Calculation procedure for the heating expansion tank
The coolant that moves through the pipes of the heating system is practically not compressed. Otherwise, the pressure in the line may jump sharply, which will lead to an emergency. Heating water in the range of 20 °C - 90 °C is accompanied by its expansion. That is why the heating system needs a special tank into which the excess coolant enters after its volume has increased.
Thus, all nodes and devices will work correctly without interruptions and accidents. Given the important role assigned to this element of the circuit, the calculation of the expansion tank for heating should be carried out in accordance with the established rules.
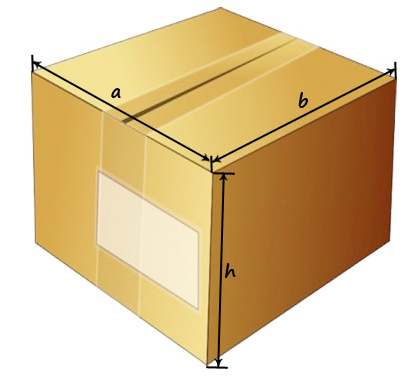
How to calculate the volume of a box in M 3
During the packing and transportation of goods, entrepreneurs are wondering how to do it right in order to save time and money. The calculation of the volume of containers is an important point in the delivery. Having studied all the nuances, you will be able to choose the box you need in size.
How to calculate the volume of a box? In order for the cargo to fit into the box without problems, its volume must be calculated using the internal dimensions.
Use the online calculator to calculate the volume of a box in the form of a cube or parallelepiped. It will help speed up the calculation process.
The cargo to be placed in a container can be of a simple or complex configuration. The dimensions of the box should be 8-10 mm larger than the most protruding points of the load. This is necessary so that the item fits into the container without difficulty.
External dimensions are used when calculating the volume of boxes in order to correctly fill the space in the body of the vehicle for transportation. They are also needed to calculate the area and volume of the warehouse required for their storage.
First, we measure the length (a) and width (b) of the box. To do this, we will use a tape measure or a ruler. The result can be recorded and converted to meters. We will use the international measurement system SI. According to it, the volume of the container is calculated in cubic meters (m 3). For containers whose sides are less than a meter, it is more convenient to take measurements in centimeters or millimeters. It must be taken into account that the dimensions of the cargo and the box must be in the same units of measurement. For square boxes, the length equals the width.
Then we will measure the height (h) of the existing container ─ the distance from the bottom valve of the box to the top one.
If you made measurements in millimeters, and the result must be obtained in m 3, we translate each number into m. For example, there is data:
Considering that 1 m = 1000 m, we will translate these values into meters, and then substitute them into the formula.
Formulas
- V=a*b*h, where:
- a – base length (m),
- b - base width (m),
- h - height (m),
- V is the volume (m3).
Using the formula for calculating the volume of a box, we get:
V \u003d a * b * h \u003d 0.3 * 0.25 * 0.15 \u003d 0.0112 m 3.
This method can be used when calculating the volume of a parallelepiped, that is, for rectangular and square boxes.
How to correctly calculate the cube of concrete for the construction of walls

For the construction of massive buildings, strong boxes are constructed from concrete reinforced with steel reinforcement. To determine the need for building materials, builders face the task of calculating the volume of concrete for such structures. To perform calculations, use the following formula - V \u003d (S-S1) x H.
Let us decipher the notation included in the formula
:
- V - the amount of concrete mix for building walls;
- S is the total area of the wall surface;
- S1 - total area of window and door openings;
- H is the height of the concreted wall box.
When performing calculations, the total area of the openings is determined by summing up the individual openings.The calculation algorithm is reminiscent of determining the need for concrete for a slab base and can easily be done independently using a calculator.
Calculation procedure for the heating expansion tank
The coolant that moves through the pipes of the heating system is practically not compressed. Otherwise, the pressure in the line may jump sharply, which will lead to an emergency. Heating water in the range of 20 °C - 90 °C is accompanied by its expansion. That is why the heating system needs a special tank into which the excess coolant enters after its volume has increased.
Thus, all nodes and devices will work correctly without interruptions and accidents. Given the important role assigned to this element of the circuit, the calculation of the expansion tank for heating should be carried out in accordance with the established rules.
