Bulk
Loose heaters are expanded clay, perlite, vermiculite, which are very resistant to fire and have a flammability class of at least G1 - an oxygen index of at least 30%.
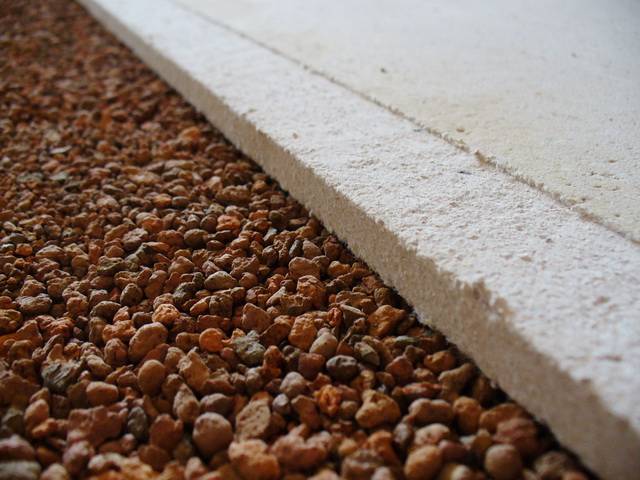
Expanded clay is obtained by firing clay. The granules are heavy, with high thermal conductivity. This non-combustible thermal insulation is of loose type, therefore it is inconvenient to install. However, it is cheap and environmentally friendly. Expanded clay is characterized by the size of fractions. So, an option up to 5 mm is sand, an indicator up to 40 mm is gravel. If large fractions are crushed, then crushed stone is obtained.
Thermal and fire-resistant qualities when using expanded clay are significantly increased. This is especially true for hard-to-reach places where such a heater can simply be poured. Expanded vermiculite is used for walls in low-rise construction. It is resistant to microorganisms, environmentally friendly, but has low moisture resistance.
Perlite
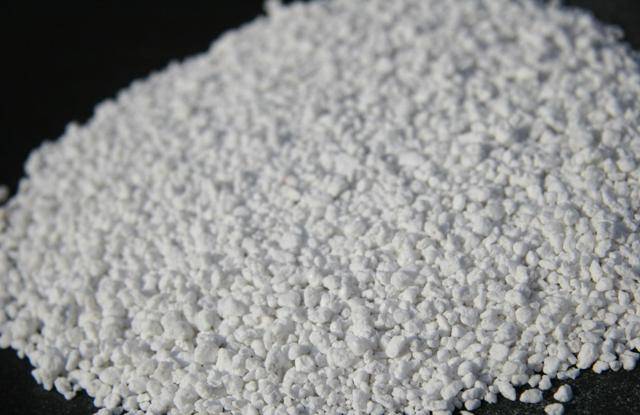
Perlite is presented in the form of volcanic glass granules. The fraction ranges from 1 to 10 mm. Due to its light weight and the ability to adjust the thickness of the protective layer, it serves as an excellent heat insulator.
In practice, 30 mm of perlite is equivalent in effect to 150 mm of brick. Perlite is applicable for thermal insulation of roofs and walls, and can be an alternative to brickwork. The disadvantage is that it absorbs moisture well and is fragile.
Related fire fighting materials
About 240 minutes of open fire withstand fireproof mounting foam. It is used as usual, to install windows and doors, but its special properties make it possible to provide the house with invisible protection. It is only necessary to provide for its use in construction.
Even when finishing a new building, you can use special paints for fire protection of wood or metal, which also protect electrical cables. When exposed to high temperatures, they sharply increase in volume and form a non-combustible heat-insulating layer, which reduces the deformation of metal structures, reduces the spread of fire on the plastic braids of electrical cables and the surface of modern finishing materials.
good to know
When choosing a building material, pay attention to its detailed characteristics. After all, if the material is not classified as “non-combustible”, then it must be assigned the corresponding “combustibility group”:
- G1 (low combustible);
- G2 (moderately combustible);
- G3 (normally combustible);
- G4 (highly flammable).
In addition to combustibility, there are other important fire-technical characteristics of materials: flammability (denoted as "B"), the ability to spread a flame over the surface ("RP"), smoke-generating ability ("D"), and toxicity ("T"). Next to the designation of the characteristic, the degree of this ability of the material is indicated (from 1 to 4). The lower this degree, the safer the material, and vice versa.
