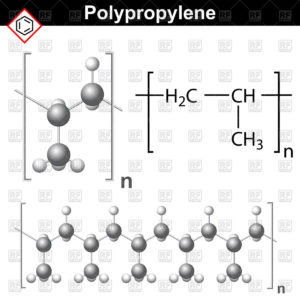
Obtaining polypropylene reaction
The reaction after loading the components continues for about 5-7 hours at a temperature above 65 degrees and a pressure of 1.0 MPa. Components are mixed in proportion:
- Propylene - 100 parts;
- Gasoline - 225;
- Catalyst complex - 9.
Polypropylene is obtained from a substance whose formula is CH2=CH(CH3) x n parts, and after manufacturing the formula turns into [-CH2-CH(CH3)-]n.
There are also methods for the propane-propylene polymerization fraction of propylene, combining 30% propylene and 70% propane. The second component is used as a solvent. Hardware pressure during production is maintained by the vapors released by the composition. A precipitate of the finished substance is precipitated in the form of a white powder, the remaining stages are duplicated according to the previous method. Also on an industrial scale, a method with the addition of a highly active metallocene catalyst is used. The reaction takes place in a heptane medium at a temperature of 65-70 degrees and a pressure of 1-1.2 MPa.
Technology:
- Fabrication of the catalyst complex;
- Liquefied propylene polymerization process;
- polymerization with ethylene;
- flushing;
- Spinning by centrifugation;
- Drying;
- Production of granules, packing.
Today, the production of such a polymer needs to improve catalysts: more active substances are being developed that can perform the same functionality at a small dosage, but with less waste generation. Then it will be possible to skip the step of washing the polypropylene composition and reconstituting the washing liquid.
Polypropylene is obtained from the substance of propene (propylene) by polymerization with various catalyst complexes when heated. There is a splitting of the double bond between atoms, a polymer is formed with pronounced strong and waterproof functions. Among the various types of plastics, it occupies an honorable second place after polyethylene; the production turnover grows annually due to the relative cheapness and high quality of the products obtained.
Table of soldering polypropylene pipes and their heating temperature
One of the main tasks of the installer when carrying out docking work is to accurately withstand the welding time of polypropylene pipes. Deviation from time intervals in one direction or another, as a rule, will lead to two main troubles:
- the shells of the pipes to be welded will not warm up enough, as a result, diffusion connection will not occur and the pipes will separate during operation - water will leak and the room will be flooded.
- The pipe shells will overheat and an influx will form at the junction of the ends - this will narrow the passage channel, increase the hydraulic resistance of the line, and lead to financial losses in individual water supply or heating due to poor pipeline conductivity.
When carrying out work, any installer is useful in a table of temperatures for soldering polypropylene pipes, indicating the heating time of the shells with a soldering device. The need for the table is due to the fact that pipes of large diameters have a higher heated surface area, mass and volume, respectively, for their heating in comparison with small products at the same temperature, more time is required.
When compiling the table, the main criterion was the experimentally determined optimum welding temperature for polypropylene pipes, equal to 260 °C.
 Rice. 8 Soldering table for polypropylene pipes
Rice. 8 Soldering table for polypropylene pipes
Also in the instructions for any welding machine there is a table that reflects the time of soldering polypropylene pipes in the docked position. Similar to the heating time of tubular casings, the holding time of the connected parts together also increases with their diameters.
When carrying out soldering work, it is useful to know at what temperature to solder plastic pipes, because the state of the environment significantly affects the cooling rate of the parts to be joined, and if the air is too cold, the tabular data will indicate incorrect values. When carrying out installation work, the permissible lower temperature limit is -10 °С, and the ambient temperature in the room or on the street from 0 to +25 °С is considered optimal.
