Types of water iron
Iron in water can be found in several forms:
- Elementary.
It does not dissolve, but enters into a chemical oxidation reaction, resulting in rust.
- Bivalent. It is almost always in a dissolved state, at a certain level of acidity it can precipitate.
- trivalent. It dissolves in water upon contact with chlorine and sulfates.
- Organic. It is part of various compounds, it is extremely difficult to remove it from water. Appears as a result of the activity of iron bacteria or is a colloidal form (microscopic particles).
Varieties of "water" iron behave differently.
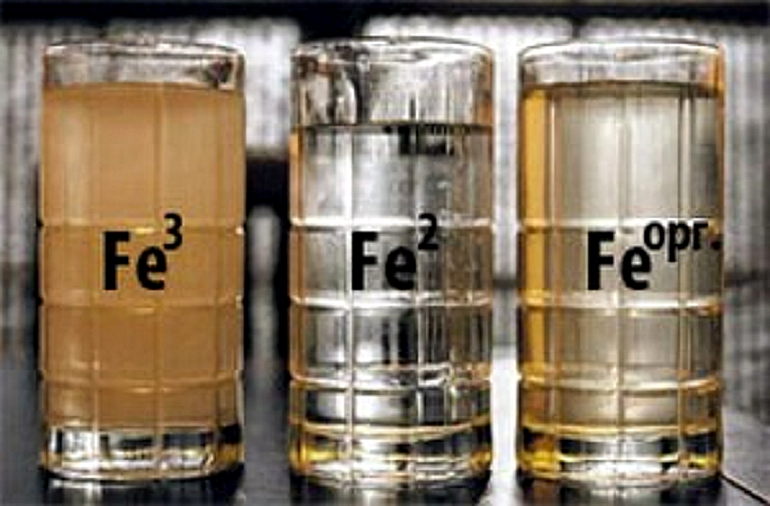
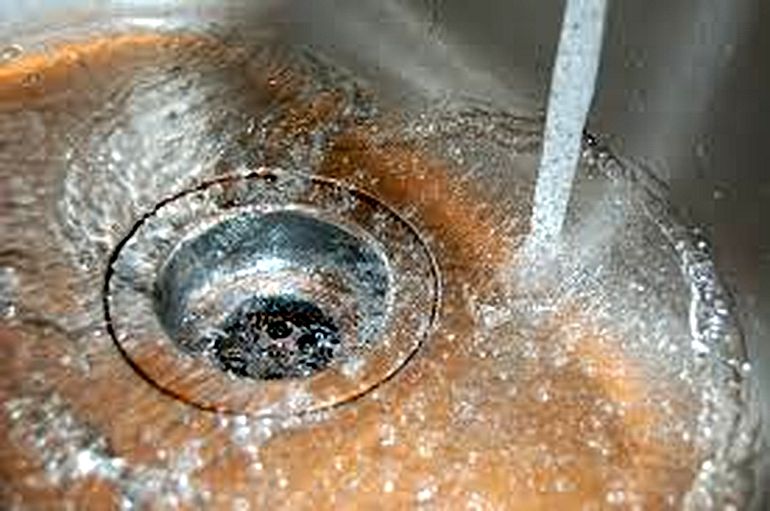
The bivalent form is manifested by precipitation in the settled liquid. The trivalent species colors the water and forms a suspension that falls to the bottom of the tank. If the orange water does not form a precipitate, you have encountered colloidal iron. Bacterial forms can be identified by the iridescent film and pipe contamination.
A well water purification system is an objective necessity
The bivalent form is most often found in wells.
Alas, there is no universal method for purifying water from a well from iron.
The effectiveness of the method depends on the type of chemical compound and the quality of the materials used.
