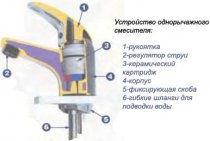
Design of the internal drainage system
Internal drainage systems from a residential building are designed to drain domestic wastewater from sanitary appliances to the yard, and then to the city drainage network.
The internal drainage network consists of sanitary appliances (washbasins, sinks, bathtubs, toilet bowls, etc.), outlet pipelines connected to the water seals (siphons) of the risers, exhaust part, outlets, cleaning devices.
Discharge pipes are used to drain waste liquid from sanitary appliances. They are laid straight along the walls above the floor with a slope of 0.03 (at d = 50 mm) and 0.02 (at d = 100 mm) towards the riser. The diameters of the outlet pipes are accepted depending on the type of devices attached to them. Outlet pipelines from toilet bowls are taken 100 mm, from other devices - 50 mm. Outlet pipes are connected to the risers of the drainage system using fittings (tees, crosses). Two-way connection of outlet pipes from baths to one riser at one mark is allowed using oblique crosses. In basements, crosses and oblique tees should be accepted. It is not allowed to use straight crosses in a horizontal plane. Hydraulic seals are designed to prevent the ingress of gases from the drainage system into the premises. They are installed under sanitary appliances.
The risers transporting wastewater from the outlet pipelines to the lower part of the building are placed openly in the bathrooms near the wastewater receivers, near the walls or in the niches of the internal walls of the building, next to the cold water riser. For two adjacent sanitary facilities, one riser of the drainage system is arranged, and in sanitary cabins (in panel buildings), one per cabin. Over the entire height, the risers must have the same diameter, equal to the largest diameter of the floor outlet or outlet pipe of the attached wastewater receiver (the toilet bowl has the largest diameter of the outlet pipe with a diameter of 100 mm).
The network of the domestic internal drainage system, which discharges wastewater into the external network, must be ventilated through risers, the exhaust part of which is led through the roof to a height of 0.3 m from the flat unexploited roof. Connection of the exhaust network of drainage risers to ventilation systems and chimneys is prohibited. The diameter of the exhaust part of the riser is equal to the diameter of the waste part of the riser.
The drainage riser in the lower part passes into the outlet, which serves to drain the waste liquid into the yard network. The outlet diameters are taken equal to the largest diameters of the risers (100 mm).
The number of outlets from one building is usually taken equal to the number of entrances in the building. Drainage outlets should, if possible, be located on one side of the building perpendicular to the outer walls. The minimum depth of the outlet laying is determined by:
depending on the freezing of the soil (the bottom of the pipe is laid above the freezing limit by 0.3 m);
taking into account the mechanical strength of the pipes (0.7 m to the top of the pipe).
Outlets should be connected to the outdoor network at an angle of at least 90 (counting from the movement of wastewater). The shortest length of the outlet pipe from the outer wall to the manhole in dry soils is 3 m, in wet soils - 5 m.
To eliminate blockages in the drainage network, it is necessary to provide devices for cleaning (revision and cleaning). Revisions serve to clean the network in both directions and are a hatch in a pipe with a lid and a rubber gasket. Cleanings allow you to clean the pipe in only one direction, they are made in the form of an oblique tee 45 and a branch 135 or two branches 45, the socket is closed with a plug.
Revisions or cleanings include:
on risers, if there are no indents on them, in the lower and upper floors, and if there are indents, also on the floors above the indents;
in residential buildings with a height of five floors or more - at least every three floors;
at the beginning of the outlet pipe sections with three or more connected devices, under which there are no cleaning devices;
on the turns of the network, (cleaning - before turns, revisions - before or after turns).
Sewer systems
Under the sewerage system, it is customary to understand the joint or separate disposal of wastewater of all three categories. In practice, common and separate sewerage systems are most widely used.
Common sewerage systems are called sewerage systems in which all wastewater: domestic, industrial and rainwater is fused through one common network of pipes and channels outside the urban area to treatment facilities.
Sewerage systems are called separate, in which rain and conditionally clean industrial water is discharged through one network of pipes and channels, and domestic and contaminated industrial wastewater through another, one or more networks.
A sewer network designed to receive and discharge atmospheric water is called a rain (storm) or drain.
If practically clean, uncontaminated industrial wastewater is discharged into the rain sewer, then it is called industrial rainwater.
A network designed to receive and discharge domestic water is called domestic.
Production is called the sewer network of an industrial enterprise, designed to receive and discharge only polluted industrial wastewater; industrial and domestic - a network designed to receive and discharge jointly industrial and domestic wastewater.