Advantages and disadvantages
Metal-plastic pipes for water supply have a lot of advantages, which cannot be ignored:
- a large selection of diameters of metal-plastic pipes. In heating and water supply systems, structures with a diameter of 16 and 32 mm are used, respectively. Accurate determination of the pipe diameter is relevant when choosing fittings - connecting elements;
- lack of moisture condensation;
- pipes can be operated even if they are exposed to direct sunlight;
- tightness;

- installation is faster than the installation of metal pipes;
- low cost of the material;
- noiseless water supply;
- aesthetic appearance;
- no linear stretch;
- plastic. Due to which water supply communications can be masked;
- non-toxicity;
- ease of replacement and repair of pipes that have failed.
Of course, metal-plastic pipes for water supply have much less disadvantages and prohibitions than advantages. These include:
- Open communications are subject to mechanical damage.
- Metal pipes for hot water supply are less resistant to water hammer and hot water.
- Metal-plastic is capable of accumulating static voltage, therefore it is not suitable for grounding.
-
Mounting units of metal-plastic pipes are destroyed when used in low temperature conditions.
- It is unacceptable to use pipes in systems with a pressure of more than 10 bar if its diameter is small.
- In rooms with category "G", according to fire requirements, the use of plastic pipes is not allowed.
- It is forbidden to use metal-plastic pipes in central heating systems in the presence of elevator units.
Polypropylene monomer formula
In production, various types of polymers are made, but 3 types are most often used:
- Isotactic. It has increased elasticity, density and its melting requires a temperature of 170 degrees. Polypropylene compounds consist only of monomers.
- Atactic. It has a pronounced fluidity, reminiscent of rubber. Soluble in ethers, melts at 80 degrees. The methyl groups are arranged randomly with respect to the entire carbon chain.
- Syndiotactic. Block copolymer with alternating propylene and ethylene monomers.
The formula for each of the species is the same, but the structural units of polypropylene are located in space differently, which distinguishes them by mechanical, chemical and physical properties. The formula indicates a construction of an unlimited number of propene molecules. Its density is the lowest among plastics, but the structure allows it to withstand mechanical stress and heat. The resulting polymer is not subject to corrosion, but with an excess of direct sunlight and oxygen, its deterioration can be observed.
Any of the types of this polymer has good resistance to chemicals. Perceptible destruction of the layer can be caused by powerful oxidizing agents, for example, chlorosulfonic acid, oleum, nitric acid. When the material is in organic solvents (benzene, toluene), swelling may occur. The water absorption rate is 0.5%, so it is considered waterproof.
Properties and Applications of Polypropylene
Isotactic polypropylene is a solid thermoplastic polymer with a melting point of 165–170°C and a density of 900–910 kg/m3.
Below are the indicators of the main physical and mechanical properties of polypropylene:
- Molecular weight: 80,000-200,000
- Tensile stress, MPa: 245—392
- Elongation at break, %: 200—800
- Impact strength, kJ/m2: 78.5
- Brinell hardness, MPa: 59—64
- Heat resistance according to the NIIPP method, ° С: 160
- Maximum operating temperature (without load), ° С: 150
- Brittleness temperature, ° С: From -5 to -15
- Water absorption for 24 hours,%: 0.01-0.03
- Specific volume electrical resistance, Ohm m: 1014—1015
- Dielectric loss tangent: 0.0002—0.0005
- Dielectric constant at 50 Hz: 2.1-2.3
polypropylene marking
Polypropylene has higher heat resistance than low and high density polyethylenes. It has good dielectric properties, which are maintained over a wide temperature range. Due to its extremely low water absorption, its dielectric properties do not change when kept in a humid environment.
Polypropylene is insoluble in organic solvents at room temperature; when heated to 80 ° C and above, it dissolves in aromatic (benzene, toluene), as well as chlorinated hydrocarbons. Polypropylene is resistant to acids and bases even at elevated temperatures, as well as to aqueous salt solutions at temperatures above 100 ° C, to mineral and vegetable oils. The aging of stereoregular polypropylene proceeds similarly to the aging of polyethylene.
Polypropylene is less susceptible to cracking under the influence of aggressive environments than polyethylene.
One of the significant disadvantages of polypropylene is its low frost resistance (-30 °C). In this regard, it is inferior to polyethylene. Polypropylene is processed by all methods used for thermoplastics.
Modification of polypropylene with polyisobutylene (5-10%) improves the processability of the material, increases its flexibility, resistance to stress cracking and reduces brittleness at low temperatures.
Polypropylene films have high transparency; they are heat-resistant, mechanically strong and have low gas permeability and vapor permeability. Polypropylene fiber is durable; it is suitable for the manufacture of technical fabrics, for the manufacture of ropes.
Polypropylene is used for the production of porous materials - foam plastics.
Polypropylene structural formula
The polypropylene formula looks like this: (C3H6) n. The structural unit of polypropylene can be written by the formula: [-CH2-CH(CH3)-]n. This polymer is available in powder form or in granular form. Due to its composition, polypropylene is very resistant to chemical reactions and does not interact with acids, alkalis, artificial solvents, and does not get damaged from them.
In the formula for the structure of polypropylene (propylene) monomer, the hydrogen atom is replaced by a methyl group. Due to the presence of a double bond, polymerization is possible, due to which a strong synthetic polymer is formed. In the resulting macromolecule, the number n denotes the number of units from the monomers. Under various polymerization conditions, the functional group CH3 located on different sides of the methyl group molecule - the property of the resulting plastic depends on this.
Varieties
You can find different types of plastic pipes that are used to make pipelines. Types of pipes used to assemble heating circuits:
- Polypropylene. The material that is most often used in the manufacture of pipelines for heating, cold, hot water supply. This is due to the many advantages of this material, low price.
- Cross-linked polyethylene. Tubes made of this material are more expensive than polypropylene ones. Suitable for indoor and outdoor mounting. Withstand temperatures from -50 to 100 degrees. Destroyed by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays.Because of this, they must be mounted in protective casings.
- Metal-plastic products. Such tubes are often used in the manufacture of pipelines. The parts consist of several layers - the outer and inner layers of polyethylene. Between them is aluminum foil.
The choice of material depends on the operating conditions, the required technical characteristics.
Smooth pressure PVC pipes for glue joint production Dyka Holland
Supplied sizes of PVC pipes. Nomenclature range
| Image | Name | Price with VAT euro/m retail | Price with VAT euro/m wholesale | Product order |
| Working pressure - 0.6 MPa. Maximum operating temperature 60º C | ||||
| Pressure PVC pipe d40x1.5, 5m, PN6 | 2,14 | 1,61 | To order | |
| Pressure PVC pipe d50x1.6, 5m, PN6 | 2,81 | 2,11 | To order | |
| d63x2.0, 5m, PN6 | 4,37 | 3,28 | To order | |
| d75x2.3, 5m, PN6 | 6,70 | 5,02 | To order | |
| d90x2.8, 5m, PN6 | 9,67 | 7,25 | To order | |
