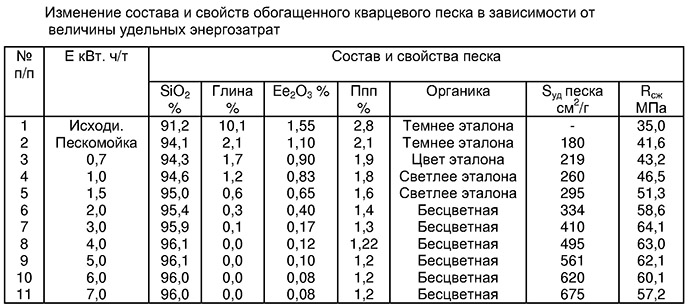
Sandblasting
One of the most effective surface cleaning methods is sandblasting. Quartz sand or other abrasive is sprayed onto the surface (glass, metal, stone, wood) to be cleaned using a compressed air or water jet.
The grains of sand fly at great speed and destroy the top layer of the surface, cleaning it from scale, corrosion and other coatings. It is necessary to ensure that together with the removed layer, for example, mold on old masonry, the stone itself is not damaged. Quartz sand for sandblasting must be selected taking into account the surface material, the degree of contamination and further processing.
Main areas of work:
- cleaning metal from rust and other contaminants; degreasing surfaces; matting glass; cleaning concrete and masonry; roughening the surface for further processing.
Today there is a wide variety of abrasive materials, but dry quartz sand remains the most popular for sandblasting.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF QUARTZ SAND USED TO FILL TRANSFORMER
To fill explosion-proof transformers, quartz sand with a granulometric composition of 0.5 to 1.6 mm is used, and the percentage of quartz must be very high. For example, the sand of the Volsk deposit (Saratov region) contains up to 98-99% of grain fractions from 0.5 to 1.6 mm, and the grains of these sands have a rounded shape, which is of great importance. During operation, the active parts of the transformer (windings, magnetic circuit) vibrate, and if the transformer is filled with sand with sharp grain edges, the insulation of the windings and taps may be damaged.
The content of quartz Si02 in the sand should be 97-98.5%; Fe203 not more than 0.08-0.12%; A1203 not more than 0.5-1.75%; CaO not more than 0.25-0.4%; MgO no more than 0.1-0.2%; other elements 0.5-0.7%. Clay impurities and other contaminants are removed from the sand by washing. The thermal conductivity of the sand of the above chemical composition is 0.00394 W / cm-deg, while cardboard is 0.0016 W / cm-deg; impregnating varnishes - 0.002 W / cm-deg. The high thermal conductivity of quartz sand makes it possible to effectively remove heat from the active parts of the transformer to the casing.
Dry quartz sand (humidity 0.05-0.1%) has a fairly high electrical strength. The breakdown voltage of quartz sand for different layer thicknesses is shown in fig. 3-3. But in the conditions of a mine, where a high percentage of relative humidity (up to 98%) and temperatures up to 35 ° C are observed, and where, in addition, “drip” directly onto the transformer is possible, sand and transformer insulation are highly moistened, the dielectric strength of sand decreases by 2 -2.5 times, which can lead to failure of the transformer.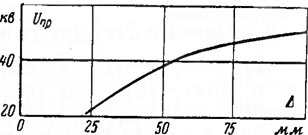
To reduce moisture absorption and increase the specific volumetric resistance of sand, it is hydrophobized - it is treated with polyorganosiloxane liquid GKZH-94 or liquid AMSR-3, GOST 10834-64. Sand treated with a 1% solution of GKZH-94 in white spirit has a volume resistivity several times higher than untreated sand (Fig. 3-4).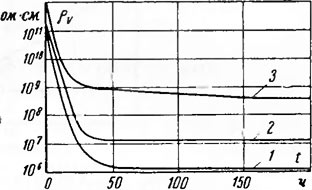
1 - unwashed sand; 2 - washed forest; 3 - sand washed and treated with a 1% solution of GKZH-94. The control values of the electrical characteristics of hydrophobized sand when the transformer is released from the factory should not be less than the values \u200b\u200bgiven in Table. 3-1.