Pressure in the heating system
Pressure in the network arises as a result of the influence of several factors. It characterizes the effect of the coolant on the walls of the system elements. Before filling with water, the pressure in the pipes is 1 atm. However, as soon as the process of filling the coolant begins, this indicator changes. Even with a cold coolant, there is pressure in the pipeline. The reason for this is the different arrangement of the elements of the system - with an increase in height by 1 m, 0.1 atm is added. This type of impact is called static, and this parameter is used when designing heating networks with natural circulation. In a closed heating system, the coolant expands during heating, and excess pressure is formed in the pipes. Depending on the design of the line, it can change in different sections, and if stabilizing devices are not provided at the design stage, then there is a risk of system failure.
There are no pressure standards for autonomous heating systems. Its value is calculated depending on the parameters of the equipment, the characteristics of the pipes, and the number of storeys of the house is also taken into account. In this case, it is necessary to follow the rule that the pressure value in the network must correspond to its minimum value in the weakest link in the system. It is necessary to remember about the mandatory difference of 0.3-0.5 atm. between the pressure in the direct and return pipes of the boiler, which is one of the mechanisms for maintaining the normal circulation of the coolant. Taking into account all this, the pressure should be in the range from i .5 to 2.5 atm. To control the pressure at various points in the network, pressure gauges are inserted that record low and excess values. In the event that the meter must not only serve for visual control, but also work with the automation system, electrocontact or other types of sensors are used.
- The density of heated water is less than that of cold water. The difference between these values leads to the fact that a hydrostatic head is created, which promotes hot water to the radiators.
- For expansion tanks, the most informative are the maximum allowable values of temperature and pressure.
- According to manufacturers, in modern tanks the coolant temperature can reach 120 ° C, and the operating pressure is up to 4 atm. at peak values up to 10 bar
Formula for calculating the volume of the expansion tank
KE - the total volume of the entire heating system. This indicator is calculated based on the fact that I kW of heating equipment power is equal to 15 liters of coolant volume. If the boiler power is 40 kW, then the total volume of the system will be KE \u003d 15 x 40 \u003d 600 l;
Z is the value of the temperature coefficient of the coolant. As already noted, for water this is about 4%, and for antifreeze of different concentrations, for example, 10-20% ethylene glycol, from 4.4 to 4.8%;
N is the efficiency value of the membrane tank, which depends on the initial and maximum pressure in the system, the initial air pressure in the chamber.Often this parameter is specified by the manufacturer, but if it is not there, you can perform the calculation yourself using the formula:
DV - the highest allowable pressure in the network. As a rule, it is equal to the allowable pressure of the safety valve and rarely exceeds 2.5-3 atm for ordinary domestic heating systems;
DS is the pressure value of the initial charge of the membrane tank based on a constant value of 0.5 atm. for 5 m of the length of the heating system.
N = (2.5-0.5)/
So, from the data obtained, we can derive the volume of the expansion tank with a boiler power of 40 kW:
K \u003d 600 x 0.04 / 0.57 \u003d 42.1 liters.
A 50 l tank with an initial pressure of 0.5 atm is recommended. since the final indicators for choosing a product should be slightly higher than the calculated ones. A slight excess of the volume of the tank is not as bad as the insufficiency of its volume. In addition, when using antifreeze in the system, experts advise choosing a tank with a volume of 50% more than the calculated one.
Determination of the optimal volume of the accumulator
There are several approaches to choosing the optimal volume of this tank. For example, they recommend tables in which the consumer is asked to proceed from the water supply created in the accumulator.
In our case, we use a formula that was developed by one of the leading manufacturers of such equipment and is perfect for just the case of a pumping station.
The formula itself will not be given - we will simply list the quantities that we need for the calculation.
Approximate maximum water flow expressed in liters per minute. Determining this expense will be the first step in our series of calculations.
Calculator for calculating the maximum water flow
Explanations for calculating consumption
Everything is quite simple. Plumbing fixtures and household appliances connected “by water” are characterized by a certain average consumption. If you specify those devices and accessories that are available or are planned to be installed in the house, the program will sum up their indicators.
It is clear that all devices are involved at the same time extremely rarely, if not at all - never. But in this regard, the calculator algorithm has a special "floating" value, which will take into account the probabilistic component of the final result.
The result obtained will be required for further calculations.
Let's return to the values for the main formula.
Three pressure values \u200b\u200bare required - pre-inflating the air chamber of the accumulator, as well as the lower and upper thresholds for the pump. That is, the minimum pressure in the system at which the pump starts and replenishes the tank with water, and the maximum at which the power to the installation is turned off.
These values, too, of course, are not taken “from the ceiling”. There are certain recommendations for choosing the optimal indicators. Information about this is well presented on our portal.
It is desirable that the pump, even with almost continuous operation of the water supply system at maximum water flow, is turned on no more than once every 4–5 minutes. That is, it turns out 12 ÷ 15 times within an hour.
All the necessary initial data are listed - you can proceed to the calculation.
Special explanations here, probably, are not required - everything has already been said above. The only thing is that the result obtained, of course, serves only as a guideline. One way or another, you will have to buy from the standard line of tank sizes. As a rule, they take the closest in volume to the big side.
Method for calculating the volume
C is the volume of liquid in the system, l.
Βt is the thermal expansion coefficient of the coolant.
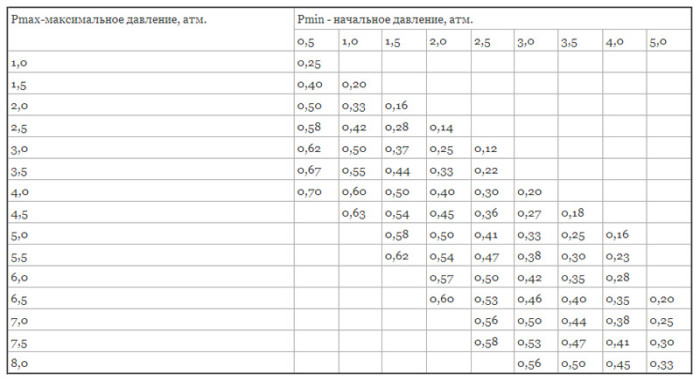
P-min and P-max - minimum (initial) and maximum pressure in the expansion tank.
The volume of liquid is considered full, including:
- pipelines (about the diameters of copper pipes for plumbing is written here),
- radiators,
- boiler,
- other elements where there is water (read about the stainless steel water heated towel rail ladder on this page).
If the volume of the system is unknown, the method of determining the power of radiators is used - at the rate of 1 kW - 15 liters.
The coefficient of expansion for water at 85 degrees Celsius is 0.034.
This value is used when more accurate information about your network is not available.
The initial and maximum pressure in the tank P-min and P-max are the operating pressure and the value at which the safety valve is activated.

But the benefits of it are undeniable.
The choice of an expansion tank that is suitable for its characteristics will be able to protect the heating network from an accident at the most inopportune moment.
Which one to choose is up to you.
Using the online calculator
The number of online calculators in the network is large, any one is good, but it is more correct to use several resources in turn and derive some average value. So it will be possible to correct errors or incorrect data on different sites. Each calculator has its own calculation method, the amount of data used is different.
Therefore, it is better to play it safe by duplicating the calculation.
Some resources, at the same time, with the issuance of the obtained value, offer variants of expansion tank models that satisfy the provided data.
The main values and coefficients are usually supplied in the form of tables or averages, but the volume of coolant in your circuit must be known.
In extreme cases, they use another method that does not give an exact value, but in the absence of other options it is suitable.
The volume of the expansion tank is assumed to be 15% of the total volume of the network, including pipelines, boilers and radiators.
It seems that adherents of accurate calculations will find this option too primitive, but in uncontested cases it is used as a palliative.
How to make a simple calculation of the capacity of an expansion tank for a heating system, see the video.
Types of tanks
The heating system can be equipped with one of the types of expansion tanks.
How to choose the right element of the heating system in each individual case? This will be discussed further.
open type
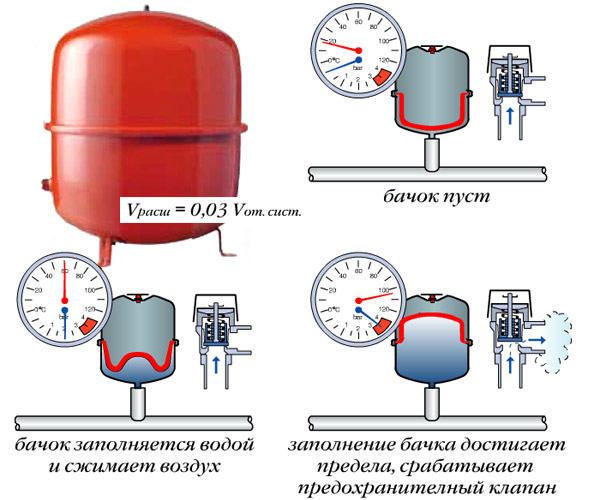
As the name implies, an open tank is a container with an open top into which coolant can be added. It does not require locking parts, a membrane partition and a cover. But due to the fact that water evaporates in such a container, and its amount must be constantly monitored (topped up), open-type tanks were gradually abandoned.
In addition, such heating is characterized by low pressure, and the tank itself is often subject to corrosion. Therefore, more modern closed-type tanks are being installed today.
closed type
In lines with a circulation pump, expansion tanks of a closed type (membrane) are installed. The highest quality samples are available in the form of a sealed red container with a rubber membrane inside. Their membrane is made of more durable technical rubber.
For products for hot water supply, the body of which is painted blue, the quality of rubber is lower (it is food grade). Such models withstand pressure worse and wear out faster.
In addition to the main function - compensation for the volume of the coolant when the temperature drops and its intake when it expands from heating, the membrane unit controls the liquid level in the heating line, removes air from the system, drains water into the sewer when it is in excess and is a buffer zone in case of a pressure surge.
Expansion tank modifications
Two types of expansion tanks are used.
Open type tanks have been known for a long time and are still used today.
Their device is so simple that it makes you put up with shortcomings.
These include:
- low operating pressure of the network, since only natural circulation of the liquid is possible;
- the need to control the amount of coolant.Boiling and evaporation of water will once open the network and stop the system, so you need to constantly check the water level in the tank;
- the only location is at the top point, which creates inconvenience when compensating for the lack of coolant.
Closed type tanks are designed
They allow the location in those places where the user needs it.
They are adapted to work at elevated pressure and forced circulation, the amount of coolant does not change at all.
open type
They are an open container, the liquid level in which rises or falls as thermal expansion occurs.
With a shortage, water is simply topped up from a bucket.
An open tank is the simplest design. does not require any shut-off valves.
Its main disadvantage is its inconvenient location - mandatory installation at the highest point of the network.
The need to control the level of the liquid makes it constantly rise to the top, delivering water there.
In addition, the pressure in the open tank system is low, preventing the use of a fluid circulation pump.
But there is one advantage - an open heating circuit does not need electricity.
If there are power outages, or there is none at all, this option becomes the only possible one.
About ways to adjust the water pressure reducer in the water supply system is written here.
The design of the closed expansion tank solves all problems.
The pressure and volume in it are adjusted using a rubber membrane, therefore such tanks are simply called "membrane".
The working volume of such a tank is filled with air (or an inert gas), when the water expands, it displaces the membrane and the air pressure increases.
As the water cools, the water pressure decreases and the membrane forces it back into the system.
The device operates in automatic mode, which does not require constant monitoring, the allowable pressure is much higher than is possible when using an open tank.
The membrane in the tank can be replaceable (flange type), or non-replaceable, disposable. The body of such a tank is painted red.
Tanks with a blue body are designed for hot water and are equipped with a membrane made of food-grade rubber with a shorter service life.
Which to choose
However, residents of private houses are often content with using an open tank, motivating this choice:
- ease of use,
- repair,
- no need for electricity.
The need to top up water, due to evaporation or other losses, is considered by some to be a slight inconvenience, while others mechanize this process (which one to choose a deep well pump) or automate (read about a deep well pump with automatics here).