Filters using strong oxidizers
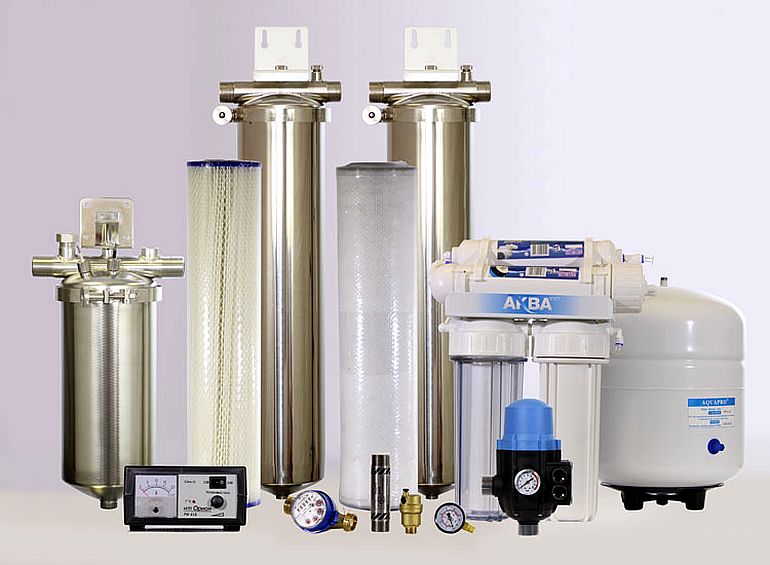
To clean water from iron for a private house, it is easiest to use filters. On sale there are installations with a different principle of operation.
Catalytic iron removers
One of the most common water treatment methods for both industrial scale and small facilities (private houses, summer cottages, cottage settlements).
The units can have a capacity from 0.5 to 30 m³/h. There are also more powerful industrial cleaners.
The filter is made in a fiberglass or stainless steel housing. Inside, a bulk filter layer-catalyst is used.
The most common brands of catalysts:
- BIRM.
- MTM.
- green sand.
- AMDX.
- Quantum.
- pyrolox.
The average cost of a household model is from 8000-8500 rubles. The catalyst layer needs periodic replacement. The average cost of 1 bag (BIRM brand) is about 3,500 rubles.
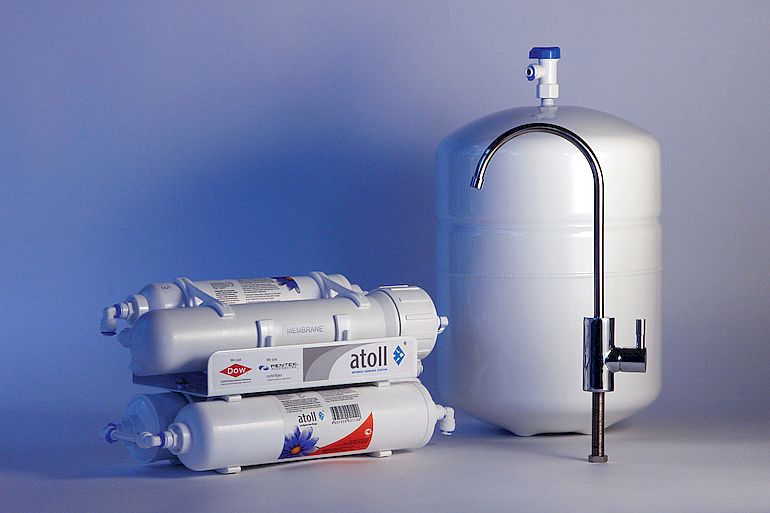
Reverse osmosis filters
Reverse osmosis filters are complex water treatment plants of a compact size, which are often placed under sinks in both houses and apartments. In reverse osmosis devices, water is purified in several stages, successively passing through 3 containers:
- Tank with activated carbon and polypropylene: purifies water from solid particles up to 0.5 microns in size.
- Container with coal: filters organic and chemical impurities (metals, oil products), up to 1 micron in size.
- Container with a membrane, cells with a size of 0.0001 microns.
After passing through all 3 tanks, the flow is divided into 2 separate ones: purified water and a concentrated solution of filtered impurities. Clean water is fed further into the water supply of the house, impurities are drained into the sewer.
The most common household filters of this type:
- Atoll.
