Basic set of equipment for greenhouses and greenhouse complexes
When designing a winter industrial greenhouse of a modern type, one should take into account the need to place systems and communications inside the building that are directly involved in technological processes:
- climate systems associated with ventilation, heating, ozonation, etc.
- energy supply and lighting;
- hydroponics, watering and irrigation systems;
- equipment for sorting and cooling products;
- control and monitoring automation devices.
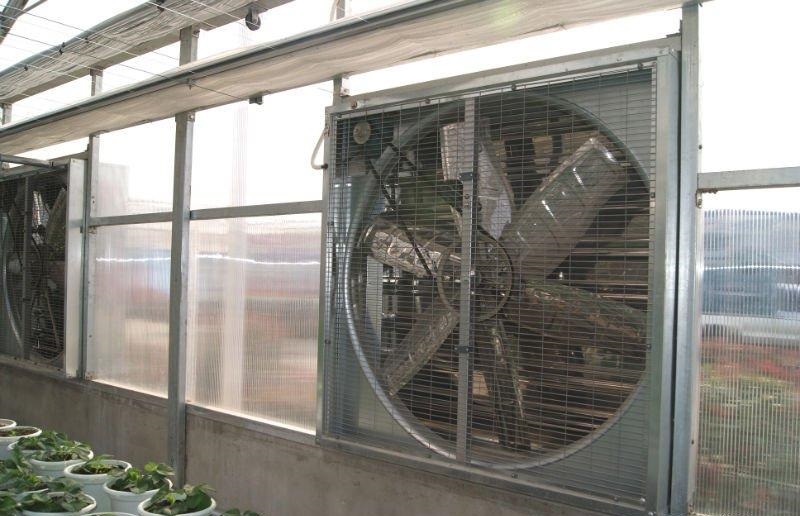
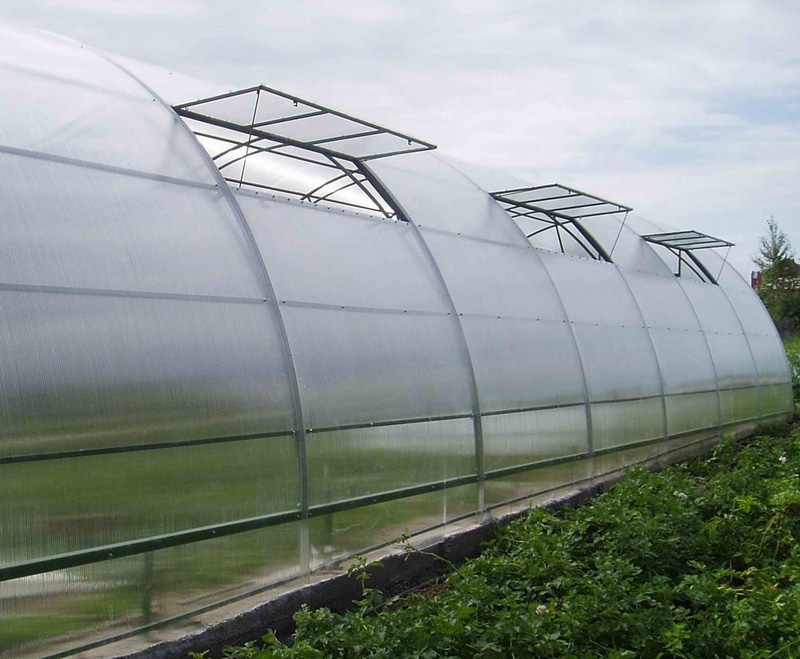
The ventilation system is usually placed on the roof and in the side walls of structures. It is a window with rack and pinion gearboxes. For the manufacture of the main profiles of ventilation windows, it is advisable to use aluminum.
Since the efficiency of using greenhouses and greenhouse complexes mainly depends on the creation of a favorable microclimate for growing crops, close attention should be paid to the design and implementation of climate systems. First of all, this concerns the organization of rational air exchange.
To ensure proper circulation of air masses, propeller fans are placed inside the building, which push hot air through the ventilation windows in the warm season to prevent overheating of plants. In addition, the mixing of air masses allows you to optimize the temperature regime and prevent condensation.
First of all, this concerns the organization of rational air exchange. To ensure proper circulation of air masses, propeller fans are placed inside the building, which push hot air through the ventilation windows in the warm season to prevent overheating of plants. In addition, the mixing of air masses allows you to optimize the temperature regime and prevent condensation.
To regulate the level of illumination and save energy, thermal screens are installed in greenhouse complexes. Aluminum-coated fixtures have proven themselves well, able to provide effective cooling on a hot day and save thermal energy at night.
Ozone systems allow increasing the content of dissolved oxygen, which has a positive effect on the yield and quality of the final product.
For the professional design of greenhouses, taking into account the infrastructure necessary for operation, technical conditions are requested for connecting the facility to electricity, gas, water supply and sewerage networks. Based on their indicators, technological systems and communications are designed that are necessary for the normal functioning of the process.
Moreover, in addition to the calculated data on water and energy disposal, fire and sanitary safety standards are taken into account, as well as regulations on land use and development rules approved by the local municipality.
The totality of all the data obtained allows us to calculate the building area of the greenhouse complex or adapt the planned infrastructure to the existing plot of land.
As you can see, modern greenhouses are high-tech facilities with the most automated production cycle. The construction of such a structure requires considerable financial investments, therefore, already at the design stage, it is necessary to take a very responsible approach to the choice of work contractors, who must not only have high professionalism, but keep up with the times, using the latest achievements and developments of specialized institutions in their work.
Underground or underground structure
It is known that in winter the ground freezes slowly.At an air temperature of ±1°C, the soil temperature at a depth of 1 meter is about 10°C. In the greenhouse device, one cannot fail to take advantage of such a natural bonus. For construction, you must first dig a hole, with a depth of 1 to 1.5 m, and install a transparent coating on top.
One of the options for a buried greenhouse is an improved design - a thermos greenhouse, which provides even greater indoor temperature and illumination even in cloudy weather. For a thermos greenhouse, it is necessary to arrange a reinforced concrete foundation. The coating is often two-layer. Inside, the walls are covered with reflective paint or other material that acts as a collector of solar energy.
The disadvantage of this variety is that it is difficult to organize proper drainage in the underground part.
A large underground greenhouse is built for a rather long time due to the need to dig a pit. In addition, you will have to take care of the steps at the entrance, waterproofing and pest protection, which implies additional costs.
Greenhouse construction technology
It should be noted that the production of industrial design greenhouses is a complex technological process that requires a serious professional approach. The construction of industrial greenhouses begins with the development of a detailed project, which must take into account all the technical requirements for the facility. At this stage, the customer must finally decide on the list of crops that he plans to grow, production volumes and optimal technologies.
It is important to take into account the basic requirements for the sites where it is planned to build a greenhouse:
- calm terrain, the maximum allowable slope level is 0.04%;
- protection from northern and northeastern winds, snow drifts;
- availability of water, communications;
- absence of sources polluting the environment;
- fertile soil suitable for use in soil mixtures.
Important! There is also a certain order of orientation of greenhouses relative to the cardinal points. It is believed that in areas located north of 60 ° north latitude, the most effective latitudinal orientation, to the south - meridional
Varieties of frames depending on the material