Table 3-1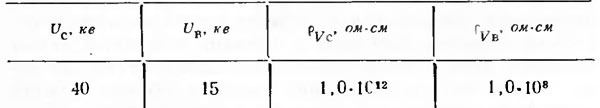
The insulation resistance of transformers of the TKSHVP type with hydrophobized sand is: between the HV-LV windings 1000-5000 MΩ, the VN winding - earth 1000-5000 MΩ. LV winding - earth 30-45 MΩ and during operation in a mine environment with a relative humidity of 98% does not fall below the permissible values equal to 1 MΩ / kV according to GOST 183-66, while the insulation resistance of transformers with non-hydrophobized sand decreases during operation up to 1-0.3 MΩ, as a result of which some transformers fail.
Applications of quartz sand
Calcined quartz sand is used:
- for sandblasting, in the manufacture of dry building mixtures, in landscape design, in urban improvement, when laying paving slabs, in gunning.
Calcined quartz sand is more expensive than other types, the cost of quartz sand is explained by the fact that the processing process itself is quite expensive. However, the quality of this type of sand is much higher - the firing process allows you to thoroughly clean the quartz sand from impurities, including clay and gravel, after which the sand is sifted fractionally and packaged in big bags - special synthetic containers that protect the material from dirt and humidity. Which also affects the quality of the sand.
In sandblasting, fine-grained quartz sand is usually used. In many countries, dry blasting is prohibited due to high risks, while in Russia, the process requires the use of a cleaning suit and careful safety precautions. In addition, hydro-cleaning is used - the supply of abrasives under running water, it is safer.
For dry building mixtures, various types of quartz sand are used, both fine and coarse. The latter are in demand in the manufacture of decorative plaster and other decorative mixtures.
In landscape design and urban landscaping, quartz sand is used to sprinkle paths, create gardens, even in sandboxes.
When laying paving slabs, sand is used as a substrate, and in gunning it is used as sand in a cement-sand mortar.
Characteristics and main properties of quartz sand
Table of application of quartz sand depending on the fraction.
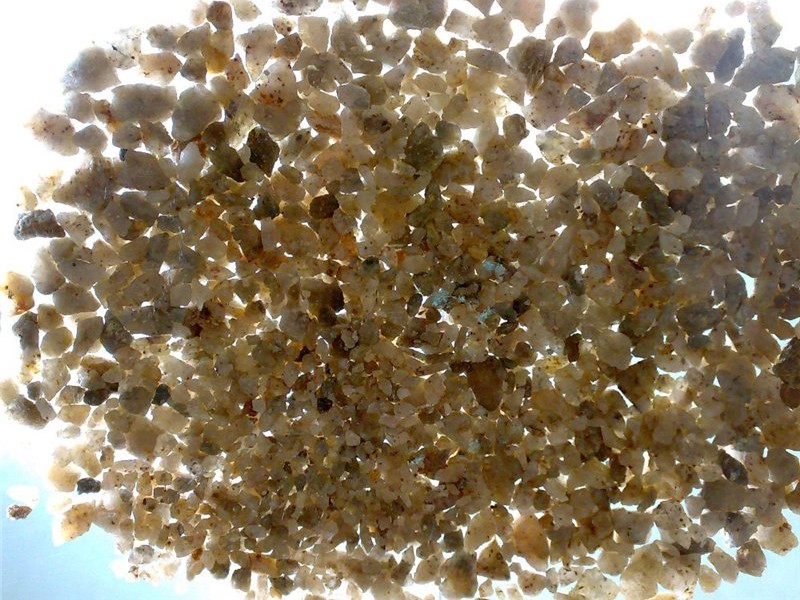
Quartz sand is loose quartz - the most durable material in nature. Such sand can be obtained both naturally, when natural stone crushing occurs, and artificially, when quartz is deliberately crushed. But most often quartz is crushed independently.