- Aquaphor.
- New water.
- Osmo barrier.
- Geyser Prestige.
The average cost of household models (enough for a house with a family of 3-5 people) is 7500-8000 rubles.
Filters using ion exchange resins
Ion exchange filters are arranged in the form of 2 containers made of plastic or steel. Each of them has a free space (top) and a part filled with reagents (bottom).
The advantages of such filters include:
- high degree of purification;
- quiet work;
- rare replacement of the filter filler (may be required 1 time in 7-10 years).
Among the shortcomings is the relatively high cost: the cheapest filters will cost 17-22 thousand rubles. Also a disadvantage is low productivity: household models can filter up to 0.5 m³ / h on average.
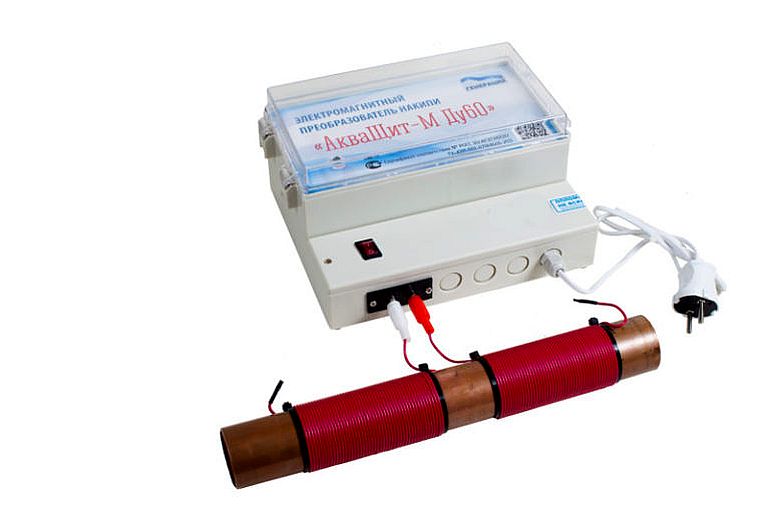
Electromagnetic filters
In such devices, filtration takes place in several stages:
- The flow is sonicated (to improve the efficiency of the next step);
- Electromagnetic cleaning is carried out (iron compounds are retained by a magnet);
- The purified stream passes through a mechanical fine-mesh filter, which retains the remaining solid impurities.
The cost of filters of this type starts from 10-12 thousand rubles. They should be used only in cases where the main impurity in the water is iron. If, in addition to iron, other unnecessary impurities are contained, it is better to use other types of filter systems.
Electrochemical aeration filters
Reagentless filters differ in design from the systems listed above. They consist of a compressor that pumps air and a container of water. Can be used with iron content up to 30 mg/l on average.
Settling of water
This method is the most accessible and easy to implement. It consists in including an additional reservoir in the water supply system of a country house or summer cottage, the capacity of which is selected according to the daily need for water. The advantages of this method are that it is cheap and can be used when the electricity is off. Against the use of the settling method are such facts as:
- complete removal of iron does not occur,
- a periodic, rather laborious procedure for shutting down the tank to clean it is necessary,
- water flow must be constantly monitored.
Permissible concentration
In water from wells, even deep ones, the metal concentration can range from 0.6 to 21 mg/l.
How to understand that the concentration of iron in the water is increased?
Signs by which you can determine the excess without analysis:
- The taste of unboiled and unfiltered water has a metallic taste and smell. If the concentration exceeds 1.2 mg / l, the taste will be felt even in drinks (tea, coffee) and in boiled water.
- On the plumbing (sink, toilet, bathroom, shower) there are reddish streaks, sometimes with sediment.
To more accurately identify the problem, you can:
- Make a paid analysis. The approximate cost of a comprehensive analysis for the content of various impurities is 3000-3500 rubles.
- Pour unboiled water into a glass and leave to stand overnight. If a reddish precipitate appears after 1-2 days, the iron concentration is exceeded.