Facade finishing
One of the main problems of fire safety of facade systems is the use of combustible heat-insulating materials. Most questions from specialists are caused by the use of thermal insulation based on expanded polystyrene (polystyrene) in the construction of the facade.
To reduce the fire hazard of such facades, cuts and edgings of openings are made from stone wool-based slabs. Horizontal cuts prevent hot gases from spreading. And edging the openings of windows and doors with stone wool does not allow expanded polystyrene to get into the flame. Thus, the fire is localized, the combustion temperature decreases.
When installing ventilated facades, it is recommended to limit the use of wind and hydroprotective membranes. They are flammable and endanger fire safety.
To date, the safest method of thermal insulation is basalt thermal insulation. The main advantages of basalt insulation: low thermal conductivity, environmental safety, durability, high sound-absorbing characteristics, resistance to aggressive environments and incombustibility.
good to know
As you know, treatment with fire-fighting flame retardants is not a panacea for fire, their action is limited in time. As a rule, they provide reliable protection for a maximum of 60 minutes, during which the fire can be localized or completely eliminated.
A distinctive feature of fire-fighting compounds for the treatment of metal structures, finishing materials and electrical cables is that they have strong heat-insulating properties. Under the influence of high temperatures, they swell and acquire the properties of expanded clay, reliably protecting both from fire and from thermal effects.
The same can be said with respect to low temperatures - the plastic sheath of electrical cables does not deteriorate or crack in the cold, and sudden temperature changes are also not terrible.
The right choice of building and finishing materials is only the first step towards safety
And in the end, what matters is how seriously and responsibly you take fire safety measures in general. After all, there are a lot of risks
Remember, your home should not only be beautiful and cozy, but also safe in every way!
How fire danger is measured
According to GOST standards for the fire hazard of materials, all products for construction are divided into several categories. There are only two main groups: combustible (G) and non-combustible (NG) materials. Non-combustible products (natural stone, cement, glass) do not smolder or burn, therefore they are considered as a single group. But materials from the category “G” are divided into subgroups according to a number of characteristics:
- Flammability (four groups from G1 to G4);
- The speed of fire spread over the surface of the material (RP1-RP4);
- Flammability (B1-B3);
- Smoke generation (D1-D3);
- Toxicity (T1-T4).
Materials marked G4, E4, D3 and RP4 are the most dangerous in a fire - they quickly flare up and burn out completely, releasing acrid smoke and harmful toxins that can cause poisoning or death.
Classification
Heat-insulating fibrous materials are non-combustible mineral insulation made of glass, basalt fiber, which can withstand +500°C. They are used in specific places:
- for insulation of pipelines in the form of cylinders with foil reinforcement;
- thin mats, plates for flashing plastic windows;
- basalt - for insulation of walls, roofs and floors.
According to GOST, wool is divided into the following categories: stone, glass, slag wool. According to the same GOST, all types of cotton wool have a combustibility of the NG class - the oxygen content index is at least 30%. Let's consider each type in more detail.
glass wool
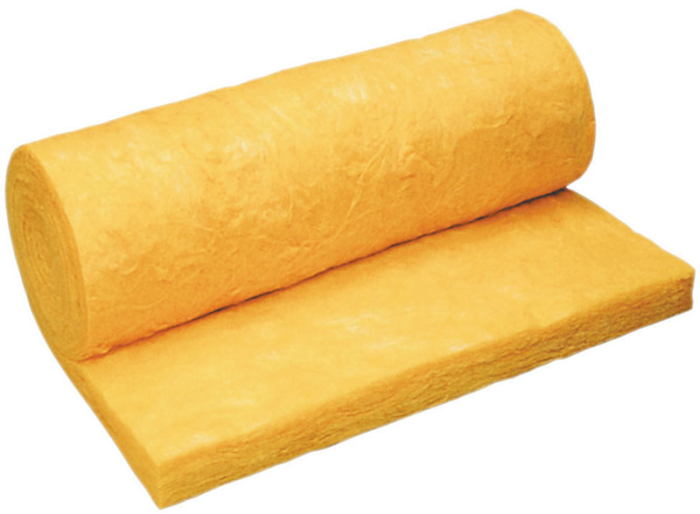
Glass wool is made from fiberglass by melting glass and drawing the fibers from it.
