Design features and options for linear drainage
The offer of components for the arrangement of linear drains is very large. Ready-made conduits can have different designs and sizes, different designs. Permissible load, installation methods, as well as connection to the sewer system, the choice of basic and additional structural elements also differ from each other.
Gutters (drainage pipes) can be made of stainless or galvanized steel, artificial materials (polypropylene, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride), conventional concrete, fiberglass reinforced concrete (fiber-reinforced concrete) or polymer concrete containing organic binders and special fillers to improve material properties.
The width of the gutters can vary according to the expected load. The standard width of gutters for private construction is 100-130 mm. Where the intensity of the catchment is increased, drains up to 200 mm wide can be used. The normative length of the gutter (one element) can be 500 mm or 1000 mm.
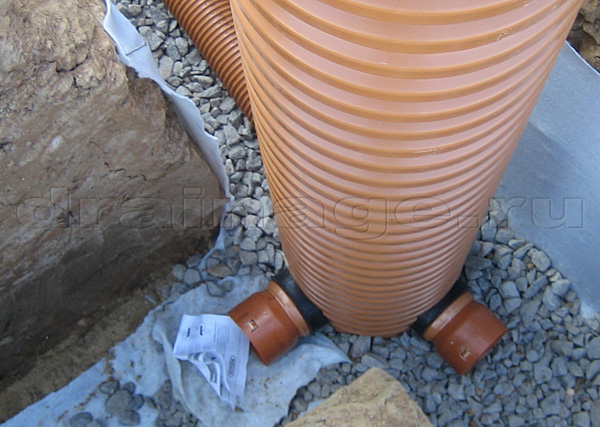
The diameter of the outlets for the collected water must also be taken into account. As a rule, standard sewer pipes are used for drainage. Their diameter is 110 mm.
If the diameters of the drainage pipes and outlets do not match, adapters must be used.
In cases where drainage is carried out on a base that is limited in height, it is also important to consider the installation depth of the channel. So, for open terraces, operated roofs, balconies, shallow-draft drains are used.
All of the above parameters (selection of materials, components for the drainage system, load calculation, determination of standard sizes, length of drainage channels, etc.) are calculated in advance. For this, a hydroproject is being developed - documentation describing the future drainage system. As a rule, the number of drains and, accordingly, the throughput of the system exceed the required minimum. This is due to the need to adapt the designed drainage system to the organization and design of the landscape on the site.
Types and functions of drainage systems
Your own home is not only an increased living space. The house must be “attached” to the land. Its correct layout and high-quality arrangement provide a number of additional opportunities, from creating a lawn, garden, beds, to the construction of additional buildings - garages, bathhouses, guest houses, gazebos, etc.
It is important that the site can be used all year round, including during the period of autumn rains or spring snowmelt. To do this, it is necessary to ensure the collection and drainage of water
The use of a drainage system provides the following benefits:
- Even during the melting of snow or prolonged rains, the water quickly leaves the site, it can be used.
- Water drainage avoids erosion of foundations, flooding of basements, damage to fence bases, gazebos, etc.
- The drainage system helps to preserve the landscape of the site. Without it, the accumulation of water is fraught with the death of garden plants, damage to lawns, etc.
Drainage systems fall into two main categories:
- surface drainage systems;
- deep drainage systems.
Surface drainage ensures the collection and removal of flood, melt and rain water. Water is directed to the storm sewer, and from there it is discharged outside the site.
Deep drainage involves the arrangement of underground channels and the laying of special drainage pipes inside them.Deep drainage systems are used to drain groundwater if its level is above 1.5 meters. Also, deep drainage is necessary for wetlands, areas located in lowlands or in close proximity to natural reservoirs. Finally, the use of deep drainage is recommended in cases where the house on the site has a basement, basement or underground garage.
Systems of deep and surface drainage may well complement each other. They have different purposes. So, deep drainage is necessary primarily to lower the level of groundwater. It supplements surface drainage in cases where storm sewers are not sufficient to effectively drain water.
Surface drainage systems are used much more frequently. Mos-drainage engineers believe that they are necessary at every site
For this reason, we will focus on them.
Gutter material plastic or concrete
There are several options for materials for the manufacture of gutters.
1. Cement concrete.
For a long time, gutters were made only of concrete, but today it is believed that this is not the best material. So, ordinary concrete quickly collapses under the influence of moisture, as well as differences between negative and positive temperatures. The total service life of cement concrete gutters is short. To increase the service life of concrete gutters, they are completed with steel or cast iron linings. These overlays reinforce the entire structure. However, the only advantage of this option is the affordable price.
2. Fiber concrete.
Fiber-reinforced concrete is a modern modification of concrete, for which the solution is additionally reinforced with fiberglass. Fibre-reinforced concrete contains cement and fine filler. Reinforcement with fiberglass can increase the strength of concrete, ensure its resistance to moisture, temperature, and dynamic influences. Fiber-reinforced concrete has such advantages as increased elasticity and impact resistance, resistance to cracking, water resistance. Together, all this significantly increases the life of the drainage system. Gutters made of fiber-reinforced concrete are produced by the German manufacturer Hauraton in the Faserfix series. Fiber-reinforced concrete gutters are also produced by Russian companies Polydrain and Standartpark.
3. Polymer concrete.
Polymer concrete is a cement mortar containing mineral fillers (quartz or granite) and organic binders (usually epoxy resin). Polymer concrete has a reduced weight and has twice the strength margin compared to conventional concrete. Also among the characteristics of the material are almost zero water absorption, frost resistance (withstands 400 freeze-thaw cycles without damage), high compressive and tensile strength, chemical and biological resistance, and abrasion resistance. Polymer concrete products are widely used in the manufacture of underground structures. At the same time, their service life exceeds 30 years.
An additional advantage of polymer concrete gutters is their smooth inner surface. This increases the throughput of the drainage system, it becomes self-cleaning. In general, polymer concrete drainage systems are the most reliable.
Polymer concrete surface drainage systems are produced by ACO, MEA, Standartpark.
4. Polymeric materials.
According to the experience of Mos-drainage engineers, one of the best options for private construction are drainage systems made of polymeric materials. The plastics used for the production of gutters are resistant to wear, durable, frost-resistant. The use of stabilizers makes it possible to achieve resistance to aggressive media and ultraviolet radiation.
In the arrangement of drainage systems, polymeric materials demonstrate the following advantages:
- light weight.This allows you to simplify the installation of the system, as well as reduce the cost of its transportation;
- smooth inner surface of the drainage pipes. Due to it, the throughput of the drainage system increases, the risk of clogging, flooding of the system is reduced;
- simple installation. Plastic pipes are not difficult to lay in the ground at the desired slope. When installing the drainage system, pipes can be shortened, cut directly at the installation site;
- a large selection of connecting elements. When using a plastic drain, several options are available for docking with the sewer. Connection with sewer pipes can be both lateral (horizontal) and lower (vertical).
Today, the main manufacturers of plastic drainage systems are Hunter, Hauraton, Nicoll, ACO, REDI, Standartpark
When choosing a specific drainage system made of polymeric materials, it is necessary to pay attention to the ease of installation and docking with the sewerage system, the range of basic and additional components of the drainage system, and ease of maintenance.
Spot drainage under roof gutters
The main element of the point drainage system is the storm water inlet. Structurally, it is a rectangular container. It is supplied with outlets. With their help, the storm water inlet is connected to the storm sewer. The height of the storm water inlets can be increased if necessary. To do this, they are installed on top of each other.
Additionally, point drainage is supplied with trash baskets, as well as siphons. Baskets are used as "filters", they collect liquid dirt and small debris. Siphons help prevent unpleasant odors.
The connection of the storm water inlet and the roof drain can be horizontal or vertical. For horizontal connection, a special nozzle is used.
The Mos-drainage company has a number of manufacturers producing equipment for point drainage.
1. Hauraton (Germany).
This company suggests using drain pipes to connect to the roof drain. They are made from impact resistant polypropylene. The top downpipe entry is vertical. The drainage system is connected to the sewerage using a horizontal socket with a diameter of 100 mm. The design is two-section, it is easy to maintain and clean when dirty. Additionally, the drainage system is equipped with a "stale air trap" (siphon), which protects against unpleasant odors.
2. Galeco (Hungary).
The assortment of this manufacturer includes containers made of PVC for collecting and purifying water from the roof. They are connected to the roof drain using the upper vertical entrance. The lower vertical outlet is used to move wastewater to the storm sewer. Additionally, Galeco drainage systems are equipped with storm dampers. These devices prevent water from flowing in the opposite direction. As a result, during heavy rains or active snowmelt, the entire system is protected from overflow.
3. Nicoll (France).
For the production of storm water inlets, Nicoll uses stabilized polypropylene. Gutters are connected to the downpipe using a vertical entry in the cover. Horizontal outlets for connection to storm sewers are provided on four sides.
The company also offers sand traps for point drainage. These devices simultaneously perform the functions of a drainage system and a sand trap. They collect and trap small debris, and also remove moisture along a horizontal side outlet with a diameter of 110 mm. The outlet is connected to the storm sewer.
It is possible to use this equipment both with the gutter systems produced by Nicoll and with systems from other manufacturers. The diameter of the pipes of the drainage system should be 80-100 mm. The device is equipped with a built-in water seal (siphon).It blocks unpleasant odors and prevents stale air from escaping. In addition, the water seal prevents dirt from entering the sewer. From above, the storm water inlet-sand trap can be closed not only with a lid, but also with an additional plastic grate. This makes it possible to collect water both from the roof drain and from the territory adjacent to it.
Finally, in addition, Nicoll produces sand traps equipped with a siphon and having a horizontal outlet. This equipment can be used for systems with labors with a diameter of 80-100 mm. Also in the Nicoll range are sand traps without siphons. They have a vertical outlet and are attached to works with a diameter of 100 mm.
4. ACO Passavant (Germany).
ACO spot drainage equipment are polymer concrete storm water inlets with a horizontal entrance. It connects to the downpipe with a nozzle. The outlet is also horizontal and connects directly to the storm sewer pipe.
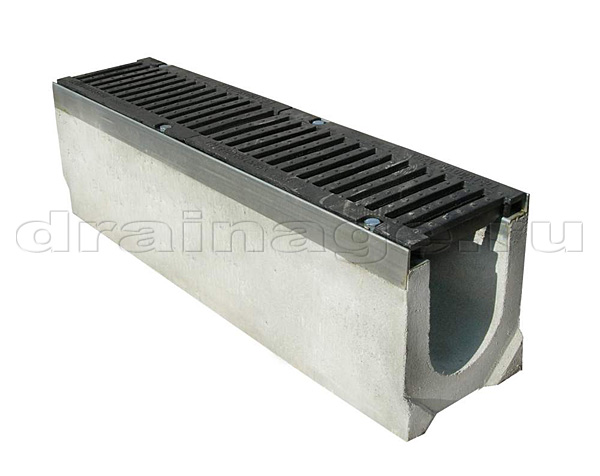
Closing grating element with main load
The closing grid is a visible element of the drainage system that remains on the surface of the earth. This imposes certain restrictions. The appearance of the lattice should be selected in accordance with the characteristics of landscape design.
The design of the closing grille is not the only selection criterion. So, if the installation technology of the drainage system is observed, it is on the grate that the main load will fall. Accordingly, the cover grilles are selected in accordance with the permissible load class applicable in a particular case. There are 6 such classes in total. To determine them, the DIN EN 1433 standard is used. Drainage systems with load class A15 are suitable for private construction. It complies with the regulations for areas with cycling and pedestrian traffic. For parking lots, private garages, entrances, drainage systems of class B125 are used.
The main parameters when choosing a closing grid are:
- material: the Mos-drainage company presents grilles made of cast iron with and without galvanization, plastic galvanized iron, galvanized or stainless steel, as well as polymeric materials;
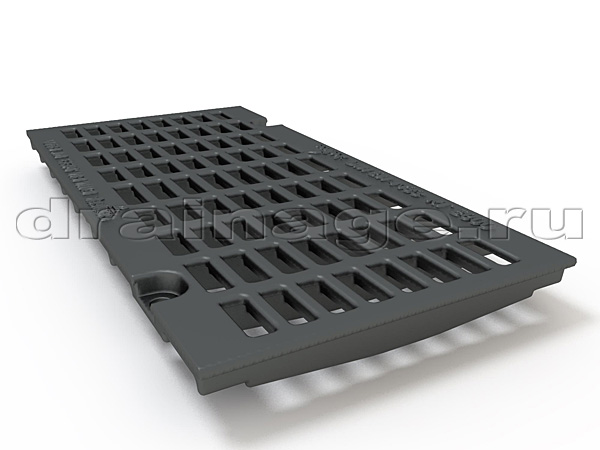
- type of through holes: slotted, perforated and cellular gratings are distinguished.
Cellular and slotted gratings are most often used in private construction. Among their advantages is optimal throughput, they are less clogged.
Closing grill maintenance is another factor of choice. For example, in addition to periodic cleaning, regular treatment with special products may be required. So, cast-iron gratings without galvanization require annual treatment with an anti-corrosion compound. If it is not carried out, the surface of the grate will rust and lose its appearance.
The fixation of closing gratings can be carried out using clips, latches and other devices for threadless fastening. You can also use gratings with anti-vandal fastening - for example, using bolts that can only be unscrewed with a special tool.
For drainage systems in private areas, it is easier to use threadless fasteners. In this case, when cleaning the drain channels, the removal and installation of the grate will take a little time. The channel itself is cleaned with an ordinary brush or scraper, and then washed with a jet of water from a hose.
What is surgical drainage
The instrument is rubber strips or tubes that are used for the purpose of evacuating secretions, blood, pus, infected fluids from air cavities (chest, abdomen, joints, or when pathological cavities form).
In the postoperative period, the drainage is placed to assess the strength of the anastomosis (the appearance of effusion or hemorrhage).
Depending on the method and technology, implementation differs in several basic types of drainage systems, the choice of a specific one for an individual patient is made individually, depending on the type and severity of the disease, individual characteristics and some accompanying factors.
There are several types of drainage:
- open drain: this is a rubber band that draws liquid into the bag. In this type, the risk of infection is higher
- closed drainage: pipes are used to drain liquid into a special bag or bottle. These include, for example, the chest and orthopedic wounds, where the risk of infection is much lower.
- active drainage: creating a vacuum that helps evacuate fluid
- passive drainage: these drains do not work in a vacuum, but based on the pressure difference between the body cavities and the external environment
The choice of a specific technique is mainly based on the location of the intervention and the tendency for fluid accumulation, secretion, and the formation of infected tissue.
Typically, drainage lasts from 24 hours to seven days, depending on the volume of the leak, blood, lymph fluid, and other secretions.
The drain system is removed when the leak stops or is reduced to less than 25 milliliters per day.
When removing the drainage system, some rules and recommendations are followed, depending on the type of system, some of them are removed step by step (with a few centimeters per day) or in one procedure. Removal requires compliance with all the rules for the treatment and disinfection of the wound.
Installation of a linear drainage system
The first stage of installation is the installation of a sand trap at the bottom of the route. Next, with the help of cords, channel laying lines are marked. The drainage channels themselves are laid in ready-made trenches on a layer of concrete. It is not necessary to reinforce the concrete. It is used only as a "cushion". The thickness of the concrete layer and the brand of concrete depend on the expected load on the drainage system.
Connection of drainage channels to outlets (sewer pipes) must be carried out through a sand trap. This is done so that liquid dirt does not clog sewer pipes. When making a vertical connection, a siphon must be used.
According to the experience of Mos-drainage engineers, linear drainage systems are built on a modular basis from unified elements. This allows you to create systems of any length and configuration.
As a rule, the main elements of the drainage system are interconnected using the tongue-and-groove scheme. This type of connection is used by most of both Russian and foreign manufacturers. It not only simplifies installation, but also avoids horizontal displacement of the gutters. Additionally, you can fix the connection using sealing compounds. This will increase its reliability.
If the channels need to be connected at an angle, they can be cut or sawn. After that, an angular docking is performed. To simplify the connection at an angle, some manufacturers produce ready-made corner elements. Also on the market are designs that allow you to assemble cruciform or T-shaped joints. Such designs, in particular, are presented in the assortment of Hauraton and Nicoll companies. Nicoll also manufactures a range of custom items. Their use allows you to adapt the channel system to any developed project.
For drainage to be effective, it must be sloped. There are several ways to solve this problem. One of the options is to perform a soil slope (arrangement of trenches with a slope). As a rule, plastic gutters are laid in such trenches, having a small thickness and low weight. If the channels are made of concrete, it is easier to use gutters with a slope of the inner surface. Also, when using concrete gutters, drains of different heights can be used, organizing a stepped slope.
vertical drainage
For draining land under conditions of intensive ground and especially pressure water supply, along with horizontal drainage (deep channels, closed drains), vertical drainage is used.
Vertical drainage - a system of boreholes for draining land, the water from which is pumped out by pumps with submerged electric motors. Depending on the location of wells in the drained area, systematic (wells are located evenly over the area) and linear drainage are distinguished. The latter is used to intercept groundwater flows. Water pumped out from wells is discharged by open channels or pipelines to main channels and water intakes.
The design of vertical drainage wells depends on soils and hydrogeological conditions: well filters are placed within the aquifer, their length must be at least 10 m. The most effective filters with gravel-sand backfill.
Well depth up to 20…50 m. Filter diameter 30…40 cm, backfill thickness 10 cm or more. The inflow of water to the wells is greater, the larger the filter diameter.
In addition to wells, pumps, electric motors, vertical drainage structures include a transformer substation, a power line, starting equipment and automation equipment. The work of vertical drainage is easy to automate. When groundwater rises, pumps are turned on, when their levels drop to drainage standards, they turn off. The pumped water is accumulated in ponds, during dry periods it is used for irrigation.
The economic efficiency of vertical drainage depends mainly on the design of wells, their depths, the nature of the use of pumped water and land.
Vertical drainage is used for draining swamps, for example, in Belarus and Ukraine. Under favorable conditions, one well provides a flow rate of up to 180…150 m3/h and drains up to 80…100 ha.
Discharge wells (amplifiers) are boreholes of small diameters (up to 10 cm) with filters placed in the aquifer. The wells are led into channels and drains. They are fixed with asbestos-cement or plastic pipes. Water from wells is supplied by natural pressure, the distance between them is 30…100 m.
Types of drainage drainage systems
Most owners of private houses and summer cottages are interested in the types of drainage. Drainage systems are widely ramified networks of channels interconnected with each other, passing around or along the building.
They protect the building, and if necessary, the entire area on which it is located, from the negative impact of surface and groundwater, removing excess moisture outside the drained area.
Such a solution allows you to drain the water that accumulates on the site, which is especially important in winter, when moisture expands in volume due to low temperatures. The most suitable type of drainage system should be chosen at the planning stage in order to allow the building to last longer without visible damage.
What's more, a well-designed drainage system will make it easier for plants to grow on the site by always providing them with enough water.
The most suitable type of drainage system should be chosen at the planning stage in order to allow the building to last longer without visible damage. What's more, a well-designed drainage system will make it easier for plants to grow on the site by always providing them with enough water.
Active drainage
Active drainage means
the application of an external force that provides
outflow of wound discharge. Functioning
drainage of this type is based on the creation
pressure difference in the wound and outside. V
currently used a lot
active drainage models, but the principle
their work is the same. outdoor
the end of the drain creates a negative
pressure, thanks to suction
effect, exudate is removed from the wound.
Active drainage is applied,
if a sealed cavity drains
(sutured wound, abscess cavity, chest
cavity, articular cavity). Can't do this
type of drainage apply when
interventions in the abdominal cavity,
like an omentum or an intestine can be
sucked into the holes of the drainage tube.
At best it will stop.
function, but may develop
necrosis of the intestinal wall.
Drainage
carried out as follows. V
drained cavity enter one or
two silicone and PVC
tubes with holes in the walls. Conduct
they should not be through the wound, but through a separate
small incision. If necessary,
for better sealing can be applied
several skin sutures. outer end
drainage is attached to a container in which
negative pressure is created. WITH
for this purpose, plastic
accordion, special plastic
spray cans or various types of suction
(water jet, electric).
Most
simple vacuum drainage
performed according to Redon. The essence of the method
is as follows. heated up to
100°C in water, the bottle is hermetically sealed
rubber stopper. As it cools
vacuum is gradually created in the vessel
up to 75 - 100 mm. rt. Art. Connecting such
systems to the drainage provides removal
from it up to 180 ml of exudate.
Very
original system for vacuum
drainage for pleural empyema was
proposed by M.S. Subbotin. Vacuum
at the end of a tube inserted into the pleural cavity
cavity created by moving
liquids in two cans according to the law
communicating vessels. Liquid from
the top jar is poured through a tube into
one of the lower ones, while in the upper bank
(hermetically sealed) the pressure drops.
Reducing the pressure in the upper can
leads to the suction of air from the second
bottom jar, which is airtight
connected to a tube installed in
pleural cavity.
V
in the absence of special
fixtures, you can use
simple hermetically sealed vial.
The vacuum in it is created by suction
air with a Janet syringe.
Such
the type of drainage is also called closed
or vacuum. It is possible to apply
only when sealing the cavity.
It is believed that active drainage
is the most efficient method. In addition to removing
content, it contributes to the rapid
reduction of the wound cavity.
When under what conditions and diseases there is a need for surgical drainage
The performance of surgical drainage is especially necessary in cases where surgery is performed in an area of the body characterized by increased secretion, or in cases where there is an increase in the accumulation of pus, blood, waste (dead tissue).
The main goals of surgical drainage include:
- removal of accumulated fluids or air in the affected area
- prevention from the accumulation of waste, pus, blood
- air accumulation protection
- to evaluate accumulated fluid
- preventing secondary infections and facilitating healing processes
The greatest use is in thoracic and abdominal surgery, but also in orthopedics, plastic surgery, during thyroid surgery. in neurosurgery and operations on the urinary tract (urinary catheter insertion is also a type of drainage system).
Depending on the underlying disease, the type of surgery, and a number of individual factors, surgical drainage is most common in the following conditions:
- Skin abscess, furuncle and carbuncle of unspecified location
- lung abscess
- Bartholin gland abscess
- Renal and perineural abscess
- Hydrocele, unspecified
- Acute sinusitis
- Chronic sinusitis
- labyrinthitis
- Salpingitis and oophoritis
- epidural hemorrhage
- Osteomyelitis
In some cases, drainage results in a rapid and measurable improvement in symptoms (such as acute or chronic sinusitis, where accumulated fluid can provoke neurological symptoms and lead to misdiagnosis of patients).
When the skin is drained, there is a rapid response to the condition of the patients and the limitation of inflammatory processes.
The decision to conduct drainage is made by the attending physician and agreed with the relevant specialists.
After certain interventions, with certain diseases, as well as in the wrong technique for insertion or removal, surgical drainage can do more harm than good.
