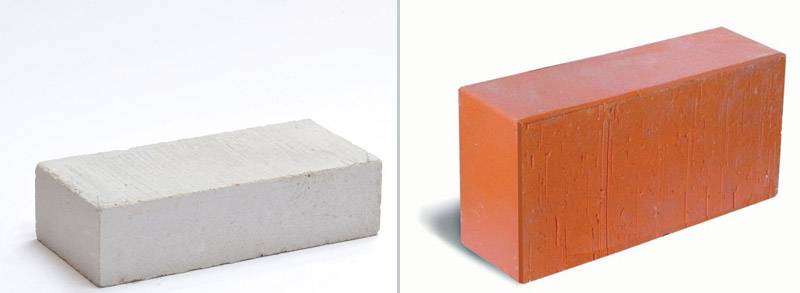
Benefits of brick building
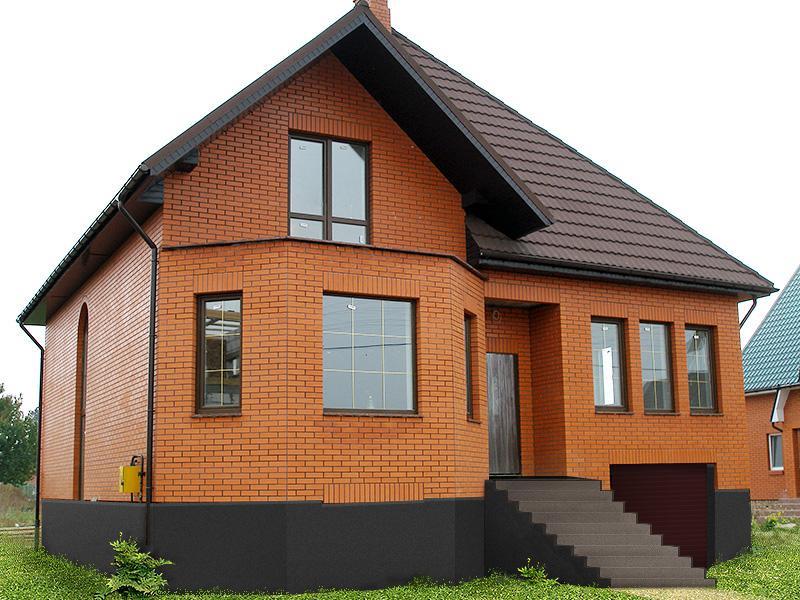
Building country houses from brick has a lot of advantages. If we compare the quality of the material that was used to build houses in Soviet times with the material used now, then the difference is really obvious. Building brick houses is still prestigious and expensive. Modern brick is made in the form of light ceramics, it has a large number of holes, which give it good thermal insulation properties. The construction of brick buildings has the main advantage - the ability to retain heat indoors for a long time.
In addition to a long service life and good heat supply, the construction of brick cottages also has other positive aspects. Brick does not burn, but fire can reduce its performance by almost 60%. The brick is not subject to rotting processes, pests, precipitation or solar radiation cannot spoil it. It is able to carry out heat exchange, i.e., to let the necessary amount of air into the room, and with the onset of summer it protects it from overheating.
Budvelniy cegla is subject to 3 main types
Budіvelny tsegla is divided into three different types: concrete block, silicate and ceramic tsegl.
- concrete block;
- aerated concrete,
- ceramic chain.
Concrete chain preparation is made by way of the inflows in a specially prepared mold with cement rozchin. With this, in everyday life one does not corrosive with a great drink through a great vaga, weak sound insulation, high thermal conductivity and road. From the positive rice of the concrete chain, it is possible to have a low water resistance of about 5%, in some types of 3%, a good quality for the laying of load-bearing walls and a resistance to a low level of atmospheric wear.
Silіkatna tsegl is 89.2% folded from sand, it is necessary to make a good vapno and good additives.