This material is very fire resistant, has low hygroscopicity, good sound insulation and low thermal conductivity.
The strength is higher than that of stone wool, but the fibers are still fragile, so it is better to wear gloves and goggles to work with it.
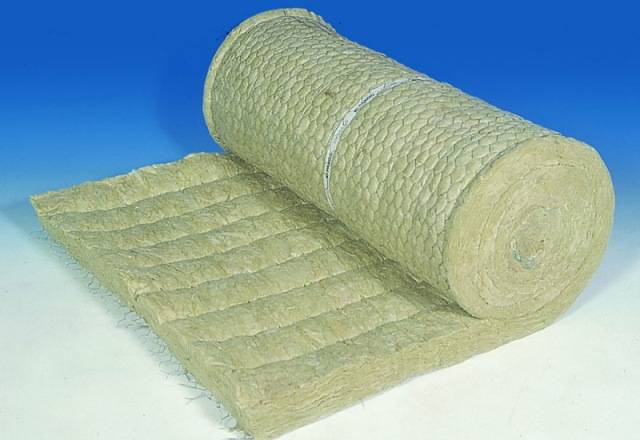
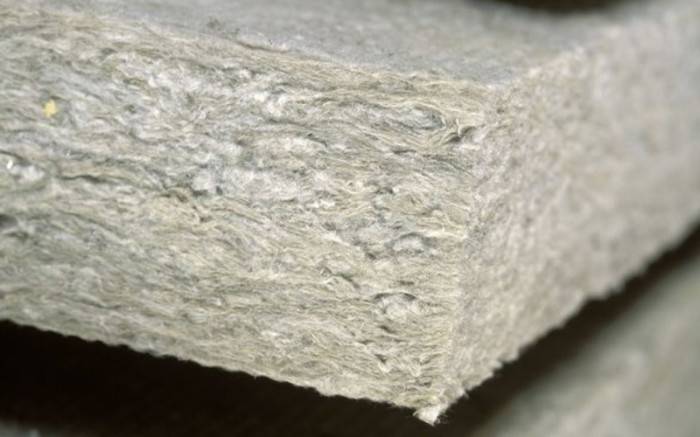
stone wool
Cotton wool on basalt fiber is made by melting rocks at high temperature (up to 1500°C). The fibers are linked by the addition of special substances, which gives durability. Basalt wool is not deformed, does not react to acid-base environments.
Additives contain phenol-formaldehyde resins, which emit harmful fumes.However, evaporation begins only when heated to 700°C - i.e. under normal conditions there is no danger.
slag wool
It is produced by processing slag and obtaining vitreous fibers.
Such a heater has a high thermal conductivity and absorbs moisture, reacts to dampness and creates an environment aggressive for metals. It has one advantage - low price.
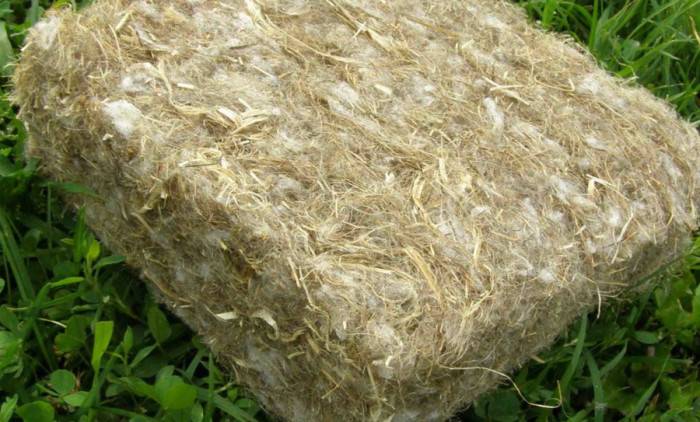
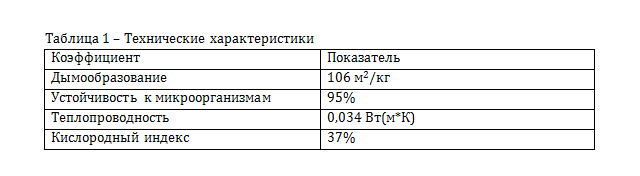
Linen insulation
It is also worth mentioning the novelty of modern production of heat-insulating materials in the form of Hot-Flax linen insulation. It is pure linen (fiber) without mineral wool impurities, which has a flame retardant treatment and does not support combustion at all.
