Types of air vents and their design features
There are automatic and manual air vent valves, the former are mainly installed at the upper points of collectors and pipelines, manual modifications (Maevsky taps) are placed on radiator heat exchangers.
Automatic devices are distinguished by a wide variety of options for locking mechanisms, their cost is in the range of 3 - 6 USD, a wide range of models from domestic and foreign manufacturers is presented on the market. The cost of standard Mayevsky cranes is about 1 USD, there are products at a higher price, designed to operate in non-standard radiator heaters.
Rice. 6 An example of the construction of an air vent with a rocker mechanism
Automatic
Automatic taps have a different design depending on the manufacturer, the main differences between the devices:
- The presence of a reflective plate inside the case. It is placed at the entrance to the working chamber, protecting internal parts from hydraulic shocks.
- Many modifications are supplied complete with a spring-loaded shut-off valve, into which the air vent is screwed, when it is removed, the spring is compressed and the sealing ring closes the outlet channel.
- Some models of automatic taps are designed for operation in conjunction with radiator heat exchangers; instead of straight lines, they have side threaded pipes of the appropriate size for screwing into the radiator inlet. If necessary, angular automatic air vents of any type can be used, for example, at the points of connection of underfloor heating circuits, hydraulic switches, if their threaded diameters of the inlet and outlet fittings are the same.
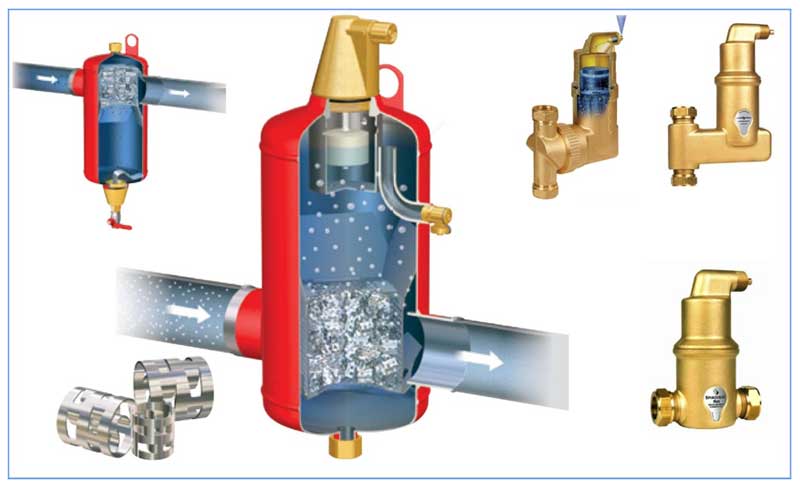
- There are analogues of air vents on the market - microbubble separators, they are mounted in series in the pipeline on two inlet pipes corresponding to the diameter of the pipes. When the liquid passes through the body tube with a soldered copper mesh, a vortex water flow is created, which slows down the dissolved air - this contributes to the rise of the smallest air bubbles, which are bled through the automatic air release valve of the chamber.
- Another common design (an example of the first was given above) is the rocker model. In the chamber of the device there is a float made of plastic, it is connected with a nipple shut-off needle (like a car). When the float is lowered in an air-laden environment, the nipple needle opens the drain hole and air is released, when water arrives and the float rises, the needle closes the outlet.