Before the warehouse of the silicate block, 89.2% of the raw material is included, the solution of the water is to make a damp and good additives. In certain cases, to the warehouse of the workpiece, add a farbuvalny pigment to add the necessary information to the block. The water absorption of silicates sometimes reaches 15%. For reasons of reasons, it is not recommended to stay in places with advanced water. Such as basements, laying of foundations, lazen, etc. The silicate block can provide good sound insulation, a reasonable price and finish the stone for laying load-bearing walls. A small amount of high thermal conductivity in porous ceramic tiles.
The dark-girchichny color of the ceramic stone was a sign of under-firing, and in some black spots - about re-baking.
The ceramic block is made from a sum of clays and a vipal track in a tunnel kiln at a temperature of 1000 . Scorched according to the required standards, the ceramic blank has a reddish-brown color and, with a slight blow, it sounds like a ringing sound. Also, the hat can be customized for the color of the ceramic workpiece. The dark-girchichny color shows about the under-burning, and the black ones about the over-burning. For the standard of a red ceramic block, the water resistance can be 6%, or it can reach 14%. Optimum well vodopoglinannya to become 8%. The ceramic block has a sharuvat structure. Vodopoglinannya to know on the middle show. Through the chosen waters, the ceramic ceils between the balls and it was impossible to move the water during the period of significant temperature fluctuations and unfriendly weather minds, the ceramic ceil began to collapse. Small cracks appear on the spadix, which later turn into crack cracks. In the aftermath of which the ceramics were losing their power.
In order to ensure that the walls of the walls were filled with water, they were warm, soft and with good sound insulation, it is necessary to properly build up the work. The ceramic block is the material of the transformations of the trivial hour and different peoples of the world.
Classification of bricks depending on the purpose of use
In construction, there are several types of bricks, depending on the application.
Construction or ordinary
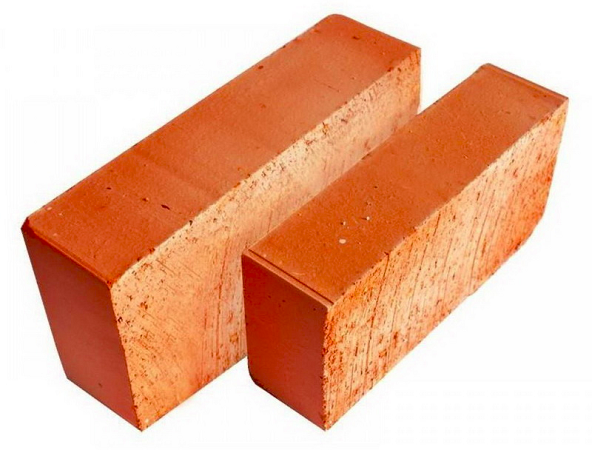
Building or ordinary brick (GOST 530-2007 dated 03/01/2008), is used in the arrangement of both the internal walls of buildings and external ones. It is also possible to use such types of bricks for building a house, but only with subsequent insulation or protective finishing of the facade. This type of brick is far from ideal and may contain small chips, which, however, do not affect its strength.
