Asbestos-cement
Asbestos-cement pipes, in principle, are widely used, since they:
- refractory;
- lungs;
- resistant to corrosion and aggressive environments;
- economical;
- wear-resistant;
- resistant to low / high temperatures.
Economy is due to several factors:
- products do not conduct current, and therefore do not need additional protection;
- they are easy to install, which ensures the acceleration of construction work;
- their coefficient of friction against the walls during the transportation of liquids is lower than that of metal pipes, which reduces the energy intensity of the process in a pressure sewer;
- asbestos cement is a good thermal insulation material, which reduces the cost of thermal insulation of the pipeline.
Asbot pipes
Connection elements: for non-pressure - asbestos-cement or polyethylene couplings, for pressure - couplings of the CAM type (seal - rubber rings). Standards: non-pressure pipes - GOST 1839-80, TU 5786-006-00281594-2002; pressure - GOST 539-80. Disadvantages: brittleness, roughness of the inner surface.
Pressure reinforced concrete
For pumping liquids, the pressure of which exceeds 0.05 mPa, pressure pipes are used. They are made of the most durable concrete - B40. Such structures must withstand up to two hundred freeze / thaw cycles with a loss of strength of not more than 5%, and have high water resistance.
Depending on the nominal pressures that concrete products must withstand, they are classified into four categories:
- third class - must withstand pressure up to 5 atmospheres;
- second class - up to 10 atmospheres;
- first class - up to 15 atmospheres;
- zero class - up to 20 atmospheres.
Usually products of the first and zero classes are put into production by special order.
Pressure reinforced concrete pipes must withstand a soil load of two meters. They are used for laying transport systems pumping inert liquids with a temperature not exceeding 400o. Their specific gravity in production pipelines is small: basically, the pipelines consist of metal pipes with a diameter of 1200 mm + 200 mm. However, in the segments of intercity water conduits, concrete pipes of large diameter - this is a diameter of 2000–5000 mm, occupy a leading position.
Connection of sewer pipes
Hermetic connection of elements is the basis for the normal operation of the sewer network. The connection must be strong, reliable, resistant to aggressive influences, elastic (if possible). These properties depend on the reliability of the base and the type of connection. Butt joints are divided into rigid and flexible. A flexible connection allows (without loss of water tightness) longitudinal displacement of the elements relative to each other by 3-5 mm and a small angle when they are mutually rotated. Flexible connection is used on pressure pipes:
- asbestos-cement - with a sealing rubber ring;
- reinforced concrete - with a sliding metal flange.
A rigid connection does not allow any displacement, but it is used much more often (on sockets and couplings) due to its cheapness.
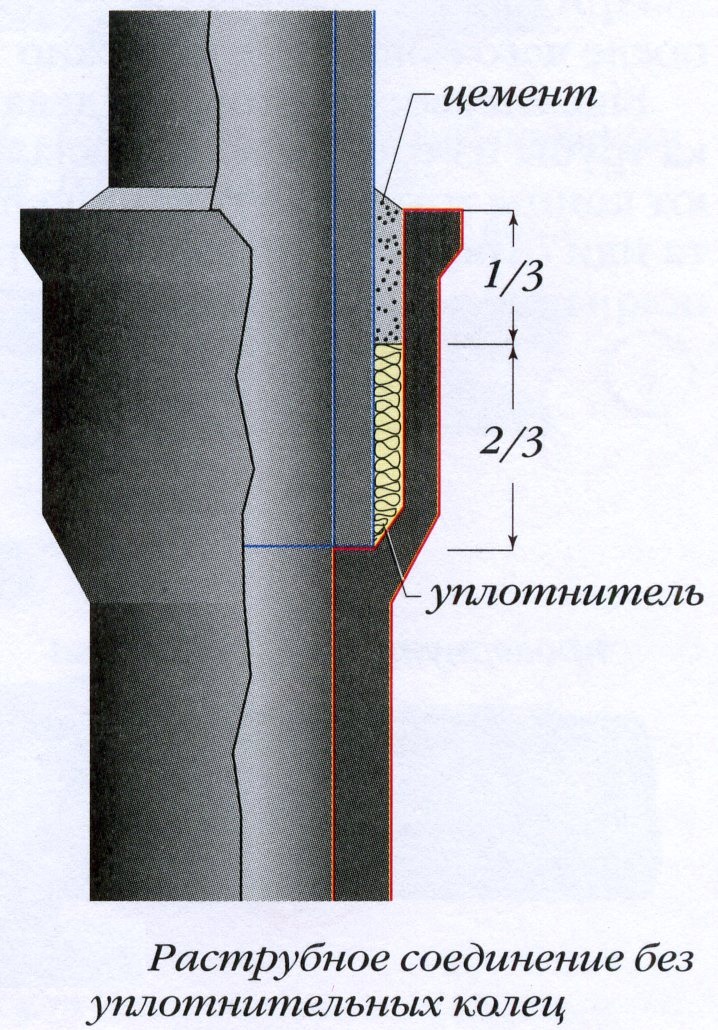
A rigid joint consists of a lock and a seal. Sealant - usually tow. Castle - asbestos cement, asphalt mastic, cement. If the asphalt lock has at least some elasticity, then the cement and asbestos-cement locks are absolutely rigid. When connected to a socket, the gap between the socket and the pipe is sealed, when connected to a sleeve, gaps are sealed on both sides. In the construction of industrial sewer networks, an asphalt lock is most often used - the socket is poured with molten mastic (3 parts - asphalt, 1 or 2 - tar, BN-Sh bitumen). Asbestos-cement locks are used to seal the joints of pipes laid on a solid foundation.
Photo diagram of a rigid connection
Flexible connections are superior to rigid connections in many respects - they are more reliable, do not require high costs using manual labor, and are easy to install. O-rings and rolling gaskets are used as sealing material:
- plastisol rings - for connecting concrete, reinforced concrete, ceramic pipes into a socket (diameter - up to 1000 mm);
- rubber rings - for socket and seam concrete;
- gaskets - for metal, reinforced concrete (pressure / non-pressure) socket.
Flexible joint of socket or seam
Seam pipes are connected with rubber rings. The ring is put on the beveled end of the pipe before laying. Smooth pressure reinforced concrete are connected by couplings. Another type of flexible connection is the welding of an embedded profiled sheet installed at the factory during the production process. The extrusion machine continuously extrudes the polyethylene. The formed sheet is recessed into the body of the concrete pipe with the ribs inward. Another sheet is welded to the first sheet with the reverse position of the ribs - it is covered with cement from the inside. Thus, profiled sheets protect against mechanical damage (abrasive particles in drains). Even with so many types of sewer pipes and connections, the choice is limited - it does not depend on preferences, but solely on the characteristics of soils, drains and the estimated intensity of transportation.
Construction of concrete pipes
How a reinforced concrete pipe is arranged - design
If a few years ago they were made from massive walls equipped with bends, then modern analogues are much more convenient and practical. The walls of modern sewer pipes can have either a separate or a common foundation. Everything depends directly on the geological conditions in which the operation of the product is envisaged.
If they need to be installed on roads that belong to low technical categories, it is better to use products that have a round base of links. At the same time, it is good if they are additionally equipped with a flat sole. In such pipes, the links can have a hole with a diameter of 1 to 1.25 meters. The thickness of their walls in this case can vary from 14 to 16 centimeters.
In the device of the plantar part there is a welded mesh made of reinforcement with a diameter of up to 10 millimeters. The metal used for the manufacture of this structural element must be of class A-II. However, today there are two types of links:
The only drawback of these classes is not efficiency. For laying sewers from such materials, a lot of concrete is needed. As a rule, these pipes are installed under embankments. Their height can reach up to 7 meters.
It should be borne in mind that the links of round sewer pipes are very difficult to evenly place on the base of the foundation or foundation. In order to avoid mistakes during the installation process, manufacturers offer a standard project of links. In addition, you can use additional meshes that allow you to strengthen the heel of the reinforcement.
Cast iron
Cast iron pipes are mainly used in the construction of external / internal (pressure and non-pressure) sewer networks, including for private houses. Material advantages:
- strength,
- fire resistance,
- wear resistance,
- good soundproofing properties,
- heat resistance.
One of the main disadvantages of cast iron is susceptibility to corrosion, which requires additional processing (bitumen, white cast iron, other compositions) of products. Nevertheless, cast-iron pipes are still used, since they are optimal for the organized drainage of effluents from food, livestock and other agricultural enterprises, farms, and chemical laboratories; transportation of mineral and thermal waters. The cast-iron track is suitable for intensive use, but unlike ceramic, it is very durable.
Cast iron pipes
Classification:
- ChK - standard cast iron non-pressure sewer: suitable for sewer systems operating under normal conditions, not subjected to extreme loads - for draining sewage from residential buildings and small businesses, easily connected to plastic elements of internal sewage;
- ChNR - cast iron pressure with a socket: capable of moving media under pressure up to 16 atm - mainly used in the sewerage of industrial facilities;
- VChShG - high-strength cast iron with nodular graphite: ductile, durable, does not crack (due to the structure improved by adding magnesium), withstands low and high temperatures, adapts to temperature changes;
- SML - silent: internally coated with a special epoxy composition, which excludes the possibility of stratification.
SML
The connection of cast iron pipes depends on their type. For sewerage, elements with sockets at the end are mainly used. During connection:
- clean the socket and the end of the pipe;
- connect (insert the smooth end of one pipe into the socket of the other);
- center;
- tow is minted - driven into the socket until it is filled by ⅔;
- the remaining third of the socket is poured with cement mortar (expanding cement M-300, M-400).
Until the cement is completely dry, it is necessary to maintain the desired level of humidity - for this, the joint is wrapped with a wet cloth and made sure that it does not dry out. Theoretically, modern means - mastics and sealants - are perfect for sealing. However, in practice, many prefer not to "mix eras" and pay tribute to cast iron - the usual tow and cement.
Pig-iron sewer with a bell
Couplings are used to connect smooth cast-iron pipes (threaded cylinders; for parts with different diameters, an adapter coupling consisting of two cylinders is used). The pipes are inserted into the coupling so that they are connected exactly in the middle (therefore, markings are made first), and sealed.
adapter sleeve
If sewer pipes form an angle with respect to each other or branching is needed, bends are used for connection.
Elbows (elbows)
For connection also apply:
- tees (for three pipes);
- crosses (for four);
- saddles (for introducing pipes of smaller diameter into the system).
Tee
cross
Saddle
In an apartment building, we cannot choose the sewerage system - except to change the apartment along with the house. So we will adapt plastic to cast iron (if the builders awarded the house with it). A standard cement-filled connection is not suitable: plastic reacts to temperature - sooner or later a flood will occur (the cement will inevitably crack, the connection will lose its tightness). You need a special adapter that is installed in the socket. They act in stages (not forgetting the slope to the riser):
- the socket is cleaned of rust and other deposits;
- sealant (silicone) is applied to its inner surface;
- insert the adapter into the socket - until it stops;
- sealant is applied to the plastic pipe and inserted into the adapter.
What to do if there is no bell:
- purchase two adapters - rubber and plastic;
- clean up the end;
- put a rubber adapter on a cast-iron pipe;
- put a plastic adapter on the rubber adapter (apply sealant on both) and assemble the parts.
Concrete
Concrete pipes are mainly used for laying external sewer networks - both pressure and non-pressure. Due to special additives, concrete acquires:
- frost resistance,
- resistance to aggressive environments,
- strength,
- waterproof,
- hydrophobicity.
Pipes are produced with or without sockets. Accordingly, there are two types of connection. Disadvantages: weight, entailing installation difficulties and extensive preparatory work (strengthening the base of the route - the installation of a sand and gravel cushion), carried out to avoid ground movement with subsequent violation of the calculated slope of the route.Standards: GOST 22000-86.
Reinforced concrete pipes
Non-pressure concrete pipes are divided into types:
- T - cylindrical, section - round, diameter - 300–1600 mm, butt joint, subtype - TP (concrete concrete), with a sole;
- TS - cylindrical, section - round, diameter - 400–1600 mm, with a socket, connection - in a socket, subtype - TSP, with a sole;
- TB - cylindrical, section - round, diameter - 100–1600 mm, connection - into a socket with a support shoulder, subtype - TBP with a sole (diameter - 1000–1600 mm);
- TO - cylindrical, connection - flanges (seal - sealant), section - oval, diameter - 1000–2400 mm;
- TE - cylindrical, connection - flanges (seal - sealant), section - ellipsoidal, diameter - 1000–2400 mm;
- TFP - cylindrical, with a sole, connection - flanges (seal - sealant), cross section - round, diameter - 1000–2400 mm.
Similarly to non-pressure pressure ones are divided into types:
- TN - cylindrical, connection - socket with a seal with a rubber ring, diameter - 300–2400 mm;
- TNP - cylindrical, polymer core, connection - socket with rubber ring seal, diameter - 400–1200 mm;
- TPS - cylindrical, steel bushing, connection - socket with rubber ring seal, diameter - 250–600 mm.
Concrete / reinforced concrete pipes are mainly used in the arrangement of industrial sewer networks. The outer diameter is indicated. The inner one is 10-20 cm smaller (wall thickness - from 5 to 10 cm). Indicating the "advantages", they write that these pipes are inexpensive. If 20,000 rubles. (plus/minus the excitement of the market) for 3 meters is inexpensive, then what is expensive? Concrete pipes are expensive, heavy, difficult to install (a crane, a platform, skilled workers - all this is needed), but in some cases they are irreplaceable (these are usually not brought to private houses).
Ceramic
Ceramic pipes used in a free-flow sewerage device are connected into a socket or by means of a coupling. Product parameters:
- length - up to 1,500 mm;
- wall thickness - 20–40 mm;
- diameter - 100–600 mm;
- resistance to loads - 240–350 MPa;
- moisture absorption - 7.5–8%;
- resistance to aggressive environments - 90-95%.
Standards: GOST 286-82. The inner surface of the products is coated with a special glaze that provides resistance to chemicals. 5 notches are made on the inner surface of the socket, the same notches are made on the smooth end of the pipe.
Ceramic
Low water absorption, high resistance to corrosion, chemically active substances, mechanical stress provide the possibility of using products in adverse conditions:
- in sewer networks laid in places with a high level of occurrence of aggressive groundwater;
- in production networks transporting chemically active effluents;
- in the device of sewer networks laid near highways.
Flaws:
- short length - complicates and increases the cost of installation;
- large weight - complicates and increases the cost of installation (requires a cushion device and the use of equipment) and transportation;
- fragility;
- high cost;
- low frost resistance - requires additional work on thermal insulation.
Ceramics are very difficult to cut, which, again, complicates installation. The length of the elements must be calculated at the design stage to avoid cutting.

Arrangement of joints of ceramic pipes
The use of ceramic pipes in the sewerage system of a private house is in most cases impractical.