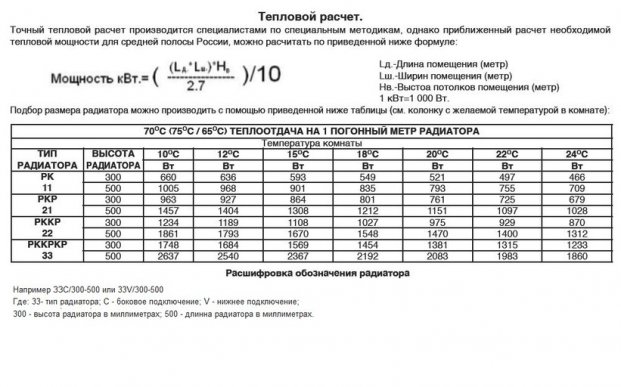
Standard calculation of heating radiators
According to building codes and other rules, you need to spend 100W of your radiator power per 1 square meter of living space. In this case, the necessary calculations are made using the formula:
K - the power of one section of your radiator battery, according to its characteristics;
C is the area of the room. It is equal to the product of the length of the room and its width.
For example, a room is 4 meters long and 3.5 wide. In this case, its area is: 4 * 3.5 = 14 square meters.
The power of one section of the battery you have chosen is declared by the manufacturer at 160 watts. We get:
14*100/160=8.75. the resulting figure must be rounded up and it turns out that such a room will require 9 sections of a heating radiator. If this is a corner room, then 9 * 1.2 = 10.8, rounded up to 11. And if your heating system is not efficient enough. then once again add 20 percent of the original number: 9*20/100=1.8 is rounded up to 2.
Total: 11+2=13. For a corner room with an area of 14 square meters, if the heating system works with short-term interruptions, you will need to purchase 13 battery sections.
Volume calculation
If you make such calculations, then you will need to refer to the standards established in SNiP. They take into account not only the performance of the radiator, but also what material the building is built from.
For example, for a brick house, the norm for 1 m2 will be 34 W, and for panel buildings - 41 W. To calculate the number of battery sections by the volume of the room, you should: multiply the volume of the room by the heat consumption rates and divide by the heat transfer of 1 section.
- To calculate the volume of a room with an area of 16 m2, you need to multiply this figure by the height of the ceilings, for example, 3 m (16x3 = 43 m3).
- The heat rate for a brick building = 34 W, to find out what amount is required for a given room, 48 m3 x 34 W (for a 41 W panel house) = 1632 W.
- We determine how many sections are required with a radiator power, for example, 140 watts. For this, 1632 W / 140 W = 11.66.
Rounding this figure, we get the result that for a room with a volume of 48 m3 an aluminum radiator of 12 sections is required.
Accurate calculations with many parameters
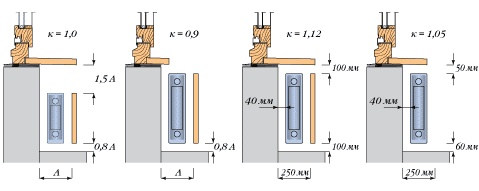
- The final formula, for a corner room, should have an additional multiplier of 1.3.
- If the house is not located in the middle zone of the country, an additional coefficient is described by the building codes of this territory.
- It is necessary to take into account the installation location of the bimetallic radiator and decorative elements. For example, a niche under the window will take 7%, and a screen up to 25% of the thermal power of the battery.
- What will the room be used for?
- Wall material and thickness.
- What are the frames and glass.
- Door and window openings introduce additional problems. Let's dwell on them in more detail.
Walls with windows, street and doorways, change the standard formula. It is necessary to multiply the resulting number of sections by the heat transfer coefficient of the room, but it must first be calculated.
This indicator will be the sum of the heat transfer of the window, doorway and wall. All this information can be obtained by contacting the SNiP, according to your type of premises.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=nSewFwPhHhM
Rooms with standard ceiling heights
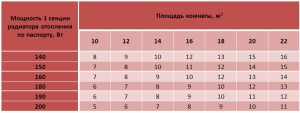
The calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators for a typical house is based on the area of the rooms. The area of a room in a typical house is calculated by multiplying the length of the room by its width. To heat 1 square meter, 100 watts of heater power is required, and to calculate the total power, you need to multiply the resulting area by 100 watts. The value obtained means the total power of the heater. The documentation for the radiator usually indicates the thermal power of one section. To determine the number of sections, you need to divide the total capacity by this value and round the result up.
A room with a width of 3.5 meters and a length of 4 meters, with the usual height of the ceilings. The power of one section of the radiator is 160 watts.Find the number of sections.
- We determine the area of \u200b\u200bthe room by multiplying its length by its width: 3.5 4 \u003d 14 m 2.
- We find the total power of heating devices 14 100 \u003d 1400 watts.
- Find the number of sections: 1400/160 = 8.75. Round up to a higher value and get 9 sections.
You can also use the table:
Table for calculating the number of radiators per M2
For rooms located at the end of the building, the estimated number of radiators must be increased by 20%.
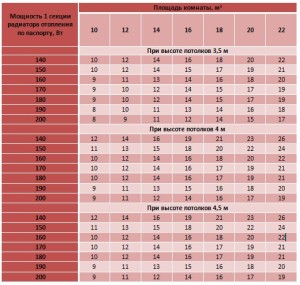
Rooms with a ceiling height of more than 3 meters
The calculation of the number of sections of heaters for rooms with a ceiling height of more than three meters is based on the volume of the room. Volume is the area multiplied by the height of the ceilings. To heat 1 cubic meter of a room, 40 watts of heat output of the heater is required, and its total power is calculated by multiplying the volume of the room by 40 watts. To determine the number of sections, this value must be divided by the power of one section according to the passport.
A room with a width of 3.5 meters and a length of 4 meters, with a ceiling height of 3.5 m. The power of one section of the radiator is 160 watts. It is necessary to find the number of sections of heating radiators.
- We find the area of the room by multiplying its length by the width: 3.5 4 \u003d 14 m 2.
- We find the volume of the room by multiplying the area by the height of the ceilings: 14 3.5 \u003d 49 m 3.
- We find the total power of the heating radiator: 49 40 \u003d 1960 watts.
- Find the number of sections: 1960/160 = 12.25. Round up and get 13 sections.
You can also use the table:
As in the previous case, for a corner room, this figure must be multiplied by 1.2. It is also necessary to increase the number of sections if the room has one of the following factors:
- Located in a panel or poorly insulated house;
- Located on the first or last floor;
- Has more than one window;
- Located next to unheated premises.
In this case, the resulting value must be multiplied by a factor of 1.1 for each of the factors.
Corner room with a width of 3.5 meters and a length of 4 meters, with a ceiling height of 3.5 m. Located in a panel house, on the ground floor, has two windows. The power of one section of the radiator is 160 watts. It is necessary to find the number of sections of heating radiators.
- We find the area of the room by multiplying its length by the width: 3.5 4 \u003d 14 m 2.
- We find the volume of the room by multiplying the area by the height of the ceilings: 14 3.5 \u003d 49 m 3.
- We find the total power of the heating radiator: 49 40 \u003d 1960 watts.
- Find the number of sections: 1960/160 = 12.25. Round up and get 13 sections.
- We multiply the resulting amount by the coefficients:
Corner room - coefficient 1.2;
Panel house - coefficient 1.1;
Two windows - coefficient 1.1;
First floor - coefficient 1.1.
Thus, we get: 13 1.2 1.1 1.1 1.1 = 20.76 sections. We round them up to a larger integer - 21 sections of heating radiators.
When calculating, it should be borne in mind that different types of heating radiators have different thermal output. When choosing the number of heating radiator sections, it is necessary to use exactly those values that correspond to the selected type of batteries.
In order for the heat transfer from the radiators to be maximum, it is necessary to install them in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations, observing all the distances specified in the passport. This contributes to a better distribution of convective currents and reduces heat loss.
- Consumption of diesel heating boiler
- Bimetal heating radiators
- How to calculate heat for home heating
- Calculation of reinforcement for the foundation
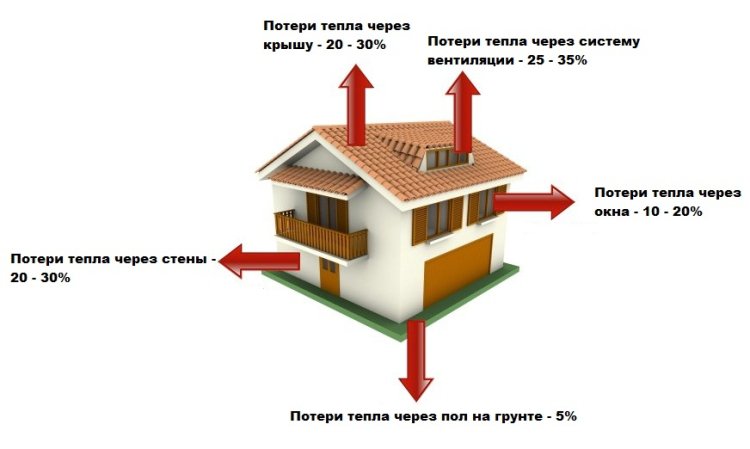
How to calculate heat losses for a private house and apartment
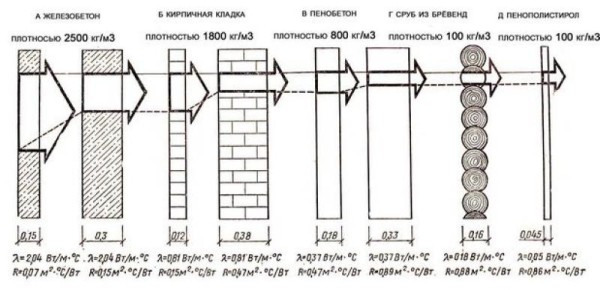
Heat leaves through windows, doors, ceilings, external walls, ventilation systems. For each heat loss, its own coefficient is calculated, which is used in calculating the required power of the heating system.
The coefficients (Q) are determined by the formulas:
- S is the area of a window, door or other structure,
- ΔT is the temperature difference between inside and outside on cold days,
- v is the layer thickness,
- λ is the thermal conductivity of the material.
All obtained Q are added up, summed up with 10-40% of thermal losses through ventilation shafts. The amount is divided by the total area of the house or apartment and added to the estimated capacity of the heating system.
When calculating the area of the walls, the sizes of windows, doors, etc. are subtracted from them. they are counted separately. The biggest heat losses are in rooms on the upper floors with unheated attics and basement levels with a conventional basement.
An important role in the normative calculations is played by the orientation of the walls. The greatest amount of heat is lost by the premises facing the northern and northeastern side (Q = 0.1). Appropriate additives are also taken into account in the described formula.
Battery types and features
Before calculating the number of batteries or sections of heating radiators per square meter for the area of a certain room in a private house or apartment, make sure that the selection of the device was correct and it really fits in your case. Let's take a look at their types briefly.
Aluminum
Aluminum radiators can be made from primary or secondary raw materials. The second ones are noticeably inferior in quality, but they are cheaper. The main advantages of aluminum batteries:
- high heat dissipation,
- light weight,
- Simple universal design,
- high pressure resistance,
- Low inertia (heat up and cool down quickly, which allows you to quickly adjust the temperature in the room),
- Moderate price (300-500 rubles per section).
Aluminum is sensitive to alkalis in the composition of the coolant, so the core is often covered with a layer of polymers, which increases the service life of the product. The main part of the models is made by casting, extrusion (extruded) sections are much less represented. Popular manufacturers. Sira, Global, Rifar and Thermal.
Bimetallic
Inside bimetallic radiators there is a steel or copper pipe, which is hidden behind an aluminum casing. Due to this, the radiator copes with high operating pressures, is less exposed to abrasive or alkaline impurities in the coolant. but at the same time retains high power, heat transfer and low inertia.
It does not require additional support during installation. You can mount it yourself.
The main disadvantage of cast iron products is their heavy weight, which complicates installation in a typical city apartment. Among the advantages:
- Large flow area, so that the battery continues to work well even in the presence of deposits,
- Keep warm for a long time
- Service life - 20-50 years,
- Stable operation at a pressure of 8-10 atm,
- Attractive retro design of cast iron sections.
According to the type of execution, radiators can be sectional, panel. lamellar or tubular. Sectional are most in demand, because. have protection against water hammer, can be easily disassembled for repair or understaffed with additional elements. They are environmentally friendly and provide good heat transfer and convection.
Calculation of sections of aluminum radiators per square meter
As a rule, manufacturers pre-calculated the power standards of aluminum batteries. which depend on parameters such as ceiling height and room area. So it is believed that in order to heat 1 m2 of a room with a ceiling up to 3 m in height, a thermal power of 100 watts will be required.
These figures are approximate, since the calculation of aluminum heating radiators by area in this case does not provide for possible heat loss in the room or higher or lower ceilings. These are generally accepted building codes that manufacturers indicate in the data sheet of their products.
Of considerable importance is the parameter of the thermal power of one radiator fin. For an aluminum heater, it is 180-190 watts.
The media temperature must also be taken into account.
It can be found in the thermal management, if the heating is centralized, or measured independently in an autonomous system.For aluminum batteries, the indicator is 100-130 degrees. Dividing the temperature by the heat output of the radiator, it turns out that 0.55 sections are required to heat 1 m2.
In the event that the height of the ceilings has "outgrown" the classical standards, then a special coefficient must be applied: if the ceiling is 3 m, then the parameters are multiplied by 1.05;
at a height of 3.5 m, it is 1.1;
with an indicator of 4 m - this is 1.15;
wall height 4.5 m - the coefficient is 1.2.
You can use the table that manufacturers provide for their products.
How many aluminum radiator sections do you need?
The calculation of the number of aluminum radiator sections is made in a form suitable for heaters of any type:
- S is the area of the room where the installation of the battery is required;
- k - correction factor of the indicator 100 W / m2, depending on the height of the ceiling;
- P is the power of one radiator element.
When calculating the number of sections of aluminum heating radiators, it turns out that in a room of 20 m2 with a ceiling height of 2.7 m, an aluminum radiator with a power of one section of 0.138 kW will require 14 sections.
Q = 20 x 100 / 0.138 = 14.49
In this example, the coefficient is not applied, since the ceiling height is less than 3 m
But even such sections of aluminum heating radiators will not be correct, since possible heat losses of the room are not taken into account. It should be borne in mind that depending on how many windows there are in the room, whether it is a corner room and whether it has a balcony: all this indicates the number of sources of heat loss
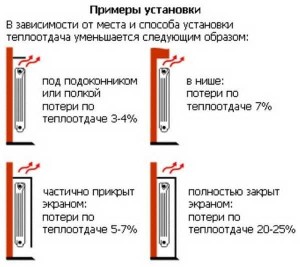
When calculating aluminum radiators by the area of the room, the percentage of heat loss should be taken into account in the formula, depending on where they will be installed:
- if they are fixed under the windowsill, then the losses will be up to 4%;
- installation in a niche instantly increases this figure to 7%;
- if an aluminum radiator is covered for beauty on one side with a screen, then the losses will be up to 7-8%;
- completely closed by the screen, it will lose up to 25%, which makes it, in principle, unprofitable.
These are not all indicators that should be considered when installing aluminum batteries.
Calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators analysis of 3 different approaches examples
The correct calculation of heating radiators is a rather important task for every homeowner. If an insufficient number of sections is used, the room will not warm up during the winter cold, and the purchase and operation of too large radiators will entail unreasonably high heating costs. Therefore, when replacing an old heating system or installing a new one, you need to know how to calculate heating radiators. For standard rooms, you can use the simplest calculations, but sometimes it becomes necessary to take into account various nuances in order to get the most accurate result.
Thermal power of 1 section
As a rule, manufacturers indicate average heat transfer rates in the technical characteristics of heaters. So for heaters made of aluminum, it is 1.9-2.0 m2. To calculate how many sections you need, you need to divide the area of \u200b\u200bthe room by this coefficient.
For example, for the same room of 16 m2, 8 sections will be required, since 16 / 2 = 8.
These calculations are approximate and it is impossible to use them without taking into account heat losses and real conditions for placing the battery, since you can get a cold room after installing the structure.
To get the most accurate figures, you will have to calculate the amount of heat that is needed to heat a particular living area. To do this, many correction factors will have to be taken into account. This approach is especially important when it is required to calculate aluminum heating radiators for a private house.
The formula needed for this is as follows:
KT = 100W/m2 x S x K1 x K2 x K3 x K4 x K5 x K6 x K7
- CT is the amount of heat that a given room requires.
- S is the area.
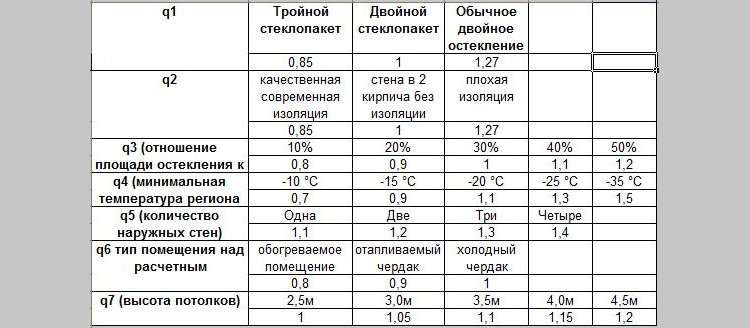
- K1 - coefficient designation for a glazed window. For standard double glazing it is 1.27, for double glazing it is 1.0, and for triple glazing it is 0.85.
- K2 is the coefficient of the level of wall insulation. For an uninsulated panel, it = 1.27, for a brick wall with one layer of masonry = 1.0, and for two bricks = 0.85.
-
K3 is the ratio of the area occupied by the window and the floor. When between them:
- 50% - the coefficient is 1.2;
- 40% — 1.1;
- 30% — 1.0;
- 20% — 0.9;
- 10% — 0.8.
-
K4 is a coefficient that takes into account the air temperature according to SNiP on the coldest days of the year:
- +35 = 1.5;
- +25 = 1.2;
- +20 = 1.1;
- +15 = 0.9;
- +10 = 0.7.
-
K5 indicates an adjustment in the presence of external walls. For example:
- when it is alone, the indicator is 1.1;
- two outer walls - 1.2;
- 3 walls - 1.3;
- all four walls - 1.4.
-
K6 takes into account the presence of a room above the room for which calculations are made. If available:
- unheated attic - coefficient 1.0;
- heated attic - 0.9;
- living room - 0.8.
-
K7 is a coefficient that indicates the height of the ceiling in the room:
- 2.5 m = 1.0;
- 3.0 m = 1.05;
- 3.5 m = 1.1;
- 4.0 m = 1.15;
- 4.5 m = 1.2.
If you apply this formula, then you can foresee and take into account almost all the nuances that can affect the heating of living space. Having made a calculation on it, you can be sure that the result obtained indicates the optimal number of aluminum radiator sections for a particular room.
If you decide to install aluminum heating radiators, it is important to know the following:
Whatever principle of calculation is undertaken, it is important to do it as a whole, since properly selected batteries allow not only to enjoy the heat, but also significantly save on energy costs. The latter is especially important in the face of ever-increasing tariffs.
Methods for assessing heat transfer
Before you buy heating batteries, consider ways to calculate the number of their elements.
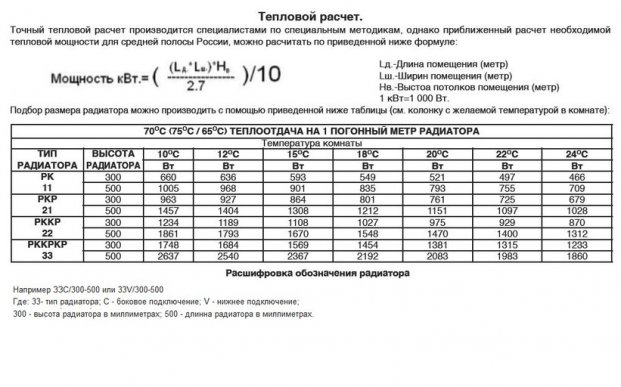
The first method is based on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room. Building regulations (SNiP) state that for normal heating, 1 sq. m. requires 100 watts. thermal power. By measuring the length, width of the room, and multiplying these two values, we get the area of \u200b\u200bthe room (S).
To calculate the total power (Q), we substitute into the formula, Q \u003d S * 100 W., our value. The passport for heating radiators indicates the heat transfer of one element (q1). Thanks to this information, we will find out the required number of them. To do this, we divide Q by q1.
The second way is more accurate. It should also be used with a ceiling height of 3 meters. Its difference lies in the measurement of the volume of the room. The area of \u200b\u200bthe room is already known, let's measure the height of the ceiling, then multiply these values. The resulting volume value (V) is substituted into the formula Q=V*41 W.
According to building codes 1 cu. m. should be heated by 41 watts. thermal power. Now let's find the ratio of Q to q1, getting the total number of radiator nodes.
Let's sum up the intermediate result, take out the data that will be needed for all types of calculations.
- wall length;
- wall width;
- Ceiling height;
- Norms of power, heating of a unit of area or volume of a room. They are given above;
- Minimum heat dissipation of the radiator element. It must be indicated in the passport;
- wall thickness;
- Number of window openings.
Standard calculation of heating radiators
According to building codes and other rules, you need to spend 100W of your radiator power per 1 square meter of living space. In this case, the necessary calculations are made using the formula:
K - the power of one section of your radiator battery, according to its characteristics;
C is the area of the room. It is equal to the product of the length of the room and its width.
For example, a room is 4 meters long and 3.5 wide. In this case, its area is: 4 * 3.5 = 14 square meters.
The power of one section of the battery you have chosen is declared by the manufacturer at 160 watts. We get:
14*100/160=8.75. the resulting figure must be rounded up and it turns out that such a room will require 9 sections of a heating radiator.If this is a corner room, then 9 * 1.2 = 10.8, rounded up to 11. And if your heating system is not efficient enough. then once again add 20 percent of the original number: 9*20/100=1.8 is rounded up to 2.
Total: 11+2=13. For a corner room with an area of 14 square meters, if the heating system works with short-term interruptions, you will need to purchase 13 battery sections.
Calculation example
If you calculate how many sections of an aluminum radiator you need for a room of 20 m2 at a rate of 100 W / m2, then you should also make adjustment coefficients for heat loss:
- each window adds 0.2 kW to the indicator;
- the door "costs" 0.1 kW.
If it is assumed that the radiator will be placed under the windowsill, then the correction factor will be 1.04, and the formula itself will look like this:
Q \u003d (20 x 100 + 0.2 + 0.1) x 1.3 x 1.04 / 72 \u003d 37.56
- the first indicator is the area of \u200b\u200bthe room;
- the second is the standard number of W per m2;
- the third and fourth indicate that the room has one window and one door each;
- the next indicator is the level of heat transfer of an aluminum radiator in kW;
- the sixth is a correction factor regarding the location of the battery.
Everything should be divided by the heat transfer of one heater fin. It can be determined from the table from the manufacturer, which indicates the heating coefficients of the media in relation to the power of the device. The average value for one fin is 180 W, and the adjustment is 0.4. Thus, multiplying these figures, it turns out that 72 W gives one section when heating water up to +60 degrees.
Since rounding is done up, the maximum number of sections in an aluminum radiator specifically for this room will be 38 fins. To improve the performance of the structure, it should be divided into 2 parts of 19 ribs each.
Find out useful information about aluminum batteries on our website:
Calculations of the number of sections by quadrature per room
The accuracy of the calculations depends on the number of factors taken into account. In general, they can be divided into three groups:
- The calculation by area is based on the assumption that at least 100 watts are needed to heat each square meter. That is, a room of 10 m2 needs a 1 kW radiator (about 7 sections). The figures are relevant for rooms with ceilings up to 2.6 m.
- Exact calculation involves taking into account the coefficients for all heat losses. The required number of sections for installing a heating radiator is calculated according to the following calculation formula - by multiplying 100 (watt / m2) by the area of \u200b\u200bthe room in m2 and by each coefficient (q).
The definition by volume gives approximately the same numbers as the formula for calculating the area. According to the recommendations of SNIP, the heat consumption in the living room of a panel house with wooden windows is 41 W per cubic meter. If there are modern double-glazed windows, the standard is reduced to 34 W per 1 m3. Heat consumption decreases for buildings with wide walls made of foam concrete, bricks, etc., as well as in the presence of high-quality thermal insulation.
How to calculate the number of sections and the estimated power of heating radiators? The simplest formulas:
N = S x 100 / P (excluding heat loss)
N = V x 41 W x 1.2 / P (including heat loss)
- N is the number of sections,
- P is the power of one section of the radiator,
- S is the area of the room,
- V - room volume 41W - heating power 1 m3,
- 1.2 - standard heat loss coefficient.
The heat transfer of the section for each specific model is indicated by the manufacturer on the edge of the product. On average, the figures are:
Metal at the base of the section
Average heat transfer rate of the section
To simplify all calculations, some specialized resources offer online calculators where you just need to enter the initial data and get the finished result in a second. How to independently calculate the number of sections of bimetallic heating radiators, read here.
Useful tips for the proper arrangement of the heating system
The assembly of 12 sections will be done by the store, while the warranty will be less than a year. If the radiator leaks shortly after the end of this period, repairs will have to be carried out on their own. The result is unnecessary problems.
Let's talk about the effective power of the radiator. The characteristics of the bimetallic section, indicated in the product passport, are based on the fact that the temperature difference of the system is 60 degrees.
Such pressure is guaranteed if the battery coolant temperature is 90 degrees, which does not always correspond to reality. This must be taken into account when calculating the room radiator system.
Here are some tips for installing the battery:
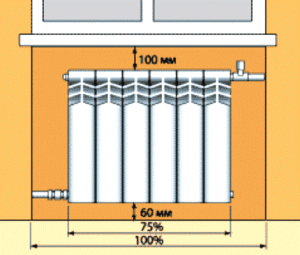
- The distance from the window sill to the top edge of the battery must be at least 5 cm. Air masses can circulate normally and transfer heat to the entire room.
- The radiator needs to lag behind the wall by a length of 2 to 5 cm. If reflective thermal insulation is attached behind the battery, then you need to purchase elongated brackets that provide the specified clearance.
- The bottom edge of the battery is supposed to be indented from the floor equal to 10 cm. Failure to follow the recommendations will worsen heat transfer.
- A radiator mounted against a wall, and not in a niche under a window, must have a gap of at least 20 cm with it. This will prevent dust from accumulating behind it and help heat the room.
It is very important to make such calculations correctly. It depends on how efficient and economical the resulting heating system will be.
All the information given in the article is intended to help the average person with these calculations.
What to do if you need a very accurate calculation
Unfortunately, not every apartment can be considered standard. This is even more true for private residences. The question arises: how to calculate the number of heating radiators, taking into account the individual conditions of their operation? To do this, you need to take into account many different factors.
The peculiarity of this method is that when calculating the required amount of heat, a number of coefficients are used that take into account the characteristics of a particular room that can affect its ability to store or release heat energy. The calculation formula looks like this:
CT = 100W/sq.m. * P * K1 * K2 * K3 * K4 * K5 * K6 * K7. where
KT - the amount of heat required for a particular room; P is the area of the room, sq.m.; K1 - coefficient taking into account the glazing of window openings:
- for windows with ordinary double glazing - 1.27;
- for windows with double glazing - 1.0;
- for windows with triple glazing - 0.85.
K2 - coefficient of thermal insulation of walls:
- low degree of thermal insulation - 1.27;
- good thermal insulation (laying in two bricks or a layer of insulation) - 1.0;
- high degree of thermal insulation - 0.85.
K3 - the ratio of the area of \u200b\u200bwindows and the floor in the room:
K4 is a coefficient that takes into account the average air temperature in the coldest week of the year:
- for -35 degrees - 1.5;
- for -25 degrees - 1.3;
- for -20 degrees - 1.1;
- for -15 degrees - 0.9;
- for -10 degrees - 0.7.
K5 - adjusts the need for heat, taking into account the number of external walls:
K6 - accounting for the type of room that is located above:
- cold attic - 1.0;
- heated attic - 0.9;
- heated dwelling - 0.8
K7 - coefficient taking into account the height of the ceilings:
Such a calculation of the number of heating radiators includes almost all the nuances and is based on a fairly accurate determination of the room's need for thermal energy.
It remains to divide the result obtained by the heat transfer value of one section of the radiator and round the result to an integer.
Some manufacturers offer an easier way to get an answer.On their sites you can find a handy calculator specifically designed to do these calculations. To use the program, you need to enter the required values in the appropriate fields, after which the exact result will be displayed. Or you can use special software.
When we got an apartment, we didn’t think about what kind of radiators we have and whether they fit our house. But over time, a replacement was required, and here they began to approach from a scientific point of view. Since the power of the old radiators was clearly not enough. After all the calculations, we came to the conclusion that 12 is enough. But you also need to take into account this point - if the CHPP does its job poorly and the batteries are a little warm, then no amount will save you.
I liked the last formula for a more accurate calculation, but the K2 coefficient is not clear. How to determine the degree of thermal insulation of walls? For example, a wall with a thickness of 375 mm made of GRAS foam block, is it a low or medium degree? And if you add 100mm thick construction foam to the outside of the wall, will it be high, or is it still medium?
Ok, the last formula seems to be solid, windows are taken into account, but what if there is also an external door in the room? And if it is a garage in which there are 3 windows 800*600 + a door 205*85 + garage sectional doors 45mm thick with dimensions 3000*2400?
If you do it for yourself, I would increase the number of sections and put a regulator. And voila - we are already much less dependent on the whims of the CHP.
Volume calculation
If you make such calculations, then you will need to refer to the standards established in SNiP. They take into account not only the performance of the radiator, but also what material the building is built from.
For example, for a brick house, the norm for 1 m2 will be 34 W, and for panel buildings - 41 W. To calculate the number of battery sections by the volume of the room, you should: multiply the volume of the room by the heat consumption rates and divide by the heat transfer of 1 section.
- To calculate the volume of a room with an area of 16 m2, you need to multiply this figure by the height of the ceilings, for example, 3 m (16x3 = 43 m3).
- The heat rate for a brick building = 34 W, to find out what amount is required for a given room, 48 m3 x 34 W (for a 41 W panel house) = 1632 W.
- We determine how many sections are required with a radiator power, for example, 140 watts. For this, 1632 W / 140 W = 11.66.
Rounding this figure, we get the result that for a room with a volume of 48 m3 an aluminum radiator of 12 sections is required.