Leak test
After checking the strength of the product and the density of the material of manufacture, the shut-off valves are audited for the level of tightness.
During the check, the following are revealed:
- density of surfaces subjected to grinding;
- tightness of the valve locking device (lever, flywheel, and so on);
- assembly quality of individual components of the product (bellows, membrane, stuffing box).
test preparation requirements
Checking the tightness of the fittings is carried out under the following conditions:
- the substance that is used for testing should not adversely affect the employees of the enterprise and the tested product;
- it is possible to carry out a check only after the first stage of the study has been successfully completed, that is, a obviously strong product that does not have cracks and other deviations on the case is subject to testing;
- only tested and fully equipped equipment that meets the specifications may be used.
The test is carried out by two qualified personnel. Verification by one specialist is prohibited.
Verification methods and their description
The following methods can be used to conduct research:
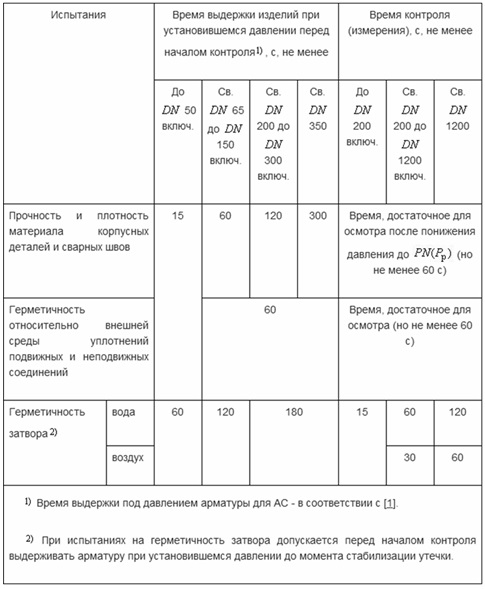
- manometric. The stop valves are installed on the stand (similar to the one described above) and filled with a gaseous substance up to a certain (conditional) pressure. The test is considered successful if no pressure drop in the system is detected within the required time (determined from the table). The manometric method is used to check valves, which consist of several parts that are not subject to the possibility of visual inspection;
Table of time intervals for carrying out one or another test of valves
- hydrostatic. The product to be tested is filled with liquid using a pump and held for a certain time. If leaks are found on the valve, the test is considered to have failed. The hydrostatic method is used exclusively for valves, all the main components of which are available for visual inspection.
For a more accurate determination of the results, luminescent substances can be added to the liquid intended for filling the fittings, which are perfectly visible under the influence of ultraviolet rays.
Test Results
In most cases, complete tightness of fittings installed on pipelines for various purposes is impossible and impractical to achieve. GOST 9544-75 regulates specific standards for individual classes:
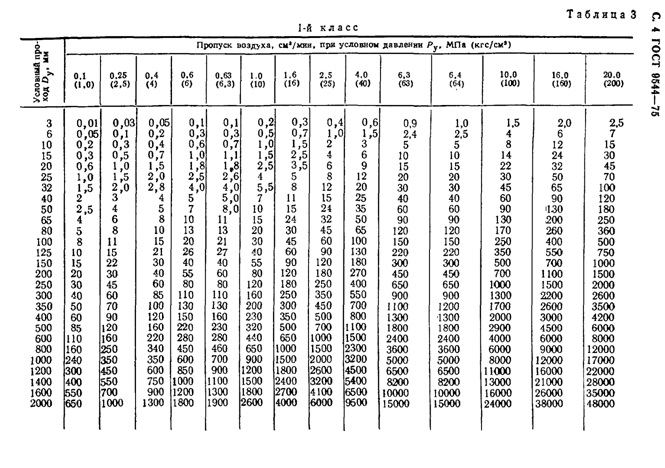
- Class I - devices that are used on pipelines filled with toxic (explosive) substances. For this reinforcement, the following deviations are allowed, presented in the table.
