How floor single-circuit heating devices work
The task of floor single-circuit boilers is to provide the room with the right amount of heat.
The floor gas single-circuit boiler is the simplest version of the heating element, the task of which is to provide the room with the necessary amount of heat obtained from gas combustion. This device is intended only for heating the coolant in the system, but with a slight upgrade, it is also possible to obtain hot water. Today, some models of this equipment with already built-in boilers are on the market.
Floor single-circuit units have the simplest and most understandable device. So, the energy carrier, that is, gas, comes to it through pipes. Here the gas is burned by means of a gas burner. The energy from the oxidation reaction is transferred to the heat exchanger, through which the heat carrier of the heating system circulates. Due to the exchange of heat between the heat exchanger and the coolant, the room is heated. The products of combustion are removed through the chimney to the street.
The power of such a boiler ranges from 10 kW to 80 kW, but only if the unit operates on a conventional atmospheric burner. It is not expensive, easy to use, as it has a simple design. It is included in the standard package of the boiler, so you do not need to pay for it separately during the purchase of equipment.
Unlike an inflatable or fan burner. It is not included in the standard set of the unit, but each person can purchase it separately if desired. Although it costs an order of magnitude more expensive, it significantly increases the efficiency (up to 98%) of the boiler, allowing it to develop its power up to 300 kW. But inflatable burners create noise during operation.
Single-circuit boiler and hot water in the house
A boiler can be built into the heating system.
The main purpose of single-circuit floor-standing gas heating boilers is to maintain the temperature regime in the room at the most comfortable level.
But often this equipment is faced with the task of not only heating the house, but also providing it with hot water.
Although a single-circuit unit is not capable of heating running hot water.
This problem is solved with the help of a boiler and indirect water heating.
Characteristics of boilers by the ability to heat water
Today you can purchase a gas heating element, both with a built-in and a separate boiler. In order for the boiler to function, an additional branching is introduced into the system specifically for the water tank.
Types of boilers with a boiler:
-
indirect heating of water, that is, the boiler is placed separately from the boiler. Such units have a variety of volumes in order to provide hot water to all residents of the house or employees in the office as much as possible. Their electronic temperature control system is connected to the gas boiler control system. The required water temperature is set on the boiler, and the boiler is responsible for its constant maintenance. That is, if the water is cooled, then the coolant from the heating system is supplied to heat it. Conversely, when the water is heated to the desired level, the coolant is no longer supplied to the boiler, but is returned to heat the house. A gas heating boiler can heat water in this order even in summer. The coolant is simply not supplied to the heating system, but only works in the boiler-boiler branch;
- heating element with built-in boiler. It is akin to the previous version by the type of water heating, but here the liquid reservoir is hidden under the boiler body. This allows you to significantly save space for the boiler room. You can even not equip the boiler room, but put a heating device in the corner of the kitchen.But here it has a significant drawback - the maximum volume of the boiler is 100 liters, so it will not be able to supply hot water to a house or apartment where there are several bathrooms or a large number of residents.
It is profitable to buy single-circuit gas floor boilers not only because of their low cost. This technique is easy to operate, does not depend on the power supply to the house and works perfectly with the old heating system.
Model range of produced digesters
|
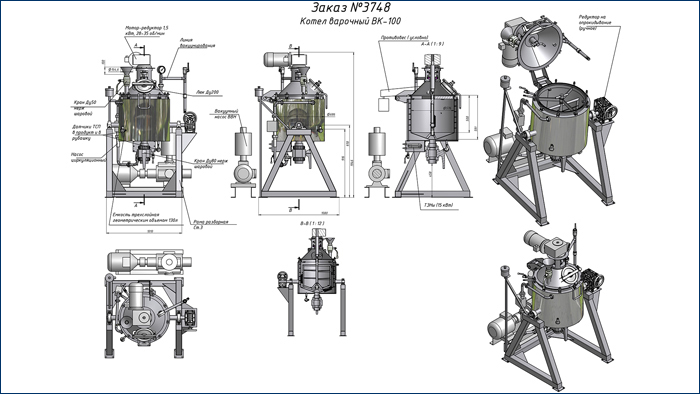