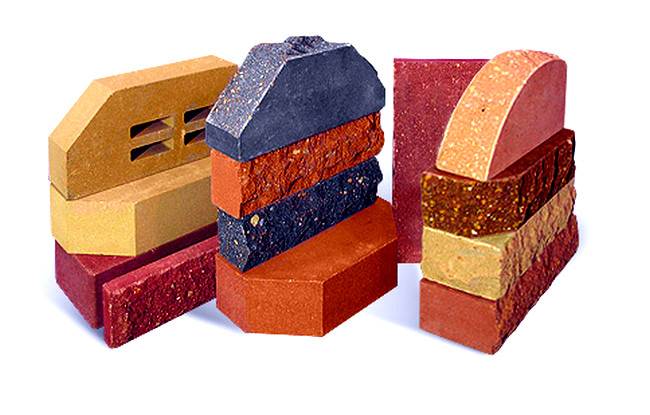
Facing brick
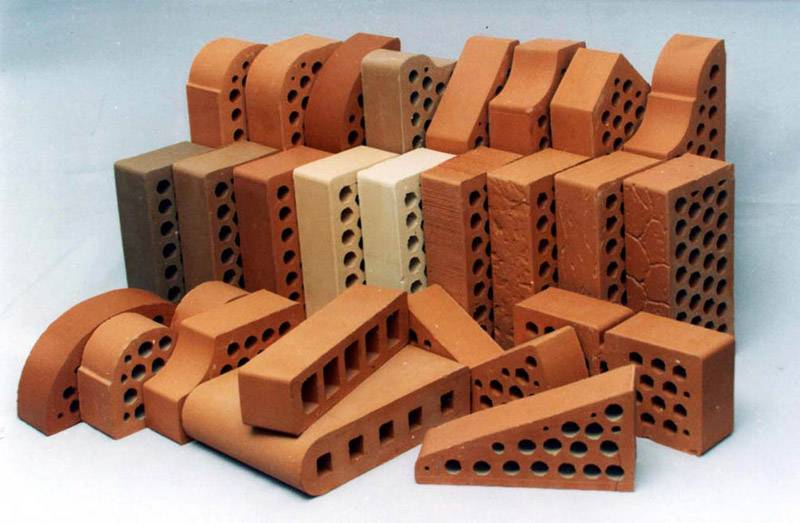
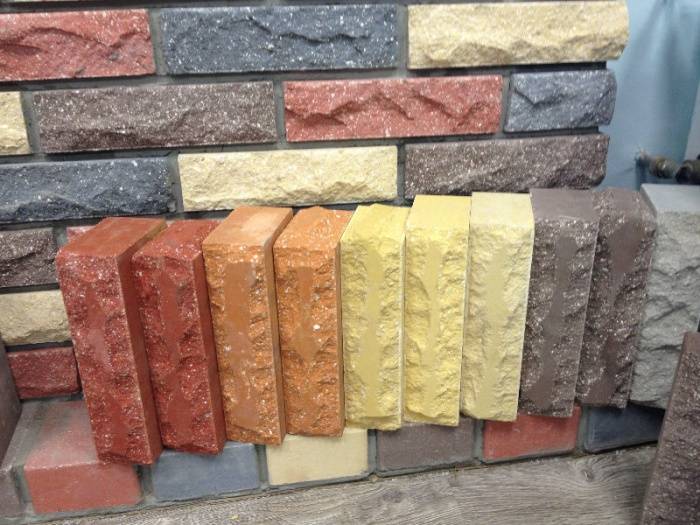
Facing brick, (other names: front, facade) is the most even and ideal material without defects. The maximum permissible deviations according to GOST are no more than 4 mm. in length, 3 mm. in width and 2 mm. in height. Ceramic, silicate or hyper-pressed brick can be used as facing.
There are two types of facing bricks - textured and shaped bricks.
1. Textured brick, with smooth or uneven edges (Ragged stone) is produced for cladding building facades and arranging fences. The edges of such a product can be either rolled, smooth or without processing.
2. A shaped version with different profile configurations, designed for laying complex shapes around windows, window sills, arches, pillars, fences, arbors. For example, shaped types of building bricks with round edges for corners are perfect for arranging complex facades of buildings, namely corners.
The gamut of colors of facing types of bricks is large and ranges from light yellow to almost black.
Furnace, fireclay brick
Furnace, fireclay brick, this refractory product according to GOST 390-96, has a regular geometric shape, a granular base and can be straw-colored, with reddish or brown patches. They serve for isolation and construction of objects exposed to constant high temperatures (stoves, fireplaces). Forming a heat-resistant shell, with the function of protecting the furnace from direct fire or hot coal.
The main qualities that such products should have are: heat resistance, high cyclicity, low thermal conductivity. Fireclay must withstand quite a long heating and many cycles up to a temperature of 1000 ° C without loss of quality and strength. The refractory version is not necessarily made in the correct shape, there are other formats of such products (ShA-25 and SHA-47) - wedge-shaped.
Clinker brick
Ceramic clinker bricks are made from refractory layers of clay, which are sintered until a homogeneous mass is formed. In the choice of clay mass as a raw material for production, they are treated carefully. The composition of the clay should be clean and plastic, it should not contain chalk and alkali metal salts, unnecessary minerals. In the process of heat treatment, the clinker acquires the highest strength and good density. Low hygroscopicity and unpretentiousness to negative temperatures. Shale clay has a suitable composition for this, it is elastic and refractory.