- Use an aquarist kit (costs about 1000-1200 rubles). It is used specifically for the determination of iron, according to the instructions.
- Use potassium permanganate. If half a glass of potassium permanganate pour 2-3 tbsp. l. water, and the solution will turn dirty yellow - there is a lot of iron in the liquid, and you can’t drink it.
- Use sulfosalicylic acid, ammonia and ammonia. The recipe is as follows: 1 ml of ammonia, 1 ml of sulfosalicylic acid and 1 ml of ammonia are taken. The reagents are poured into 25 ml (1 tablespoon) of water and stirred. If after 15 minutes the solution becomes yellowish, the concentration of the metal is increased.
This is interesting: Handles on kitchen facades: we explain in detail
How to clean water from lime
The choice of softening method depends on the location of the liquid intake and the intended use. When purifying water from a well, apply:
- Settling. The filled containers are kept for several days, during which time the lime particles sink to the bottom, and as a result, the liquid is cleaned and ready for use (minus - there is a threat of infection and the presence of heavy metals).
- Boiling. At high temperatures, the structure of the molecule changes, turning into a solid state (this is how scale is formed). The disadvantage of this method is the duration of the process and the possibility of solid particles of limescale entering the body.
Chlorine, when boiled, forms a dangerous compound - chloroform, which, with prolonged exposure to the body, contributes to the activation of cancer cells.
Household jugs with a filter "for hard" water.The liquid, flowing down, passes through a device consisting of activated carbon, freeing itself from impurities.
If there is running water, it is effective to use:
- mechanical method. Running water passes through a bulk filter (quartz sand, coal, shungite, silicon are used as fillers). The disadvantages include the bulkiness of the structure (1.5 m) and the removal of only large, more than 20 microns, particles of harmful impurities.
- Disc filters with replaceable cartridge. The devices operate automatically (foamed polystyrene serves as a filter material). The disadvantages of such cleaning are the cost of the method (cartridges are changed as they get dirty), as well as the fact that a large pressure is required.
Well water has a lot of impurities taken from groundwater, but it is easier to clean it than from a well.
Ways to purify water from iron
Since iron impurities in water are a common problem, a large number of effective treatment methods have been devised against them. There are industrial cleaning methods, and devices for apartments and private houses.
Reverse osmosis
The most effective method for removing iron-containing impurities. Can remove ferrous and trivalent iron.
The flow of water passes through a fine-membrane membrane. The holes in the membrane are so large that only water molecules pass through. Due to the larger size, iron impurities cannot pass through the pores and remain on the grid, after which they merge through the drainage (the grid does not clog).
Ionic way
Filtration method that removes iron, manganese, calcium. The filter uses an ion exchange resin that replaces iron with sodium and softens the water.
Disadvantages and features:
- the filter can only be used at metal concentrations up to 2 mg/l;
- the filter can be used if the water hardness is above normal;
- The filter can only be used for water that is free from organic matter.
Chemical method (oxidative)
The method is usually used only in industrial water treatment plants.
For cleaning, chlorine, oxygen, ozone and potassium permanganate are used. These oxidizers convert iron to trivalent iron, which is then precipitated and removed.
For apartments and houses there is a simplified filtration system - catalytic. Magnesium dioxide is used as a neutralizer, which oxidizes iron-containing impurities and accelerates their precipitation.
Removal of ferric iron
Most systems are designed to clean the liquid from ferrous iron.
Against trivalent impurities, ultrafiltration membranes with a cell size of 0.05 μm (micron) are used. The membrane retains impurities, which are then removed to the drain by backwashing.
Biological method of iron removal
Designed to remove iron bacteria. They are usually found in water at iron concentrations in the range of 10-30 mg/l, but may appear at lower levels.
To remove them, the water is treated:
- chlorine or chelating agents;
- bactericidal rays.
Reagent-free cleaning
The principle is based on the interaction of MnO2 with iron: during the reaction, an insoluble compound is formed that precipitates. For cleaning, filters with membranes containing manganese oxide are used. The membranes need to be cleaned periodically. The filters also have an auto-flush function that flushes accumulated particles down the drain.