Rice. 7 Principle of operation of separator-type air vents for bleeding microbubbles
Manual
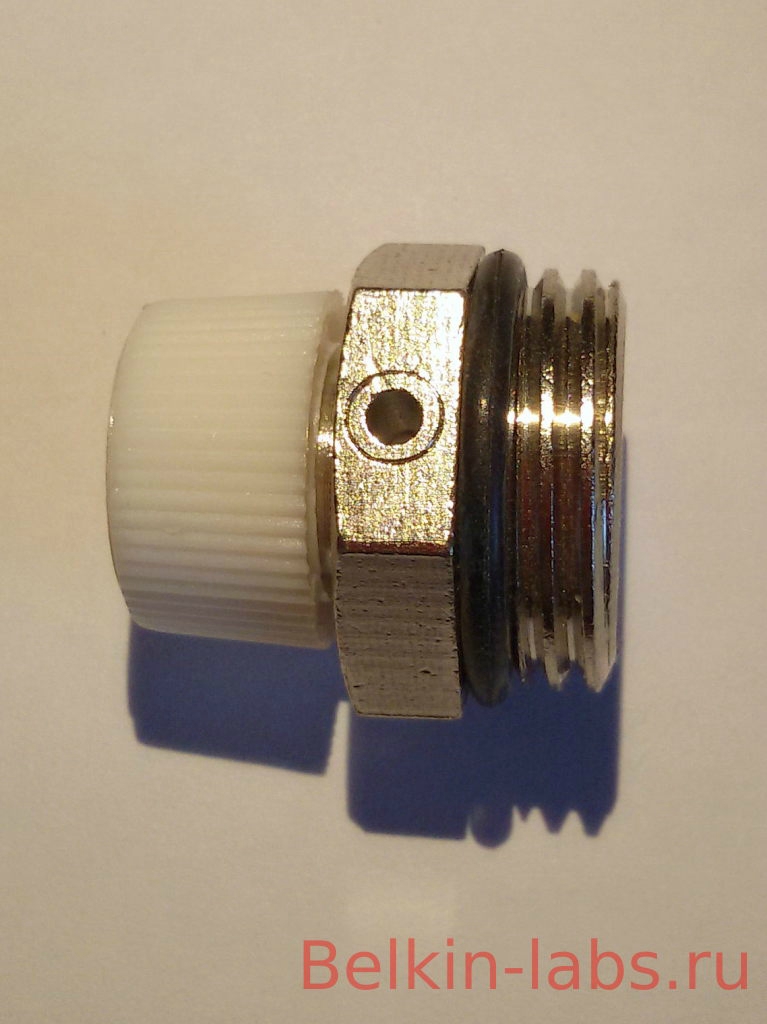
Manual devices for removing air from the system are called Mayevsky taps, due to the simplicity of the design, mechanical air vents are everywhere installed on radiators. On the market, you can find manual taps in the traditional design for installation in various places, and some modifications of shut-off valves are equipped with Mayevsky taps.
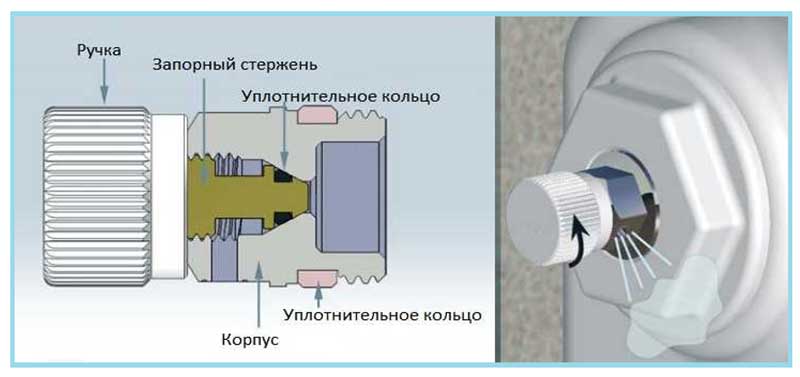
A mechanical air vent for removing air from the heating system works as follows:
- In operation, the cone screw is turned in and securely seals the housing outlet.
- When it is necessary to remove excess air from the battery, one or two turns of the screw are made - as a result, the air flow under the pressure of the coolant will exit the side hole.
- After the air is released, the water begins to bleed, as soon as the water jet acquires integrity, the screw is screwed in again and the de-airing operation is considered completed.