This brick has many colors and textures. Therefore, clinker bricks are used for cladding walls, plinths, paving garden paths.
Determination of hygroscopicity
Water absorption of a brick is one of the most important indicators for hygroscopicity as a percentage.
The higher the hydroscopicity of a brick, the lower its strength.
After all, the hygroscopicity of bricks has a rather impressive effect on the frost resistance of the material. For this reason, when the material is saturated with moisture, its strength will significantly decrease in comparison with dry material. To do this, it is necessary to take into account this important indicator when choosing a brick for the construction of a country estate.
In order to find out the hygroscopicity of a brick, the material is placed in an oven for several hours at a temperature of 110-120 ºС.After heating, the brick is cooled at natural temperature, then weighed. Then it is immersed in water for 2 days and weighed again. The difference in weight determines how much is absorbed into the material as a percentage. For building bricks, the increase in mass should not exceed 5%, and for finishing blocks, no more than 14%.
Types of bricks depending on the nature of the filling
Depending on the filling, the brick can be hollow and full-bodied. The choice of this or that brick will depend on the sphere and the object for the construction of which it is supposed to be used.
solid brick
As the name implies, such a brick has no voids. In a standard silicate product, hollowness in the form of pores does not exceed 12–13%, for a full-bodied variant. In a clinker product, the porosity of the material is up to 5%. Bearing walls are erected only with solid bricks.
hollow brick
For hollow silicate brick, the hollowness index ranges from 24–30%. Indicators of ceramic products are slightly different. Hollowness can reach 45%. Holes or chambers perfectly retain heat, increasing the percentage of overall sound insulation of walls. There is a decorative and facing brick with 4, 6, 8, and even ten chambers, both round and rectangular. Naturally, the filling of bricks affects the strength of the entire structure being erected. Hollow options are used mainly for the construction of partitions. Types of bricks with voids are not used in the construction of fireplaces and stoves.
Features of moisture retention as an operational characteristic
The ability of a material to absorb and retain water is called water absorption. Brick blocks in the erected structure are subject to atmospheric influences, since they have constant contact with the environment. The moisture they come into contact with, they absorb
It is important that the water absorption rate is optimal and meets the standards established for each type of brick. Too high level of moisture absorption contributes to the deterioration of the microclimate in the house due to water that does not have time to evaporate
And at sub-zero temperatures, it turns into ice and expands, as a result of which cracks form in the brick, and this makes it unusable, the strength of the building decreases. If the value is too low, the brick blocks adhere weakly to the mortar, which also worsens the strength.
What does it depend on?
The indicator of the level of water absorption of a brick directly depends on its porosity and the presence of voids in it. The more of them, the more moisture the block absorbs. Therefore, a hollow brick will have a higher hygroscopicity than a solid one. In addition, the ability of the material to absorb moisture depends on its type. There are 3 varieties:
- silicate;
- ceramic;
- concrete.
The composition of the silicate brick includes sand, a little lime with binding impurities. This type of material is the most hygroscopic. Ceramic is made from clay by firing at an elevated temperature, reaching 1000 degrees. The water absorption of ceramic bricks is also quite high, in addition, the layered structure retains moisture inside for a long time, which leads to the destruction of the block when the air temperature drops below 0 degrees. Concrete is made from cement mortar. Such brick blocks have the lowest water absorption rate, but, unfortunately, this is its only advantage over other types of bricks.
Requirements for water absorption of bricks
There are certain limits for the optimal water absorption of bricks. These standards are established depending on its type, purpose and taking into account further operating conditions of the erected structure. The table shows indicators that indicate the boundaries of the possible level of moisture absorption by the building material.
| Classification criterion | brick block | Water absorption level, % |
|---|---|---|
| View | Concrete | 3—5 |
| Silicate | 15 | |
| Ceramic | 6—14 | |
| Purpose | Private | 12—14 |
| Facing | 8—10 | |
| For interior work | 16 |
How is it determined?
The level of water absorption by a brick block is determined by testing the material according to the method identical for all its types, with the exception of some features for silicate bricks. Studies are carried out on intact samples taken from the batch in the amount of three pieces. They are pre-dried in an oven at a temperature in the range of 110-120 degrees. Then the block, naturally cooled at room temperature not higher than 25 degrees, is weighed and lowered into water for 2 days.
After this time, it is taken out of the water and weighed, taking into account the mass of liquid that has flowed into the scales and wet building materials. The water absorption index is defined as the difference between the water-soaked and dry block. The parameter is calculated as a percentage for all 3 samples. The final result will be equal to their arithmetic mean.
Types of secondary brick raw materials
Brick battle retains all the basic properties of the primary material. There are the following types of combat:
- ceramic, characterized by low moisture absorption, good frost resistance and high density. Weight m³ from solid feedstock 2000, and hollow up to 1400 kg;
- silicate, has low frost resistance and absorbs moisture well. The weight of m³ of pebbles from materials that do not contain voids is 1.8 ... 1.95 tons, and the weight of hollow products is from 1.1 to 1.6 tons;
- fireclay, characterized by high refractory properties and low ability to absorb moisture.
The battle of building bricks, according to the size of the pebbles obtained, is divided into the following fractions:
- small - ≤ 20 mm:
- medium - 20 ... 40 mm:
- large - from 40 to 100 mm.
Before separation into fractions with the help of special sieves, the raw material is thoroughly cleaned of foreign inclusions and debris. In individual construction, uncleaned brick battle can often be used, containing parts of different types of brick materials, concrete inclusions and reinforcement.
The thermal conductivity of all considered varieties is characterized by close values.
The increase in demand for scrap is due to the following reasons:
- constant growth of the already quite high cost of aggregates (crushed stone, gravel, natural sand, expanded clay and others);
- in the process of masonry, a brick battle is always formed;
- on many plots acquired for individual construction, there are old buildings that have served their time, interfering with new construction and subject to indispensable dismantling. It is easier to use the obtained secondary raw materials than to incur additional financial costs for its removal from the site;
- constant growth in the city of buildings to be dismantled.
Building bricks are divided into 3 main types
Building bricks are divided into three varieties: concrete block, silicate and ceramic bricks.
- concrete block;
- silicate;
- ceramic brick.
Concrete bricks are made by pouring cement mortar into specially prepared molds. At the same time, it is not in great demand in construction due to its large weight, poor sound insulation, high thermal conductivity and high cost. Of the positive features of concrete bricks, one can note low water absorption of about 5%, in some types 3%, excellent strength for laying load-bearing walls and resistance to rapidly changing atmospheric conditions.
Sand-lime brick is 89.2% sand, the rest is lime and binder additives.
The composition of the silicate block includes 89.2% sand, the rest is lime and binder additives. In some cases, a coloring pigment is added to the composition of the workpiece to give the block the desired shade. Water absorption in silicates sometimes reaches 15%.For this reason, it is not recommended to use it in places with high humidity. Such as basements, laying foundations, baths, etc. The silicate block has good sound insulation, an acceptable price and is strong enough for laying load-bearing walls. The disadvantage is the high thermal conductivity in comparison with ceramic bricks.
The dull mustard color of ceramic bricks indicates under-firing, and in some places black, on the contrary, indicates over-firing.
The ceramic block is made from a mixture of clays and fired in a tunnel kiln at a temperature of 1000ºС. Fired according to the required standards, the ceramic billet has a reddish-brown color and, with a slight impact, makes a sonorous sound. Also, marriage can be distinguished by the color of the ceramic blank. A dull mustard color indicates underfiring, and in some places black indicates overfiring. According to the standard of the red ceramic block, the minimum water absorption should be 6%, but can reach 14%. The optimum water absorption is 8%. The ceramic block has a layered structure. Water absorption is on average. Due to the absorbed moisture of ceramic bricks between layers and the impossibility of rapid release of water during periods of significant temperature fluctuations and adverse weather conditions, ceramic bricks begin to collapse. At the beginning, small cracks appear, which later develop into through cracks. As a result, ceramic brick loses its properties.
In order for the water absorption of the walls built of red brick to remain warm, durable and with good sound insulation, it is necessary to do the finishing work correctly. The ceramic block is a material that has been tested for a long time and by various peoples of the world.
Hyper-pressed, clinker and silicate material
With all the positive characteristics, the red clay brick block remains not strong enough to finish the basement sections of the walls, the porch group or the facades of the paving of roads. For these purposes, clinker bricks with a strength of 400-500 units are used. and frost resistance of 50-100 units.
The clinker block is obtained by high-temperature firing of special mixtures of limestone, marl and red clay. The thermal conductivity of clinker is 7-8 times higher than that of hollow and two times higher than ordinary material, therefore it is used mainly for exterior decoration of buildings. A very durable and wear-resistant material, it can be used to build both fortresses and mansions with equal success.
Advantages of silicate brick
Front
silicate brick
has a number of invaluable advantages:
1.
First of all, the price
silicate brick below the price
ceramic bricks for
15-30%. This is because the production
silicate brick is less time consuming
and less expensive process. So
production cycle of silicate
brick 15-18 hours. For comparison,
ceramic brick it is 5-6 days.
2.
Silicate brick is more economical -
walls from it can be made thinner than
when using ceramic bricks.
At the same time, sound and heat insulating
the characteristics of these walls will not be worse.
And if you use it in construction
hollow silicate brick, walls
become even lighter. Pressure
on the foundation will decrease, and
the strength of the walls will remain the same
level.
3.
Walls made of silicate bricks
have a very finished look.
and do not need additional finishing.
Since silicate brick is excellent
dyed in mass can be used
for masonry stained silicate
brick. Tinted silicate brick
colored with alkali-resistant pigments
and can be any color and shade.
Building bricks are divided 3 main types
Building brick is divided into three types: concrete blocks, silicate and ceramic brick.
- concrete block;
- silicates;
- ceramic brick.
Production of concrete bricks is done by the Bay in a specially prepared form of cement mortar. In this case, the construction is not in great demand because of the large weight, poor sound insulation, high thermal conductivity and high cost. Among the positive features of the concrete brick can be noted a low water absorption of around 5%, in some types of 3%, excellent strength for masonry bearing walls and resistance to rapidly changing weather conditions.
Silicate brick in the 89.2% is made up of sand, the rest of the percentage of lime binders and additives.
The composition of the silicate enters a block of 89.2% sand, the rest of the percentage of lime binders and additives. In some cases, a part of the preform color pigment added to give the required tint block. Water absorption in silicates are sometimes as high as 15%. For this reason it is not recommended to use in places with high humidity. Such as the basement and, laying foundations, baths, etc. Silicate block has good sound insulation, reasonable price and strong enough for masonry bearing walls. A disadvantage is the high thermal conductivity compared with the ceramic brick.
Dim-mustard color ceramic bricks indicates nedoobzhige, and sometimes black on the contrary - to pereobzhige.
The ceramic block is manufactured from a mixture of clay and by firing in a tunnel furnace at 1000 ? C. Burned to the required standard ceramic blank has a reddish-brown color and with a slight kick of the ringing sound. Also, marriage can be distinguished by the color and ceramic workpiece. Dim-mustard color shows on nedoobzhige, and sometimes black on pereobzhige. According to the standard red ceramic block minimal water absorption should be 6%, but can reach 14%. Optimal same water absorption is 8%. In the layered structure of the ceramic block. Water absorption is on the average. Due to the absorbed moisture between the layers of ceramic bricks and the ability to quickly release water in a period of significant temperature changes and adverse weather conditions ceramic bricks begin to deteriorate. At the beginning there are small cracks, which subsequently develop into the through cracks. The result is that ceramic brick loses its properties.