Quartz sand is most often a very loose homogeneous material, which, depending on the specific subspecies of quartz and the nature of its crushing, differs in fractions. The minimum grain size will be about 0.05 mm, the maximum - 3 mm. Very often quartz material contains additional impurities in small quantities, but may contain up to 90% silica.
Whatever way it is mined, it undergoes additional thorough cleaning, sifting, and also sorting into fractions. This makes it possible to divide the material into grades, as well as to weed out low-quality sand and debris from it.
It has several more properties that distinguish it favorably from all other types of sand. This is a high adsorption capacity, an unusual resistance to mechanical and thermal stress, and a high degree of adhesion to various materials and mixtures.
Areas of use
It covers manufacturing, construction, the food and pharmaceutical industries, and other industries where the use of such material is often quite unexpected, but quite justified.
Use in construction
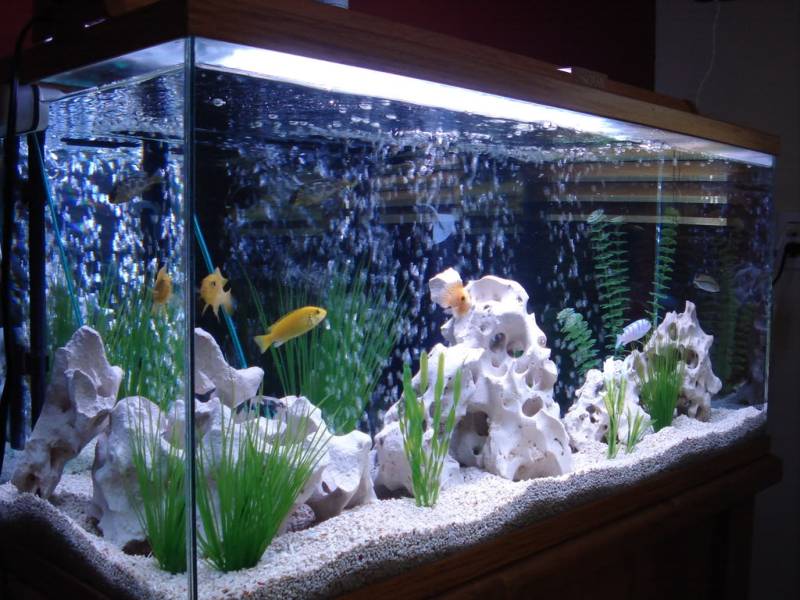
The principle of operation of the filter with quartz sand for water purification in the pool
Quartz sand is quite often used to make all kinds of blocks and bricks. Concrete blocks with the addition of quartz material have a rather calm color scheme of pastel shades. And this, in turn, makes it possible to successfully apply them for facade construction and decoration. The same goes for bricks. Moreover, bricks and blocks are extremely durable. Therefore, bricks for kilns are often made with the addition of precisely the quartz type of sand.
Special attention deserves cement and various mixtures for asphalt laying. So, their most high-quality options are still produced on the basis of sandy quartz. As for cement, all brands of modern Portland cement are now on sale with the addition of sand. This increases the adhesion of the future solution to the surface. In some cases, such an amount of this material is added to the cement that it is not necessary to add it additionally.
Expensive asphalt pavements also have quartz-type sand in their composition. This is especially true for roads where there is increased traffic. After all, the load on the coating is quite large, so the durability of the asphalt should be appropriate.
Quartz sand is the best additive in plasters for exterior or interior types of decoration. In this case, you can choose not only the brand corresponding in functionality, but also its shade. And this will greatly affect the final shade of the plastered coating.
Quartz sand-based plastering mortars are the most beautiful and reliable. For a long time, they do not give absolutely no cracks, and they also facilitate the process of imparting ideal smoothness to the surface due to the fact that it is the quartz mixture that is selected for a particular fraction suitable for work.
