Installation of a sewerage system
Do-it-yourself storm sewer, if desired, can be completed in a few days.
Any owner of a country house or cottage can do it on their own, since there are no particular difficulties in this, the process resembles the laying of a conventional outdoor pipeline.
Installation of storm sewers begins with digging a trench. However, before starting earthworks, it is necessary to outline a plan for laying gutters and pipes for future sewage.
Video:
It is also worth remembering the required slope, and the depth of the trench should correspond to the diameter of the pipes.
If pipes are supposed to be insulated, then the thickness of the insulation layer should also be taken into account.
The order of work is as follows: the trench is dug to the desired depth, stones and other large objects are removed, and the resulting holes are covered with earth.
This can be a purchased plastic tank or you can make it yourself by pouring concrete into a pre-prepared formwork.
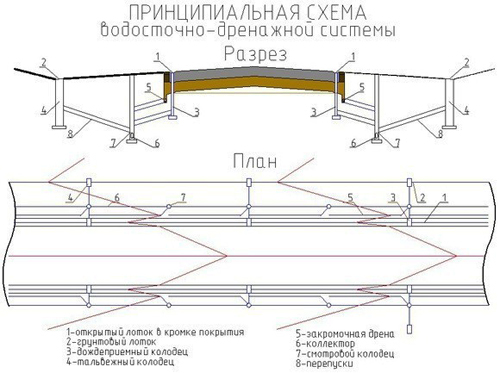
When the trenches are ready, pipes are laid in them, all connections are made with fittings. Manholes are installed in straight sections in the case when the length of the pipeline exceeds 10 meters.
Also, such wells are installed in the places of branching of the network. Sand traps are mounted at the junction of the gutters and the storm pipeline.
Video:
Before the final backfilling of the pipes, the system must be tested, if nothing is leaking anywhere, and there is no stagnation of water, then earthworks can be completed.
The final touch is the installation of gratings on the gutters.
Principles for determining the minimum slope
So, in order to determine the slope of the storm sewer according to SNiP, attention is drawn to:
- type of conduit;
- diameter of pipes to be laid;
- surface coating.
As mentioned, when using 200 mm pipes, the slope must be at least 0.7 cm, and the slope must be provided at every linear meter.
As for pipes d = 150 mm, here the slope is already slightly larger, about 0.8 cm / m.
It is worth noting that the building codes and regulations also contain a clause stating that if there is an urgent need, then the magnitude of the slope in certain areas can be reduced. For pipes of 200 mm, the minimum figure is 0.5 cm, and for 150 mm it should not be less than 0.07 cm.
The same document also regulates the maximum slope, it is 1.5 cm / m.
Storm sewer pipe, 200 mm in diameter
All rules and regulations must be observed, because otherwise the risk of clogging may increase significantly.
For example, if you make a very large slope, then the water will leave too quickly, respectively, the sand settling from it will silt the surface of the pipe from the inside.
Open type storm sewer slope
As for the slope of an open-type storm sewer, its value is determined by the type of surface, for example, where the ditches are asphalted - 0.3 cm / m, and where with crushed stone and cobblestone, then 0.04-0.5 cm / m.
Self-installation of a gutter system on the roof of the house
The gutter system is designed to remove atmospheric precipitation from a pitched roof. The service life of the drain is from 5 to 12 years, with proper installation and operation. But you can often see how an almost new drainage system becomes unusable: it breaks or sags. In this article, we will tell you how to independently install the drain in compliance with all technological requirements.
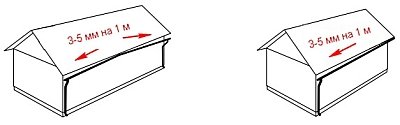
It is better to install the drain with at least one partner. The drain is attached under the roof overhang. The slope of the gutter should be within 2-3 millimeters per meter in the direction of the drain.
Depth of storm sewer
This parameter depends on the geological conditions in a particular region and the experience of operating engineering networks. It is regulated by SP32.13330.2012 (in an updated version). Specifically for a private house, the numbers are not spelled out - the rules relate to systems arranged in a residential area.
In the absence of experience (non-canalized area, for example) in the operation of networks, they rely on the level of soil freezing, which is different in all regions.
Pipes with a diameter of less than 500 mm are laid 30 cm below the freezing depth mark. Pipes with a diameter of more than 500 mm are laid 50 cm below the freezing depth mark. It is permissible to lay pipes to a depth of 70 cm from the surface (layout). This is the distance to the top of the pipe. At the same time, thermal insulation of the pipeline and its protection from mechanical influences are provided. The depth of the collector is determined by statistical and thermal calculation. The maximum depth is not standardized - it is determined by calculations for each individual case
The materials used, soil characteristics, applied technologies are taken into account.
Reality is very far from book truths. Sometimes it is impossible to follow the rules for a number of reasons. Deviations are acceptable, but any non-standard solution that is not prescribed in the rules and regulations needs the approval of the relevant authority, that is, the project must be agreed upon.
Linear storm sewer
In order for the project to be approved, all applied technical solutions must be justified, and in a comparative way. That is, you need to compare the technical and economic parameters of different options and prove that either the best or the only possible one is designed.
Grade Angle Measurement
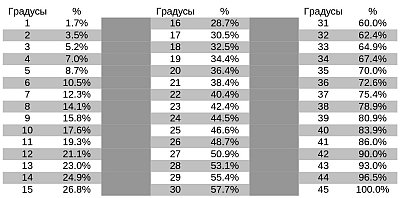
For the correct choice of materials and the design of the truss system, it is important to calculate the angle of the slope. This action is performed using a goniometer or by mathematical calculations and is expressed in degrees, percentages and the ratio of indicators
The simplest is the mathematical calculation. To do this, you need to know the width of the blood and its height. Using trigonometric formulas, the angle is calculated in the form of cosine, sine or tangent. The result obtained using the table is converted into percentages.
It can also be calculated by another method. To do this, divide the height of the future roof by half the width of the room, and multiply the result by one hundred. The result is compared against the table to determine the slope and it is also expressed as a percentage.
In the presence of a goniometer, all actions consist in determining the angle and selecting materials to create a roof. Only after that you can make the right choice, be sure to compare it with the requirements of SNiP.
The design and types of drainage
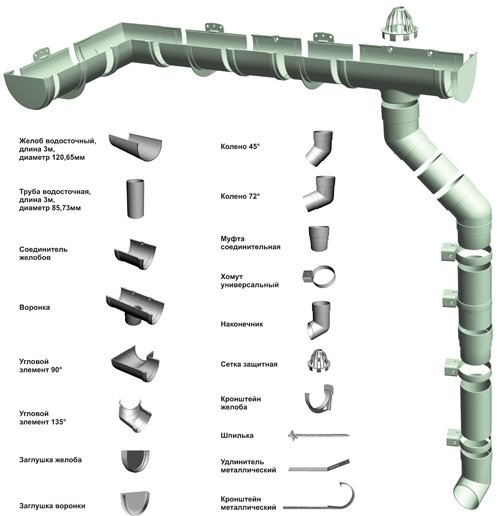
The design of the drainage system consists of the following elements:
- mounting brackets;
- gutters;
- drainpipes;
- funnels;
- additional accessories.
The mounting bracket (hook) is a structural element of the drainage system, which is necessary for attaching downpipes and gutters to the walls and roof of the building. Their shape is decisive for the design of brackets that are intended for mounting these products.
During installation work, special attention is paid to the installation site of the brackets, because the slope of the gutter will depend on their spatial location. Hooks are galvanized to prevent premature corrosion.
Gutters may differ in shape, therefore, in each individual case, they are determined by calculation. The main rule when choosing their shape is the larger the section of the gutter, the more water it can take. The modern drainage system assumes the presence of these parts around the entire perimeter of the building. To this end, they are equipped with special corner parts, thanks to which the gutters go around the corners of buildings.To prevent water runoff, a plug is used in the blind corner of the gutter, and special connecting accessories are used to connect them together. The regulatory documentation indicates that the slope of the gutter SNIP normalizes based on the requirements of 1 mm of slope per 1 meter running gutter.
Drainpipes are recommended to be installed on the sunny side of buildings, depending on the shape they can be round or square. Square downpipes have a much higher throughput capacity, so they are preferable to install for roofs with a large area. It should be noted that the shape of the drainpipe must correspond to the shape of the gutter, otherwise it will not be possible to join them normally. For the implementation of turns and bends, special accessories are additionally used in the form of curved knees in the lateral or frontal plane.
The funnel of the gutter system is designed to collect water from the gutters, so its diameter is determined by the amount of water collected from the roof. For large volumes of liquid, funnels with a large receiver and outlet pipe cross section are used.
Drainage systems may differ from each other according to the material of manufacture of component parts. There are currently two main types:
- plastic;
- iron galvanized.
When choosing a particular type of drainage system, one should take into account the fact that the installation of a plastic system is much easier, plastic parts are not afraid of scratches. Whereas galvanized parts, with external damage, spread corrosion very quickly. Galvanized parts of the drainage system are additionally covered with a protective polymer layer, which significantly extends the service life. But, in case of damage to the protective polymer coating, there is a very rapid process of oxidation and corrosion of the defect site.
Plastic drainage systems are cheaper than their metal counterparts, it is much easier to perform the standard slope of the gutter with them, but they have a significant drawback. At temperatures below zero, the plastic becomes very brittle and brittle, as a result of which it breaks even under the pressure of a snow mass.
Calculation of storm sewers
There is a whole array of numbers and formulas in the calculation of storm sewers, but if we simplify everything utterly, several parameters are important:
- system performance (volume of drains);
- pipe slope;
- pipe diameter;
- depth of the pipeline and collectors.
The efficiency of surface runoff removal depends on the diameter of the pipes. The diameter, in turn, depends on the amount of precipitation in the area and the area of the service area (including the drainage system, if one collector is used). All the necessary numbers are in the regulatory documentation, and they are enough if you follow the rules.
Combined system (stormwater and drainage)
The volume of effluents is calculated by the formula:
Q=q20×F×Ψ
- Q is the volume of stocks.
- q20, l/sec., per ha — precipitation intensity factor.
- F is the area of the serviced territory (recalculated in hectares; roof slopes - in a horizontal projection).
- Ψ is the coefficient of absorbency of coatings.
The q20 value is obtained from the local meteorological center. Ψ standard:
- 1.0 - roof;
- 0.95 - asphalt;
- 0.85 - concrete;
- 0.40 - crushed stone (rammed);
- 0.35 - soil (including turf, lawns).
For each storm water inlet, a separate calculation is made. Then the obtained figures are summed up and the diameter of the pipes is determined.
The set of rules regulates the smallest diameter of pipes. For gravity networks, it is 150 mm (and it goes as acceptable, and desirable - 200 mm). Using other pipes, violate the provisions of the joint venture. In production networks, the use of 150 mm pipes requires justification.
Point system
Parameters valid for pipes 150 mm:
- calculated highest speed: for metal pipes - 10 m / m, for non-metallic - 7 m / s;
- calculated filling of rectangular channels and pipes of cross section - full;
- the smallest slope (the need for a smaller slope should be justified): for 150 mm pipes - 8 mm / meter, for 200 mm pipes - 7 mm / m;
- connection slope - 2 mm/m;
- the slope of individual trays is 5 mm/m;
- the smallest dimensions of trapezoidal cuvettes, ditches: along the bottom - 30 cm, along the depth - 40 cm;
- between the outlet and attached pipes, an angle of at least 90 degrees is required, otherwise a well is installed, and in it - a riser with the connection of storm water inlets with a drop;
- require a well device: long straight sections (every 35 m - for private households), turns, drops, turns on collectors, connected pipes of different diameters;
- the radius of the turning curve of the trays must be at least 1 pipe diameter;
- the radius of the turning curve on the manifold from 120 cm (inclusive) must be at least 5 pipe diameters, manholes are needed both at the beginning and at the end of the curve;
- collector diameter for pipes up to 500 mm - 1000 mm (1000x1000);
- installation of a collector with a diameter of 700 mm for pipes of 150 mm is permissible;
- the depth of the collector with a diameter of 700 mm should not exceed 1200 mm;
- the diameter of deep wells (from 3 m) should be at least 1500 mm;
- the minimum design speed of effluents through pipes and channels is 60 cm/s.
Combined system
It is impossible to rely on the given figures using pipes of a smaller diameter: already 110 mm need a minimum slope of 2 cm / m. In each case of violation of the rules, you will have to make an individual calculation of storm sewers.
There is advice to use AutodeskBuildingSystems, but it's like hammering nails with a microscope. Theoretically, it is possible to calculate storm water in any program that, in principle, can design engineering networks, but in practice we do not recommend it. Firstly, this kind of software is never free (except perhaps the trial version, but it is always cut off). Secondly, it is difficult for an ignorant person to understand professional software. Thirdly, such software is not needed for our small task.
You can calculate rainwater drainage on specialized resources that provide calculators or programs that work in a browser (we launch and count). Most (maybe all) of them do separate calculations:
- hydraulic,
- surface runoff from the territory,
- volume of water from the roof,
- collector capacity,
- pipeline slope,
- network depth.
If these parameters help to build a stormwater… good luck.
We have written down the rules and regulations, formulas and figures, based on SNiP and SP, but according to common sense, the calculation of rain sewers should be entrusted to specialists - no matter how trite it may sound. Yes, all the figures are given, but the main factor was, is, will be the climatic parameters, although they are indicated in the joint venture, but not completely. The joint venture does not know what kind of soil is on your site: sand passes water instantly, clay does not pass at all. Calculation error = flooded area with all the consequences.
Determine the slope of the drainage system

If the slope is too large, the drainage system may not be able to effectively drain storm water, which will overflow over the edges and, again, fall onto the walls, gradually washing out the binders from them.
What slope of the drain can be called optimal? Usually this value is 2-5 millimeters per linear meter.To achieve the desired result, you only need two tools - a long cord and a building level. Using them, it is necessary to carefully mark the mounting points of the brackets, so you can get the exact slope of the drainage system.
Storm sewer construction
In general, installation work on the installation of storm drains is carried out in the same way as when laying external pipelines of a conventional sewer.
Selection of pipes for the underground part of the pipeline
If external storm sewer networks are installed, SNiP allows the use of the following types of pipes:
Asbestos cement is a traditional material used for the construction of external sewerage pipelines, including storm water. The disadvantages of the material include its high fragility and significant weight (a meter of a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm weighs more than 24 kg). Steel pipes have much less weight (a meter of pipe weighs about 10 kg), but they are prone to corrosion, so it is unprofitable to use them for the construction of stormwater.
Recently, plastic pipes have been used for the construction of storm drains. They are light (a meter weighs no more than 5 kg), but durable and resistant to corrosion. In addition, they are easy to connect, it does not require welding. Can be used:
- PVC pipes, if external networks are installed, then for their construction it is necessary to use a special type of pipes, they are painted orange;
- Multilayer polymer pipes. To date, this is the best option. These pipes have a smooth inner surface, so there is no hydraulic resistance.
Installation of the roofing part
Work goes like this:
- Holes are made in the ceilings for the installation of storm water inlets, all connections are carefully sealed.
- Branch pipes are strengthened during the construction of a point system or trays - during the installation of a linear storm drain.
- Install drain risers or pipes.
- A water discharge unit is assembled into a collector or outlet into tray systems.
- All devices are attached to walls and floors with clamps. Places for installing clamps are planned in advance, not forgetting to observe the recommended slope values.
Underground laying
- Installation begins with the installation of trenches. During the construction of systems such as storm sewers, the depth of laying is most often determined not by the depth of freezing, but by the experience of operating systems at the construction site.
- Trenches are dug with a slope, that is, their depth should gradually increase.
- At the bottom of the trenches, a sand cushion is made, the layer height is 20 cm.
- A pit is being prepared for the installation of the collector.
- Pipes should be laid in the prepared ditches, the pipes are connected to each other and connected to the collector using conventional fittings.
- If the sewer network consists of a single branch with a length of more than 10 meters, then in its middle it is worth planning the installation of a manhole. Such wells should be placed at the branching sites of networks.
- Sand traps are installed at the junction of water intake gutters and stormwater pipe systems.
- Now it remains to backfill the trenches, and cover the open structures (trays) from above with bars.
Mounting Features
Installation of a water drainage system is the most important point that requires a responsible approach and compliance with numerous rules. Immediately before installation, markup should be made indicating the installation locations of brackets (hooks), corners and drainpipes. The marking starts from the highest points of the system and consistently moves down. The optimal slope of the gutters is about 2-5 millimeters per linear meter, and the minimum slope of the gutter is 1 millimeter per linear meter. The most convenient tool for marking is a long thin cord and a level.During the marking, the places for attaching the brackets (hooks) are marked, on which the gutters and pipes will subsequently be hung.
After finishing the markup, proceed to the installation of brackets, which must correspond to the shape of the gutters. Brackets at the highest points must be set taking into account the level below 5 cm from the roof plane. After that, the brackets of the lower level are installed, for which the cord is pulled and the required slope of the gutter is determined. Intermediate brackets are installed with an orientation to the upper and lower levels.
The gutters are butted together, while the joints are additionally strengthened with a silicone-based sealant, rubber gaskets or rivets. Droppers, which are designed to drain water from the under-roof space, must go into the gutters by at least 2 centimeters.
After installation, the drainage system is filled with water, in places where the slope of the drainage gutter is insufficient, water will collect. If it is made of plastic, you will need to adjust the parameters of the bracket. When installing a galvanized drain, you can change the angle with a hammer and a wooden boss.
The next step in the installation of a water drainage system is the installation of funnels in the following order:
- slots are made in the gutters with a hacksaw;
- on galvanized gutters, the edges are additionally bent;
- the funnel is positioned in such a way that the front fold firmly and securely adheres to the edge of the gutter;
- the clamps on the funnel must be inserted behind the back of the chute.
When using plastic parts, special-purpose glue is used to fasten the gutter and funnel. After installing all the funnels on the downpipes, plugs are installed that prevent the passage of water in the wrong direction.
Lastly, they proceed to the installation of additional accessories, which include a leaf catcher grate and a cable heating system. The operation of the drainage system involves periodic cleaning of blockages, the main of which is foliage. Regardless of the slope of the gutter, its clogging with foliage will not make it possible to effectively drain the liquid. To avoid this and significantly extend the period between cleanings, a grate is used - a leaf catcher, which is mounted directly on the gutters and has a perforated surface along the entire length.
In winter, significant difficulties arise with the drainage of water as a result of freezing of the drainage system. To avoid this, an anti-icing system is installed, the main task of which is to maintain the performance of the drainage system at low temperatures. The most common option is to install a heating cable along the entire length of the gutter system and a temperature controller to control the heating.
Video instruction on how to install a rectangular gutter.
Storm sewer system design
The sewer system for removing water from the site is a complex communication
The sewer system for removing water from the site is a complex communication that covers the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe object from which it is necessary to remove water. The entire network is a complex mechanism of communicating vessels (pipes or gutters), through which water is diverted from the sloping site first to a common pipeline, and then to the central drainage well. There, according to the laws of the Russian Federation and the rules of SNiP 2.04.03-85 “Sewerage. External networks and structures, as well as GOST, prescribed clearly and clearly, rain and melt water must be treated and only then be discharged into the nearest reservoirs, collectors or the nearest roadside ditches.It also contains exact calculations and formulas for the construction of a sewer system for removing rain or melt water from the area of private and state facilities.
Important: the discharge of rain or melt water from the sewer-stormwater network into water bodies in an untreated state is prohibited. This is a criminal offence.
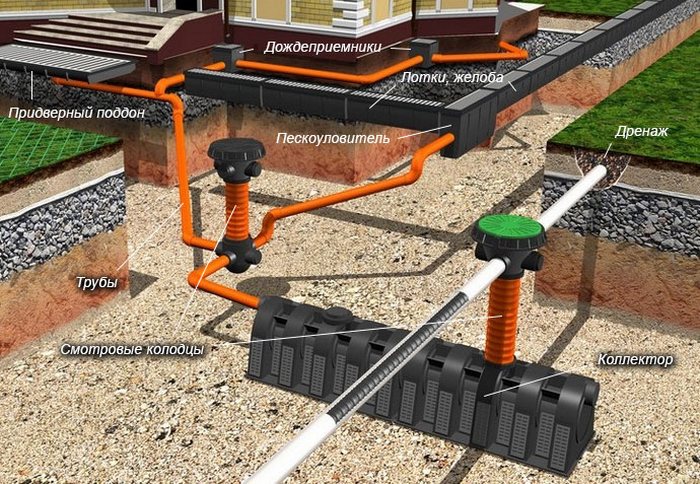
Storm communication consists of the following elements:
- Trays or gutters covered with a grate to receive water flows from the object;
- Rain inlets that direct water further through pipes;
- Sand traps that contribute to the purification of wastewater from particles of small debris in the form of dust and sand;
- filtering devices.