| d110x2.7, 5m, PN6 | 12,55 | 9,41 | To order | |
| d125x3.1, 5m, PN6 | 16,43 | 12,33 | To order | |
| d140x3.5, 5m, PN6 | 20,30 | 15,23 | To order | |
| d160x4.0, 5m, PN6 | 27,11 | 20,33 | To order | |
| d180x4.4, 5m, PN6 | 32,65 | 24,49 | To order | |
| d200x4.9, 5m, PN6 | 39,29 | 29,47 | To order | |
| d225x5.5, 5m, PN6 | 51,43 | 38,57 | To order | |
| d250x6.2 5m, PN6 | 63,90 | 47,93 | To order | |
| d280x6.9, 5m, PN6 | 75,40 | 56,55 | To order | |
| d315x7.7, 5m, PN6 | 94,64 | 70,98 | To order | |
| d355x8.7, 5m, PN6 | 120,73 | 90,54 | To order | |
| d400x9.8, 5m, PN6 | 151,36 | 113,52 | To order | |
| Working pressure - 0.75 MPa. Maximum operating temperature 60º C | ||||
| d63x2.0, 5m, PN7.5 | 4,39 | 3,29 | To order | |
| d75x2.2, 5m, PN7.5 | 5,83 | 4,37 | To order | |
| d90x2.7, 5m, PN7.5 | 8,42 | 6,32 | To order | |
| d110x3.3, 5m, PN7.5 | 12,53 | 9,40 | To order | |
| d125x3.7, 5m, PN7.5 | 15,88 | 11,91 | To order | |
| d160x4.7, 5m, PN7.5 | 25,63 | 19,22 | To order | |
| d200x5.9, 5m, PN7.5 | 39,92 | 29,94 | To order | |
| d250x7.3, 5m, PN7.5 | 61,94 | 46,45 | To order | |
| d315x9.2, 5m, PN7.5 | 97,88 | 73,41 | To order | |
| Working pressure - 0.8 MPa. Maximum operating temperature 60º C | ||||
| d110x2.7, 5m, PN8 | 13,63 | 10,23 | To order | |
| d125x3.1, 5m, PN8 | 17,19 | 12,89 | To order | |
| d140x3.5, 5m, PN8 | 21,94 | 16,45 | To order | |
| d160x4.0, 5m, PN8 | 27,90 | 20,92 | To order | |
| d200x4.9, 5m, PN8 | 42,91 | 32,18 | To order | |
| d225x5.5, 5m, PN8 | 55,65 | 41,73 | To order | |
| d250x6.2, 5m, PN8 | 68,95 | 51,71 | To order | |
| d315x7.7, 5m, PN8 | 102,51 | 76,89 | To order | |
| d400x9.8, 5m, PN8 | 164,40 | 123,30 | To order | |
| Working pressure - 1 MPa. Maximum operating temperature 60º | ||||
| d32x1.6, 5m, PN10 | 1,80 | 1,35 | To order | |
| d40x1.9, 5m, PN10 | 2,59 | 1,94 | To order | |
| d50x2.4, 5m, PN10 | 4,12 | 3,09 | To order | |
| d63x2.4, 5m, PN10 | 5,22 | 3,92 | To order | |
| d75x2.9, 5m, PN10 | 7,40 | 5,55 | To order | |
| d90x3.5, 5m, PN10 | 10,73 | 8,05 | To order | |
| d110x4.2, 5m, PN10 | 15,73 | 11,80 | To order | |
| d125x4.8, 5m, PN10 | 20,21 | 15,16 | To order | |
| d140x6.7, 5m, PN10 | 37,09 | 27,81 | To order | |
| d160x6.2, 5m, PN10 | 33,41 | 25,06 | To order | |
| d200x7.7, 5m, PN10 | 51,48 | 38,61 | To order | |
| d225x10.8, 5m, PN10 | 96,09 | 72,07 | To order | |
| d250x9.6, 5m, PN10 | 80,08 | 60,06 | To order | |
| d280x13.4, 5m, PN10 | 148,44 | 111,33 | To order | |
| d315x12.1, 5m, PN10 | 169,92 | 127,44 | To order | |
| d355x13.6, 5m, PN10 | 214,63 | 160,97 | To order | |
| d400x15.3, 5m, PN10 | 229,16 | 171,87 | To order | |
| Working pressure - 1.25 MPa. Maximum operating temperature 60º C | ||||
| Pressure PVC pipe d63x3.0, 5m, PN12.5 | 6,34 | 4,75 | To order | |
| Pressure PVC pipe d75x3.6, 5m, PN12.5 | 9,07 | 6,80 | To order | |
| Pressure PVC pipe d90x4.3, 5m, PN12.5 | 13,00 | 9,75 | To order | |
| Pressure PVC pipe d110x5.3, 5m, PN12.5 | 19,48 | 14,61 | To order | |
| Pressure PVC pipe d125x6.0, 5m, PN12.5 | 24,84 | 18,63 | To order | |
| Pressure PVC pipe d160x7.7, 5m, PN12.5 | 40,75 | 30,56 | To order | |
| Working pressure - 1.6 MPa. Maximum operating temperature 60º C | ||||
| d12x1.0, 5m, PN16 | on request | on request | To order | |
| d16x1.5, 5m, PN16 | on request | on request | To order | |
| d20x1.5, 5m, PN16 | 1,30 | 0,97 | To order | |
| d25x1.9, 5m, PN16 | 2,18 | 1,63 | To order | |
| d32x2.4, 5m, PN16 | 2,54 | 1,90 | To order | |
| d40x3.0, 5m, PN16 | 3,92 | 2,94 | To order | |
| d50x3.7, 5m, PN16 | 6,01 | 4,51 | To order | |
| d63x3.8, 5m, PN16 | 7,90 | 5,93 | To order | |
| d75x4.5, 5m, PN16 | 11,14 | 8,36 | To order | |
| d90x5.4, 5m, PN16 | 16,00 | 12,00 | To order | |
| d110x6.6, 5m, PN16 | 23,78 | 17,83 | To order | |
| d125x7.4, 5m, PN16 | 32,62 | 24,46 | To order | |
| d140x8.3, 5m, PN16 | 41,49 | 31,12 | To order | |
| d160x9.5, 5m, PN16 | 58,18 | 43,63 | To order | |
| d180x10.7, 5m, PN16 | 73,57 | 55,17 | To order | |
| d200x11.9, 5m, PN16 | 90,74 | 68,05 | To order | |
| d225x13.4, 5m, PN16 | 115,04 | 86,28 | To order | |
| d250x14.8, 5m, PN16 | 123,32 | 92,49 | To order | |
| d280x16.6, 5m, PN16 | 154,47 | 115,85 | To order | |
| d315x18.7, 5m, PN16 | 195,62 | 146,71 | To order |
Scope of application
The main scope of metal-plastic pipes is the water supply and heating system. The pipes consist of an internal aluminum component, on which a layer of high-quality polyethylene is applied using modern technologies. Thanks to this technology, the layers of the metal-plastic pipe alternate. They consist of five layers. This multi-layer design makes it safe to use.
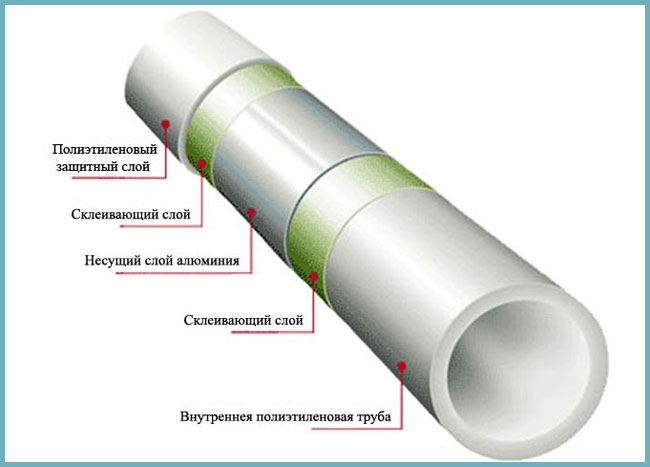
- The polyethylene layer allows you to reduce mechanical deformation and damage, so the installation of pipes in the children's room will also be completely safe. After all, everyone knows how kids love to hit toys on various objects.
- The aluminum layer creates hydraulic as well as mechanical protection of the pipe. It reduces the likely risks of thermal deformation of the previous layer.
- The inner layer is heat resistant. It consists of polyethylene, which protects the aluminum layer from corrosive effects and has a smooth inner surface.
In addition, metal-plastic pipes are used in other areas:
- for heating the soil in greenhouses;
- for installation of "warm" floors;

- heating greenhouses and winter gardens;
- in heating systems of pools;
- for the supply of chemical components;
- for transporting compressed air;
- in air conditioning systems;
- for repairs in multi-storey buildings, where a connection from the riser is required when replacing the water supply system. It is also used in industry and office buildings.
Additional Information
Metric measurement system, DIN standard for PVC pipes
Dyka brand pipes made of unplasticized PVC (UPVC) can be produced in accordance with the requirements of German DIN standards.