The oxygen index is 37%, approaching polymeric, self-extinguishing materials.
There is no smoke without fire
A cigarette thrown into the dry grass, a lightning strike, a fire made by tourists or a scorched hayfield - every warm season, suburban areas are under constant threat of fire. According to statistics, about 90% of forest fires are associated with human activities and only about 10% - with natural factors. For this reason, most fire disasters occur just near housing - cottage settlements, forestries, farms and various household objects.
Under the influence of the wind, an uncontrollable flame spreads at great speed and in a matter of hours can get from a forest or meadow to a cottage village, spreading to houses and outbuildings. Every year, forest fires cause human casualties, destruction of more than 3 thousand country cottages and causing material damage amounting to billions of rubles. How to protect your home from the effects of fire and ensure the safety of loved ones and the safety of personal belongings?
Cellular types
Cellular non-combustible materials resemble frozen foam in structure. This type of insulation can withstand high temperatures.
Foam glass
Inorganic type insulation with a cellular structure similar to soap suds. The basis is crushed glass, which is mixed with carbohydrate. Foam glass has the following positive characteristics:
- environmentally friendly, durable;
- resistant to fire and temperatures;
- does not absorb moisture and does not pass steam;
- not susceptible to acids, bacteria, fungi, does not attract rodents.
Foam glass can be used in almost any industry - construction, chemical, energy, engineering industries. The only drawback is the high price.
This material is especially recommended for the insulation of basement walls.
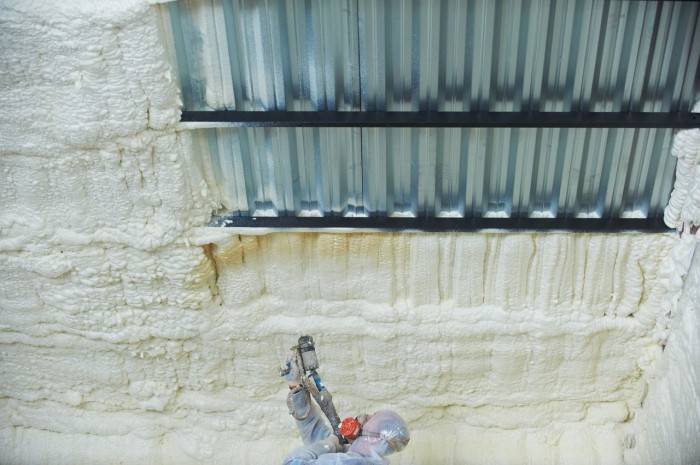
PPU
Polyurethane foam as a non-combustible material has a serious list of qualities:
- when exposed to open fire, it does not emit harmful substances;
- low moisture absorption coefficient (1.5%);
- not afraid of temperature changes and mechanical loads;
- Great for sealing and thermal protection.
This convenient and easy-to-install material is used to isolate saunas, baths and other facilities.
Protecting the façade from fire
The choice of facade cladding for many homeowners depends entirely on aesthetic preferences - the cladding material largely determines the first impression of the building and provides ample opportunities for decorating the walls of the building with decorative elements. However, it would be more correct to choose building products according to fire-technical parameters - many modern materials with polymer additives quickly catch fire and are not able to contain the flame even for 20-30 minutes.
It is worth noting that external protection with cladding is needed for walls made of any material. Wood walls are the most vulnerable - any type of wood does not provide 100% fire protection even when impregnated with fire retardants. Building houses made of brick, aerated concrete or foam blocks guarantees fire resistance, however, both brick and concrete crack and can collapse under the influence of high temperatures during large-scale forest fires or burning neighboring buildings.
Siding, a popular type of facade cladding, which can be made of a variety of materials and perform not only a protective, but an aesthetic function, will help to effectively protect the walls of a building from fire.In the 19th century, siding made of overlapped wooden lining plates began to be used in North America for the first time - simple finishing work made it possible to quickly give the cottages a cozy and neat look and protect the wall material. Half a century later, other types of siding appeared in the USA and Canada - vinyl, metal and basement. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of siding of various types.