Rice.8 Air vents from airing radiators
Radiator
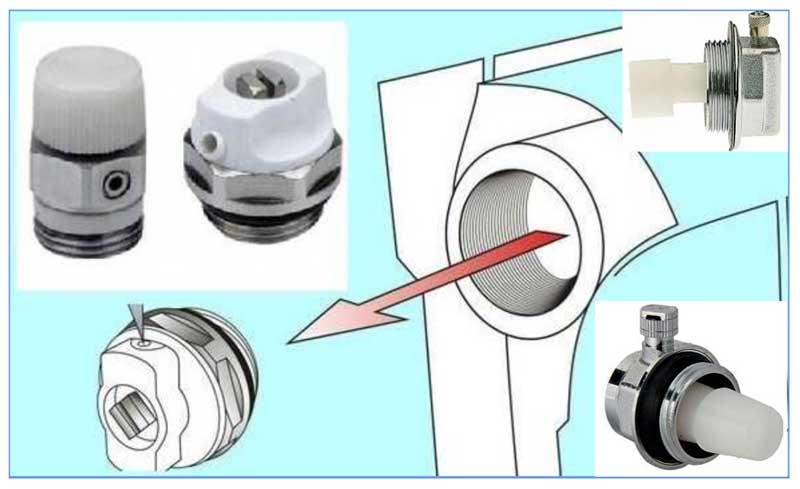
Cheaper manual mechanical air vents are most often installed in radiators, if the body consists of two parts, the element with the outlet pipe can be turned around its axis to direct the drain hole in the right direction. The radiator device for bleeding air from the heating system has the following options for unscrewing the bleed screw:
- Swivel handle made of plastic or metal.
- Special plumbing tetrahedral key.
- Screw with a slot for a flat screwdriver.
If desired, an automatic-type angular air vent can be installed in the radiator - this will entail additional costs, but will simplify the airing of the batteries.
Consequences
What can happen if the heating system starts to be filled through the supply line, through which the coolant moves under normal conditions during the operation of the system?
Rising up the main riser, the coolant begins to spread along the upper supply line, after which it descends to the lower points. However, on the way to the upper parts of the heating system, it gradually moves towards the accumulated air, and under the influence of gravity, all the air is directed downward. As a result, a dense air plug is formed in the heating system.
Under the action of the coolant and gravity, the air is directed downward, thus completely filling the space of risers and radiators, which can completely deprive some heaters and risers of circulation. In other words, the coolant will circulate in the system, bypassing some heating devices.
It turns out that the individual elements will remain completely cold due to the fact that an air lock has formed in the heating system. How to get rid of it in this case? With a similar filling of the system, it is rather problematic to bleed air. Therefore, if an incorrect start was performed, the only way to get rid of the air would be to drain the coolant into the sewer system and restart through the return line.
How to expel air from the system
The easiest way, and if the system is done correctly, is to go to the valve, open it, let the air out until the water flows, and close it. I have been doing this in my system for more than ten years and everything suits me.
This is Mayevsky's crane. For this invention, he should probably be given the Nobel Prize!
This valve must be operated in the following way. We hold the white part with one hand, because it will hang out and water will splash our walls. With the second hand, we unscrew the screw in the middle. But how do we hold a mug into which water will merge? Right! Third hand!
This is an improved faucet (see my complaints about the standard one)
Note that there is no guarantee that after winding, the hole will look straight down. But still better than normal. Interestingly, if the genius Mayevsky invented the standard crane, then who invented this crane? But, by the way, Mayevsky is an unknown hero. Someone came up with - and went.
If the system is gravity-flowing and there are no air release valves in it, but there are slopes, then you need to wait until the air comes out by itself through the expansion tank. In this case, there should be no circulation in the system. The system must be cold. You can wait a long time. It can be a day, or three days, or a week. It all depends on the length of the mains, on the diameter of the pipes and on the steepness of the slopes. Such an expectation is also typical when pouring the system from above. In other words, if your system is working, but badly, and you would like the bubbles to come out on their own, then you need to turn off the boiler, turn off the motor, if any, and let the system cool down. The heating system has circulation and this circulation will interfere with the exit of air in those areas where the circulation and exit of the bubbles go in different directions.
Automatic air vents should be installed at the highest heating points. They should not be included in the security group. Now there are such strange security groups like tridents. There is a pressure gauge on one tooth, an emergency valve on the other, and an air vent on the third. I think this trident is a stupid and brazen move to get extra money out of us. The air vent on this trident is superfluous. It was turned on in order to cut off extra money from us. There is no air at the outlet of the boiler. Air accumulates at the highest points. And the boiler is not this upper point. The boiler is, one might say, a continuation of the return flow. And there is no air in the return line.
The air vent is superfluous, but what a beautiful detail!
Is it possible to expel the air with a strong pressure of water?