PVC adhesive pipe dimension table according to DIN
| Diameter, mm |
Nominal size (mm) |
Wall thickness (mm) | ||
| 6 bar | 10 bar | 16 bar | ||
| 12 | 10 | 1.0 | ||
| 16 | 12 | 1.2 | ||
| 20 | 16 | 1.5 | ||
| 25 | 20 | 1.5 | 1.9 | |
| 32 | 25 | 1.8 | 2.4 | |
| 40 | 32 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 3.0 |
| 50 | 40 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 3.7 |
| 63 | 50 | 1.9 | 3.0 | 4.7 |
| 75 | 65 | 2.2 | 3.6 | 5.6 |
| 90 | 80 | 2.7 | 4.3 | 6.7 |
| 110 | 100 | 3.2 | 5.3 | 8.2 |
| 125 | 110 | 3.7 | 6.0 | 9.3 |
| 140 | 125 | 4.1 | 6.7 | 10.4 |
| 160 | 150 | 4.7 | 7.7 | 11.9 |
| 180 | 160 | 5.3 | 8.6 | 13.4 |
| 200 | 180 | 5.9 | 9.6 | 14.9 |
| 225 | 200 | 6.6 | 10.8 | 16.7 |
| 250 | 225 | 7.3 | 11.9 | 18.6 |
| 280 | 250 | 8.2 | 13.4 | 20.8 |
| 315 | 300 | 9.2 | 15.0 | 23.4 |
| 355 | 350 | 10.4 | 16.9 | 26.3 |
| 400 | 400 | 11.7 | 19.1 | 29.7 |
| 450 | 400 | 13.2 | 21.5 | |
| 500 | 500 | 14.6 | 23.9 | |
| 560 | 500 | 16.4 | 26.7 | |
| 630 | 600 | 18.4 |
Supplied in standard size 5 meters long, grey.
The metric piping system - gray adhesive PVC pressure pipes - is manufactured by Dyka in accordance with the Dutch water industry standard KIWA BRL 502/02. This standard was derived from the specifications established by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) - ISO 161/1 and ISO 4065.
Dyka's production facilities for piping systems are registered with the Dutch water authority and the Dutch quality control authority KIWA/NEN.
Dyka brand unplasticized PVC piping products are approved by the World Health Organization (WHO) for use in potable water.
Pipe dimension table according to KIWA BRL 502/02
| External diameter, mm | External diameter tolerance | Wall thickness | ||||
| 6.3 bar | 7.5 bar | 10 bar | 12.5 bar | 16 bar | ||
| 16 | 16.0/16.2 | 1.6/2.0 | 2.0/2.4 | 1.5/1.9 | 1.5/1.9 | 1.5/1.9 |
| 20 | 20.0/20.2 | 2.0/2.4 | 2.0/2.4 | 1.5/1.9 | 1.5/1.9 | 1.5/1.9 |
| 25 | 25.0/25.2 | 2.0/2.4 | 2.2/2.7 | 1.6/2.0 | 1.5/1.9 | 1.9/2.3 |
| 32 | 32.0/32.2 | 2.2/2.7 | 2.7/3.2 | 1.9/2.3 | 2.4/2.9 | 3.0/3.5 |
| 40 | 40.0/40.2 | 2.7/3.2 | 3.2/3.8 | 2.4/2.9 | 2.4/2.9 | 3.0/3.5 |
| 50 | 50.0/50.2 | 3.1/3.7 | 3.7/4.3 | 2.4/2.9 | 3.0/3.5 | 3.7/4.3 |
| 63 | 63.0/63.2 | 4.0/4.6 | 4.7/5.4 | 2.9/3.4 | 3.0/3.5 | 3.8/4.4 |
| 75 | 75.0/75.3 | 4.9/5.6 | 5.9/6.7 | 3.5/4.1 | 3.6/4.2 | 4.5/5.2 |
| 90 | 90.0/90.3 | 6.2/7.1 | 7.3/8.3 | 4.2/4.9 | 4.3/5.0 | 5.4/6.2 |
| 110 | 110.0/110.4 | 7.7/8.7 | 9.2/10.4 | 4.8/5.5 | 5.3/6.1 | 6.6/7.5 |
| 125 | 125.0/125.4 | 9.8/11.0 | 11.7/13.1 | 6.2/7.1 | 6.0/6.8 | 7.4/8.4 |
| 160 | 160.0/160.5 | 7.7/8.7 | 7.7/8.7 | 9.5/10.7 | ||
| 200 | 200.0/200.6 | 9.6/10.8 | 9.6/10.8 | 11.9/13.3 | ||
| 250 | 250.0/250.8 | 12.1/13.6 | 11.9/13.3 | 14.8/16.5 | ||
| 315 | 315.0/316.0 | 15.3/17.1 | 15.0/16.7 | 18.7/20.8 | ||
| 400 | 400.0/401.0 | 19.1/21.3 | 23.7/26.3 | |||
| 500 | 500.0/501.0 | 12.3/13.8 | 14.6/16.3 | 19.1/21.3 | 23.9/26.5 | 29.6/32.8 |
| 630 | 630.0/631.0 | 15.4/17.2 | 18.4/20.5 | 24.1/26.8 |
Supplied in standard size 5 meters long, grey.
Dyka brand pipelines have been tested and approved by the Water Research Council (WRC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) for drinking water use in accordance with ISO 727.
Pipe size table according to BS3505
| nominal size, inch |
External diameter tolerance | Wall thickness | |||
| Class C Min/Max |
Class D Min/Max |
Class E Min/Max |
Class 7 Min/Max |
||
| 1/2 | 21.2/21.5 | 1.7/2.1 | 3.7/4.3 | ||
| 3/4 | 26.6/26.9 | 1.9/2.5 | 3.9/4.5 | ||
| 1 | 33.4/33.7 | 2.2/2.7 | 4.5/5.2 | ||
| 1 1/4 | 42.1/42.4 | 2.2/2.7 | 2.7/3.2 | 4.8/5.5 | |
| 1 1/2 | 48.1/48.4 | 2.5/3.0 | 3.1/3.7 | 5.1/5.9 | |
| 2 | 60.2/60.5 | 2.5/3.0 | 3.1/3.7 | 3.9/4.5 | 5.5/6.3 |
| 3 | 88.7/89.1 | 3.5/4.1 | 4.6/5.3 | 5.7/6.6 | |
| 4 | 114.1/114.5 | 4.5/5.2 | 6.0/6.9 | 7.3/8.4 | |
| 5 | 140.0/140.4 | 5.5/6.4 | 7.3/8.4 | 9.0/10.4 | |
| 6 | 168.0/168.5 | 6.6/7.6 | 8.8/10.2 | 10.8/12.5 | |
| 8 | 218.8/219.4 | 7.8/9.0 | 10.3/11.9 | 12.6/14.5 |
Supplied in a standard size 6 meters long, dark grey.
Please note that the metric and imperial metric systems are two completely different systems. The sizes of PVC pipes produced on the basis of these systems are incompatible, and such pipes cannot be used in a single piping system without special adapters.
Afinara supplies connecting fittings for the transition between DIN and BS3505 standard products. Dyka's adapter series includes products for PVC pressure pipes for solvent bonding and for socket.
Installation
To make a heating system from plastic pipes, you do not need to hire builders. To do this, you need to prepare tools, materials and do the work yourself. Stages of work:
- Prepare pipes for heating in a private house, in an apartment. They are cut to the required dimensions using special scissors. The edges are cleaned from dirt, dust, degreased.
- Connections of individual elements can be made with couplings or end-to-end. To do this, you need to use a special soldering machine.
- After heating the individual parts on a heated soldering iron, they are connected to each other.
It remains to wait for the plastic to cool, to perform a test run of the pipeline.
Plastic pipes are becoming more popular every year. This is due to the technical characteristics of the material, low price. For the assembly of heating systems, you can use different types of polymers. When choosing a material, you need to take into account a number of requirements, features. After purchasing individual elements of the pipeline, you can assemble it yourself. To do this, you need to study the technology, carry out installation work.
Polypropylene pipes for heating how to choose
Watch this video on YouTube
Reinforced polypropylene pipes
The conclusion that polypropylene pipes - the operating temperature of which corresponds to the temperature of hot water in the heating system, can be successfully used is not entirely accurate.
To eliminate the effect of thermal expansion, manufacturers have developed a new type - a reinforced polypropylene pipe.

Experts recommend using only reinforced polypropylene pipes for the heating system - the temperature they can withstand fully complies with the standards of a modern heating system.
Installation of polypropylene pipes
When installing polypropylene pipes, their linear expansion due to changes in water temperature should be taken into account. Therefore, fastening to the wall must be done without rigid fixation of products.
An important condition must be observed - polypropylene pipes must be able to move slightly with an increase or decrease in temperature. This means that you should not pull them to the string and firmly attach them to the walls.
Otherwise, damage to the layers of the pipe is possible, which can lead to a break.
This means that you should not pull them into line and firmly attach them to the walls. Otherwise, damage to the layers of the pipe is possible, which can lead to a break.
And most importantly, you need to remember that polyethylene pipes - what temperature they can withstand, which means that in such conditions they must be operated.
Pipes made of this material are not recommended to be strongly bent. Though 
In devices where reinforced polypropylene pipes are used, the temperature of the working medium must be within the range of up to 95 degrees. When laying pipes in a concrete screed, for example, when installing underfloor heating, the channel should be made slightly wider than the diameter of the products. This is necessary so that during linear expansion the pipe has the ability to change its dimensions.
When using pipes for supplying cold water, their rigid fastening is allowed, since in this case the operating temperature of polypropylene pipes is low and there is no linear expansion of the material. In addition, the cost of such products is low compared to reinforced pipes, in which hot water is used as a heat carrier.
Reinforcement leads to the fact that the pipeline becomes much more reliable and stronger.
What pressure can polypropylene pipes withstand
In accordance with the technical specifications, the service life of polypropylene pipes is about 50 years. This figure depends not only on the temperature of the working medium in the pipe, but also on its pressure.
Polypropylene pipes can be operated at working medium pressure up to 30 kg/sq. see. The higher the temperature, the lower the level of allowable pressure. To put it simply, pipes made of this material must have a working pressure level of up to 10 bar.
Ideal conditions for a polyethylene pipe - the water temperature is not more than +70 degrees at a pressure of 4 to 6 atmospheres.
Polypropylene pipes are in great demand in the construction or repair of pipelines for various purposes. However, it is necessary to take into account their working capabilities: temperature and pressure.
The popularity of polypropylene pipes for use in the laying and installation of water and heat networks has grown significantly in recent years. The reliability and durability of the system is perhaps the main criterion when choosing pipes from this material. However, the question of what temperature this material can withstand in heating systems deserves a separate discussion.
How to get polypropylene from propene
The method for obtaining polypropylene was first created by chemists Carl Ren and Giulio Natta in 1954.In modern industry, the monomer for the production of polypropylene is a substance whose formula is C3H6, the reaction takes place using a Ziegler-Natta catalyst or metallocene catalysts.
With the first of the catalysts, isotactic polypropylene is produced. Due to the much lower thermal effect than in the production of polyethylene, heat removal does not require specific methods or additional cooling equipment. The process is carried out in a liquid hydrocarbon solvent:
- gasoline;
- N-heptane;
- white spirit.
The technology consists of stages:
- Preparation of the catalyst complex;
- The polymerization reaction of polypropylene inside the polymerizer;
- The output of unreacted monomers (what polypropylene is made of);
- Decomposition of the catalyst complex with alcohol;
- Purification of the resulting polymer, separation from the solvent;
- Drying in a stream of nitrogen;
- Processing of received products.