Ozone cleaning
A generator set is used for filtering. Inside it, oxygen is cooled to +60º, dried, and enters the ozone generator. Then the resulting gas passes through the water stream, purifying it from iron and enriching it with oxygen.
Aeration
The method is based on the effect of oxygen. Pressurized air is supplied to the water tank from the well.
Oxygen oxidizes ferrous iron, causing it to precipitate, which is then washed off into the drain.
Aeration systems are relevant at low iron concentrations (up to 10 mg/l).
Home cleaning without filters and installations
If you need to clean a small amount of water from iron (a bottle, for example), you can proceed according to the following scheme:
- Let the water stand for at least 1 night. Impurities will settle to the bottom, after which the water will need to be filtered through a fine mesh.
- Boil the strained water.
- Freeze a container of boiled water.
After that, the water will get rid of most impurities and become more drinkable, even if it previously contained a high concentration of iron.
If additional purification is needed, activated charcoal can be used. It must be wrapped in cotton wool and used as a filter: pass water through it.
How to purify water
You can lower the concentration of iron compounds yourself in several ways. The cleaning method depends on the volume of fluid consumed and how many impurities it contains.
settling
The easiest way to clean up a resource extracted from a well. An additional reservoir is being built, designed for the volume of the expected fluid consumption per day, and sediment occurs in it.
pros
- A simple, cost-effective way
- There is always a supply of clean water.
- Installing a tank in the attic will create gravity. And rid the water of hydrogen sulfide.
Minuses
- Cleaning is not complete
- The container must be periodically cleaned, which is not very convenient, since it requires disconnection from the system.
- Closely monitor the amount of fluid consumed.
Aeration
The precipitated precipitate at the outlet after cleaning is captured by mechanical filters.
- Free-flow - Water contacts oxygen to the maximum, this is due to atomization. Atomizers move liquid into a reservoir. For more productive cleaning in the tank, if necessary, a compressor is installed.
- Pressure type of cleaning - involves the flow of fluid into the system under high pressure. Working in parallel, the pressure and the compressor create bubbling and foaming, which allows the liquid to contact the air as much as possible.
In addition to removing iron, the aeration method eliminates hydrogen sulfide.
- The main advantage of this cleaning is environmental friendliness. The process eliminates the use of reagents.
- Flaws. There is still a certain amount of iron in the water. The operation of the system depends on the availability of electricity. Periodically it is necessary to clean the container and filters.
Ozonation
The process is efficient but labor intensive.
The use of chlorine is a thing of the past. After cleaning with this reagent, it partially remains in the liquid and is harmful to humans and the environment.
Ozonation is considered to be the most reliable method, the effectiveness of which is created by the action of ozone and its derivatives on impurities contained in water.
Organic iron is removed from the liquid by cumulative action. The process of cleaning extracted fluid from a well by ozonation is quite complicated. Requires installation of expensive equipment. An accurate calculation is necessary for productive work, it is very difficult to do it on your own (you need to calculate how much ozone is needed and the time of its exposure to water in accordance with the amount and type of impurities contained in it).
Ion exchange
Such purification is carried out by filters containing resin and free ions. As water passes through the filter, sodium ions are swapped with iron ions. Therefore, the method is called ion exchange.
When the filter has used up all its resources, they must be restored.
Reverse osmosis
Purification of water from iron and impurities is done by a filter containing a membrane, it is she who performs filtration at the molecular level. The reverse osmosis method of iron removal is considered the most productive. Dissolved particles are removed. To improve the quality of filtration and stop the failure of the membrane, it is necessary to pre-purify the water with mechanical filters.
Reverse osmosis completely purifies water from all types of pollution. The method is the most effective, but very expensive.
The work of microfiltration, nano- and ultra- membranes is similar to reverse osmosis.
Introduction of reagents and catalysts
The use of chemical reagents for liquid iron removal is mainly used in industry. Fluid needs to be cleaned up. It is required to remove chemical compounds. The principle is similar for all cleaning systems - a chemical reaction occurs between the iron and the reagent, as a result of which a precipitate forms.
Catalysts are used together with aerated water or with the use of reagents for the oxidation of iron.
The catalytic method of deironing water occurs with the help of filters containing a material with catalytic properties. Water passes through porous fillers, which provide high-quality cleaning.
What are the dangers of iron impurities in water
 The high content of iron in water negatively affects human health, spoils household appliances and plumbing
The high content of iron in water negatively affects human health, spoils household appliances and plumbing
More often, Fe is in a liquid in a divalent state - dissolved, invisible to the human eye. Without knowing about the enrichment of water with this element, you can use a supersaturated liquid for a long time, which leads to negative health consequences:
- kidney failure;
- disorders of the digestive tract;
- problems in the liver;
- heart pathology;
- skin allergic reactions;
- harmful effect on the nervous system.
Washing with such water is unpleasant, unsafe.
For household appliances, a high concentration of Fe in water is dangerous due to the formation of corrosion and plaque. Laundry from washing in such a liquid acquires a yellow tint.
How to find out about the presence of iron in water from a well
Iron is almost always present in water. In a normal situation, its presence can only be determined by chemical analysis, but quite often it is noticeable at a glance.
Iron impurities in water are usually found in the form of a soluble ferrous compound - Fe (OH) 2 hydroxide, insoluble ferric iron compounds - Fe (OH) 3, Fe2 (SO4) 3 and FeCl 3, which are called rust in everyday life, and similar substances that have appeared as a result of the vital activity of iron bacteria and is a mixture of insoluble sediment with organic matter. Most often, combinations of such forms are found.
At first glance, it is difficult to determine what impurities the water from the well contains - it is quite transparent and odorless. At home, the excess of iron in water can be judged by the following signs:
- Liquid has a metallic taste. To feel it, just rinse your mouth. This taste does not disappear when boiled, it will be felt in tea or coffee.
- An oily film on the surface of the water (evidence of the presence of ferrous iron, oxidized by iron bacteria to insoluble trivalent).
- Red streaks, rusty deposits on the sink, in the shower, in the kettle, etc.
- The appearance of a red or brown precipitate in a container of water.
Ways to purify water from iron
Since iron impurities in water are a common problem, a large number of effective treatment methods have been devised against them. There are industrial cleaning methods, and devices for apartments and private houses.
Reverse osmosis
The most effective method for removing iron-containing impurities. Can remove ferrous and trivalent iron.
The flow of water passes through a fine-membrane membrane. The holes in the membrane are so large that only water molecules pass through. Due to the larger size, iron impurities cannot pass through the pores and remain on the grid, after which they merge through the drainage (the grid does not clog).
Ionic way
Filtration method that removes iron, manganese, calcium. The filter uses an ion exchange resin that replaces iron with sodium and softens the water.
Disadvantages and features:
- the filter can only be used at metal concentrations up to 2 mg/l;
- the filter can be used if the water hardness is above normal;
- The filter can only be used for water that is free from organic matter.
Chemical method (oxidative)
The method is usually used only in industrial water treatment plants.
For cleaning, chlorine, oxygen, ozone and potassium permanganate are used. These oxidizers convert iron to trivalent iron, which is then precipitated and removed.
For apartments and houses there is a simplified filtration system - catalytic. Magnesium dioxide is used as a neutralizer, which oxidizes iron-containing impurities and accelerates their precipitation.
Removal of ferric iron
Most systems are designed to clean the liquid from ferrous iron.
Against trivalent impurities, ultrafiltration membranes with a cell size of 0.05 μm (micron) are used. The membrane retains impurities, which are then removed to the drain by backwashing.
Biological method of iron removal
Designed to remove iron bacteria. They are usually found in water at iron concentrations in the range of 10-30 mg/l, but may appear at lower levels.
To remove them, the water is treated:
- chlorine or chelating agents;
- bactericidal rays.
Reagent-free cleaning
The principle is based on the interaction of MnO2 with iron: during the reaction, an insoluble compound is formed that precipitates. For cleaning, filters with membranes containing manganese oxide are used. The membranes need to be cleaned periodically. The filters also have an auto-flush function that flushes accumulated particles down the drain.
Ozone cleaning
A generator set is used for filtering. Inside it, oxygen is cooled to +60º, dried, and enters the ozone generator. Then the resulting gas passes through the water stream, purifying it from iron and enriching it with oxygen.
Aeration
The method is based on the effect of oxygen. Pressurized air is supplied to the water tank from the well.
Oxygen oxidizes ferrous iron, causing it to precipitate, which is then washed off into the drain.
Aeration systems are relevant at low iron concentrations (up to 10 mg/l).
Home cleaning without filters and installations
If you need to clean a small amount of water from iron (a bottle, for example), you can proceed according to the following scheme:
- Let the water stand for at least 1 night. Impurities will settle to the bottom, after which the water will need to be filtered through a fine mesh.
- Boil the strained water.
- Freeze a container of boiled water.
After that, the water will get rid of most impurities and become more drinkable, even if it previously contained a high concentration of iron.
If additional purification is needed, activated charcoal can be used. It must be wrapped in cotton wool and used as a filter: pass water through it.
Briefly about water in general
The extraction of the resource is carried out from different layers of the soil
- Verkhovodka
- Water from sandy soil (a well is drilled to a shallow depth)
- artesian water
surface water
- Verkhovodka contains organic iron.
- Lignins and tannins
- Compounds with humic salts
- Bacterial substance (bacteria make trivalent particles from divalent particles)
The amount of iron impurities in the top water does not exceed the norm, but is higher than the MPC (maximum permissible concentration). Remove humic iron compounds from such a liquid.
Well on sandy soil
The soil layers of a source of this type contain oxygen, with the help of which bacteria change the valency of iron. The extracted resource from sandy soil layers is close in composition to perched water, which allows the content of humates in it.
Limestone wells (artesian)
The resource from the artesian basin is superior in environmental friendliness to water extracted from sandy soil and perched water.The impact of the environment on it is minimal. Depth of occurrence from 50m to 200m. However, the water contains iron salts and minerals in excess. This happens due to the interaction of water with certain types of soil. Given the magnitude of the depth, and it is not small, oxygen access is limited, respectively, the source is filled with ferrous iron.
In the water layer there are these types of chemical compounds
- Iron bicarbonate - Fe(HCO3)2
- Carbonate - FeCO3
- Sulfate - FeSO4
- Sulfide - FeS
- Trivalent sulfate Fe2(SO4)3 and organic iron are extremely rare in the limestone layer.
- To determine the presence of ferrous iron in the resource, it is enough to give it free exposure to air and leave it for a while. Oxygen will create oxidation, which will cause the iron to sink to the bottom.
- In centralized and private water supply, turbidity of water with a yellowish or brown tint is also observed - this is a characteristic sign of the presence of ferric iron. When the liquid settles, a precipitate forms.
- A yellow tint is also a sign of organic iron, only in this variant there is no formation of particle settling.
- An iridescent film covering the water indicates the presence of organic iron.
- It happens that the smell of metal is heard from the liquid, which is also considered a sign of an increase in the MPC of iron.
Why is water purification necessary?
Considerable difficulties are created by lime (calcium and magnesium bicarbonates), which is present in excess quantities in the waters of many regions, and negatively affects such aspects:
- on health: metabolism is disturbed, the condition of the skin, hair, teeth worsens;
- on the functions of internal organs: the formation of insoluble calcifications that affect the functioning of the genitourinary, biliary and cardiovascular systems, muscle and nerve tissues and increase blood clotting;
- on cooking (the duration of the process increases, and the taste of the products changes).
The poor quality of lime water creates the following problems:
- domestic difficulties: soap does not foam, plaque forms on the walls of dishes, white stains remain on clothes after washing;
- affects the mechanisms: when heated, calcium carbonate forms a dense insoluble precipitate on the systems of boiler and boiler equipment, household appliances, plumbing parts, leading to breakdown and increase in power supply;
- negatively affects the engines and carburetors of machines and other equipment where water is used;
- hard lime water is detrimental to plants, preventing the absorption of beneficial trace elements.
When using lime water, the risk of developing skin diseases in infants increases by 87%.
Effect of water on iron
The principle of operation of the deironing cleaning plant is based on the fact that ferrous iron oxidizes upon contact with atmospheric oxygen and, turning into trivalent, precipitates. It remains only to speed up this process, for which the water is additionally saturated with oxygen.
iron water
Valex:
My water treatment system works like this. A submersible pump is installed in the well. It pumps water into a barrel with a volume of 250 liters. The top of the barrel is closed with a lid with holes. On the lid, upside down, I installed a regular plastic bucket of 10 liters. In the center of the bucket, above the lid of a high barrel, there is a watering nozzle, like a shower head, directed to the bottom of the bucket.
Water with an excess of iron, pumped under pressure, flies out of the hole in the watering can and hits the bottom of the bucket. Upon impact, it breaks into water dust and, under the influence of this, is saturated with oxygen to the limit. After that, the drops, already enriched with oxygen, flow down the walls of the bucket and through the drilled holes fall back into the storage barrel.
Valex:
- So, I have implemented aeration. The barrel itself is filled automatically. The water level is regulated by electrodes of different lengths.As soon as it goes down, the submersible well pump turns on.
After the water tank, the forum member mounted another pump that maintains the necessary pressure in the water pressure system of the house. After the pump, a self-made column is installed - a container for a cationite filler, which additionally purifies and softens the water, making it suitable for drinking.
The column is made of a polyethylene pipe with a diameter of 20 cm. The forum member closed the ends of the pipe with plastic plugs on studs, and used rubber from the camera as a gasket.
The container with cation exchanger must be regularly flushed with a reverse flow of water.
Valex:
- Flushing takes about 45 minutes, during the process the borehole pump is turned off, and all wastewater from the storage barrel and column is sequentially (for this, taps are switched) is discharged into the sewer.
The higher the concentration of iron in the water, the faster the cation exchanger “caking”. Therefore, to calculate the frequency of flushing, the following value is taken: on average, 1 liter of cation exchanger absorbs about 1 gram of iron.
Based on the analysis of water and water consumption, the frequency of flushing is calculated. The standard flushing frequency is once every 7 days, but it can be more.
lmv16:
- Even with low water consumption, washing should be done at least once every 2 weeks, the number of washings can even be increased. If you do not regularly backwash, then there is a high probability that the filler will become heavily clogged with iron, and it will have to be picked out of the column with a spatula.
- I would recommend using not a bucket, but an inverted barrel with a neck of a smaller diameter than the storage barrel. And the longer the barrel where aeration takes place, the better.
Such systems for cleaning from excess harmful impurities have become so popular among members of the forum that we can talk about a whole series of home-made non-pressure aeration installations.
OAK-OAK:
- I have an excess of iron levels - 48 mg / l, this is above the norm .. I thought a lot about how to stop harming myself and my family and came to the conclusion that forced aeration is the best way to clean water from excess iron.
Because the amount of impurities was off the charts, OAK-OAK modernized the aeration unit by installing a system of three barrels of 500 liters each.
To speed up the oxidation process, aeration is carried out around the clock.
The hourly air flow supplied by the compressor is 3000 liters/hour. As a result, the concentration dropped to 0.15 mg/l!
Drinking water safe for the body.
At FORUMHOUSE you will learn about the features of choosing a water supply and heating system, read about all the nuances of installing a home-made water treatment system. Get acquainted with the story of how our forum member independently assembled a non-pressure aeration installation.
We have collected all the experience of FORUMHOUSE users on home-made water treatment systems.
In our video you will learn about the latest innovations in water treatment systems. And from another one about the water supply system of the house from a well based on a condensing boiler.