We serially produce a wide range of models of digesters in round and rectangular designs, of any volume and configuration. Modern automatic control systems are used. Heating of digesters is carried out by heating elements or steam. The digester can be manufactured in a vacuum version. Modern automatic control systems for boilers are used, incl. with TOUCH panels |
|
Cooking pot with copper bowl
|
The tilting digester is a thermally insulated multilayer tank made of food-grade stainless steel with a jacket for steam (water, oil, glycerin). The digester is equipped with a control panel that allows you to automate the process of preparing the product. The control panel includes the ability to automatically maintain the temperature of the product, take into account the cooking time and automatically stop the cooking process with an audible signal to the operator. The tilting digester can be equipped with frame-type agitators with fluoroplastic scrapers (scraper, paddle, anchor). |
 |
 |
|
Device: consists of a stainless or copper hemispherical bowl (3) placed in a steam jacket or jacket-strips up to 6 atm (4) and a shell (1) and additionally thermal insulation with lining. Fastened to the uprights (5) or to the frame using bearing assemblies on the steam jacket. Equipped with safety valve (9) and pressure gauge (10). Heating steam is supplied through the valve (8), air is discharged through the valve (2), condensate through the hole (6). The finished mass is unloaded through the lower fitting with a crane. A gland seal (7) is provided between the drain fitting and the bottom opening in the jacket. Can also be tilted |
|
Remote control with TOUCH-panel |
 |
|
Specification for digesters B4-ShKB with copper bowl tiltable |
|||
| Unit name | Volumes boilers |
quantity | |
|
1 |
Three-layer container for example 150l, Mixing device |
100l/ 150l/ 200l/ 250l/ 300l/ |
|
|
1-1 |
Boiler tipping system if needed |
100l 150l 200l 250l 300l |
|
|
If not steam but electric heating is needed, |
50l boiler-25kg 100l-50kg 150l-75kg 200l-100kg 250l -125kg 300l- 150kg 400l- 200kg 500l- 250kg 600l-300kg 800l-400kg 1000l-500kg |
||
Scheme of the device of the digester tilting B4-ShKB
Recommended:
| food pump | Homogenizer | digester | Syrup boiler |
| vacuum reactor | Vacuum evaporator | Vacuum capacity | Dissolver |
| Mixing settings | Zhirotopka | Vacuum Mixer Homogenizer | Bulk material mixers |
| Autoclave | Bioreactor | fermenter | Stainless steel tanks |
| vacuum cutter | Pasteurization bath | Curd bath | Cheese bath |
Which heat exchanger to choose for the boiler
In order for the unit to have a long service life and efficiency, it must have a good quality heat exchanger.
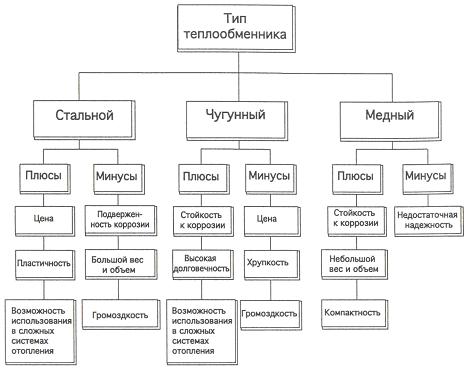
The modern market offers the following types of heat exchangers:
- cast iron is the most cost-effective option. It is durable (it works without repair for about 50 years), has good heat dissipation, is not subject to corrosion, and does not burn out. However, this part may burst upon impact in case of improper transportation and careless installation, since cast iron is a brittle alloy;
- a steel heat exchanger in a single-circuit floor-standing gas boiler is also a common option. Buyers are attracted by its resistance to mechanical damage, that is, it will not crack or bend with a direct impact. It has a lighter weight, unlike cast iron, which will simplify its delivery and installation. However, steel is subject to corrosion and therefore, without an anti-corrosion coating or defects in it, it will rust very quickly. And this will entail costly repairs. The service life of a steel heat exchanger is 5-15 years;
- copper - it is characterized by a low specific gravity, high corrosion resistance and a long service life. However, there is one significant drawback - the high price, because boilers with a copper heat exchanger are very rare and they are reluctant to buy it.
Important:! Whichever heat exchanger is chosen, first of all, you need to check its integrity. Secondly, the presence of a quality certificate
Only with him the equipment will be freely installed by gas services. In addition, the certificate confirms the originality of the product, and such a product will last much longer than a cheap fake.
Classification and technical characteristics of copper-aluminum heat exchangers.
All manufactured heat exchangers can be divided into several groups depending on the features of their installation and operation.
Water heat exchangers.
These devices are used when replacing old or designing new ventilation and air conditioning systems.
In turn, water units are divided into several groups depending on the number of rows in which the copper tube for the heat exchanger is laid:
- one row - such units act as closers in ventilation systems or serve to heat air at temperatures from -10 degrees Celsius. In these products, aluminum lamellas are located at a distance of 1.8 mm from each other;
- two rows - these devices are used to heat air in ventilation systems. Their lamella pitch is 1.8 or 2.2 mm;
- three rows - products are designed to heat air when using a counterflow water start-up scheme (when water and air move in opposite directions). Also, such units are installed in production facilities where, according to the production technology, the products are heated or dried (for example, in drying chambers). Lamellas in heat exchangers of this type recede from each other by 1.8 mm;
- four rows - these devices are used to cool the air in ventilation systems. Their lamella pitch is more significant than that of all previous subgroups, and is 2.5 mm.
Duct air heaters.
This type of units is designed for use in duct-type air ducts and, in terms of its dimensions, fully correspond to the parameters of any air ducts existing and being designed today.
According to the number of rows of copper tubes included in them, the pitch of the lamellas and the shape, all duct air heaters (KVN) are also divided into several groups:
- two rows of tubes, lamella pitch - 2.2 mm, rectangular shape - such a device is designed to heat air in ventilation systems;
- three rows of tubes, lamella pitch - 1.8 mm, rectangular shape - can be used both for heating air in ventilation systems, and as a heat exchange element of the "air curtain" system.
Another subgroup is made up of units of this type, designed for round ducts.
Heat exchangers for central air conditioners.
Such devices are of a wide variety and can be used both in the repair of failed air conditioners, and as separate air heaters or air coolers in ventilation systems or special industrial installations.
The variety of produced models is based on the fact that in most cases careful calculation of both external parameters and technical characteristics of the unit is required. Therefore, quite often they are made to order.
Special heat exchangers.
These products can be used both in air conditioning or ventilation systems, and in a wide variety of technological installations. Their capabilities are much wider than any other types of similar equipment. For example, in addition to water, other liquid and gaseous media can pass through their copper pipes:
- steam or compressed air;
- "anti-freeze" (propylene glycol, ethylene glycol or other liquids with a similar resistance to freezing);
- refrigerants (except ammonia, which adversely affects copper);
- technical oil.
The number of rows of copper tubes in such heat exchangers can vary from 1 to 16, and the lamella pitch is from 1.8 to 8 mm.
Tips for installing and using copper-aluminum heat exchangers.
Installation of copper-aluminum heat exchangers of any type is recommended to be carried out in such a way that the device is located vertically. True, it is worth noting that these units can work in any position that allows normal circulation and discharge of the medium from copper tubes.
It is also important that, in the selected position, venting and condensate removal can be easily carried out.
When choosing a place to install a heat exchanger, it is important to follow some manufacturers' advice:
- heat exchangers in which water acts as an energy carrier cannot be installed in rooms where the working medium inside the tubes can freeze;
- there must be enough free space in the room to connect and maintain all equipment and structures necessary for the normal operation of the device;
- the room air and the medium acting as an energy carrier should not contain any impurities that can cause corrosive processes when interacting with copper and aluminum.
It is very important that the working medium circulating through the coolant pipes also meets certain requirements. For example, if hot water is poured into the pipes, then its temperature should not exceed 180 degrees Celsius, and the pressure should not exceed 1.6 MPa
The speed of its circulation cannot be less than 0.5 m/s and more than 2 m/s.
In addition, it is worth taking care of the purification of water entering the heat exchanger. A filter installed in front of the inlet will prevent solid particles from entering the tubes that can completely block the passage. And the use of water freed from calcium salts will help to eliminate the gradual narrowing of the channel due to the appearance of deposits on its walls. After all, it is this water that is used in the central heating system.
It is also necessary to prevent freezing of water in the heat exchanger when the temperature drops. If it is not planned to use the device in an unheated room during the cold season, then the water must be drained from it, and the tubes must be dried from the inside by blowing with compressed air.
As for the maintenance of the device, it is not too difficult and any preventive work (for example, cleaning of working surfaces) is required no more than once a year
In addition, it is necessary to regularly inspect the heat exchanger, paying close attention to its “weak” points. To do this, it is worth checking the tightness of the bolts, if any, the tightness of the copper tubes, and also make sure that the aluminum plates are not dirty or deformed.
Which heat exchanger material is better
boat
The heat exchanger is a structural element of the boiler, which allows the transfer of heat from the combustion chamber to the coolant. An important role is played by the material of manufacture of the part. So, there are steel, cast iron and copper heat exchangers. True, the latter are intended only for gas boilers, but cast iron and steel products are universal, due to which they are used in the design of boilers of any type.
Material properties
The price set for a copper heat exchanger is quite low, but it is categorically not recommended to use it in solid fuel boilers. The part under the influence of a flame quickly burns out. Only additional hot water heat exchangers are made of copper, but they are not located in the furnace, but are immersed in water. In addition, copper is not compatible with aluminum radiators and pipes, which leads to premature wear of the heating system.
Cast iron and steel have the best qualities: they are universal, and also do not burn out in the firebox flame. Hard water is harmful to cast iron, which leaves deposits on the surface of the heat exchanger
In addition, cast iron is subject to mechanical damage, which means that it must be transported with extreme caution. The price of a plate-type heat exchanger installed on a steel heat exchanger corresponds to the cost of a cast-iron product, because in many respects these parts are similar
True, steel has less weight, and is also not as critical to mechanical stress as cast iron. It is worth noting that both materials are susceptible to corrosion, however, in cast iron with its thickness, it is less pronounced.
Where and what heat exchangers are used?
As stated above, a copper heat exchanger is only appropriate in gas boilers. This material has a small mass, and therefore the parts made from it are suitable for installation in wall-mounted heating equipment.
Also, steel heat exchangers are used to equip wall-mounted boilers. The same components have proven themselves in the design of floor boilers. With cast iron, everything is more complicated: a heat exchanger made from it has a significant weight, which means that its scope is limited. Of course, cast iron can be used in wall-mounted boilers, but then you have to sacrifice the size of the heat exchanger, and this will limit the quantitative heat transfer. Therefore, cast iron products are best suited for floor heating equipment.
Length
{D}
year
{E}
Hull material
{F}
engine type
{G}
location
{J}
price
{I} {H}
You do not have sufficient rights to add comments.
You may need to register on the site.
Heat exchanger material
At present, three main types of heat exchangers are used in the manufacture of boilers: copper, steel, cast iron and stainless steel. Recently, heat exchangers made of aluminum have also been used, but since it is known that aluminum reacts with water, we do not consider them in this article.
It is safe to say that when you seek the advice of a specialist, you will have to choose one of these options.
Boilers with steel heat exchangers.
They are the most common, especially among the products of domestic manufacturers: - and this is mainly due to the availability of the material and the relative ease of its processing.
The main advantages of boilers with steel heat exchangers are the relatively low price and good plasticity of the material.
The latter is of great importance, since during operation the heat exchanger is periodically subjected to direct thermal action of the burner flame, as a result of which so-called thermal stresses arise in it, which can lead to the formation of cracks in the heat exchanger housing.
The disadvantages of steel heat exchangers include their susceptibility to corrosion.
During the operation of the boiler, both the internal and external surfaces of the heat exchanger are exposed to corrosion, as a result of which its destruction may occur.
The disadvantages of a steel heat exchanger are also its relatively large weight and volume.
These characteristics reflect the degree of inertia. In other words, part of the gas will be spent on heating the heat exchanger and the water in it, i.e. Not all heat is used for its intended purpose - for heating the coolant.
The greater the weight and internal volume of the heat exchanger, the more fuel will be wasted.
Cast iron heat exchanger
It is characterized by corrosion resistance and durability. Cast iron places high demands on compliance with the rules for designing and operating the boiler.
Its uneven heating (for example, due to the appearance of deposits in the overburner part when using poorly treated water) causes material cracking.
There is also the concept of "low-temperature corrosion" - cracking of a cast-iron heat exchanger due to the temperature difference in the heating zone and the place where water enters it from the return line of the heating system.
To avoid this, an additional element is included in the circuit - a four-way mixing valve that adds hot water from a straight line to the "return" at the boiler inlet.
If, instead of the promised 20 years of operation, the cast-iron heat exchanger has served a season, the seller, as a rule, citing non-compliance with operating conditions, refuses to replace the heat exchanger free of charge, the cost of which is often 50-60%. boiler cost.
Unfortunately, it is expensive imported boilers that are the most vulnerable, and this is due to the high casting technology, which makes it possible to manufacture heat exchangers with thinner walls.
The disadvantages of cast iron heat exchangers are high cost, fragility (susceptibility to cracking due to improper operation), high inertia due to large weight and volume, and bulkiness.
Heat exchanger - copper
Its positive qualities are corrosion resistance, low weight and volume (low inertia), compactness.
The fact is that a copper heat exchanger is capable of transferring more heat with much smaller dimensions, and per unit of its mass there is a much greater thermal effect than a steel and, especially, a cast-iron heat exchanger.

Practice shows: in terms of durability, copper heat exchangers of boilers equipped with the necessary functions are practically not inferior to cast iron ones.