It occurs during inflammatory lesions of the ears.
- Unilateral. Heard in only one ear.
- Bilateral. Heard in both ears.
Etiology
There are a lot of reasons that could provoke the appearance of noise in the ears and head, and these are not only pathologies of the hearing aid.
The most common causes of tinnitus and head noise are:
- ailments of the external ear. Sulfur plug, otitis media, as well as the presence of a foreign body in the auricle can provoke noise;
- diseases of the middle ear. Most often, the appearance of tinnitus is a harbinger of exudative otitis media or otosclerosis. Often these pathologies are also accompanied by dizziness. Tinnitus often manifests itself due to trauma to the eardrum, the presence of a tumor-like formation of a benign or malignant nature;
- ailments of the inner ear. Common causes of noise in the ears and head are such pathologies: labyrinthitis (also accompanied by severe dizziness), neuritis of the auditory nerve, hearing loss, presbycusis.
Causes of noise in the ears and head, not related to pathologies of the hearing aid:
- hypertension. Against the background of this disease, not only constant tinnitus is manifested, but also dizziness of varying degrees of intensity;
- vascular atherosclerosis. In this case, a symptom such as tinnitus is not uncommon. In severe cases, it becomes permanent and gives the patient a lot of discomfort. Simultaneously with it, such a symptom as dizziness, caused by atherosclerotic lesions of the cerebral vessels, may appear;
- often the reason why a person has tinnitus is various metabolic ailments. So, various noise effects of a person begin to disturb with hypoglycemia, diabetes, thyrotoxicosis, thyroiditis;
- stenosis of the carotid arteries and jugular veins. Tinnitus is one of the characteristic symptoms of these ailments. The clinical picture is also supplemented by headache, dizziness, impaired consciousness, general weakness, and so on;
- osteochondrosis progressing in the cervical spine. In this case, the noise in the hearing aid appears quite often. It is usually accompanied by other symptoms, such as pain in the neck and ear, difficulty performing simple neck movements, dizziness, and sometimes loss of orientation in space;
- severe stress;
- viral hepatitis;
- industrial poisoning. In this case, the clinical picture is quite pronounced. A person manifests not only tinnitus, but also nausea, vomiting, dizziness, diarrhea, headache and other signs;
- head injury of varying severity. In this case, tinnitus is accompanied by dizziness;
- some liquid getting into the ear.
In some cases, some tablets and injections of the following groups of pharmaceuticals can also provoke the appearance of noise:
- cardiovascular pharmaceuticals, in particular digitalis;
- aminoglycoside antibiotics;
- loop diuretics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Variants of the manifestation of tinnitus
According to statistics, approximately 15-30% of the world's population periodically experience ringing or noise in the ears, 20% of them characterize it as loud. Tinnitus is diagnosed with the same frequency in both women and men from 40 to 80 years old. However, pronounced noise with hearing loss is more typical for men, who, by virtue of their profession, are more often among strong industrial and production noises.
Noise can be different for different people. Some are bothered by a monotonous hiss, someone is whistling, tapping, ringing, buzzing or humming. Tinnitus is often accompanied by partial hearing loss, headaches (cephalgia), sleep disturbance. Noise may be accompanied by low-grade fever, discharge from the auricle, nausea, dizziness, pain, swelling and a feeling of fullness inside the ear. The intensity of sounds is different: from a weak ringing to a strong hum or roar. Often the patient, describing the nature of the noise, says that it resembles the noise of a waterfall or a passing vehicle.
Most people are forced to get used to their pathological condition, however, for many, loud noise leads to insomnia, irritability, inability to concentrate on work or daily household chores. Some complain that a loud constant hum prevents them from hearing other surrounding sounds and speech. In fact, this rumble is not so loud, but they hear poorly due to the hearing loss that accompanies tinnitus.
What ear diseases cause ringing
Diseases of the organ of hearing often cause tinnitus. The inner ear may be damaged, as well as the nerves through which the impulse is transmitted to the brain. To surely eliminate the ear ringing, you need to find out the exact location of the pathology.
Spasm of the posterior auricular artery occurs due to hypertension, as well as oxygen starvation caused by anemia, low levels of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Elevated blood pressure causes pulsatile tinnitus. The flow of oxygenated blood to the brain is reduced because the arteries become constricted. Begins to ring from one or both sides in time with the pulse. It can also make noise in the ears due to spasm of the cerebral vessels.
- In case of anemia, there is ringing or noise in the ears, weakness, dizziness are felt, “midges” flash before the eyes.
Hum, ringing in the ears occurs in the case of Meniere's disease, when an excess amount of fluid forms in the cavity of the inner ear. Increased pressure on the cells of the vestibular apparatus disturbs the sense of balance. It becomes difficult to stand and sit, dizziness, nausea, coordination of movements disappears, cold sweat breaks through, blood pressure drops.
Medical method of treatment
If the noise phenomena are caused by otitis media and inflammation of the ear canal, then the doctor will prescribe alcohol compresses or anti-inflammatory drops. The murmurs should disappear after two days of treatment. If during this period the sound continues to disturb, antibiotics are prescribed.
If a pulsating knock is heard in the ears during hypertension, the doctor prescribes drugs to restore pressure. There are many medicines that improve the circulatory system of the brain and strengthen the vascular system. Widely used: Pantogam, Citramon and Vinpocetine.
Sometimes osteochondrosis can cause such a problem. In this case, therapeutic massage should be prescribed.
After the end of the course of treatment, it is important to visit the doctor again to make sure that you are fully recovered.
Sound wave
Sound waves - these are mechanical vibrations that, propagating and interacting with the organ of hearing, are perceived by a person (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Sound wave
The section that deals with these waves in physics is called acoustics. The profession of people who are commonly called "hearers" is acoustics.A sound wave is a wave propagating in an elastic medium, it is a longitudinal wave, and when it propagates in an elastic medium, compression and rarefaction alternate. It is transmitted over time over a distance (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Propagation of a sound wave
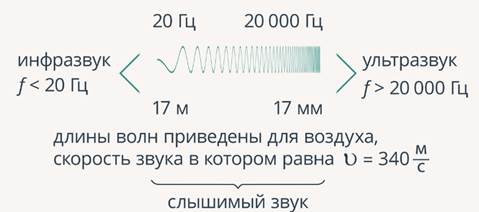
Sound waves include such vibrations that are carried out with a frequency of 20 to 20,000 Hz. For these frequencies, the wavelengths correspond to 17 m (for 20 Hz) and 17 mm (for 20,000 Hz). This range will be called audible sound. These wavelengths are given for air, the speed of sound propagation in which is equal to.
There are also such ranges that acoustics are engaged in - infrasonic and ultrasonic. Infrasonic are those that have a frequency of less than 20 Hz. And ultrasonic ones are those that have a frequency of more than 20,000 Hz (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Ranges of sound waves
Every educated person should be guided in the frequency range of sound waves and know that if he goes for an ultrasound scan, then the picture on the computer screen will be built with a frequency of more than 20,000 Hz.