If the area to be heated is small and no increase in network pressure is required, then only an open tank can be dispensed with.
The final decision is dictated by specific conditions and equipment.
Buying an expansion tank
as a device of great importance and responsibility, should not be made "by eye", especially if you need a "membrane"
You need to calculate the volume of the tank. taking into account all the individual parameters of the heating system of your home.
What capacity
Order an estimate from specialists. The option is reliable, but it will take time, money and a personal visit to the organization where such a calculation will be made.
Which, by the way, must first be found.
Calculate the volume yourself. using the required formulas. This option is good when all the necessary data are known, otherwise, no calculation will be possible.
An affordable and simple option, but it is advisable to duplicate the calculation on several resources to obtain the most accurate result.
Options with determining the volume of the tank “by eye”, or with an approximate calculation, taking 1 kW of power corresponding to 15 liters of water in the system, as unreliable and dangerous, are immediately rejected.
It is better to spend a little time on the calculations than to be in an unheated house in the cold (how to connect a heating cable for plumbing).
Method for calculating the volume
C is the volume of liquid in the system, l.
Βt is the thermal expansion coefficient of the coolant.
P-min and P-max - minimum (initial) and maximum pressure in the expansion tank.
The volume of liquid is considered full, including:
- pipelines (about the diameters of copper pipes for plumbing is written here),
- radiators,
- boiler,
- other elements where there is water (read about the stainless steel water heated towel rail ladder on this page).
If the volume of the system is unknown, the method of determining the power of radiators is used - at the rate of 1 kW - 15 liters.
The coefficient of expansion for water at 85 degrees Celsius is 0.034.
This value is used when more accurate information about your network is not available.
The initial and maximum pressure in the tank P-min and P-max are the operating pressure and the value at which the safety valve is activated.
But the benefits of it are undeniable.
The choice of an expansion tank that is suitable for its characteristics will be able to protect the heating network from an accident at the most inopportune moment.
Which one to choose is up to you.
Using the online calculator
The number of online calculators in the network is large, any one is good, but it is more correct to use several resources in turn and derive some average value. So it will be possible to correct errors or incorrect data on different sites. Each calculator has its own calculation method, the amount of data used is different.
Therefore, it is better to play it safe by duplicating the calculation.
Some resources, at the same time, with the issuance of the obtained value, offer variants of expansion tank models that satisfy the provided data.
The main values and coefficients are usually supplied in the form of tables or averages, but the volume of coolant in your circuit must be known.
In extreme cases, they use another method that does not give an exact value, but in the absence of other options it is suitable.
The volume of the expansion tank is assumed to be 15% of the total volume of the network, including pipelines, boilers and radiators.
It seems that adherents of accurate calculations will find this option too primitive, but in uncontested cases it is used as a palliative.
How to make a simple calculation of the capacity of an expansion tank for a heating system, see the video.
Getting ready to determine the volume of concrete how to calculate without errors
When preparing to perform calculations, it should be remembered that the need for a concrete mixture is determined in cubic meters, and not in kilograms, tons or liters. As a result of manual or software calculations, the volume of the binder solution will be determined, and not its mass. One of the main mistakes that beginner developers make is to perform calculations before the type of foundation is determined.
The decision on the design of the foundation is made after the following work has been completed
:
- production of geodetic measures to determine the properties of the soil, the level of freezing and the location of aquifers;
- calculation of the load capacity of the base. It is determined on the basis of weight, design features of the structure and natural factors.

- type of base being built;
- foundation dimensions, its configuration;
- brand of mixture used for concreting;
- soil freezing depth.
The accuracy with which the volume of concrete is calculated depends on the data used for the calculation.
They are different for each type of foundation.
:
when calculating the tape base, its dimensions and shape are taken into account;
for a columnar base, it is important to know the number of concrete columns and their dimensions;
you can calculate the cube of concrete for a solid slab by its thickness and dimensions.
The accuracy of the result obtained depends on the completeness of the data used for the calculation.
Device selection according to the calculation
Before proceeding with the calculation of the membrane, you need to know that the larger the volume of the heating system and the higher the maximum temperature index of the coolant, the larger the tank itself should be.
There are several ways in which the calculation is carried out: contacting specialists at the design bureau, performing calculations on their own using a special formula, or calculating using an online calculator.
The calculation formula looks like this: V = (VL x E) / D, where:
- VL - the volume of all main parts, including the boiler and other heating devices;
- E is the coefficient of expansion of the coolant (in percent);
- D is an indicator of membrane efficiency.
Volume determination
The easiest way to determine the average volume of the heating system is by the power of the heating boiler at the rate of 15 l / kW. That is, with a boiler power of 44 kW, the volume of all highways of the system will be equal to 660 liters (15x44).
The expansion coefficient for a water system is approximately 4% (at a heating medium temperature of 95 °C).
If antifreeze is poured into the pipes, then they resort to the following calculation:
The efficiency rating (D) is based on the initial and highest pressure in the system, as well as the starting air pressure in the chamber. The safety valve is always set to maximum pressure. To find the value of the performance indicator, you need to carry out the following calculation: D = (PV - PS) / (PV + 1), where:
- PV - the maximum pressure mark in the system, for individual heating, the indicator is 2.5 bar;
- PS - the membrane charging pressure is usually 0.5 bar.
Now it remains to collect all the indicators in the formula and get the final calculation:
The resulting number can be rounded up and opt for an expansion tank model starting from 46 liters. If water is used as a heat carrier, then the volume of the tank will be at least 15% of the capacity of the entire system. For antifreeze, this figure is 20%. It is worth noting that the volume of the device may be slightly larger than the calculated number, but in no case, not less.
Selection of an expansion tank for the heating system
The choice of an expansion tank for heating is an important step in creating an autonomous heating system. This device must comply with the parameters of the system, otherwise its normal operation will not be possible.
An expansion tank is a special container, thanks to which it is possible to compensate for the thermal expansion of the liquid circulating in the heating system. When water is heated, its volume increases, the dynamics of volume increase is about 0.3% for every 10°C.
The liquid has a low compressibility coefficient, so the excess volume will have nowhere to go in a completely sealed system without a special reservoir, which will lead to an accident - due to increased pressure, connections may leak or pipes burst. It is also impossible to replace the expansion tank with a valve to dump the "excess" heated coolant, because when cooled, the liquid in the pipeline will compress, forming a vacuum - this will lead to depressurization of the system and air entering there - as a result, heating will not function.
Pressure in the heating system
Pressure in the network arises as a result of the influence of several factors. It characterizes the effect of the coolant on the walls of the system elements. Before filling with water, the pressure in the pipes is 1 atm. However, as soon as the process of filling the coolant begins, this indicator changes. Even with a cold coolant, there is pressure in the pipeline. The reason for this is the different arrangement of the elements of the system - with an increase in height by 1 m, 0.1 atm is added. This type of impact is called static, and this parameter is used when designing heating networks with natural circulation.In a closed heating system, the coolant expands during heating, and excess pressure is formed in the pipes. Depending on the design of the line, it can change in different sections, and if stabilizing devices are not provided at the design stage, then there is a risk of system failure.
There are no pressure standards for autonomous heating systems. Its value is calculated depending on the parameters of the equipment, the characteristics of the pipes, and the number of storeys of the house is also taken into account. In this case, it is necessary to follow the rule that the pressure value in the network must correspond to its minimum value in the weakest link in the system. It is necessary to remember about the mandatory difference of 0.3-0.5 atm. between the pressure in the direct and return pipes of the boiler, which is one of the mechanisms for maintaining the normal circulation of the coolant. Taking into account all this, the pressure should be in the range from i .5 to 2.5 atm. To control the pressure at various points in the network, pressure gauges are inserted that record low and excess values. In the event that the meter must not only serve for visual control, but also work with the automation system, electrocontact or other types of sensors are used.
- The density of heated water is less than that of cold water. The difference between these values leads to the fact that a hydrostatic head is created, which promotes hot water to the radiators.
- For expansion tanks, the most informative are the maximum allowable values of temperature and pressure.
- According to manufacturers, in modern tanks the coolant temperature can reach 120 ° C, and the operating pressure is up to 4 atm. at peak values up to 10 bar