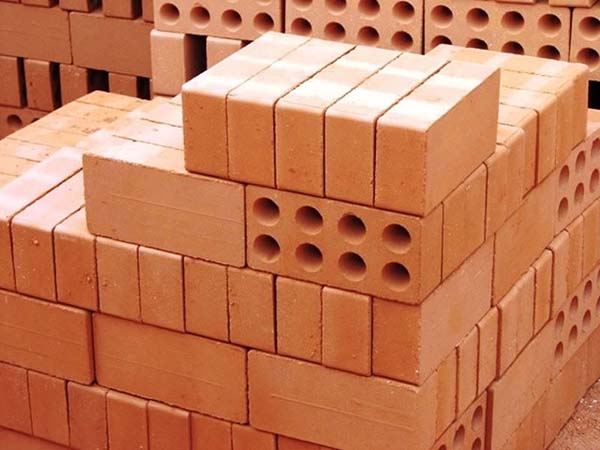
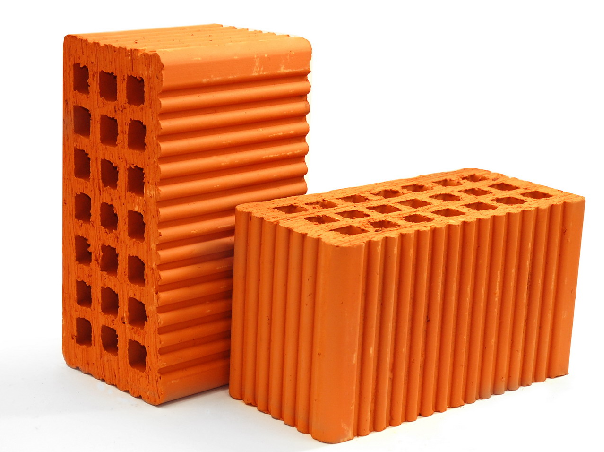
Hollow, enlarged and ordinary ceramic stone
Ordinary bricks have the highest strength, in the range of 200-300 units. they do not have specially made voids, although the proportion of internal pores can reach 8%. The weight of a standard size brick is 4.1 kg. Of all ceramic materials, this one has the highest thermal conductivity - 0.72 W / m ∙ C, therefore it is used only for arranging load-bearing structures and walls.
Hollow bricks are made with special voids, the volume of which can be up to 50%. The weight of a single block is 3.4 kg, but the thermal conductivity is reduced to 0.5 W/m*S. Strength reaches 200 units, so this material can be used for laying residential buildings.
One and two-story buildings are built of brick with a maximum void content of up to 45%, it is easy to distinguish it by the row arrangement of holes. For high-rise buildings, material with 22% of voids is used, they are usually made in the form of squares and are located in the body of the stone in a checkerboard pattern.
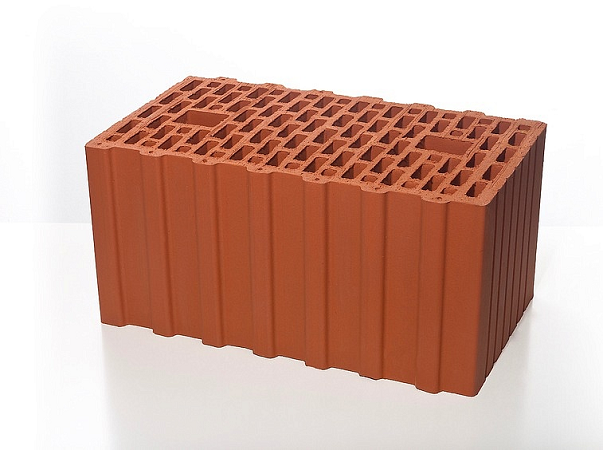
Often, red ceramic brick is stereotypically perceived only as an ordinary, very durable and rather cold wall material. In fact this is not true. The industry produces oversized porous brick stones from fired clay. For example, a 4.5 NF RAUF ceramic block has dimensions of 250x250x138 mm, weight 7 kg, and thermal conductivity 0.22 W/m*C. One such block replaces four hollow stones.
A block of 10.8 NF with a size of 380x253x219 mm can replace ten standard red brick stones. With a weight of 14 kg, the material has a thermal conductivity of 0.15 W/m*C.