Theoretically it is possible, in practice it is very difficult. This requires a powerful pump with high pressure (more than two atmospheres). In this way, air can only be expelled from an open system. Also, there should not be too many branches in the system, or those branches that are not run must be closed. Usually, with this method, the expansion tank overflows heavily. It takes a lot of experience and skill to use this method.
Expulsion of air by draining water
But this is the most popular way to "pump" gravity systems. A large volume of water is drained from below with simultaneous filling from above. The bubble is thus shifted, broken and removed from the place where it is stuck. This method is personified with the torment of the Russian (I don’t know, like other peoples) people with gravity-fed open heating.
I hope for a successful solution to the problems of air congestion in your heating. Dmitry Belkin.
Article created 09/14/2015
How does an automatic air vent work?
The filled cold coolant in the heating main tends to release air when heated, to bleed it, automatic air venting from the heating system is used.
The principle of operation of all automatic devices is to open the bleed hole when air appears in the inner area of the air vent housing. The element that reacts to the presence of air is a float immersed in the inlet pipe of the device, which is connected to a valve that closes the air outlet. The automatic device works according to the following principle (Fig. 3):
- When the heating is functioning normally, the float located in the space of the cylindrical working chamber is in the upper position and the cone-shaped rod connected with it closes the outlet channel.
- If air accumulates in the upper part of the tank, the float goes down along with the locking rod and the air valve is unlocked, the air is bled from the device.
Rice. 4 Automatic air release valve from the heating system
Device
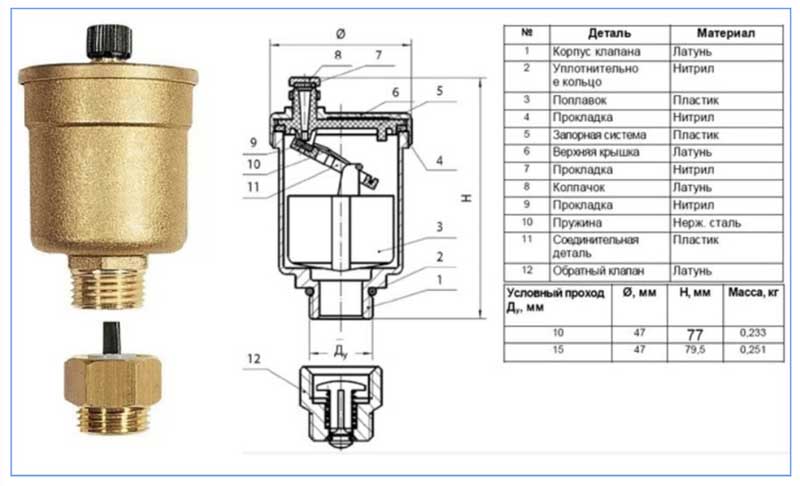
There are various designs of automatic air bleed valves on the market, consider the design and operation of one of the common types.
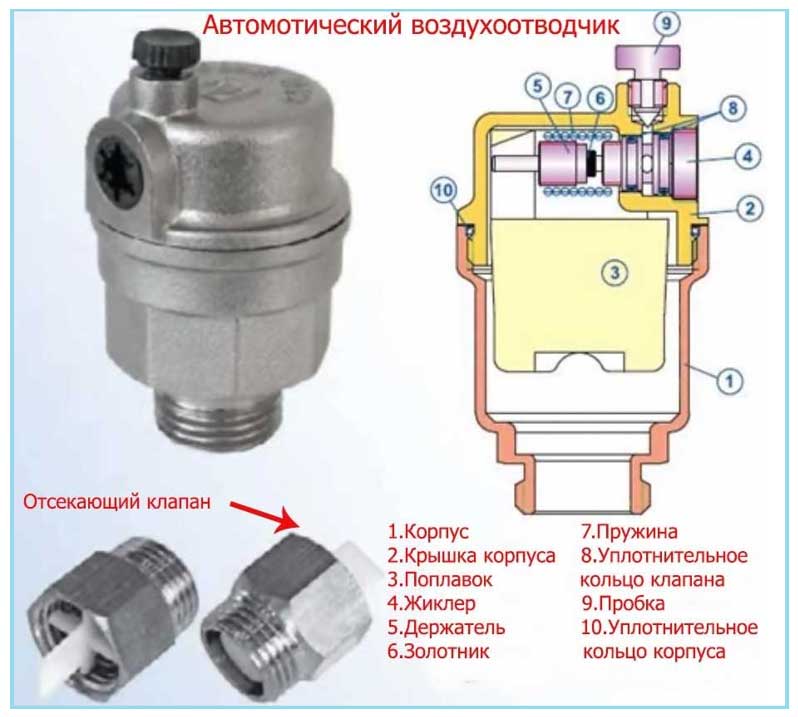
This model (Fig. 4.) has a composite body structure made of brass, including the main part 1, which is screwed into the pipeline, and its cover 2 with a locking mechanism, connected to the base through a sealing ring 10.