Applications in industry and water treatment
The distinguishing characteristic of quartz sand is the homogeneity of its crystals, which makes it an ideal material for glass production.
Quartz sand is quite successfully used in our time in porcelain, faience and glass production. All this is due to its strength, which it transfers to subsequent manufactured items. As a rule, most items made of such material are made of quartz sand.
This also includes the use of sand for the manufacture of lenses of various types, which already applies to the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the fact that its abrasive properties are very high, the glass is perfectly smooth and durable. At the same time, transparency is absolutely not lost, since white quartz sand is widespread, which is used in this case.
Particular attention is paid to quartz sand in the food industry. Namely, it is widely used for water purification
Due to its good adsorption, this substance is able to retain and absorb all the smallest harmful impurities from the liquid. Therefore, many expensive filters today work precisely thanks to him. After all, the ability to monomineralism is observed only in this sand, not in river sand, not in ravine sand.
The only drawback here is the need to periodically change the sand, because, otherwise, it will simply lose its properties gradually, become dirty and unsuitable for perfect cleaning. In addition to all this, the degree of enrichment of the liquid with useful microelements contained in quartz will noticeably decrease.
So, the main properties and areas of use of quartz sand are considered today. With the development of science, the areas of use of the material are developing even more, while the quality of the sand itself is improving. Therefore, even despite its high cost, you need to use it.
Photo of quartz sand






























We also recommend viewing:
- The best vapor barrier for your home
- How to choose drywall
- Which cement is better to choose
- Types of drywall fasteners
- Extruded polystyrene foam
- Dry backfill
- The use of concrete contact
- Types of heaters and their properties
- Masonry mix for bricks
- The best grout for tile joints
- Types of anchors for concrete
- The best dry putty
- What plaster mixes are better
- Overview of the best additives in concrete
- Dimensions of asbestos-cement pipes
- How to choose ceramic tiles
- What is the best underlay for laminate flooring?
- An overview of the best waterproofing materials
- Which brick is better
- Types of profiles for drywall and their application
- How to choose a roofing material for a roof
- Which tile adhesive is better to choose
- Facade finishing materials
- The best mounting adhesive for foam blocks
- Wall primer
- Glass fiber in the interior
- Types and properties of sealant
- How to choose drywall
Help the site, share on social networks 😉
INTRODUCTORY REMARKS
Until recently, transformers for industries with explosive atmospheres were conventionally oil or air cooled. Despite the fact that oil is a good filler in insulating and thermal terms, its use for mine transformers is undesirable, since: a) it ignites easily, burns, emitting large amounts of smoke; b) absorbing atmospheric moisture, significantly reduces the electrical strength; c) upon contact with air, it oxidizes, decomposing the insulation; d) requires constant monitoring of its level in the tank. Filling explosion-proof transformers with non-flammable liquids instead of oil, such as sovtol, sovol, organofluorine liquids, etc., has not yet found wide application. Sovol and sovtol are toxic, relatively expensive, and emit soot and harmful gases under the action of an electric arc. Organofluorine fluids are very expensive, and are vigorous solvents for insulation and varnishes commonly used in the manufacture of transformers.
Explosion-proof air-cooled transformers produced by the industry are also not without significant drawbacks.
The active part of such a transformer, in order to ensure the requirements of explosion safety, must be in a strong shell filled with air having a low thermal conductivity. As a result, it is necessary to limit the electromagnetic loads of active materials and use expensive organosilicon insulation. As a result of constant air exchange, the insulation is exposed to moisture, especially during non-working periods, which makes it necessary to have large insulation distances both in the air and on the surface of the insulation structures.
Methods for providing explosion protection for different versions of transformers are different. In air transformers, the so-called flange explosion protection is used, which is provided by the width of the flanges and the size of the safe gap between them. The essence of this explosion protection is that during an explosion inside the shell, incandescent particles, as well as flames, cannot be thrown into the surrounding explosive environment, i.e., they cannot transmit the explosion due to the large width of the shell flanges and the small gap between them, provided that the mechanical strength shell is sufficient. The value of the critical clearance bcr between the flanges for the methane-air mixture depends on the width of the flanges A, if it is less than 50 mm. With flange widths greater than 50 mm, the critical gap is almost constant at 1.2 mm (Fig. 3-1) . In 1928in the USSR, for the first time, a method was proposed to achieve explosion protection using quartz filling, which involves immersing electrical parts of equipment in quartz sand.
Quartz sand has the following properties; a) has a sufficiently high electrical strength;
b) non-flammable, chemically inert and non-toxic; c) has a relatively high thermal conductivity; d) has a volume expansion coefficient close to that of steel.
Mining Features
Quartz can be divided into primary and secondary. The first variety is formed directly during the decay of granite, located under a layer of clay, mixtures. This is a decomposed granite, which lies in one place for a long time, without being exposed to water, sun, air.


Mining of primary quartz
It is extracted from the places of occurrence, transported for processing. Then the clay is dissolved, the quartz is dehydrated, calcined. The material is divided into fractions, packaged.

Extraction of secondary quartz
Raw materials are collected from reservoirs by a pump. Then the mixture is transferred to the places of accumulation. They form a quarry on the ground, collect deposits with the help of an excavator and other equipment.
Physical properties of quartz sand
Sand is characterized by all the properties of quartz:

- bulk density 1300-1500 g / cm3 abrasion - 0.1 crushability - 0.3 hardness (Mohs scale) - 7 (for comparison, the hardness of diamond - 10) use by radioactivity - class 1
The density of quartz sand is determined by two different approaches.
There is bulk density, and there is true density. Bulk is calculated as the ratio of the mass of the material in a bulk state to its volume. This value includes the pores in the sand grains and the air spaces between them.
That is, this value may vary depending on the moisture content of the material. True density is a constant value, it is the ratio of a substance in an absolutely dense state to its volume. The moisture content of the sand does not matter.
To change the density, the chemical composition or molecular structure must be changed. Bulk density is less than true. The density of the material is an important characteristic that must be taken into account when calculating storage space, its transportation and movement by handling equipment.
Abrasion, crushability and hardness of quartz sand are indirect indicators of its strength. To determine the values, the grains are tested on a rotating wearable circle of metal, the mass of fractions is compressed mechanically and scratched by the grain of the standard and, conversely, by the grain standard.