A separate sewerage system may be complete or incomplete.
A complete separate system is called a system that includes two or more completely independent sewer networks: a network through which only rain or rain and conditionally clean industrial water is drained; a network for the removal of domestic and part of the contaminated industrial waters allowed to be discharged into the domestic sewer; a network through which polluted industrial waters are discharged, which are not allowed for joint discharge with domestic ones.
Incomplete separate is called a system of sewer networks, provided for the removal of only the most polluted industrial and domestic wastewater; Atmospheric water in this system flows into the water channels through the cuvettes of driveways, open flumes, ditches and thalwegs.
Varieties of the combined and separate systems are semi-separate and combined sewer systems.
A semi-separated sewerage system consists of the same independent sewer networks as a complete separate system, and one main (intercepting) collector that diverts domestic, industrial, melt water, street washing water and part of the most polluted rainwater to the treatment plant.
Combined sewerage systems are such systems in which in some areas of the city an all-alloy system has been preserved, in others - a complete separate system, in others - an incomplete separate system.
The key to success Finding a company that specializes in the development of projects Water supply and sanitation
Full range of works:

The design organization fully assumes all obligations for the collection of initial data and the development of the V&V scheme.
- Specialists of the design organization, together with the customer, collect the initial data.
- Implementation of the Report in accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 5, 2013 N 782 "On water supply and sanitation schemes" Procedure for the development and approval of water supply and sanitation schemes.
- Face-to-face defense of Preliminary decisions.
- Face-to-face defense at public hearings.
It is rational in the implementation of city schemes and schemes of municipal districts with a large number of small settlements.
Remote development of ViV Scheme:

The design organization provides the customer with requests and questionnaires for filling out, provides remote support for the collection of initial data and protection of the decisions made.
Implementation of the Report in accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 5, 2013 N 782 "On water supply and sanitation schemes" Procedure for the development and approval of water supply and sanitation schemes.
Remote protection Preliminary decisions, via videoconference.
Remote protection at public hearings, via videoconference.
Rational in the implementation of schemes of small settlements, in order to optimize costs.
The choice of materials for the installation of a linear drainage system
When choosing trays for installing a surface drainage system, it is necessary to take into account the purpose of the site along which they will run. Where cars will pass, concrete trays with reinforcement and galvanized plates will have to be used. In pedestrian areas, it is possible to replace concrete products with plastic structural elements.
Some owners of estates are trying to save money on buying ready-made channels, produced in the factory in accordance with the requirements of building codes, and cast them on their own in the ground. You should not do this, since it is difficult to compete with the quality of finished reinforced concrete products. At the same time, the savings are not so great if we add to the cost of the materials necessary for preparing the solution the time for filling the channels and drying them.
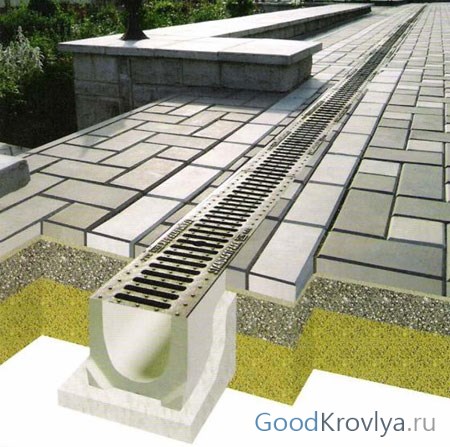

The water intake grate is selected based on the allocated budget and the load class recommended for private construction:
- A15 - in the areas of movement of pedestrians and cyclists;
- B125 - in parking lots intended for passenger vehicles and access roads.
The service life of the gratings depends on the material of manufacture. Cast iron grills are considered the most durable, because they serve 25 years. Almost half the service life of galvanized metal gratings is only 10 years. Well, polymer gratings will have to be changed in five years, since they are designed for this period of use. Usually ready-made trays are sold together with grills in the kit, and the price of concrete products is more expensive than plastic ones.
Important points of drainage systems
It is very important these days to remember the future, because if you save on various accessories and building materials, in the future you can pay much more money to repair failed structures. Indifference to water disposal in residential premises very often causes many problems.
For example, without proper sewerage, if water gets into the ground, the foundations of buildings often settle, cracks form on the surfaces of the facades, mold appears on the walls and a number of other unpleasant phenomena. In the same way, without a well-planned external drainage system, the coating in the yard quickly collapses, grassy lawns are eroded, which can sometimes even lead to the death of trees and flowers. To the greatest extent, such phenomena are observed in the private sector, when the house is surrounded by a fence with a concrete foundation, which prevents the rapid and free outflow of water from the territory. As a result, water in the soil and on its surface stagnates for a long time.