In the non-working state, the liquid entering through the inlet pipe from below raises the plastic float 3, it presses through the flag on the spring-loaded (spring 7) holder 5 with the spool 6, which locks the through passage in the jet 4.
The jet 4 is located in the side part of the air vent and is connected to the body through the sealing ring 8, in the upper part of the device there is a plug 9, which regulates the passage channel of the outlet for air release or closes it completely if necessary.
When air appears in the float chamber, it displaces the water in which the float 3 floats, the element lowers along with the flag, and the spring 7 pushes the spool holder away from the outlet channel - air is bled. With a decrease in the volume of discharged air, water enters the working chamber again, the float emerges and closes the channel using a locking mechanism.
Usually, when connecting an air vent, adapters are used from a shut-off check valve, which is a spring-loaded locking mechanism and a flag associated with it. When the air vent is screwed in, it presses on the flag of the shut-off valve, the latter goes down and opens the way for water to the vent body.
When dismantling the trap for replacement, maintenance or repair work, the released spring-loaded flag, together with the shut-off valve, rises and closes the coolant inlet channel.
Fig.5 Manual air valve of the heating system in the battery
Specifications
The main material for the manufacture of housings for manual and automatic air valves for bleeding air from heating systems is nickel-plated brass (bronze is used much less often), the taps have the following characteristics:
- Installation - at the highest points of the heating circuits in a straight section.
- Permissible temperature of the working environment - from 100 to 120º C.
- Maximum pressure 10 bar (atmospheres).
- The connecting diameter of the outlet pipes is 1/2″, 3/4″ (the most common sizes are indicated in the metric layout Dy 15 and Dy 20, which corresponds to 15 and 20 mm), 3/8″, 1″ inch.
- Type of connection - direct and angular.
- The location of the outlet fitting is on the top, on the side.
- Scope of supply - sometimes supplied with shut-off valve
- Working medium - water, non-freezing heat transfer fluids with glycol content up to 50%.
- The float material is polypropylene, teflon.
- The service life of brass appliances can reach 30 years.
Where does the air in the system come from
Practice shows that it is impossible to ideally isolate the water heating network from the external environment. Air penetrates into the coolant in various ways and gradually accumulates in certain places - the upper corners of the batteries, the turns of the highways and the highest points. By the way, the latter should be equipped with automatic drain valves shown in the photo (air vents).
Varieties of automatic air vents
Air enters the heating system in the following ways:
- Along with water. It's no secret that most homeowners replenish the lack of coolant directly from the water supply. And from there comes water saturated with dissolved oxygen.
- As a result of chemical reactions. Again, not properly demineralized water reacts with the metal and aluminum alloy of the radiators, releasing oxygen.
- The pipeline network of a private house was originally designed or installed with errors - there are no slopes and loops are made, facing upwards and not equipped with automatic valves. It is difficult to expel air accumulations from such places even at the stage of refueling with coolant.
- A small fraction of oxygen penetrates through the walls of plastic pipes, despite the special layer (oxygen barrier).
- As a result of repair with dismantling of pipeline fittings and partial or complete draining of water.
- When microcracks appear in the rubber membrane of the expansion tank.
When cracks occur in the membrane, the gas mixes with water.
Note. Water taken from wells and shallow wells is prone to chemical reactions, since it is saturated with active salts of magnesium and calcium.
Also, a situation often arises when, after a long downtime in the off-season, the pressure in a closed heating system decreases due to air ingress. Lowering it is quite simple: you just need to add a couple of liters of water.A similar effect also happens in open-type systems, if you stop the boiler and the circulation pump, wait a couple of days and restart the heating. When cooled, the liquid contracts, allowing air to enter the lines.