The frame is the basis of the greenhouse. It is made from different materials and their combinations. It all depends on the place where the structure will be located, operating conditions, the financial capabilities of the owner and the availability of a construction team for work.
Main frame materials:
- tree;
- metallic profile;
- galvanized pipe;
- polypropylene pipes;
- metal-plastic pipes.
Each of these options is good in certain cases. Wood is a cheap and easy-to-work material. But its durability is not the highest. The metal is very durable, but contributes to the formation of condensation drops, which is very harmful to plants. The same applies to galvanized pipes, but they are better than steel pipes because they do not need anti-corrosion treatment.
It is cheaper and easier to make a greenhouse from plastic or metal-plastic pipes. The construction will turn out to be light and will not require a capital reinforced concrete foundation, like a metal frame. But, unfortunately, metal-plastic pipes do not withstand difficult weather conditions very well.
Polypropylene pipes are a greenhouse frame option beloved by many farmers. It is an affordable and lightweight material. By itself, polypropylene is warm, which is a guarantee against the appearance of unwanted condensate. You can mount a small greenhouse from pipes even alone.
Industrial greenhouses and their types
Industrial greenhouses are usually distinguished by their shape, size and seasonality of use.
Industrial greenhouses made of polycarbonate are:
- Arched. Perhaps the most popular type of greenhouse.Its advantages include good illumination, resistance to strong side winds, it can withstand a lot of precipitation (good in winter and rainy weather). The design in the form of an arch allows you to build a large-scale greenhouse complex;
- Lancet. All characteristics and shape are very similar to the arched greenhouse, however, the lancet design has a pointed roof. Such a roof does not allow snow to accumulate, and sunlight freely penetrates the greenhouse;
- Gable. The least popular polycarbonate industrial greenhouse among farmers. This form must withstand a large load, this requires the manufacture of a reinforced frame. In terms of area, the gable greenhouse is inferior to the arched view.
By size, industrial greenhouses made of polycarbonate are divided into small, medium and large. Drawings, as a rule, are made according to such parameters. The photo of the greenhouse complex you need can also be found in special magazines.
In addition to the standard dimensions of greenhouses, you can order the desired design that will satisfy the needs of the farmer.
Industrial greenhouses are also divided according to the season of their use:
Seasonal. Seedlings in such greenhouses are grown from spring to autumn.
Industrial greenhouses of this type have an important advantage - they do not need to be dismantled for the winter, the manufacture of such greenhouses implies a strong frost-resistant structure that can withstand snow loads. Of the minuses, it can be distinguished that the soil in such a design will freeze strongly in frosts.
This is due to the fact that the ground outside the building is covered with snow, which at least somehow warms it. And snow simply does not get into the greenhouse. As a result, after 3-4 years the soil will not be so fertile. However, professional farmers have found a way out of this situation: they themselves cover the ground with snow in the greenhouse complex.
Year-round industrial greenhouses. You can run a business using such greenhouses all year round without compromising finances. This building requires special equipment, including lighting, heating. Most often, the production of this type of greenhouse involves the cultivation of flowers, sales of which in winter will pay off all the costs paid for the maintenance of a year-round facility. The so-called winter greenhouses have a good financial return.
There are a lot of options for organizing protected ground, but which greenhouse design will be the best in a particular case - here you need to figure it out properly
Each farmer with imagination can improve the classic version and invent his own greenhouse in this way, but if you do not take into account the basic requirements and do not take into account the calculations of professionals, an early harvest may be in jeopardy.
What materials are in demand for farm greenhouses
For the construction of the frame, metal, wood and plastic are used. Most often they are combined in various variations. At some points of the structure, maximum strength is needed, while at others, it is necessary to minimize the thickness of the profiles so that they cast as few shadows as possible. The covering of greenhouses for industrial use can be film, glass or polycarbonate.
Polyethylene - cheap and unreliable
Polyethylene film is easy to install and has a low price. But it is fragile and breaks easily. Polyethylene does not hold heat well and is suitable for use only in the summer, for the winter it will have to be removed and stored somewhere. This is ideal for seasonal buildings, but it is not suitable for permanent structures.
 Polyethylene is used for large greenhouses only seasonal type
Polyethylene is used for large greenhouses only seasonal type
In addition to cheap polyethylene films, there are also films made of fluororubber and other more durable polymer compounds. They have great resistance to ultraviolet radiation and temperature extremes.Such sheathing will last much longer, but these materials are much more expensive.
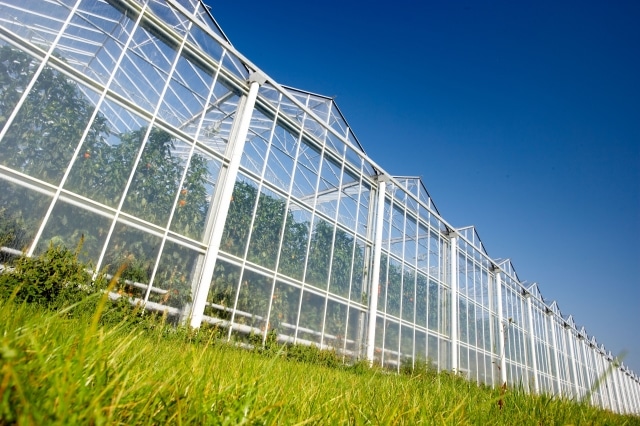
Glass is durable and expensive
A glass greenhouse can last for decades. Glass is a well-known and traditional material for covering greenhouse structures. The main plus is unsurpassed light transmission. Glass, even after half a century, will not become cloudy and will not lose its transparency.