- Wood siding - is a panel of wood chips pressed under pressure, fastened with binder additives (resins and wear-retarding substances). Despite additives, wood siding is moderately moisture resistant and can gradually deform from waterlogging. Since this type of cladding is based on wood shavings, its combustibility is increased and does not allow high-quality protection of the walls of the house from fire;
- Steel siding - usually made in the form of thin steel sheets with galvanization and polymer coating. Steel belongs to the group of non-combustible materials, does not emit toxins when heated and can withstand temperatures up to +800 C °, as well as exposure to water and aggressive fire extinguishing chemicals;
- Socle siding - is a polymer product belonging to the group of low-combustible building materials. Plinth siding panels do not ignite as quickly as wood, and are able to hold the fire for a short time;
- Vinyl siding - made on the basis of PVC panels that do not support combustion, but easily melt (combustibility class G2) and are prohibited for use in fire hazardous buildings. In hot regions (summer temperatures from +30 C °), vinyl lining can be deformed due to heating in the sun, and burst or crack during winter frosts.
Evaluating the presented choice of building materials, we can highlight the non-combustible steel cladding - at the moment it is the best suitable, reliable and safe material for protecting the walls of the house from fire. In addition to high strength, the construction and decoration of houses using modern varieties of steel siding can make it possible to create a cottage with an original and attractive design: for example, Ecosteel polymer-coated steel cladding sheets on the Russian market imitate the surface of a brick wall and different types of wood.
Building a fireproof roof
The choice of roofing is one of the most important steps in shaping both the external appearance and the internal structure of the house. The heavier the chosen material, the more powerful the rafters and walls of the house should be, and the shape of the roof determines both the external impression of the cottage and the ease of use of the roof during the rainy season. Consider the pros and cons of the most popular roofing materials in terms of fire resistance.
- Ceramic tiles are high cost and are one of the most popular eco-friendly roofing materials for luxury housing construction. Ceramic tiles are made from natural clay, which is molded and fired at a temperature of more than 1000 ° C. Ceramic tiles are waterproof, non-combustible and perfectly withstand any weather conditions and high temperatures. The main disadvantage of the material is its weight, which is about 45 kg/m2 (i.e. the top layer of a roof with an area of 200 m2 will weigh about 9 tons). Country construction using ceramic tiles is quite expensive due to the need to strengthen the entire truss system and load-bearing walls of the house;
- Cement-sand tiles - is one of the cheapest non-combustible roofing materials, made from concrete tiles and has several significant drawbacks: hygroscopicity, high weight and temperature instability.As a rule, the use of cement-sand tiles in the Russian climate does not result in savings, but in additional costs - when the temperature drops, the tiles saturated with moisture often crack and collapse due to the fact that the water that has turned into ice has increased in volume. An additional problem is the creation of a supporting structure for a cement roof - due to the significant weight (40-59 kg / m2), cement-sand tiles require the creation of powerful rafters;
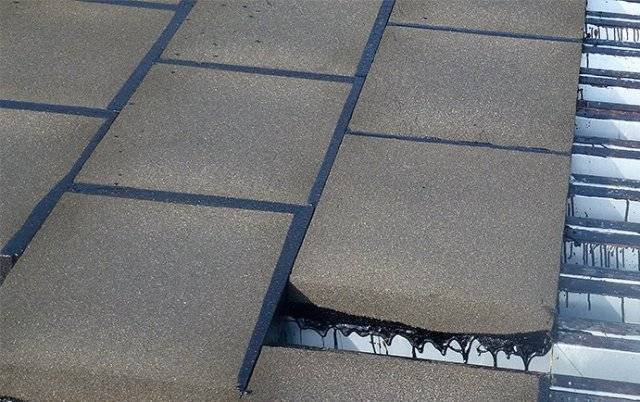
- Bituminous tiles - made from bituminous tiles, which are coated with fiberglass, cellulose and polyester, as well as a special coloring matter. Bituminous tiles have an average level of flammability (G3) and are not able to ignite from a spark. However, in the event of a fire inside the house, a roof made of this material will quickly sag and collapse - bituminous tiles melt from heat and may slightly deform even due to exposure to the sun on a hot day;
- A metal tile, a material invented in neighboring Finland, is made of durable steel with a polymer coating and is well suited for use in the harsh Russian climate. Metal tiles not only belong to the class of non-combustible substances, but also have significant advantages as a building material: its weight is several times less than that of other types of tiles, and strength and durability approach the maximum mark;
- Euroslate - this term refers to a whole group of roofing materials made from corrugated bitumen sheets. Euroslate is very popular on the market due to its low cost, however, in the construction of schools, kindergartens, hospitals and other buildings with increased safety requirements, the use of this material is strictly prohibited: in the temperature range from +230 ° C to 300 ° C, euro slate ignites spontaneously and begins to emit toxic substances and smoke. The material is also unstable to the usual for Russia differences in winter and summer temperatures - under the influence of sunlight, the Euro-slate softens, and becomes brittle during the winter frost season.
As with facade cladding, when choosing a roofing material, it is better to give preference to steel. Metal tiles will effectively protect the house from external influences, withstand internal fire of the building, exposure to moisture and sharp temperature fluctuations characteristic of many regions of Russia. The combination of steel siding and metal roofing is one of the most effective home fire protection solutions. In addition to its unique properties, metal tiles are lightweight and easy to install, so that the construction of the cottage can be completed in the shortest possible time.
Materials for wall enclosing structures
When choosing material for walls, the future homeowner is guided by his own motives, which are not always objective. Sometimes everything depends on the price, in other cases they think, for example, about the environmental friendliness of the building. After all, many argue that in a wooden house "it's easier to breathe."
If, after much deliberation, you nevertheless chose a tree for building a house, be sure to take care of fire safety. Special impregnations - flame retardants will help you with this, but the time for which they are able to contain the spread of fire is small - about 60 minutes.
If you prefer brick walls, you should know: brickwork after a fire must be dismantled, since this material is destroyed under the influence of high temperatures.
Or maybe you prefer the latest building technologies to wood and brick. New solutions for wall enclosing structures: foam blocks, gas blocks, polystyrene concrete. More about them.
Floor coverings
Fireproof flooring materials include stone and ceramic tiles, they can also be used for finishing stairs.By increasing the amount of these materials in the home, we reduce the risk of fire spreading. But sometimes we still cannot do without artificial materials, for which the status of “combustible” is firmly entrenched. But even among them there are exceptions. So, for example, manufacturers have developed a special linoleum.
When choosing LINOLEUM, it is necessary to pay attention to the marking, which characterizes the fire safety of the material. This material has improved characteristics compared to conventional PVC coatings: G1 (low combustible), RP1 (does not spread flame over the surface), V2, D2, T2 (moderately flammable, smoke-generating, toxic)
The latter is dangerous only with an open source of fire, does not spread the flame over the surface and allows you to evacuate without being poisoned by combustion products. By choosing the right marking, you can opt for this material and thus take care of the passive safety of your home.
This material has improved characteristics compared to conventional PVC coatings: G1 (low combustible), RP1 (does not spread flame over the surface), V2, D2, T2 (moderately flammable, smoke-forming, toxic). The latter is dangerous only with an open source of fire, does not spread the flame over the surface and allows you to evacuate without being poisoned by combustion products. By choosing the right marking, you can opt for this material and thus take care of the passive safety of your home.
Choosing a heater
Despite the fact that the insulation layer is located in the thickness of the walls or roofing cake, its properties also greatly affect the effectiveness of the fire protection of the house. A layer of high-quality non-combustible insulation eliminates the risk of internal fire under the roof or sheathing of the cottage, and also prevents the flame from spreading inside the house. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of the three most popular materials on the modern market for thermal insulation of country houses.
- Expanded polystyrene - is made from polystyrene by heating and introducing foaming agents. All varieties of expanded polystyrene belong to the group of synthetic materials of increased flammability. Expanded polystyrene flares quickly and becomes the initiator of further flame spread, and also releases acrid smoke and toxins such as hydrogen bromide, hydrogen cyanide and phosgene when burned. To reduce the flammability of expanded polystyrene, various additives are introduced into the material during manufacture, which reduce smoke formation and increase the ignition temperature;
- Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) - is a foamed polystyrene - a lightweight porous material, 98% air. XPS belongs to the category of medium combustible materials, does not spread flame over its surface, but emits smoke that is hazardous to health when burned. Despite its shortcomings, expanded polystyrene is in demand on the market and is widely used to create underfloor heating, wall and ceiling insulation;
- Stone wool is a new generation of environmentally friendly insulation and is a solid mats and blocks of fibers obtained from gabbro-basalt rocks. Stone wool belongs to the class of non-combustible materials and does not melt at temperatures up to 1000 ° C. In addition to fire resistance, this insulation has a number of other advantages (strength, vapor permeability, minimal thermal conductivity and ease of processing), making it an ideal choice both for insulating the roof and walls of a house, and for creating a heat-insulating layer in the ceilings between floors. Due to its excellent thermal insulation performance, stone wool is officially recommended for thermal insulation of buildings with high fire safety requirements.
Summing up, we note that despite the large selection of building materials, only some of them fully comply with fire requirements and are able to effectively protect a residential building from the spread of fire. The most durable, economical and easy-to-install products for creating refractory roofing and facade cladding are steel products - metal tiles and steel siding that meet the most stringent fire safety standards. To create the most fire-resistant structure of the cottage, the steel roof and cladding can be supplemented with a heat-insulating layer of stone wool - it is from this combination of materials that multi-layer fire walls are created that can hold fire for several hours.
oxidation reaction
Recall that chemical reactions are processes in which new substances are formed. This can happen in several ways: with a significant change in the electronic structure of the atoms involved in the reaction, and without changing their structure. The second case is simpler - it mainly refers to exchange reactions, when molecules transfer entire blocks to each other, while not changing their composition and structure. Such reactions include, for example, extinguishing soda with vinegar. Reactions with a more significant change in the electronic structure are more complex and often much more violent. Two substances must necessarily participate in them: an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent, which conditionally exchange electrons with each other. As a result, the structure of bonds changes dramatically: they are rearranged from a less favorable configuration to a more favorable one (this drives the reaction forward), and the “extra” energy is released in the form of heat and radiation. Not all redox reactions proceed this way, but the combustion reaction, which interests us most, follows this path. So, what is required for the normal course of a combustion reaction? First of all, the oxidizing agent and reducing agent themselves. The first under normal conditions is most often oxygen - O2. The two atoms in this molecule are strongly bonded, but energetically they "prefer" to bond with atoms of other elements. If they are given such an opportunity (put into contact with fuel), a violent reaction will occur. What we usually call fuel, or fuel (wood, gasoline, peat, etc.), from the point of view of chemistry, is called a reducing agent, with which oxygen atoms are firmly bound. Some substances can ignite on contact with oxygen even at room temperature - potassium metal, for example. However, for most types of fuel, it is also necessary to heat it.
At the molecular level, high temperature means that all the atoms are moving very fast, which makes it easier for them to get close enough to each other (and collide with enough force) to react. If the combustion process were limited to the above, it would not play so an important role in the life of nature and man. What makes it exceptional is the chain mechanism by which this reaction proceeds.
Consider another well-known example of oxidation, the rusting of iron. It proceeds quite slowly, and there is only a small risk that a tiny spot of rust will quickly spread throughout the sample. However, the combustion reaction of iron (there is one!) proceeds in a completely different way: thin iron “wool”, or sawdust, placed in an atmosphere of pure oxygen, flares up and burns out completely in a few moments. This is because the heat released during the reaction heats up the material, allowing it to more easily react with oxygen. In addition, many of the unstable intermediates formed during combustion lead to very rapid flame propagation.By the way, for some mixtures (oxygen and hydrogen, for example), this process leads to an almost instantaneous reaction, which we call an explosion. There is only one necessary element of the combustion reaction left: the products that are obtained during this process. In many cases, during the combustion of fuel, gaseous substances are formed (carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides), some of which can no longer be oxidized further. Remaining in the reaction zone, they only interfere with the process, as they do not allow new oxygen molecules to come into contact with the fuel. In most cases on Earth, this problem is solved due to the presence of gravity and convective processes in the atmosphere: all this contributes to constant mixing in the reaction zone and its enrichment with oxygen. This is not at all the case in space, where combustion dies out instantly, even if hypothetically there is still oxygen nearby: the reaction products surround the reaction zone so tightly that the chain process is interrupted. To sum up: combustion is based on a set of complex processes, each of which is critical for fast and stable reaction. All factors together are often combined into a “fire tetrahedron”, the faces of which are oxygen (or other oxidizing agent), a combustible substance, temperature, and the existence of a chain reaction. All firefighting and fire protection methods work in one way or another by removing one of the faces of the fire tetrahedron. It is this fact that we will use to understand how fireproof materials work.