Unfortunately, both options, due to the high percentage of voids, have a strength of only 35-60 units. and can only be used for one-story construction.
The difference between ceramic bricks according to the method of manufacture and type of molding
The production of ceramic bricks is divided into two main types according to the molding method. Brick of plastic type of molding and brick of semi-dry type of molding.
1. Plastic molding bricks. Plastic molding involves several processes and is performed from plastic clay masses with a moisture content of 15-21%. The main types of building bricks are produced by extrusion through the profile mouthpieces of various screw presses. There are both vacuum installations and conventional ones. Solid stone is usually pressed on equipment without vacuum, and hollow options - on vacuum plants and presses.
2. Semi-dry bricks. Products of semi-dry molding are also produced from clay using pressing and firing. But the main difference from the plastic method is that the raw material is preliminarily brought to a certain moisture content (about 8–14%). Then it is pressed in molds, and only then it is fired in carousel or tunnel kilns. The low humidity of the blanks allows the finished products to maintain the correct shape and a clear surface.
Solid red ceramic brick
Its advantages and disadvantages
This type of ceramic material, according to domestic and foreign standards, must have no more than thirteen percent of voids inside. Such a brick looks like a rectangular bar with smooth (which is more common) or corrugated sides - spoon and bond.
Due to the almost monolithic structure, the building material is quite strong in bending and compression (especially its high grades, such as M250 and M300). Also, a small number of pores determines the weak absorption of moisture, which gives good resistance to frost.
But there is also the other side of the coin (low porosity).Walls made of such bricks, being strong and durable, are not too warm, so they are insulated without fail (or they can be lined with hollow facing bricks from the outside). In addition, solid bricks are more expensive and heavier than hollow bricks - they require more clay.
Scope of application and features of masonry

As a rule, the dimensions of a brick are related as follows: one to one second and one fourth. Such characteristics make it possible to lay strong walls using dressing in rows, alternating longitudinally and transversely located products relative to the masonry axis.
- You should always start work from the corners, checking each row with a level or cord.
- For foundations and plinths, bricks with high strength and frost resistance should be taken, then lower grades can be used.
About how much it weighs and what kind of solid red ceramic brick has dimensions and technical characteristics, this section will tell.
Characteristics and features
A solid single ceramic red brick should not weigh more than 4.3 kilograms (as a rule, the weight of single stones varies from 3.2 to 3.6 kilograms). This is enshrined in the standard - GOST 530-2012.
- The dimensions of domestic single products are 25 by 12 by 6.5 centimeters. The European marking designates them with RF symbols.
- One and a half bricks (3.7 kilograms) have a thickness of 8.8 centimeters, double (4.2-5 kilograms) - 13.8 centimeters.
Parameters:
- The density of ceramic solid red brick is from 1.6 to 1.9 tons per cubic meter.
- The number of pores is about 8 percent.
- Frost resistance - from F15 to F50.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient of ceramic solid red brick is from 0.6 to 0.7 watts per meter per degree Celsius.
- Strength - from M75 to M200.
We will talk about the varieties and prices of solid red ceramic bricks below.
The video below is devoted to the dimensions of ceramic red solid bricks:
Product varieties
There are the following types of whole products:
- Ordinary brick ceramic red full-bodied - the cheapest and most in demand.
- Chamotte (refractory) brick - made from a special refractory clay called fireclay. Able to endure temperatures up to 800 degrees.
- Front (facing) brick. May have a corrugated or smooth surface. But it is worth noting that full-bodied facing products are used less frequently than hollow ones.
- Shaped brick - has not a rectangular, but a different shape. Its edges, faces and corners can be rounded or beveled. It is used to create arches, columns, and other figured products.
Cost of materials
A simple single ordinary red ceramic solid brick of domestic production of the M150 brand will cost from 6-8 rubles per piece. Facing foreign full-bodied ceramic red bricks can cost from 35 rubles per piece (and more). Chamotte brick will cost from 33 rubles apiece.
Next, we will talk about the characteristics that a hollow red ceramic brick has, its dimensions and price.
The video below will tell about the difference between hollow and solid red brick: