How to make an air recuperator with your own hands
Factory-made recuperators are quite expensive, therefore, knowing how to work with hand-held metalwork and electric tools, such a device can be made independently. In this case, the main key to success will be the availability of free time and the desire to achieve the goal. All work can be divided into several stages: preparation and manufacture, installation and performance testing.
Preparatory stage
During this period of work, it is necessary to determine the type of device and the availability of the necessary materials and tools. After the type of the heat exchanger is determined, it is necessary to draw up a sketch (drawing) indicating the main dimensions, which will prevent overspending of materials.
Homemade air recuperator made using polycarbonate
So, for the manufacture of a plate structure, you will need:
- sheet metal 0.5-1.5 mm thick (aluminum, copper, galvanized, etc.) - for the manufacture of heat exchanger plates;
- other material (wood, plastic, etc.) - to create a gap between the heat exchanger plates;
- material for the manufacture of the body (metal, plywood, lumber, plastic);
- glue and sealant;
- insulation;
- connecting flanges, with a diameter corresponding to the pipes of the ventilation system;
- fans;
- metal profile (corner, profile pipe, etc.) - for the manufacture of a structure that provides fastening to a wall or ceiling;
- fastening elements (screws, self-tapping screws, etc.);
- electric jigsaw and grinder;
- screwdriver or electric drill;
- metalwork tools (screwdrivers, wrenches, hammer, etc.).
Manufacture of a plate-type heat exchanger
Having drawn a sketch and prepared the necessary tools and materials, you can start manufacturing, which is carried out as follows.
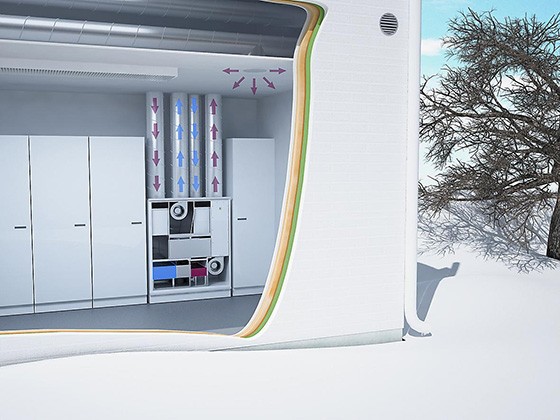
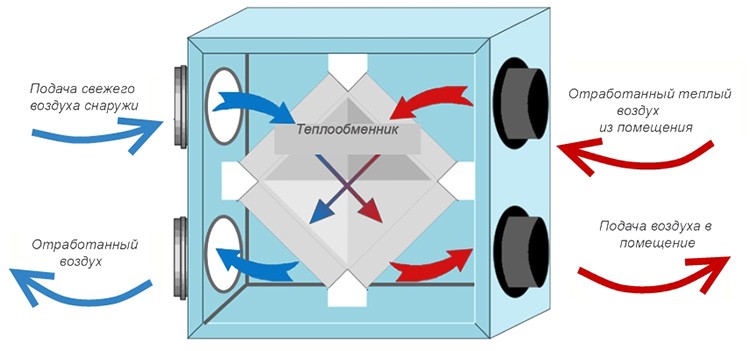
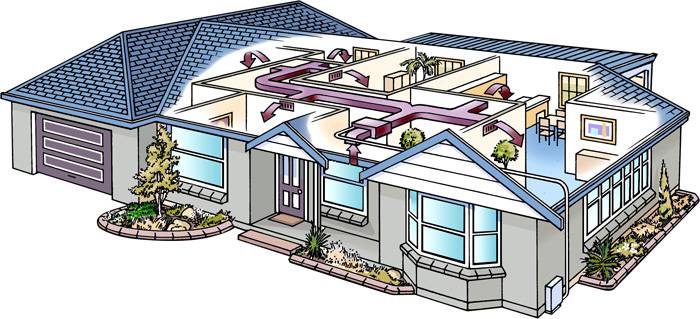
The principle of operation of the air handling unit with recuperation
The operation of the supply and exhaust ventilation system with a heat recovery device is carried out as follows:
- from the interior of a house, apartment or other capital structure equipped with a heating system, air is taken in, the temperature of which is higher than outside;
- at the same time, cold air from the street is also sucked into the ventilation system of the building;
- warm and cold air meet in the heat exchanger of the heat exchanger, where heat is transferred from one air stream to another;
- cold and clean air from the street is heated and only after that it is fed into the interior of the building;
- for air intake, air intakes equipped with fans are used.
Schematic diagram of the heat exchanger
Making an air recuperator for the home with your own hands
A simple plate heat exchanger can be made by hand.
For work you need to prepare:
- four square meters of sheet material: iron, copper, aluminum or textolite;
- plastic flanges;
- a box made of tin or plywood, MDF;
- sealant and mineral wool;
- corners and hardware;
- cork sheets on an adhesive basis.
- From sheet material, you need to make square plates measuring 200 by 300 millimeters. In total, seven dozen blanks will be required. The main thing at this stage is accuracy and exact observance of the parameters.
- A cork coating is glued to the blanks on one side. One blank remains uncoated.
- The blanks are assembled into a cassette, turning each subsequent ninety degrees. The plates are held together with glue. The uncoated plate is the last one.
- The cassette needs to be fastened with a frame, for this a corner is used.
- All joints are carefully treated with silicone.
- Flanges are attached to the sides of the cassette, a drainage hole is drilled at the bottom and a tube is inserted to remove moisture.
- So that the device can be periodically removed, guides for the corners are made on the walls of the case.
- The resulting device is inserted into the housing, the walls of which are insulated with mineral wool material.
- It remains only to insert the air exchanger into the ventilation system.
The best household recuperators
Given that plate heat exchangers require the organization of a full-fledged ventilation duct, and not every private house has such an opportunity, it is recommended to install small rotary models for domestic needs.
Table 1. Budget models of household recuperators
| Image | Model | Case diameter, mm | Efficiency, % | Power consumption, W | Air volume, m.cub. | Average cost, rub |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Prana-150 | 150 | 91 | 7-32 | 25-115 | 21000 |
 |
Prana-200G | 200 | 88 | 7-32 | 25-135 | 22600 |
 |
TeFO 1 | 110 | 75 | 3,6-36 | 35 | 13000 |
 |
TeFO 3 | 125 | 75 | 52 | 91-100 | 23000 |
 |
Clean Air 16-K | 125 | 78 | 2-16 | 70 | 15900 |
 |
Clean Air 16-M | 150 | 80 | 2-24 | 120 | 17900 |
 |
Mitsubishi Electric VL-100 U-E | 168 | 77 | 26 | 105 | 18110 |
 |
Vents TwinfreshRA-50 | 280 | 90 | 46 | 50 | 18540 |
Small household rotary air exchanger
Air recuperator for home purpose and principle of operation
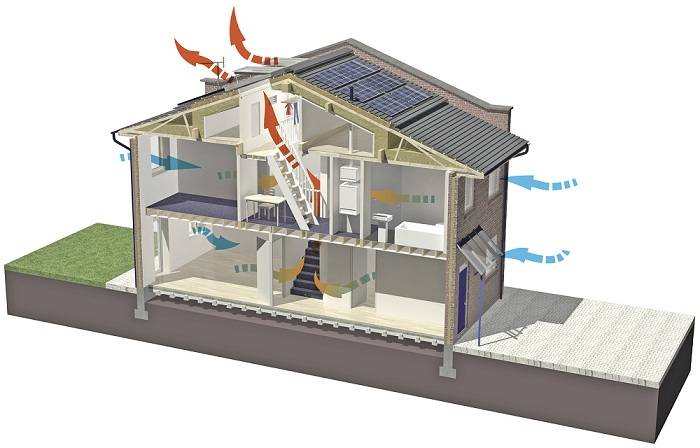
Air recuperation can solve two problems at once:
- provide access to fresh air in the house;
- significantly reduce heating costs.
The need for such devices is growing along with the popularity of new construction technologies.
Frame houses, the use of plastic windows and doors, modern finishing methods make the premises more and more airtight. On the one hand, this is not bad, there are no drafts and heat loss in the house. On the other hand, mold can develop in a sealed room, and the lack of fresh air provokes the reproduction of pathogenic microbes and bacteria.
Which areas need an air exchanger?
- in living rooms with metal-plastic window frames;
- in the garage, where the concentration of exhaust gases and toxic fumes is increased;
- in a bath, sauna, swimming pool, greenhouse and other rooms with high humidity.
Good ventilation is needed in the kitchen - a place of high concentration of vapors and food aromas
news
- Rating of the worst districts of Moscow
- Ventilation of premises and ventilators for premises - all the pros and cons
- Scientists have discovered a new enemy of the office worker - OZONE
- Dangerous places in Moscow
- A third of the world's inhabitants suffer from water shortages.
- The rain will wash away everything: both hair and skin. Atmospheric precipitation is dangerous for the life of citizens
- Anatomy of comfort (microclimate of a country house)
- Do not leave Moscow ... (reasoning of an ordinary Muscovite)
- How to breathe in kindergarten?
- Autumn is the best time to deal with allergies.
- If there is nothing to breathe on the street.
- Breathe Deeper (Review of the Household Ventilators Market).
- If there is nothing to breathe in the apartment. Once again about the ventilation of urban apartments)
- In search of a clean city, area. We choose an apartment.
- Is it possible to organize a "breathing" office
Types of recuperators for forced ventilation
Heat exchangers differ in design, technical characteristics and materials used in the manufacture, which ultimately determines the scope of use of a particular model and the method of its installation. Installation of such systems can be performed inside the wall, outside or inside the apartment (country house).
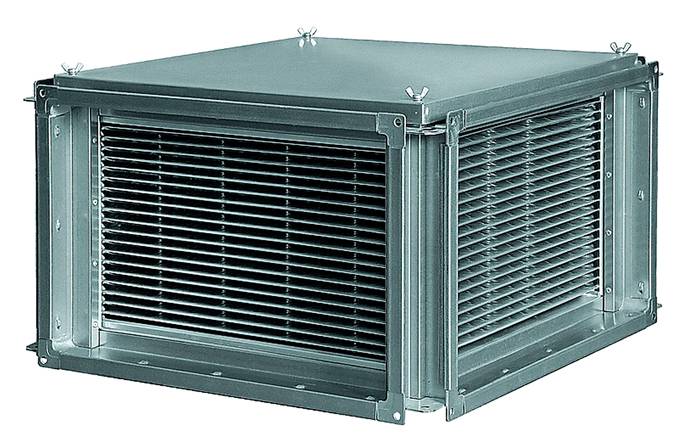
Plate heat exchangers
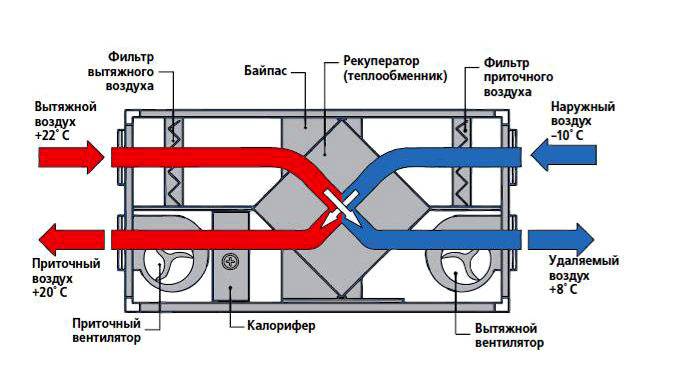
This type of device is highly efficient and affordable. The basis of this type of recuperators is a plate heat exchanger made of copper, aluminum or galvanized steel. The plates are fixed rigidly, warm and cold air do not mix, the process of heat transfer occurs simultaneously in both directions.
Appearance and direction of air flows in a plate heat exchanger
Among the disadvantages of this type of device, it should be noted the formation of condensate on the heat exchanger plates when used in winter, which requires a device for its removal or the presence of a defrosting system.
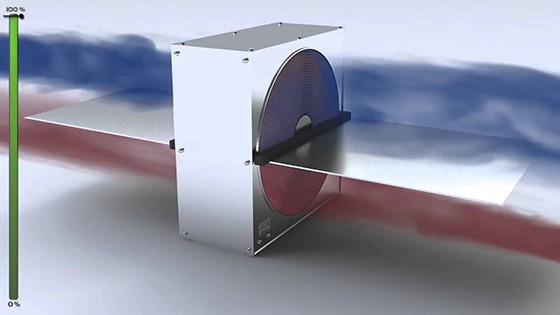
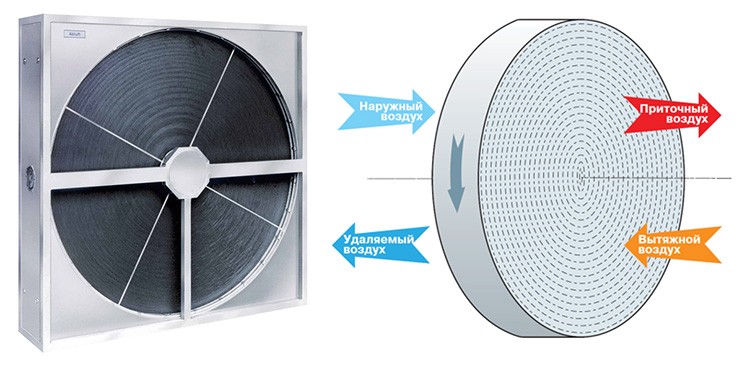
Rotary models
The basis of the design of such models is a heat exchanger rotating around its axis, made in the form of a rotor (rotors) equipped with petals.This is an open system, the disadvantage of which is the possibility of penetration of odors from the external environment into the interior of the premises. The advantages of rotary heat exchangers are such indicators as:
- low probability of formation of condensate on the surface of the heat exchanger;
- high work efficiency;
- ease of maintenance and use.
The performance of rotary models is carried out by changing the speed of rotation of the heat exchanger.
Scheme and appearance of a rotary heat exchanger
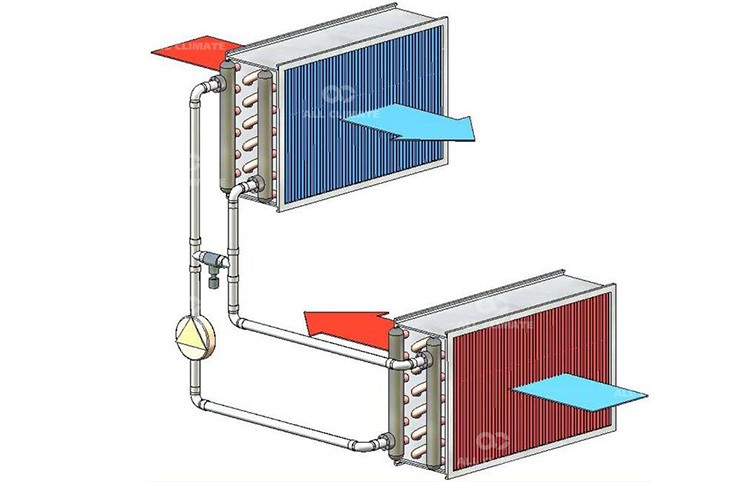
Models with intermediate heat carrier
The designs of this type of recuperators provide for the presence of two heat exchangers through which water or a glycol solution circulates. One of the heat exchangers is located in the exhaust duct of the ventilation system, and the second one is in the supply duct. Accordingly, warm air transfers its heat to the heat carrier in the heat exchanger of the exhaust duct, and on the heat exchanger in the supply duct, the heat carrier gives it to the air coming from outside.
The temperature regime is regulated by changing the rate of circulation of the coolant.
The advantage of this type of device is the absence of contact between air flows, which excludes the possibility of transferring contaminants from one to another. The disadvantages are: low efficiency and the need for fairly frequent maintenance.
Scheme of the device of the heat exchanger with an intermediate heat carrier
Other types of recuperators
In addition to the above types of devices of this type, which are the most common, there are several more:
- roof - designed for outdoor installation, used in ventilation systems at industrial facilities;
- chamber - the basis of the design is a working chamber, divided by a damper, through which the direction of movement of air flows changes;
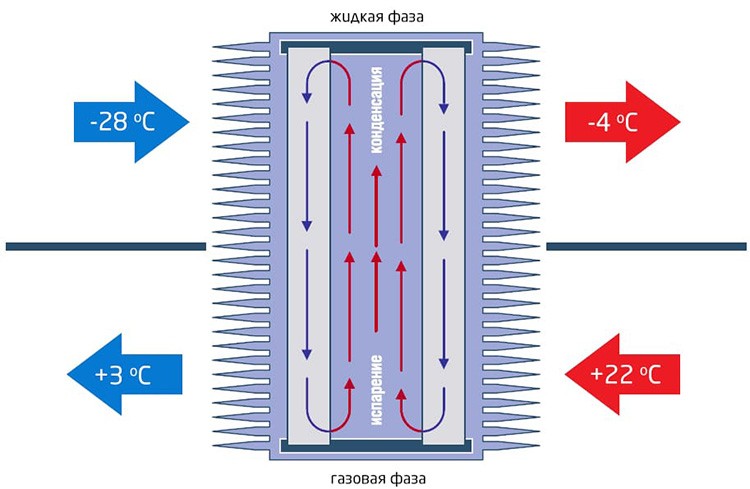
- heat pipes - are a closed system of tubes filled with freon and serving as a heat exchanger.
Scheme of operation of a chamber heat exchanger
These types of devices have the following distinctive features:
- for roof models - high efficiency and cost;
- for chamber models - high efficiency and the possibility of odors and suspended particles from one type of air flow to another;
- for heat pipes - low efficiency and the impossibility of penetration of contaminants from one air stream to another.
The scheme of operation of models operating on the principle of heat pipes
What is a recuperator
The term "recovery" means reverse movement. In the device of the same name, air is exchanged between the room and the street. The heated air masses, passing through the device, partially warm up the incoming flow. This is not a simple airing of the room with the help of a window, when all the heat is irretrievably lost. Recuperation is a method of ventilation with economical heat consumption.

A heat exchanger is built into the device, which stores the room heat and releases it to the incoming air. Ventilation with heat recovery is beneficial primarily to owners of private cottages with an individual heating system. They incur costs for each kilowatt of thermal energy, so they can really experience the savings from using this device.
A recuperator for an apartment may not be so relevant in terms of savings. But there is another benefit of using this device: it effectively cleans the air coming from the street from unhealthy urban impurities and allergens.
Filters in the heat exchanger effectively trap pollen and dust particles
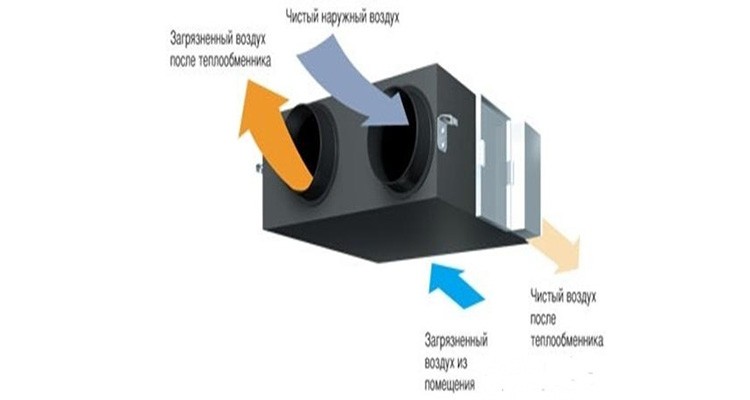
The air exchange device consists of two chambers. Moving through these chambers, the air flows do not mix.
The heat exchanger accumulates heat from one stream and transfers it to another
Such a device can save up to seventy percent of heat, returning it to the room.
Installing a ventilation system with a heat exchanger will cost more than a conventional design, but these costs pay off quickly enough.Taking into account the thirty percent savings on air conditioning and heating of the home, the installation of a recuperator pays off in an average of three to four years. And this is without taking into account the undoubted health benefits of the whole family, because the cost of drugs for allergies and acute respiratory infections will be reduced by an order of magnitude.
Recovery will provide the house with fresh air
The principle of calculation when selecting a PES with a heat exchanger
In both cases, we expect approximately the same calculations. At the "head of the table" is the performance or air consumption. Productivity - the amount of air passed per unit of time. Measured in cube. m/hour. To select this indicator, we calculate the volume of air in ventilated rooms and add 20% (for the resistance of filters, grilles). The resistance of the built-in heat exchanger is already taken into account in the unit's passport data.
 Dantherm HCV5
Dantherm HCV5
Attention! When calculating independently, rounding and tolerances should be done with an increase towards the margin (power, productivity, volume). Consider the example of a country house with ceilings of 2.4 m, 2 bedrooms (12 m2 each), a living room (20 m2), a bathroom (6 m2) and a kitchen (12 m2) are served.
Consider the example of a country house with ceilings of 2.4 m, 2 bedrooms (12 m2 each), a living room (20 m2), a bathroom (6 m2) and a kitchen (12 m2) are served.
Total air volume: (2 12 + 20 + 6 + 12) 2.4 = 148.8, we take 150 m3.
Note. The choice of a more powerful installation is justified if it is possible to increase the area of the premises and to increase the resource of the unit.
Air handling units with built-in heat exchangers
| Indicator | PES model | |||||
| VUE 100 P mini | VUT 200 G mini | VUT 400 EH EC ECO | Dantex DV-350E | DAIKIN VAM350FA | Dantherm HCV5 | |
| Manufacturer | VENTS, Ukraine | VENTS, Ukraine | VENTS, Ukraine | Dantex, England | Daikin, Japan | Daitherm, Denmark |
| Productivity, m3/hour | 100 | 200 | 450 | 350 | 350 | 520 |
| Consumed energy (without heater), W | 86 | 116 | 300 | 140 | 200 | 350 |
| Heat exchanger type | Plates, paper | Plates, aluminum | Countercurrent, polystyrene | Countercurrent, polymer | Counterflow, aluminum | Plates, bimetal |
| Recovery efficiency, up to % | 68 | 85 | 98 | 88 | 92 | 95 |
| Note | Coarse filters | G4 filters, heating optional | Filters G4, F7, heater | 3 operating modes, filters | Fully automatic, replaceable filters | Full automatic, room version |
| price, rub. | 13800 | 16500 | 20800 | 32200 | 61700 | 85600 |
 VUE 100 P mini
VUE 100 P mini
For those who fundamentally do everything with their own hands, the system performance calculations will concern the fans built into the channels. Their performance should already be calculated during the design (calculation) of channels, depending on the volume of air. To select the appropriate heat exchanger, we calculate the total capacity of the fans operating for the inflow to the heat exchanger, and subtract 25% (for system resistance, variable cross section and synchronous operation). One duct fan must also be installed at each inlet and outlet of the heat exchanger.
For our example:
Factory heat exchangers
| Indicator | Heat exchanger model | |||
| KORF PR 40-20 | VERTRO KR 40-20 | NED REC 40-20 | Remak Vento HRV 40-20 | |
| Manufacturer | Russia | Russia | EU | Czech |
| Productivity, m3/hour | from 1000 | from 1000 | from 1000 | from 1000 |
| Heat exchanger type | Plates, aluminum | Channel, aluminum | Plates, aluminum | Plates, aluminum |
| Recovery efficiency/efficiency, up to % | 70/60 | 70/60 | 70/60 | 70/60 |
| price, rub. | 17400 | 18000 | 18220 | 20400 |
Question: What do the numbers 40–20 mean in the labeling of factory recuperators?
Answer: Dimensions of inlet and outlet channels in millimeters. 40–20 are the minimum dimensions of factory heat exchangers.
When installing such a device in a cold place, for example, in the attic, remember that it and the air ducts should be insulated.
Another type of recuperators is autonomous channel heat exchangers. They are also called ventilators. These devices serve only one room and belong to the so-called decentralized ventilation system. They do not require calculations, it is enough to choose a model for the volume of the room.
 Tempero 100T
Tempero 100T
Air ventilators
| Indicator | Model of duct ventilator | ||||
| PRANA-150 | VENTS TWINFRESH R-50/RA-50 | O'ERRE TEMPERO | MARLEY MENV 180 | SIEGENIA AEROLIFE | |
| Manufacturer | Ukraine | Ukraine | Italy | Germany | Germany |
| Productivity, m3/hour | up to 125 | 60 | 62 | 68 | 45 |
| Consumed energy (without heater), W | 7-32 | 3-12 | 12-32 | 3,5-18 | 8,5 |
| Heat exchanger type | Plates, polymer | Plates, bimetal | Channel, aluminum | Plates, bimetal | Channel, bimetal |
| Recovery efficiency, up to % | 67 | 58 | 65 | 70 | 55 |
| Note | Remote control, "winter start" | 4 modes, 2 filters | 32 dB, 5 modes | 40 dB, G4 filters | Synth. filter, 54 dB |
| price, rub. | 9 300 | 10200 | 14000 | 24500 | 43200 |
rmnt.ru
14.10.14
Recuperator for a private house types and selection criteria
Recovery systems are divided into several varieties:
- lamellar devices;
- rotary systems;
- roof devices.
Each type of air exchanger is designed for specific conditions and has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Plate devices
These are the most common heat exchangers, which have a simple design and are distinguished by exceptional reliability. The plate heat exchanger for a private house has an efficiency of up to 78 percent for plastic and metal models and up to 92 for devices with cellulose heat exchangers. The difference is due to the fact that cellulose exchangers return not only heat, but also moisture in the air stream, and moisture, as you know, has a higher heat capacity.
Advantages of plate devices:
- high efficiency;
- reliability in operation;
- Autonomous operation without additional energy consumption.
- plate exchangers are installed only in systems with exhaust and inflow;
- such a heat exchanger freezes up in extreme cold and requires a suspension of work for the duration of defrosting (an exception is cellulose models);
- recuperators of this type do not return the humidity of air flows (with the exception of cellulose).
Rotary devices
Rotary air exchangers are the second most popular type of device. The device is made of aluminum and is driven by an electric motor.
The drive belt rotates the flat and zigzag rotor elements. Each part of the device, when moving through the exhaust zone, heats up and transfers heat to the incoming flow.
- high efficiency;
- preservation of air flow humidity;
- compact dimensions, allowing the device to be used in small ventilation systems;
- the rotor does not freeze over even in severe frosts.
dependence on electricity.
Roof air exchangers
Heat recovery in ventilation systems using plate or rotary devices can be carried out using a special roof unit. Typically, such high-performance systems are installed in large rooms that do not have internal separation. These are mainly hangars, large garages or retail outlets.
The system takes air from under the ceiling and returns it to a zone that is comfortable for a person
The obvious advantage of this type of air exchange is its efficiency, but such devices are not suitable for a private house or apartment.