Recommendations for choosing drainage systems
It is recommended that drainpipes that drain melt and rain water from the roof slopes be connected to a common sewer system, which will significantly reduce the amount of rain and melt water in the yard.After all, it is known that the miser pays twice, and this rule is no exception for drainage systems. Otherwise, in the near future it will be necessary to completely repair the entire surface of the yard and restore the damaged basement of the building, which will result in a substantial sum of money.
Drainage and drainage systems will reliably protect your home from excessive moisture, help to significantly extend the life of the yard cover and all structures located in the yard. The drainage systems that were used in the twentieth century have completely lost their relevance due to low efficiency. And today, the installation of reliable modern high-tech drainage systems is already a common necessity in order to increase the comfort of living in a house. You can even install drainage trays in the yard of your own house, but it is better to seek help from specialists who have professional skills and are able to develop a draft drainage system for any territory, taking into account its specifics. Qualified craftsmen will select the most effective consumables and elements for installation, determining the total cost of materials and work.
Legislative basis for the development of V&V Schemes
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of September 5, 2013 N 782 Moscow "On water supply and sanitation schemes" Procedure for the development and approval of water supply and sanitation schemes.
- Federal Law of December 07, 2011 No. 416-FZ "On Water Supply and Sanitation";
- Urban Planning Code of the Russian Federation;
- Federal Law of October 06, 2003 No. 131-FZ “On the General Principles of Organization of Local Self-Government in the Russian Federation”;
- Federal Law of July 27, 2010 No. 190-FZ "On Heat Supply";
- Federal Law No. 210-FZ dated December 30, 2004 “On the Basics of Tariff Regulation of Public Utilities Organizations”;
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 14, 2013 No. 502 “On approval of requirements for programs for the integrated development of communal infrastructure systems in settlements, urban districts”;
- Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation dated October 10, 2007 No. 99 “On Approval of Methodological Recommendations for the Development of Investment Programs for Public Utilities Organizations”;
- Order of the Ministry of Regional Development of the Russian Federation dated May 06, 2011 No. 204 “On the development of programs for the integrated development of municipal infrastructure systems in municipalities”.
Existing systems and schemes of water disposal
Sewerage is one of the types of engineering equipment and improvement of settlements, residential, public and industrial buildings, providing the necessary sanitary and hygienic conditions and a high level of amenities for work, life and recreation of the population.
Sewerage is understood as a set of equipment, networks and structures designed for the organized reception and removal of polluted wastewater through pipelines outside settlements or industrial enterprises, as well as for their purification and neutralization before disposal or discharge into a reservoir.
Sewerage according to its purpose is divided into internal and external. Internal sewerage is used to receive wastewater in the places of their formation and divert these effluents outside the building into the external sewer network. External sewerage is used to transport wastewater outside the settlement or industrial enterprises to treatment facilities. Treatment facilities serve to neutralize wastewater, release treated water into a reservoir without disturbing its natural state and treat sludge for its further disposal.
Depending on the origin, type and quality characteristics of impurities, wastewater is divided into three main categories: domestic (domestic), industrial (industrial) and rain (atmospheric).
Schemes of courtyard, intra-quarter and street sewerage networks
After collection by internal devices, wastewater enters the yard sewer network. It can be either a combined system for all wastewater, or a separate system (for domestic and storm drains).Such a network serves one or more houses and structures within the yard. If the drainage system receives runoff from several yard networks located in the same block, then it is called intra-quarter.

Fig 02 - Scheme of yard and intra-quarter sewerage networks
At the end of the intra-quarter network, a control well is arranged, after which the drainage branch is connected to the street network. It collects drains from several intra-quarter networks located along the street. The section from the control well to the street network is called the connecting branch.
Schemes of water disposal of settlements
There are several generally accepted schemes for the drainage of settlements. They are designed during the development of the city, and they are also formed historically - as districts and enterprises join the city. They differ in the location of the collectors, the tracing of the main collector, the presence of structures.
The choice of a particular scheme depends on several objective factors:
- the location of the reservoir; if it is a river, then the direction of the flow of water in it, these factors affect the location of the installation of wastewater treatment facilities;
- topographic features of the territory; since networks are gravity and pressure, the location of pumping stations depends on the terrain;
- groundwater occurrence conditions and soil composition; this affects the depth of pipelines and collectors, the presence and location of pumping stations;
- features of the planning of the city or enterprise;
- the number of sewerage networks (when using a separate drainage system).