As for the centralized heating systems of apartment buildings, air enters them exclusively together with the coolant or at the time the network is filled at the beginning of the season. How to deal with it - read below.
An example from practice. Air pockets had to be expelled from the open heating system every day due to a completely clogged sump. A working pump created a vacuum in front of it and thus drew oxygen into the pipelines through the slightest leaks.
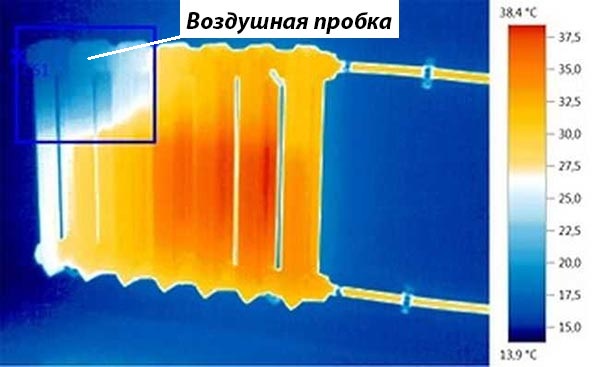
The thermogram shows the area of the heater where the air bubble usually lingers
With what and how to bleed air from a heating radiator
In order to control the gas content of the system both in an apartment and in a private house, a manual or automatic air release valve is used. They should be considered in more detail.
- Automatic air valve;
- Air separator;
- Mayevsky crane.
The automatic air valve is able to independently release the air that has accumulated in the radiator. It consists of a brass body, float, articulated arm and valve. A special cap protects against leakage, and the protection under the spring protects against external contaminants.
The system works according to the following principle:
- As long as there is no air, the float keeps the valve closed;
- In the process of gas accumulation, the float begins to lower and gradually open the valve;
- The accumulation of air leaves the compartments, and the system returns to its original state.
It is important to note the fact that all automatic options are equipped with connectors that are suitable for a screwdriver or octagonal keys. Thanks to this shape, you can open the valve even in manual mode if the automatic mode suddenly breaks.
As for the air separator, this system is a little more complicated. The principle of its action is to absorb air, turn it into bubbles and bring it out. Most often, separators are combined with sludge, which is able to trap dirt, sand or rust. If we talk about the design, then it is presented in the form of a metal cylinder, which includes an air outlet at the top and a valve at the bottom, which serves to discharge foreign contaminants. Inside such an installation is a grid that creates a vortex flow.
The same method is used if there is a water circuit that is connected to the heating. The release in the water supply is carried out as bleeding. That is, through the bleeder, you can also release a stream of air or water with impurities.
How to remove excess air from the battery


The algorithm of actions on how to properly bleed air from the heating system is given below:
Examine the battery and find a small valve (or Mayevsky's tap, as it is most often called). Install it at the top of the radiator. Sometimes there are several such devices. But often they manage with one valve.
Turn off the faucet until you hear a hiss of air
It is necessary to unscrew carefully, smoothly.
Place a container under the valve.
You need to wait until all the accumulated air comes out. When the water comes out in a thin stream and stops bubbling, then the air has left the system
Some experts advise draining about 2-3 buckets of water after the water starts to run without gases. This is done for reinsurance, so that you do not have to perform such operations again.
Screw the valve back.

Some nuances

When the plug is unscrewed, the same algorithm of actions is performed as with a conventional tap. When the cork is screwed into place, one must not forget to wrap either FUM tape or linen on the thread. This will avoid leaks and give the connection a tight seal.
If air has accumulated in the heating system of a private house, the water will have to be drained using an expansion tank.

How often do you need to bleed air?

If the apartment has aluminum radiators. then before starting the system, it is necessary to drain the water. This will help increase battery life significantly.
Causes and consequences
Air pockets are caused by the following factors:
- Errors were made during installation, including incorrectly made kink points or incorrectly calculated slope and direction of pipes.
- Too fast filling of the system with coolant.
- Incorrect installation of air vent valves or their absence.
- Insufficient amount of coolant in the network.
- Loose connections of pipes with radiators and other parts, due to which air enters from the outside into the system.
- The first start and excessive heating of the coolant, from which, under the influence of high temperature, oxygen is more actively removed.