Regulated pass rates for class 1 devices
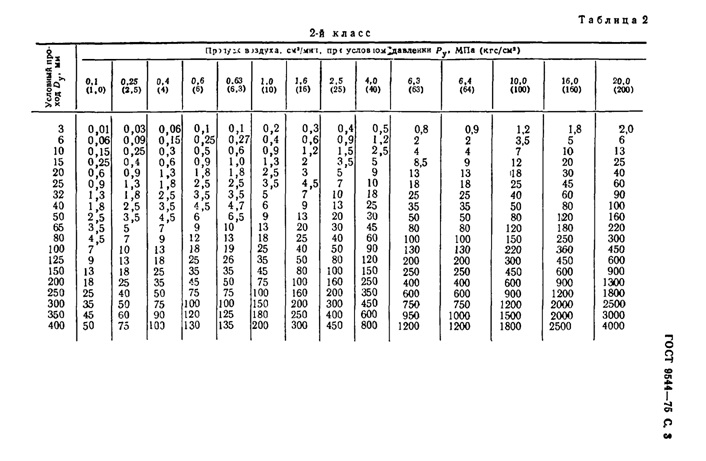
- Class II - these are devices installed on pipelines with flammable substances. For this class, the following standards apply (see table).
Permissible standards for tightness of locking devices of class 2
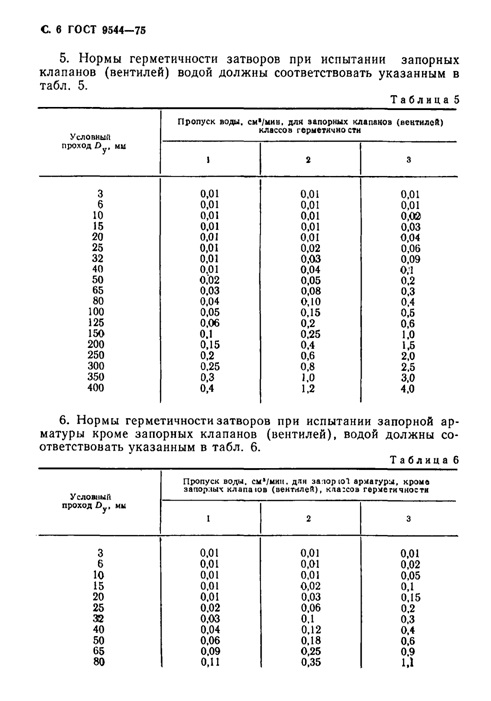
- Class III is fittings for pipelines with other passing media. The regulated strength standards of this class are divided into:
- norms established for valves;
- norms for other types of stop valves.
Permissible deviations for shut-off valves belonging to the 3rd class of tightness
The testing of reinforcement is presented in the video.
All checks of locking devices for pipelines are carried out by qualified specialists on certified devices.
Scope of maintenance work
Maintenance interval
During operation, shut-off valves and check valves are subject to the following types of maintenance and repair:
— service TO 1;
— seasonal service TO 2;
— current repair (TR);
— diagnostic examination; medium repair (SR);
— overhaul (CR); technical certification.
Medium repair (SR) of fittings is carried out without dismantling from the pipeline. Overhaul (CR) is carried out with the dismantling of fittings in a specialized repair company.
Table 2 Terms of maintenance, inspection and repair of valves
|
Name of fittings |
Т0 1, months |
TO 2, months |
TR, months |
Diagnostic examination, years |
SR, years |
KR, years |
Technical Inspection, years |
|
1. Stop valves DN 50-250 |
3 |
6 |
12 |
15 |
15 |
— |
— |
|
2. Stop valves DN 300-1200 |
1 |
6 |
12 |
15 |
15 |
30 |
30 or after the expiration of the period established by the previous survey |
Typical scope of work during maintenance (TO 1) of shutoff valves
The following works are carried out in the scope of maintenance of TO 1.
For valves:
-visual check of tightness relative to the external environment, including: flange connection (leaks are not allowed);
stuffing box seal (leaks are not allowed; in case of leaks in the stuffing box seal, perform maintenance according to the manufacturer's DS); checking the parallelism of the body-cover flanges; cleaning of external surfaces, elimination of smudges;
control of the presence of lubrication in the electric drive gearbox (in accordance with the ED of the electric drive);
-checking 100% of the degree of opening or closing of the valve along the height of the spindle relative to the base parts of the body;
-visual check of the condition of the electric drive and supply cables; checking the condition and fastening of the motor terminals;
- checking the fastening, tightness of the protective cover of the armature spindle;
- release of excess pressure from the valve body at an ambient temperature above 30 °C.