Share such generally accepted schemes of sewerage networks:
- zone;
- radial;
- fan (parallel);
- perpendicular;
- crossed.
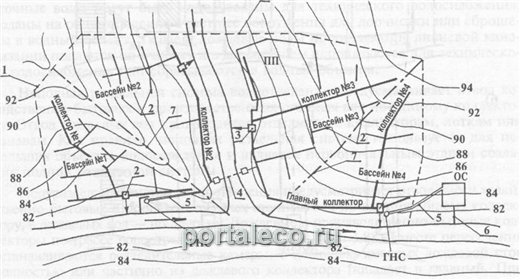
The crossed layout of drainage networks is widely used in such a relief, in which the service area decreases towards the river. In this case, the collectors are laid perpendicular to the direction of the river flow, and the main collector is parallel to the coastline. Effluent flows through it to the treatment plant. This scheme is sometimes used in the reconstruction of old systems.

Figure 03 - Drainage schemes of settlements
With a perpendicular scheme, all collectors from the sewage pools are laid perpendicular to the shoreline of the reservoir - the shortest route. Parallel, or fan - collectors are placed in parallel or at some angle to each other. Drains from them are reduced to the main collector, which is laid perpendicular to the reservoir. Often such a scheme is used with a steep slope of the territory to the river.
The radial drainage scheme is designed to drain sewage from different areas and territories of the settlement by independent systems. With a parallel (fan) scheme, which is often used for uneven (hilly) terrain, the settlement is divided into zones for which separate systems are arranged. The sewer collector of the lower zone is arranged as a pressure collector to the main collector, and then all the effluents enter the treatment plant and are discharged into the reservoir.
| We work throughout Russia | Contacts. Tel/fax + 7(812) 627-93-38; info@dc-region.ru |
- Terms of use
- Personal data processing policy
Water disposal systems.
The drainage system, also called the sewer system, includes the following main elements: internal drainage systems in residential buildings or industrial premises; intra-quarter or intra-site drainage networks; external (off-site) drainage networks; control tanks; pumping stations and pressure pipelines; treatment facilities; releases of treated wastewater into water bodies; emergency discharges of sewage into water bodies. Drainage systems are divided into general alloy, separate and combined.In turn, separate systems are divided into complete separate, incomplete separate and semi-separate.
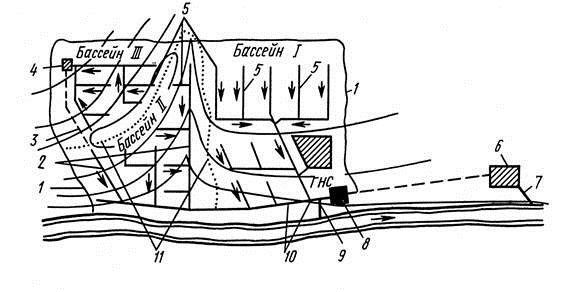
The general alloy drainage system has one drainage network designed to drain waste water of all categories: household, industrial and rainwater (Fig. 3.6). Storm outlets can be arranged along the length of the main collector of the combined alloy system for direct discharge into the river of part of the runoff passed through the drainage system. This is done in order to reduce the size and number of collectors at the end of the system and reduce its cost accordingly.
Rice. 3.6. Alloy water disposal scheme:
RNS - district pumping station; GNS - main pumping station; OS - treatment facilities; PP - industrial enterprise
1 - the border of the city; 2 - external (external) drainage network of pipelines; 3 - storm outlets; 4 - siphon; 5 - pressure pipelines; 6 - release of treated wastewater; 7 - watershed lines
Storm outlets are arranged in such a way as to exclude the possibility of overflowing the main collector during heavy rain. The design and placement of storm outlets ensure their inclusion in the work, i.e. discharge of water into the river, not earlier than 30 minutes after the start of an intense downpour. During this time, the most polluted part of the surface runoff from the urban area through the combined collector enters the city treatment facilities, and the less polluted part, when the main collector is filled, will begin to flow directly into the river. It is clear that the release of untreated wastewater into the river is associated with its possible pollution. Therefore, the dimensions of the outlets of storm outlets and, accordingly, the flow rate of untreated water discharged through them are determined based on the assimilating capacity of the watercourse. The use of a combined water disposal system is advisable if there is a full-flowing river in the city.