Cellular polycarbonate is an excellent substitute for glass
Polycarbonate coating is easy to install and durable. Compared to its glass counterpart, its light transmission is slightly lower, but in terms of thermal insulation and impact resistance, it will give the glass a decent head start.

When choosing a model of a farm greenhouse, one should rely on the types of plants planned for cultivation, as well as the seasonality of operation and the volume of agricultural products. The efficiency of the greenhouse business largely depends on the technologies used, but the greenhouse design also plays an important role.
The preliminary planning and choice of the type of structure should be approached with all attention. Without specialized agrotechnical knowledge, it will not be possible to earn money here.
Industrial greenhouses arrangement and layout of beds
After completing the construction and sheathing of an industrial greenhouse, it is necessary to decide what the layout of the beds in it will be. There are three main options.
- Standard narrow beds on the soil with gaps for the movement of people and, if necessary, transport.
Growing strawberries in a greenhouse
- Multi-tiered beds and racks - with their help, farmers try to use the internal volume of the greenhouse more efficiently. Plants are placed one above the other on separate tiers, and in such a way that the upper crops do not interfere with the lower ones and do not block their access to light. A similar layout is typical for growing seedlings or strawberries.
Multi-tiered cultivation of strawberries in a greenhouse
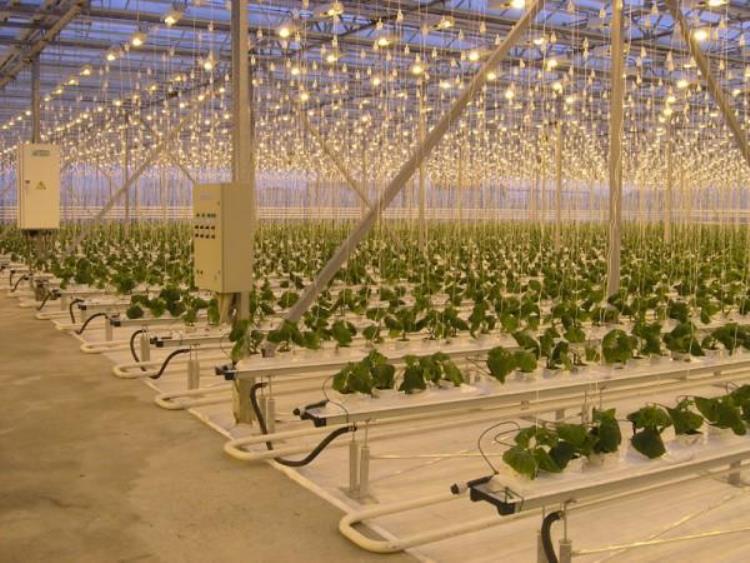
- Hydroponics. In this case, there are no beds as such - the plants are grown in an artificial environment (porous materials, aqueous solutions or humid air), and they receive all the nutrients along with irrigation. Hydroponics allows you to get high yields with significant savings in water and nutrients, which are delivered directly to the roots of each individual plant.
Greenhouse based on tiered hydroponics
The choice depends on the specifics of the plants grown, as well as on the budget for the initial investment in an industrial greenhouse. With the right approach to business and the use of modern agricultural techniques, such a structure will pay off very quickly and will begin to bring not only fresh and tasty vegetables and berries, but also tangible profits.
>Our address
Necessary equipment
When drafting a greenhouse complex, special attention should be paid to the issue of the required equipment. With the right choice, you can significantly reduce operating costs and increase yields.
To ensure a continuous work cycle, you will need:
- Continuous water drainage system.
- To maintain a certain temperature, it is necessary to install a reliable heating boiler or several units.
- An automatic ventilation system is required.
- To save water resources and fertilizers, you will need a water filtration unit.
Industrial greenhouses provide an opportunity to get good yields in a small area. This production does not depend on weather conditions, which will guarantee the smooth operation of the greenhouse complex. This is the main reason for the popularity of this type of business.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=gjBtvDxcxp4
Construction of industrial greenhouses frame
According to the form, there are three types of industrial greenhouses, presented in the table below.
Table.The main forms of industrial greenhouses.
| Name | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Arched or arched | In cross section, the greenhouse has a semicircular shape. It consists of frame arches connected to each other with horizontal ties. | Resistance to wind load, less consumption of materials for the frame, the ability to create structures of huge sizes. Regardless of the time, sunlight hits the roof and diffuses inside. |
| gable | Greenhouse standard shape with rectangular walls and a roof with two slopes, like a country house. | The same height of the walls throughout the building area. Very strong construction, but at the same time requiring a large amount of materials for the frame. |
| Lancet | A subspecies of the arched greenhouse, in cross section it has the shape of a pointed arch, elongated in height and pointed at the end. | The advantages are the same as those of arched greenhouses, while less snow accumulates on the lancet roof. |