- cleaning of external surfaces, elimination of smudges.
Checking the tightness of the gate valve gate is carried out through a drainage pipeline or pressure valve and is combined with maintenance.
Checking the tightness of the wedge gate valves is combined with the maintenance. Information about the maintenance of T01 is entered in the passport (form).
Typical scope of work for seasonal maintenance (TO 2) of valves
Maintenance of TO 2 is carried out in preparation for the autumn-winter and spring periods of operation.
During the maintenance of TO 2, all the operations of TO 1 are carried out, as well as:
For valves:
checking (testing) for full opening, closing of the valve gate in the local control mode;
checking the operation of limit switches, their revision; checking the setting of the torque limiting clutch;
checking the smoothness of movement of all moving parts of the valve; replacement (control) of the lubrication in the electric drive (lubrication must correspond to the seasonal temperature parameters of the given region); checking the protection of the electric motor against overloads and phase imbalance;
checking (testing) for full opening, closing of the valve gate in the telecontrol mode;
checking the spindle thread for damage; checking the straightness of the retractable part of the spindle;
removal of water from the gate space through the drain pipeline of the gate valve;
checking and draining the condensate from the spindle guard.
Maintenance of the valve electric actuator is carried out in accordance with the "Instructions for the operation and maintenance of the electric actuator".
Information about the carried out seasonal maintenance T02 is entered in the passport (form).
Seasonal maintenance (TO 2) is carried out during scheduled shutdowns of the linear part of the oil pipeline and at disconnected sections of the process oil pipelines of the PS.
Plumbing
§ 22. Revision and grinding of valves
The revision of the reinforcement consists in its disassembly
and inspection of the locking working body and seal
stuffing box. Depending on the design and purpose
fittings identify the need for replacement
sealing material in the locking body or lapping
individual details. If the stuffing box
insufficient, it should be sealed or replaced with a new one.
In order to through the shut-off valve at
completely closed working body, water did not pass, it is necessary
install a gasket under the working body.
Lapping of fittings. Reach full
shut-off valves intended for steam
and gas, as well as valves, it is possible through mutual
lapping of adjacent parts. Lapping of parts is performed
grinding materials by hand or on
special fixtures.
Used as abrasives
lapping powders and pastes, while the grains of the powders
must pass through a mesh with holes with a diameter
0.15 mm. In some cases, lapping is used
glass dust. Lapping powders and pastes
selected depending on the hardness of the rubbed
surfaces. For rough grinding of cast iron and bronze
surfaces use brown-gray emery
powder.
Pastes are made from powder - 70-80% (according to
mass) and paraffin - 30-20%.
For preliminary lapping of hard and viscous
metals use corundum powder from gray to
Brown. For the final touch
lapped sealing surfaces use paste
GOI, which consists of chromium oxide, stearin and silicon
gatel. GOI paste is produced in three varieties: coarse -
black, medium - dark green,
thin - light green.
For lapping the cork, the body of the cork valve for
fastened in a vice. The cork is then covered
grinding material, inserted into the body, put on it
crank and turn the cork into one and the other
side by 180°. In this case, the cork is periodically raised.
Lapping is carried out until the cork is completely
surface will not fit snugly into the socket.
The correctness of lapping is checked as follows
The surface of the cork and body is wiped dry. Then
draw a line on the cork with chalk, after which the cork
inserted into the body and turn it several times in
one and the other side. If the chalk line evenly
will be erased over the entire surface, which means the cork is lapped
right. The final grinding is checked by pressing
scoop with water or air pressure,
1. Supervision, maintenance and revision of gate valves
During the operation of pipelines
one of the main responsibilities
service personnel is
constant and careful monitoring of
condition of the outer surface
pipelines and their details (welded
seams, flange connections, including
fixture. pipe fittings)
anti-corrosion protection and insulation,
drainage devices, compensators,
supporting structures, etc.