Organization of drainage in alternative ways
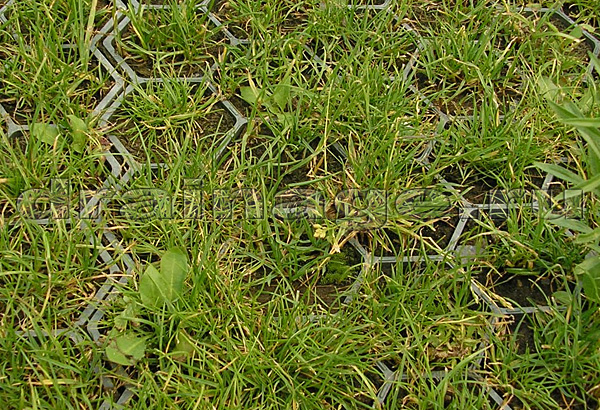
You can deal with excess moisture on the site not only with the help of traditional drainage systems. So, one of the effective options is the use of lawn grates for grass cover. Such lattices are honeycomb panels. They are colored green. As a rule, panels are made of high density polyethylene. Such lawn grids can withstand loads up to 200 t/m2. During installation, the panels are laid on a sand and gravel base. The thickness of the base is determined by the load class for a particular zone.
The laid "honeycombs" are 90% overgrown with lawn grass. It is regularly mowed so that the site looks like a lawn. The use of lawn grids allows for high-quality drainage, as well as protecting the soil surface from trampling, erosion, and damage by car tires. After rain, moisture goes into the soil through the "honeycomb". The site drained in this way always remains dry, water does not stagnate on it.
Another interesting drainage option is offered by TerraWay, a German developer of the technology of the same name. TerraWay is a solid, environmentally friendly coating. It consists of fractionated inert materials (granite, gravel, glass, quartz sand, etc.), as well as a two-component polymer binder. Such a coating has a porous structure that allows air and moisture to pass through. This provides drainage and gas exchange for plant root systems. At the same time, TerraWay surpasses asphalt pavement in terms of wear resistance and strength.
It is assumed that this coating can be used for arranging paths, sports and playgrounds, parking lots, etc. Thanks to its characteristics, even after heavy rain, water will not linger on the surface.
TerraWay has a number of additional advantages.
- Ice does not form on the coating, as it does not retain moisture.
- The covering is elastic and differs in good coupling with a sole of footwear. This allows you to reduce fatigue of the joints of the legs, reduce the load on the foot.
- The coating can have almost any appearance. So, in its production, you can use various fillers, as well as various polymer pigments. This allows you to change the texture of the material, create drawings and ornaments on its surface. Additionally, TerraWay can have internal lighting. The coating has the ability to transmit light. This can be exploited by placing fiber optic light sources underneath.
- High maintainability. Repairing damage is easy. To do this, it is enough to cut out the damaged area of \u200b\u200bthe coating and refill it with the composition.
- Simple care. To care for the coating, you can use any tool and any equipment. The exception is a metal tool, it can damage the coating.
In order for the coating to provide high-quality drainage, it must be laid on a sand-gravel "cushion" using a technology similar to that of asphalt laying. The components that make up the coating are mixed in a mixer. After that, the mass is placed on the prepared site. After a day, the coating hardens, it can be exploited.
Point drainage
Drainage can be equipped according to the point principle. Such systems are used to organize local collection of excess moisture. Spot drainage is used in doorways, under roof drains, under watering taps, etc. Where rapid drainage of excess water is required, point drainage can complement linear systems. Such catchment combinations are used in driveways, front yards, walkways, and the like.
Point drainage may include:
- drainage systems or storm water inlets;
- settling tanks (drainage drains);
- storm dampers;
- ladders.
One of the main functions of spot drainage is to collect water flowing from roofs through downpipes. In such cases, high-quality drainage helps prevent basement flooding, increase the service life of the blind area and building foundations. The water drained from the roof with the help of point drainage is directed to the storm sewer system, bypassing the blind area and the foundation.
Some manufacturers offer equipment complexes that serve to provide roof drainage, as well as to drain water collected from the roof into storm sewers. Among such manufacturers are Hunter (Great Britain), Nicoll (France), ACO Passavant (Germany), First Plast (Italy). Such equipment can be delivered not in a complex, separately. Companies that produce only point drainage devices leave the possibility of docking drainage devices and roof drainage systems.
It is better to develop a point drainage system when designing the house itself. In this case, under each roof drain, it is possible in advance, before creating a blind area, to equip the places where the storm water inlets will be placed.