Arched industrial greenhouses

Industrial greenhouse with gable roof
Sketch of an industrial lancet greenhouse
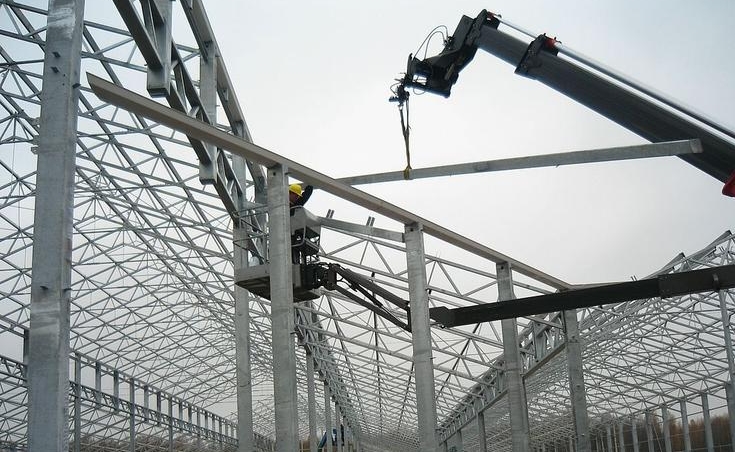
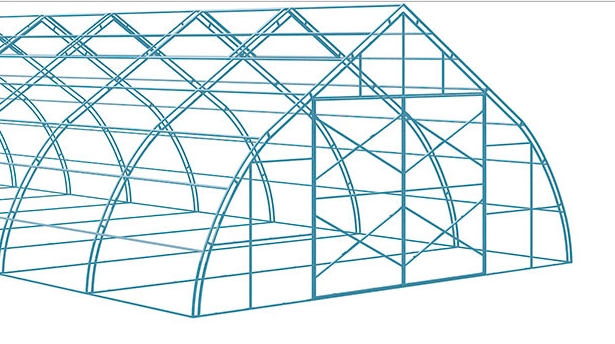
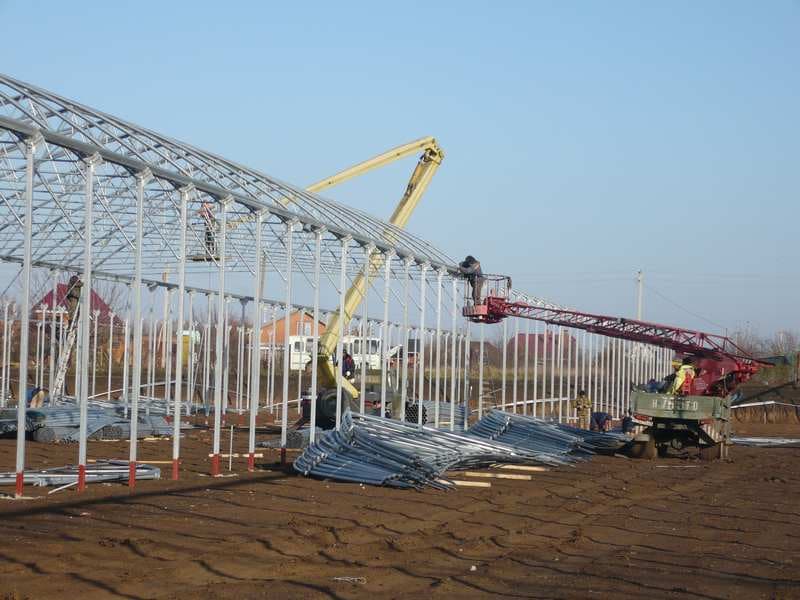
The vast majority of such structures use steel as the material for the frame, or, to be more precise, steel profile pipes and an angle profile. This is due to the fact that these materials win in terms of strength, durability and cost. In addition, to date, builders have gained vast experience in the construction of such metal structures, therefore the construction of the next frame for an industrial greenhouse does not require much time and effort or the involvement of some rare and specific equipment.
Construction of an industrial greenhouse with a metal frame

To strengthen the frame and increase its strength, double arcs are often used.

Another way to strengthen the frame is to introduce vertical and horizontal "bonds", also known as cross beams.
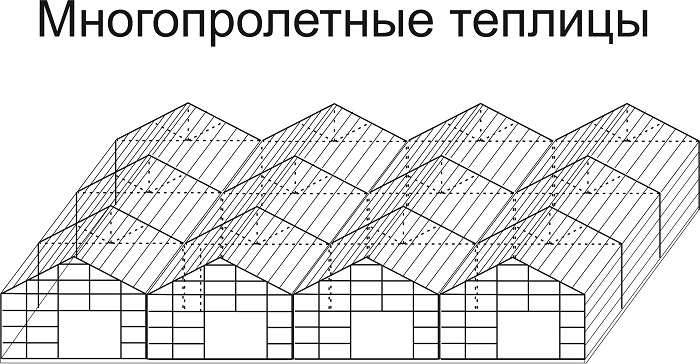
To create sufficiently large structures with their own microclimate, supported by ventilation and heating, several arched or gable spans are combined together. Thus, multi-span greenhouses of a huge area are obtained, presented in the images below.
Multi-span greenhouses, scheme
Multi-span greenhouses
Types of complexes for professional cultivation of plants
The size and type of an industrial greenhouse is determined by the needs of the farm and the financial capabilities of the investor. A modern greenhouse structure consists of several blocks with their own microclimate maintenance systems. Individual conditions are created for each type of plant in such a module so that the yield is maximum.

Depending on the operating conditions, such structures are divided into two types:
- Year-round.
- Seasonal (spring-autumn).

The construction of industrial greenhouses is carried out on the following sites:
- with fertile soil;
- having clean water sources;
- with a minimum slope
- protected on the north side from the wind by trees or buildings.
On the one hand, a high greenhouse must be erected in a small depression, and on the other hand, groundwater in this place must be deep enough so as not to have a harmful effect on the microclimate and plants inside.
Important! Large greenhouses have a high windage. They should be equipped in areas protected from the wind, so that there is no space left between the ground and the base of the structure.
Structurally, industrial greenhouses are arched, lancet, one- and two-slope, straight, block or hangar. The frame is made of metal structures, wood or plastic. And as a covering material, polyethylene, polycarbonate or glass is used.
 Scheme of a farm greenhouse of an lancet type
Scheme of a farm greenhouse of an lancet type
According to the cultivation technology, they are divided into five types:
- Soil (ground).
- Shelving.
- Subirrigation.
- Hydroponic.
- Mixed.
There are many methods of indoor cultivation of fruit and vegetable plants and new ones are constantly appearing. Designers are forced to follow the innovations of agricultural technologies and regularly update the list of modifications. But in most situations, the construction of industrial greenhouses requires an individual approach. Before choosing the type of construction, many nuances are analyzed, and only then the design of the original greenhouse begins.

The subtleties of doing business
You can reduce the cost of production by increasing profits by purchasing materials from the manufacturer. This can be done by concluding contracts for the supply of products. And in order to conclude an agreement, it is necessary to register an IP.
Only an individual approach to each client will help to win the competition and eventually purchase professional equipment that will allow you to establish a serious technological process.
Related video: Greenhouses - Video review
A selection of questions
- Mikhail, Lipetsk — What discs for metal cutting should be used?
- Ivan, Moscow — What is the GOST of metal-rolled sheet steel?
- Maksim, Tver — What are the best racks for storing rolled metal products?
- Vladimir, Novosibirsk — What does ultrasonic processing of metals mean without the use of abrasive substances?
- Valery, Moscow — How to forge a knife from a bearing with your own hands?
- Stanislav, Voronezh — What equipment is used for the production of galvanized steel air ducts?
Characteristics of the structure
The main difference between industrial greenhouses and country greenhouses is the scale of the structure. According to these parameters, industrial facilities are significantly superior to backyard counterparts. The area of such buildings can be measured in hundreds, and sometimes thousands of square meters.
Such large structures require a multiple reinforced framework capable of supporting the load of the greenhouse cladding. It is also necessary to take into account the periodically added snow load. Breakage of the frame can completely paralyze the work.
To maximize the profit from the harvest, the following technical capabilities are used in large-scale greenhouses:
- heating;
- ventilation;
- artificial lighting;
- use especially ;
- isolation from weeds and harmful insects;
- saturation of the interior of the greenhouse with carbon dioxide.
Types of greenhouses
According to the type of construction, the following types of greenhouses are distinguished:
- arched;
- rectangular;
- wall-mounted;
- pyramidal;
- polygonal.
Arched greenhouses are the best option. Due to the shape, less material is required for the manufacture of the greenhouse, which affects the final cost.
Rectangular greenhouses are the simplest in execution and well lit. However, in winter, a lot of snow accumulates on them, which can damage the structure.
Wall greenhouses are attached to a house or other building, which significantly reduces material consumption. Such a greenhouse is recommended to be installed on the south side of the building.
Pyramidal greenhouses are small, take up little space. They are difficult to manufacture, which affects their cost. However, such a design will not only benefit the owner, but will also become a true decoration of the garden.
Polygonal designs can decorate any site. Outwardly, they resemble gazebos. Most often, these greenhouses are used to grow flowers and herbs for sale.
Industrial greenhouse Farmer-7.5 design
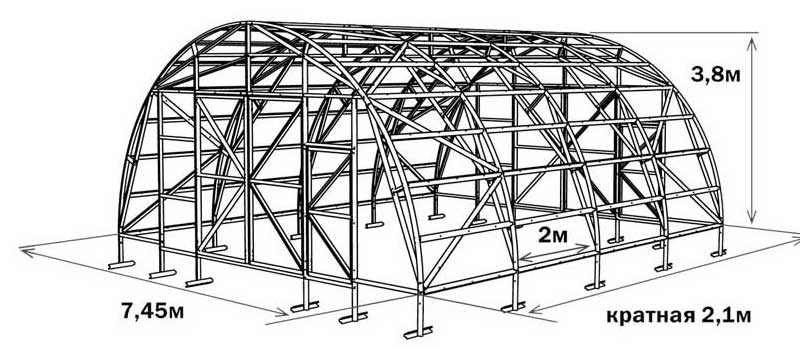
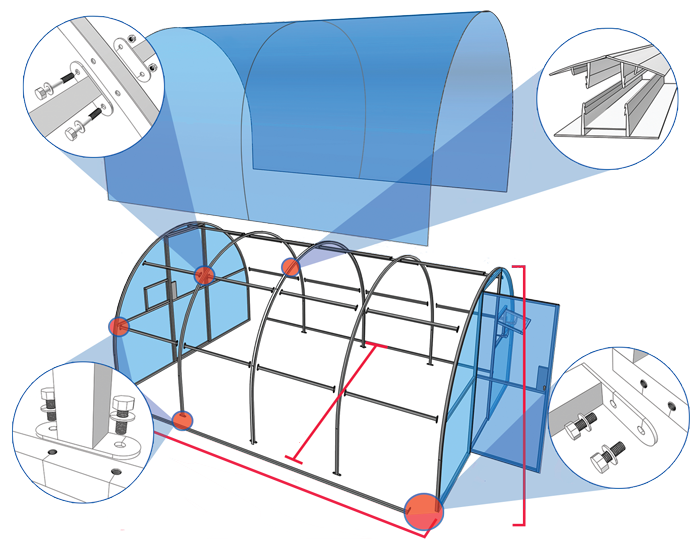
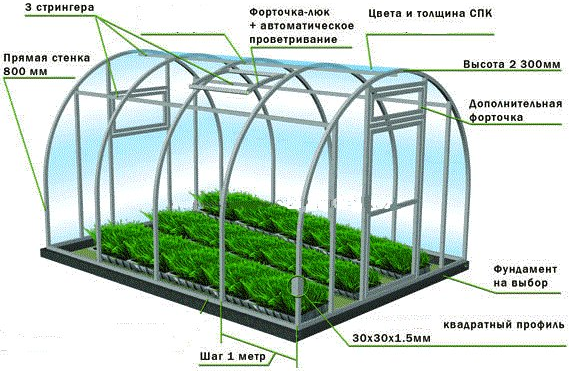
Consider one of the standard models of industrial greenhouses supplied to the modern market. This building is called "Farmer-7.5".It is an industrial arched greenhouse with a frame assembled from a galvanized profile and bolted. All structural elements are equipped with tie-beams and crossbars, which give the structure high strength and resistance to snow load.
Scheme of the industrial greenhouse "Farmer-7.5"
The height of "Farmer-7.5" is 3.8 m, the width is 7.5 m, the length starts from 4.2 m. Moreover, the latter characteristic is always a multiple of 2.1 m - the standard width of a cellular polycarbonate sheet, which is used in this greenhouse as cladding. The recommended thicknesses of the SPK are 6, 8 and 10 mm. When installed on a deep-seated strip foundation and installation of heating systems, the Farmer-7.5 greenhouse is designed for year-round cultivation of vegetables, flowers and berries.
Greenhouse "Farmer-7.5", inside view
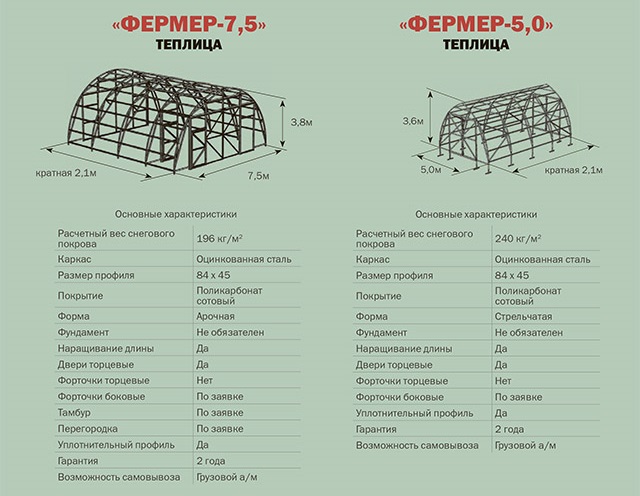
Characteristics of greenhouses "Farmer-7.5" and "Farmer-5.0"
Below is a brief assembly guide.
Step 1. The pediment of the greenhouse is assembled - an arch is formed from individual components, vertical posts, a frame for the door and ties are added to it, designed to strengthen the structure.

Assembly of greenhouse gables

Assembly of the pediment is almost finished
Step 2. Horizontal runs are attached to the pediment.

Fixing horizontal purlins
Step 3 An intermediate frame arch is assembled. It differs from the pediment from the first operation in the absence of vertical posts and a large number of ties.

Assembly of the intermediate arch of the frame
Step 4. The first section of the greenhouse is assembled from the pediment, intermediate arch and girders, which is subsequently installed on the foundation.

Assembly of the first section of the greenhouse
Step 5. With intermediate arches and horizontal runs, the greenhouse is built up to the desired length.

Building a greenhouse frame
Step 6. A pediment is assembled from its other end, as in step 1. Runs are attached to it and attached to the rest of the frame elements.

Frame assembly

Continuation of assembly
Step 7. The gates and doors are assembled and mounted on the frame.
Step 8. Polycarbonate is cut and installed on the gables and roof of the Farmer-7.5 greenhouse.
Scheme of assembly and sheathing with polycarbonate
Sheathing frame with polycarbonate

Assembled industrial greenhouse "Farmer-7.5"
Industrial greenhouses ventilation, heating and lighting
The main system for any industrial greenhouse is irrigation. It can be performed in two ways - sprinkling and drip irrigation. In the first case, sprayers of water are installed in the greenhouse, which falls on top of the plants and soil in the form of small particles. As a result, crops receive a sufficient amount of moisture with minimal fluid consumption.

Greenhouses industrial
Sprinkler irrigation is carried out using three types of installations:
- installations fixed between the beds;
- fixed installations under the ceiling;
- mobile sprinkler installed under the ceiling.

Mobile sprinkler system
Drip irrigation is performed according to a different scheme - a drip tape or hose is pulled between the beds. From the many holes in them, individual drops of water stand out, which fall into the soil near the root zone of plants. As a result, the latter receive a sufficient amount of moisture with minimal fluid consumption and the complete absence of problems with weeds or waterlogging of the soil.

Drip irrigation
Important! Regardless of the irrigation system, an industrial greenhouse will need a powerful filter or even a set of them. This will not only rid the liquid of impurities harmful to plants, but also extend the life of sprinklers or drip hoses.
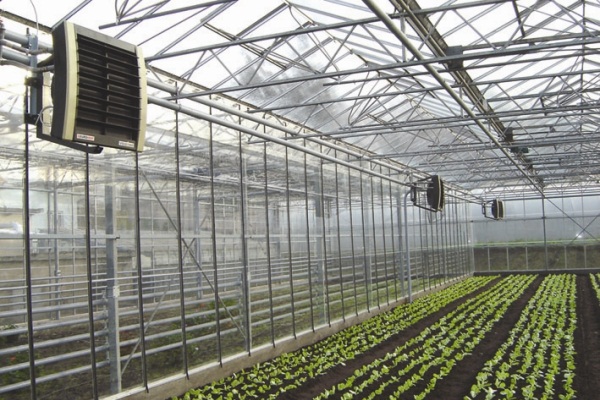
Equally important for an industrial greenhouse, especially year-round, is heating, which is carried out in various ways:
- convection heater;
- air heaters;
- infrared lamps;
- underfloor heating system.
In the first case, rather powerful heaters are installed inside the greenhouse, in which initially cold air passes through the heating element and then is released into the environment. A more advanced type of such heating of an agricultural building is air heaters, which can be built into the greenhouse ventilation system.
Alternative heating for industrial greenhouses
Greenhouse ventilation systems
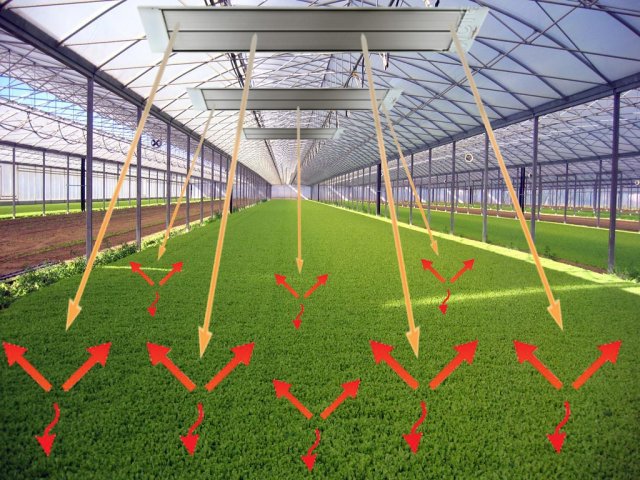
A very effective, but at the same time the most expensive type of heating are infrared lamps suspended from the ceiling. As the name implies, they emit electromagnetic waves in the infrared range, which do not heat the air itself, but directly the soil and plants on it.
Infrared greenhouse heating
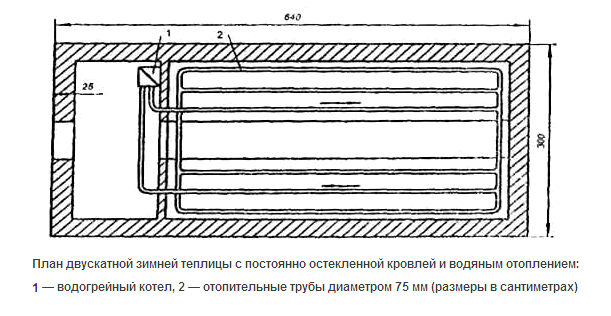
The last heating option is a kind of compromise between quality and efficiency. This is a "warm floor" system, which is a network of long plastic pipes mounted under fertile soil in an industrial greenhouse at the stage of its construction. Water is supplied through pipes, preheated in an electric or gas boiler. It gives energy to the ground around it, acting as a radiator of a huge area.

The "warm floor" system in the greenhouse
Greenhouse plan with water heating
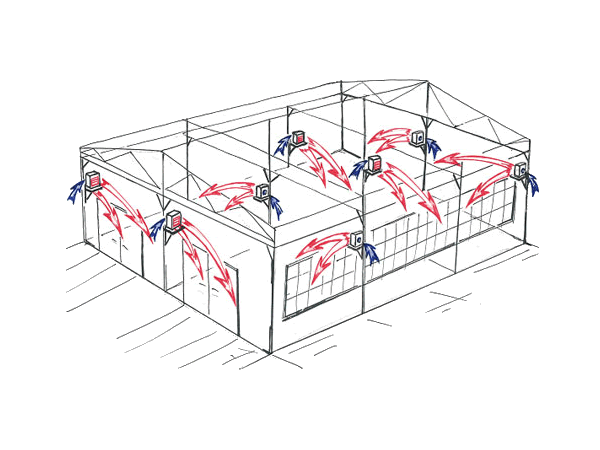
Ventilation for an industrial greenhouse is of particular importance in the summer, when it is quite hot "overboard", and even more so in the greenhouse. Given the lack of wind inside the building, the most effective way to ensure an optimal microclimate is to install fans on two opposite walls - one takes the air masses from the outside, the other takes them out of the greenhouse
Such a system can be supplemented by the installation of a plurality of vents-transoms, and necessarily installed on thermal cylinders.
Air handling units

Automatic ventilator for greenhouses Vent-L
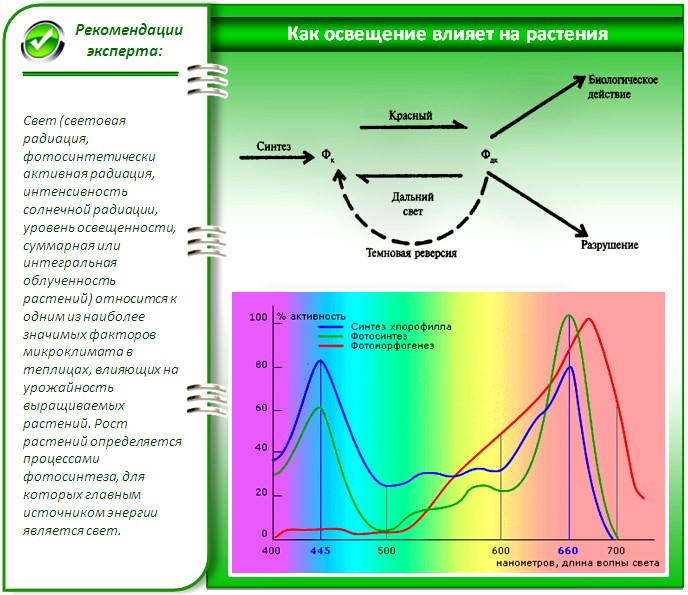
In late autumn, winter and early spring, the number of sunny days is very small, and even then the light often falls at a small angle to the horizon, passing through the air. As a result, the intensity of photosynthesis decreases in plants - sunlight is not enough for this. To compensate for their deficiency, the use of sodium or LED lamps suspended from the ceiling of the greenhouse will help. At the same time, wavelengths are selected at which, according to the results of experiments, the efficiency of photosynthesis increases - 440-470 and 660 nm.

Greenhouse LED Lighting
Dependence of the activity of the processes occurring in plants on the wavelength of light
All systems for creating a microclimate in an industrial greenhouse are as automated as possible and financially justified. The use of temperature, ventilation, humidity and light level control using sensors and computing tools allows, with a high initial investment, to increase the yield of the greenhouse and reduce the cost of maintenance personnel.
Important! The rate of plant growth and yield is also affected by the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Inside industrial greenhouses, the value of this parameter can be increased in two ways - either using gas generators with burners, or using CO2 spray from cylinders
Types of coating materials for greenhouses
If the frame guarantees the stability and strength of the greenhouse, then the coating material - light and heat. The most popular materials for covering greenhouses that are used in agriculture:
- glass;
- polycarbonate;
- polyethylene film;
- agrofibre;
- PVC film.
Glass is a traditional material for organizing greenhouses. It is transparent, but does not allow enough sunlight to pass through the spectrum that is optimal for plants. In addition, glass is very fragile, difficult to install and relatively expensive.
It is much more rational to use sheets of cellular polycarbonate. It transmits light well, durable due to its structure.Sheets are produced in large sizes, which speeds up and facilitates installation. Polycarbonate does an excellent job of covering the greenhouse - it retains heat and transmits enough light.
The easiest material to install and operate is film, which is also the cheapest. Modern industry has long coped with all the disadvantages of polyethylene. Films are no longer afraid of direct exposure to sunlight. Strength is provided by a mesh frame. The film transmits the sun's rays well, but is easily torn - this is its main drawback.
As you can see, to build a greenhouse, you need to analyze a lot of information. If this fact discourages you, you can always resort to ready-made copies made at the factory. In this case, you will only need to decide on the size and location on your site where the greenhouse will be installed.
Any small amateur horticultural farm, sooner or later, can be restructured into a larger one that brings a stable income. This is how farm enterprises are born, created no longer for the sake of a fresh cucumber on the table, but for the purpose of making money. The delivery of this process to production "wheels", the systematic and trouble-free cultivation of crops in seasonal conditions is impossible without such complex complexes as industrial greenhouses.