The main method of monitoring reliable
and safe operation of technological
piping is periodic
audit carried out by the service
technical supervision together with
mechanics, supervisors and installations
(productions).
The results of the audit serve as the basis
to assess the condition of the pipeline and
possibility of its further exploitation.
As a rule, the revision of pipelines
should be timed to
scheduled preventive maintenance
pipeline fittings, individual
units, installations or workshops. Timing
inspection of pipelines during
pressure up to 10 MPa (100 kgf/cm2)
set by the administration
enterprises depending on the speed
corrosion and erosion wear
pipelines, operating experience,
the results of the previous outdoor
inspection, revision. Deadlines should provide
safe, trouble-free operation
pipeline between revisions
.
For high pressure pipelines
[over 10 MPa (100 kgf/cm2)] installed
following types of revision:
selective, general selective and
complete. Timing of selective audit
set by the administration
enterprises depending on the conditions
operation, but at least once a
4 years .
Technological fittings
pipelines - the most responsible
element of communication, therefore, should
necessary measures to be taken
organization of constant and thorough
supervision over the serviceability of fittings, and
also for timely high quality
carrying out inspections and repairs.
Revision and repair of pipeline fittings,
including non-return valves, as well as
actuating devices of fittings (electro-,
pneumatic, hydraulic, mechanical
drive) is usually produced in the period
pipeline revisions. Audit and repair
fittings should be produced in
specialized workshops or
repair areas. In some cases
at the discretion of technical supervision
revision of reinforcement is allowed by its
disassembly and inspection directly on
installation site (welded fittings,
large, inaccessible and
etc.). When inspecting valves, they must be
the following work has been done:
a) external examination;
b) disassembly and inspection of the condition of individual
details;
c) inspection of the inner surface and, when
the need for non-destructive control
methods;
d) lapping of sealing surfaces;
e) assembly, testing and pressure testing on
strength and density.
When planning revisions and repairs
fittings should and in the first place
inspect and repair fittings,
working in the most difficult conditions
while observing the principle of alternation.
Reinforcement repair and test results
formalized by act.
—
CAUTION 3
ÐÑе ÑабоÑÑ Ð¿Ð¾ Ñевизии Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° ´ÐºÐµ.
a
ÐÐ»Ñ Ð¾Ð¿ÑÐµÐ´ÐµÐ»ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ð¾Ð±Ñема Ñевизии ÐμÐμÐ Ð Ð ÐμÐÐðвРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРоñññññññññññññññññññññ
a
ROOM SHEETS Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ
a
|
оððððððμμ¿¿²²²μððððð²²²μññ½ððñññμμñ ,ñ½ðññðÐμðμ'''μμð ½ððð »¹ ¹¹... - 20 Ð Ð Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ±ÑаÑнÑÑÑклкпанов. 1 — пÑиÑиÑ. 2 — напÑавл ÑÑÑий ÑÑÑÐо —½.°Ðк. ÑаÑелоквенÑилей a |
еÑение об оÑказе Ð¾Ñ Ð¿ÐµÑвиÑной Ñевизии аÑмаÑÑÑÑ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμñðññ¾¾¾³¾¾¿¿¿ñðð ° ° ¸¸¸ññññññ ° ° ° Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μ Ð Ð μ Ð Ð ² 100%
a
ÐÑе ли Ñевизии.
a
LOCK PLAYERS LOCK ENGLISH EUNCH PLAYERS Ñевизии и ÑÐанÑевÑÑÑÑоединений без наÑÑÑÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ ÐµÐµ ÑеÐоооооооо
a
LCD Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ñевизии и ÑанÑевÑÑÑоединений без наÑÑÑÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ð¸Ñ ÑелѾнннн
a
LOCK PLAYERS LOCK ENGLISH EUNCH PLAYERS Ñевизии и ÑÐанÑевÑÑÑÑоединений без наÑÑÑÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ ÐµÐµ ÑеÐоооооооо
a
back Ñевизии Ð · Ð Ð Ð · · Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ñ Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ½ Ñи ÑÑÑбопÑоводов ÑлоÑа.
a
RO RO ROCK ONLAGE ROUND Ñевизии, оÐμððððð𺺲²ºººººººººººººÐ¾Ð½ðнÐμÐμÐðоÐðÐμÐμÐðÐðоÐðÐ °ÐðÐÐðÐðÐðÐ °ÐÐðкР°Ð °ÐðÐðÐðиР°Ð °Ððккииии ¿ÑовеÑки аÑмаÑÑÑÑ.
a
Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð'¾ð¾¾¾¾¾ññññññ¾ñ¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾²¾¾ SHEETS иÑепежа.
a
Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ñ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ññ¾ð¸ñðððððððððððððððð SHEETS иÑепежа.
a
Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð'¾ð¾¾¾¾¾ññññññ¾ñ¾¾¾¾¾¾¾¾²¾¾ SHEETS иÑепежа.
a
Run. ñðμμððñμμμμ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ¿Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μ SHEETS, оμð½½½¸¸¸¸¸¸¸μμ½½ð𸸸μμμμÐðμ²²² ° ° ° РРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРо · Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμðð¹ °ððÐð¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹¹
a
List of works carried out during the overhaul of the heating network
1. Channels, chambers and supports of above-ground laying
1.1. Restoration of damaged or replacement of unusable building structures, channels, chambers, manholes, pavilions and supports of above-ground gaskets.
1.2. Restoration of damaged ones, replacement of worn-out ones or laying of additional drainages from chambers and channels, as well as associated drainages to lower the groundwater level in existing networks.
1.3. Full or partial change of waterproofing of channels and chambers.
1.4. Restoration or replacement of movable and fixed supports, as well as systems of fastening pipelines for above-ground laying, on overpasses and artificial structures (bridges, overpasses).
1.5. Opening and cleaning of channels from silting with the restoration of insulation.
1.6. Change of metal stairways in chambers and overpasses or more than 50% of running brackets.
1.7. Changing hatches.
2. Pipelines, fittings and equipment for heating networks and pumping stations
2.1. Replacement of pipelines that have become unusable with an increase, if necessary, in the diameter of pipes (by no more than two standard sizes), the use of compensators, valves and other devices of more advanced designs, more advanced types of heat-insulating structures, as well as deviations, if necessary, from the existing routing.
2.2.Full or partial replacement of thermal insulation, restoration and re-application of anti-corrosion coating and waterproofing on existing pipelines.
2.3. Replacement or installation of additional valves or other shutoff valves, compensators and fittings or their repair with the replacement of worn parts.
2.4. Replacement of worn-out control and safety fittings and automatic devices, means of automation, telemechanics and communication or repair with the change of the main worn parts.
2.5. Change or repair with the change of parts of electric, electromagnetic, hydraulic and other drives of valves, autoregulators, pumps, fans, as well as starting equipment for them.
2.6. Change or repair with the change of parts of power and lighting equipment and working lighting cabinets in chambers, channels, collectors, pavilions, at overpasses and pumping stations.
2.7. Change and repair with the change of parts of pumps, mud collectors, steam traps, storage tanks and other thermal mechanical equipment of pumping and accumulator stations.
2.8. Repair, retrofitting and replacement of heat shields and heat measuring instruments.
2.9. Repair with the change of unusable parts and the construction of devices for protection against electrochemical corrosion on existing networks.
2.10. Elimination of valve distortions resulting from pipeline settlement during channelless laying, associated with the overcooking of pipeline structures (compensators, flange joints, branches) or supports.
2.11. Cleaning the inner surface of pipes and thermal mechanical equipment from scale and corrosion products by mechanical or chemical means.
Publications on the topic of the article
| Directory. Heating network | Heat supply: as-built documentation, quality control, acceptance and commissioning | Directory of housing and communal services |
| Directory. Heating and heat supply | Library of a specialist in plumbing and sewerage | Executive documentation in housing and communal services: Acts |
| Job descriptions in housing and communal services | Housing Management Specialist Library | Executive documentation in electrical engineering (electrical installations; communication lines; security systems; electrical work) |
Article views: 14976 from 09/03/2009