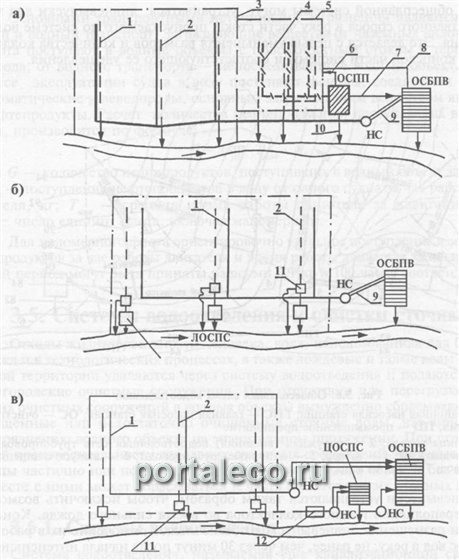
A complete separate sewerage system has two or more collectors designed for separate disposal of wastewater of a certain category (Fig. 3.7).
Rice. 3.7. Complete separate drainage system:
a - without treatment of surface runoff; b and c - with treatment of surface runoff, respectively, at local and centralized treatment facilities;
OSBPV - treatment facilities for domestic and industrial water; OSPP - treatment facilities of an industrial enterprise; LOSPS - local treatment facilities for surface runoff; TsOSPS - centralized treatment facilities for surface runoff; NS - pumping station;
1 - household network; 2 - storm network; 3 - city boundary; H - production network; 5 - the boundary of an industrial enterprise; 6 - return of water to production after cleaning; 7 - water supply for post-treatment to the city's wastewater treatment facilities; 8 - supply of purified water to an industrial enterprise; 9 - pressure pipelines; 10 - release of treated industrial wastewater into the reservoir; 11 - separation chambers; 12 - regulating ozeovouao
Water disposal systems and schemes
Material content
-
Water disposal systems and schemes
-
Schemes of sewerage of settlements and its elements
-
Drainage network routing
-
Types of pipes and laying the drainage network
-
Structures on the network
-
Sanitation rates, non-uniformity coefficient and determination of estimated wastewater costs
-
Hydraulic calculation of the drainage network
-
Laying of sewerage pipelines at the intersection with underground pipelines, crossings over obstacles
-
Laying a drainage network in the places of construction of transport and pedestrian tunnels
-
All pages
Waste water classification
As a result of the use of water by a person in everyday life and in production and during the transportation of waste, it changes its physical and chemical properties and forms a waste liquid.
According to the origin and nature of pollution, all wastewater from cities and towns, as well as industrial enterprises, can be divided into three groups: domestic (household and fecal); industrial, atmospheric (rain).
Domestic wastewater is generated from water coming from sinks, washbasins, bathtubs, taps, as well as from baths, laundries, showers and water from washing floors (household water). The bulk of pollution is organic matter of plant and animal origin, containing biogenic elements such as: carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, etc.
Industrial wastewater is extremely diverse in composition and concentration of contaminants. Industrial wastewater pollutants are waste and production losses.
According to their composition, industrial wastewater can be divided into three groups: containing predominantly mineral pollution, organic compounds, mixed pollution (organic and mineral).
Atmospheric (rain) waters are formed from rain (or melting snow) and are polluted with waste on the surface of a city or industrial enterprise.
Atmospheric wastewater in cities, as a rule, contains mineral, organic pollution.
Under the drainage system of a settlement is meant a complex of structures designed for the disposal of wastewater and their treatment (Fig. 1.).
Rice. 1. City sewerage system:
1 - city boundary; 2 - collectors; 3 - pressure pipeline; 4 - pumping station; 5 - street network; 6 - treatment facilities; 7 - release into the reservoir; 8 - main pumping station; 9 - emergency release; 10 - main collector; 11 - boundaries of sewerage basins.
The drainage system consists of the following main elements: internal drainage devices of buildings, external drainage network, pumping stations, pressure conduits, treatment facilities wastewater and sludge disposal and releases into the reservoir.
Internal drainage devices of buildings are designed to receive wastewater and discharge it outside the building. The devices consist of appliances (sinks, washbasins, sinks, bathtubs, toilet bowls, urinals, drains, etc.), from a network of discharge pipes, risers and outlets to the yard drainage network.
An external drainage network is a network of pipelines that drain wastewater by gravity to pumping stations or treatment facilities. Depending on the purpose and place of laying, there are: an intra-quarter network that receives wastewater from individual buildings and is laid within the quarter; a street drainage network that receives wastewater from intra-quarter yard networks and laid along street driveways. The street network is connected by one or more collectors.
A drainage network located within one courtyard area and combining outlets from individual buildings is called a courtyard network.