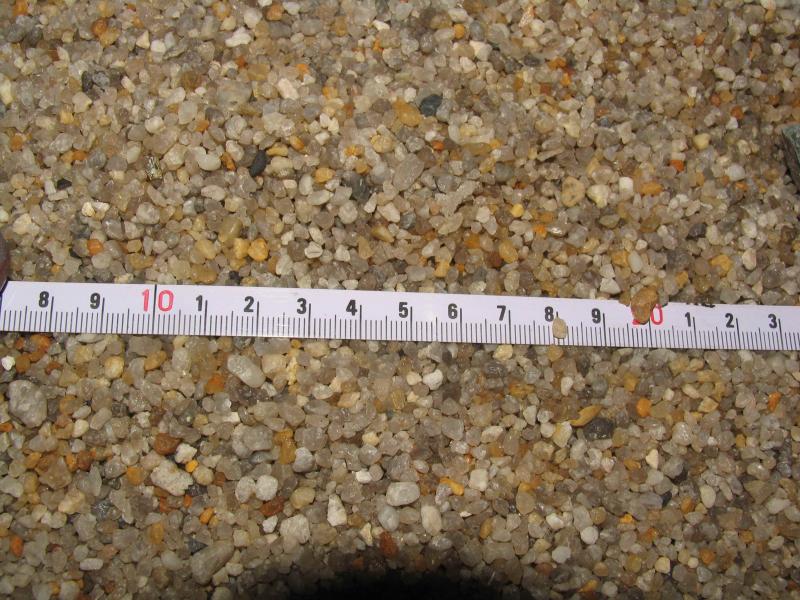
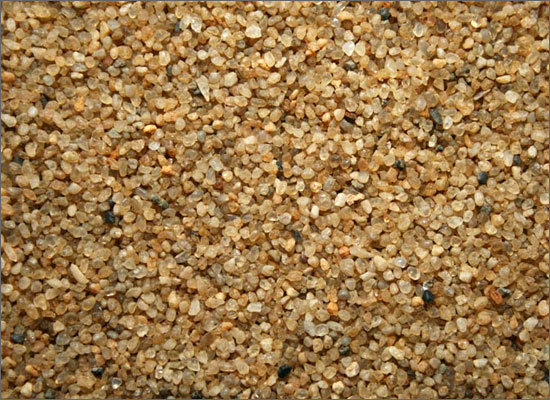
Fractions of quartz sand:

- pulverized - less than 0.1 mm fine-grained: 0.1-0.8 mm medium-grained: 0.8 - 1.6 mm; coarse-grained: 1.6 - 6.0 mm
Pulverized and fine-grained quartz sand is used as part of various building materials, such as building mixtures, putties, grouts, abrasive materials, thin plasters and paints.
Quartz sand of medium grain size is used for filtering and cleaning liquids, for sandblasting, for building mixtures, facade and interior plasters, self-leveling floors, concrete mortars, in landscape design, for backfilling sports grounds.
The material of large fractions is used for the manufacture of paving slabs, concrete blocks, landscape decoration. It is also used for filtering.
Sand of all fractions is used in the glass, foundry and chemical industries.
Classification
Quartz sand is divided into:
- river (is the cleanest and most expensive);
- marine (particles are mixed with clay and silt elements. Demand for it is less than for river);
- soil (cellar, located under a layer of clay, soil. It is characterized by an acute-angled shape and roughness. It is used in construction work);
- ravine (has impurities of silt.These are rough fractions of an acute-angled shape. They are part of the solutions of plaster, concrete);
- mountainous (the origin is located in a mountainous area. According to its characteristics, it is close to a ravine).
Quartz sand is divided into natural and artificial. In the first case, rounded, natural sand appears as a result of the action of water and air. Quartz grains become smooth and round.

Its advantages include the following:
- Silicon oxide IV is 98%.
- Contains no organic impurities.
- Resistant to mechanical and chemical influences.
- High temperatures withstand easily.

Mining and production of quartz sand
The extraction of quartz fractional sand is carried out by an open pit method or by a dredger from natural deposits in the floodplains of rivers and lakes.
A small amount of impurities and a large amount of quartz - this is what distinguishes developments in which quartz sand is mined from quarries in which ordinary construction sand is mined. The extracted raw material goes through a number of technological processes: washing from mud deposits and cleaning from impurities by a chemical method.
This process is called enrichment, it serves to obtain sand of the required quality. As a result, the content of quartz rock increases, and the purest material is obtained, which, after drying on special installations, passes through a series of sieves and is distributed into fractions. The resulting product is called fractionated quartz sand.

The process of extraction by a dredger is as follows: a mixture of sand and water from the bottom of the reservoir is pumped and transferred through a special pipeline to the storage site. The water gradually separates from the extracted soil and goes back into the reservoir through the drains. The resulting material is sent to the enterprise for its further enrichment and separation into fractions.
Artificial quartz sand is obtained from veined quartz rock, which is first sent to the crushing complex. There, the raw material is crushed into grains. This is followed by procedures similar to when working with quarry sand: the material is washed, dried and separated by a technical sieve into fractions.