Air can cause the greatest harm to systems with forced circulation. During normal operation, the bearings of the circulation pump are in the water at all times. When air passes through them, they lose lubrication, which leads to damage to the sliding rings due to friction and heat, or completely disables the shaft.
Water contains oxygen, carbon dioxide, magnesium and calcium in a dissolved state, which, when the temperature rises, begin to decompose and settle on the walls of pipes in the form of limescale. Places of pipes and radiators filled with air are most susceptible to corrosion.
Signs by which you can determine if there are air pockets in pipes and radiators
Due to the air in the heating system, the batteries heat up unevenly. When checked by touch, their upper part, in comparison with the lower one, has a noticeably lower temperature. The voids do not allow them to warm up properly, therefore the room is heated worse. Due to the presence of air in the heating system, when the water is very hot, noise appears in the pipes and radiators, similar to clicks and water flow.
You can determine the place where the air is located by ordinary tapping. Where there is no coolant, the sound will be more sonorous.
Note! Before removing air from the network, you should find the cause of its appearance and eliminate it. Especially carefully check the network for leaks.
When heating is started, it is extremely difficult to identify loose connections, since water quickly evaporates on a hot surface.
Especially carefully check the network for leaks. When heating is started, it is extremely difficult to identify loose connections, since water evaporates quickly on a hot surface.
Where does air come from in the heating system?
This question is asked quite often and I do not know the exact answer to it. Only guesses.
Air can be taken from the water itself, in which it is somehow present. If there is a lot of water, then there will be a lot of air. After a fresh filling of heating with water, air is actively released for several months.
Air can collect in dead ends, such as closed expansion tanks, and escape gradually. through the same water. This process is even longer. Hang closed expansion tanks upside down, as I described in the article about open and closed heating systems.
If you have a special air trap in the form of a vertical pipe with an automatic air vent at the end, then this can also be a source of bubbles. The fact is that automatic air vents often “freeze” and stop venting air. Then the tube is filled with air and the bubbles accumulated in the tube are torn off from below by the air flow and carried away into the system. In this case, I'm saying that bubbles start to walk around the system.
If you have an exceptionally strong circulation pump installed and there is a small hole in the system, then I think air can be sucked into the hole due to the Venturi effect. I have observed this many times in a water pipe, when there is a hole from which water does not flow, but into which air is sucked in by a stream of water. That is, if the water is turned off, then water flows from the hole. And if you open the water at the end, then the water from the hole stops flowing. But in reality, I have never seen this in heating systems. In heating systems, the water velocity is not so high. But that doesn't mean it can never happen.
Personally, in my heating system, the air stops bothering me about six months after the heating is freshly filled with water. I don't have automatic air vents. All valves are manual only. And my system is small and the house is small.
Air faucets and radiator set
Almost all modern radiators provide for the possibility of installing Mayevsky manual cranes for air release. Some manufacturers even complete their products with them. Optionally, instead of a manual air vent, you can also put an automatic one, but in practice it does not look very presentable.
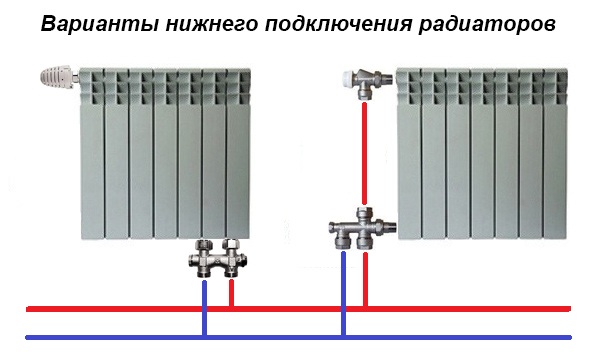
Recently, the laying of heating mains below the floor level and the use of radiators with a bottom connection have become increasingly popular.Then a small gap remains between the battery and the floor, where it is not always possible to place any fittings. In this case, there is a special connection headset with built-in taps, shown in the picture (left):
On the right is a headset for the lower connection of a conventional radiator with side plugs, it also has valves plus the possibility of attaching a thermal head. Such solutions look very aesthetically pleasing, but will require maximum financial costs. More information about the headset is shown in the video: