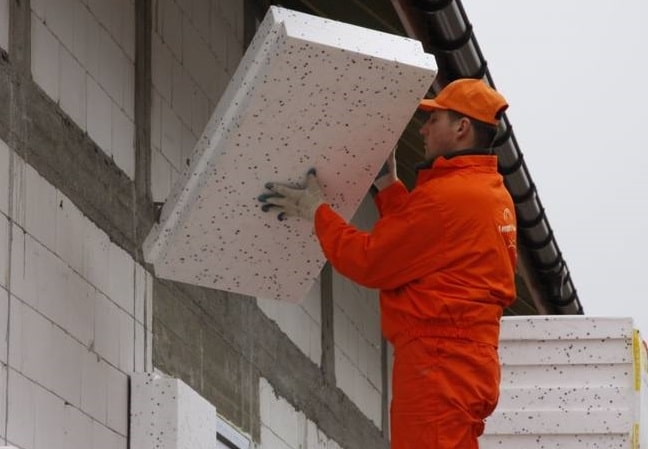
Heat insulator features
The production of foam for wall insulation includes the following technological operations:
- The granules of the material are loaded into the extruder, where they are heated to 130-140°C;
- Blowing agents - porophores are added to the portion;
- The thickened mass is squeezed out of the extruder onto a conveyor belt, after which it is cut into dimensional plates;
A mixture of semi-finished foam foam for wall insulation from the outside consists not only of expanded polystyrene and porophores - antioxidants are added to it, designed to prevent thermal oxidation during processing and damage to the integrity of the insulation during operation, fire retardant substances to increase fire resistance, as well as antistatic, light-stabilizing and modifying additives that protect thermal insulation material from external factors.
The main positive parameters of the material:
- The low moisture absorption of expanded polystyrene is the main advantage;
- The minimum coefficient of thermal conductivity, which allows, when calculating the thickness, to choose thin plates;
- High vapor permeability of foam plastic: a 20 mm thick plate replaces one layer of roofing material, but at the same time it also insulates the working surface;
- High compressive strength and other mechanical loads. The extrusion method in the production of thermal insulation allows you to evenly distribute the cells of the material, improving the quality of density and strength;
- Easy and quick installation of insulation due to low weight and good density;
- Long service life of extruded foam - up to 50 years;
- Excellent sound insulation and minimal chemical activity.

Penoplex size range:
- Plate length - from 120 to 240 cm;
- Plate width - 60 cm;
- Thickness - from 2.0 to 12.0 cm.
Disadvantages of extruded foam:
- Combustibility of groups G3-G4, formation of toxic smoke during ignition;
- Polymer additives in the composition of the material during solar irradiation can evaporate toxic substances. Therefore, the optimal use of penoplex is external, for example, insulation of brickwork;
- Refined products and some organic substances can deform foam plastic, the thickness of which can be any. These are substances such as: formaldehyde and formalin, acetone and methyl ethyl ketone; liquids with ethyl in the composition, benzene components, polyester resins, synthetic paints and fuels and lubricants.
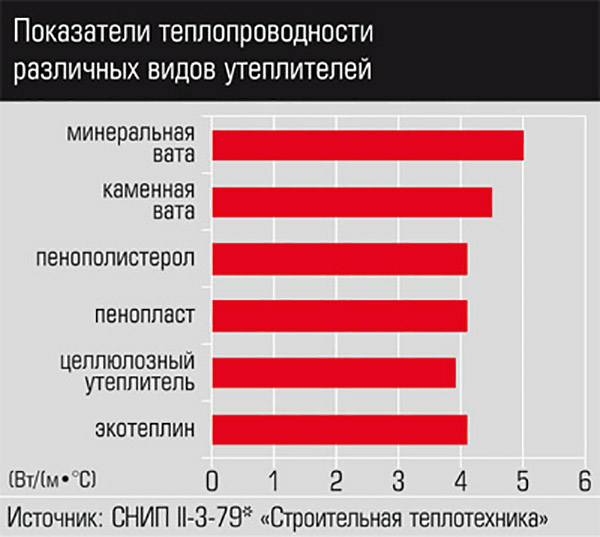
Thermal conductivity properties determine the quality of foam insulation. The greater the coefficient of thermal conductivity, the smaller the centimeters will be a layer of insulating material. Laying the insulator from the inside or outside - depends on the characteristics of vapor permeability and strength (density). You can compare the parameters of popular materials for floor insulation and other surfaces by examining the data in the table: 
From the table it is clear that foam insulation has an average thermal conductivity value, which is slightly less than that of polyurethane foam, mastics and roll materials. But you can choose penoplex only because the layer of such liquid insulation does not have joints and seams, like plate heaters, no matter how many layers are applied to the surface.
Calculations
To achieve high-quality and effective heat preservation and full protection from the cold, you need to know how to calculate the thickness of the insulation. A similar calculation of the thickness of the insulation is carried out according to existing formulas, which take into account:
- thermal conductivity;
- resistance to heat transfer of a load-bearing wall;
- coefficient of thermal conductivity;
- thermal uniformity coefficient.
The listed characteristics are no less important at the moment when the thickness of the foam is calculated.
When determining the dimensions of the selected slab made of a particular material, it is worth considering that the thickness of each product allows the use of laying in 2 layers. After calculating the thermal insulation, you can make sure that it is most convenient and beneficial to use mineral wool boards as a heater, and the thickness of such a heater should be from 10 to 14 cm.
Calculations are carried out according to a specially created formula, and in order to obtain accurate data characterizing the heat insulator used, one must take into account:
coefficient of thermal conductivity of the bearing wall;
if the wall is multilayer, then it is important to take into account the thickness of its individual layer;
thermotechnical homogeneity coefficient; we are talking about the differences between brickwork and plaster;
It is important to know the thickness of the bearing wall.
By multiplying the sum of all indicators by the thermal conductivity of the selected insulation, you can calculate the thickness of the heat insulator.
Based on these data, the choice of products sold on the construction market is based.
It is equally important to decide on the following:
- where exactly will the heater be placed; it can be the inner surface of the walls or the facade of the building;
- what material will be used as a cladding; the facade of the building can be finished with facing bricks or decorative plates;
- how many layers of heat insulator will be used in the construction of the structure.
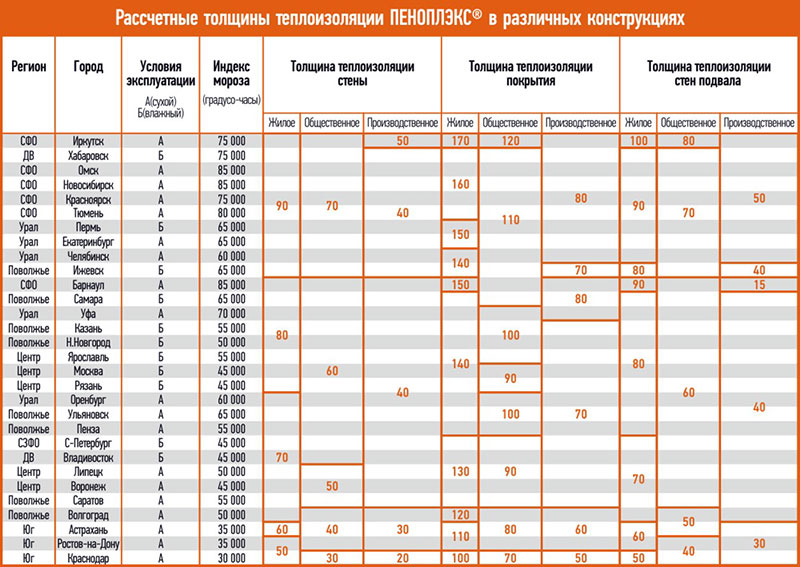
When choosing the thickness of the insulation, it is important to take into account the characteristics of the region in which the building is located. In the coldest areas, you will need a material whose thickness reaches 14 cm, and in warm regions it is enough to mount plates 8-10 cm thick
The video shows the procedure for determining the thickness of the insulation:
Based on the results of the calculations, you can easily choose the most suitable heat-insulating material, keep the heat in the house and protect the walls of the building from destruction under the influence of negative, low temperatures.
Until the second half of the 20th century, few people were interested in environmental problems, only the energy crisis that erupted in the 70s in the West sharply raised the question: how to save heat in a house without heating the street and without overpaying for energy.
There is a way out: wall insulation, but how to determine what the thickness of the wall insulation should be in order for the structure to meet modern requirements for heat transfer resistance?
The effectiveness of insulation depends on the characteristics of the insulation and the method of insulation. There are several different methods with their own merits:
- Monolithic construction, can be made of wood or aerated concrete.
- A multi-layer structure, in which the insulation occupies an intermediate position between the outer and inner parts of the wall, in this case, ring masonry is performed at the construction stage with simultaneous insulation.
- External insulation in a wet (plaster system) or dry (ventilated facade) method.
- Internal insulation, which is performed when it is impossible to insulate the wall from the outside for some reason.
To insulate already constructed and operated buildings, external insulation is used as the most effective way to reduce heat loss.
How to insulate aerated concrete, mineral wool or foam
Mineral (stone) wool and polystyrene are the main heaters for aerated concrete houses. Much less often, low-density aerated concrete (D200) and sprayed polyurethane foam are used.
Warming should be carried out only outside the building so that the dew point is closer to the outer layer of the wall.
The dew point is a place in the wall with zero temperature. In this zone, a zone of increased condensation (moisture) is formed, the wall in this place constantly freezes and thaws.
If we compare polystyrene and mineral wool, then cotton wool is a more expensive and correct solution for aerated concrete walls, it's all about vapor permeability.Cotton wool has excellent vapor permeability, which ensures the removal of moisture from the wall to the outside of the house. Thus, indoors will be drier and more comfortable. Any thickness of mineral wool insulation can be made, but it is more economically feasible - from 100 mm.
Styrofoam does not pass steam well, keeping it in the wall and creating high humidity in the house. Moreover, it is necessary to insulate aerated concrete walls with foam plastic with a thickness of 100 mm or more, in order to guarantee the shift of the dew point from the wall to the insulation. Otherwise, on the border between the foam and the wall, moisture will constantly freeze and thaw, reducing the life of the wall.
In general, we recommend using mineral wool or foam plastic with a thickness of 100 mm or more, but it is better to give preference to mineral wool.
Thermal insulation method
The effectiveness of insulation depends on the characteristics of the insulation and the method of insulation. There are several different methods with their own merits:
- Monolithic construction, can be made of wood or aerated concrete.
- A multi-layer structure, in which the insulation occupies an intermediate position between the outer and inner parts of the wall, in this case, ring masonry is performed at the construction stage with simultaneous insulation.
- External insulation in a wet (plaster system) or dry (ventilated facade) method.
- Internal insulation, which is performed when it is impossible to insulate the wall from the outside for some reason.
To insulate already constructed and operated buildings, external insulation is used as the most effective way to reduce heat loss.
Standard length, width and brick thickness
Since the brick has its own standard dimensions (6.5 x 12 x 25), the thickness of the brick wall will also have several standard dimensions, taking into account the thickness of the seam between adjacent bricks.
There are other sizes, but they mainly differ in height, and the height of the brick does not affect the thickness of the wall.
| Number of bricks, pcs | Wall thickness, cm |
| 0,5 | 12 |
| 1 | 25 |
| 1,5 | 38 |
| 2 | 51 |
| 2,5 | 64 |
In addition to a thickness of 65 mm, there is a brick thickness of 88 mm - one and a half bricks and 138 mm - double. Those. dimensions 8.8x12x25 and 13.8x12x25. In general, the thickness (height) of the brick does not affect the thickness of the brickwork.
The main criterion for choosing the thickness of a brick wall is the purpose and location of the wall itself.
We calculate the thickness of the insulation
Thermal insulation of the outer wall reduces heat loss by two or more times. For a country, most of whose territory belongs to the continental and sharply continental climate with a long period of low negative temperatures, like Russia, the thermal insulation of enclosing structures gives a huge economic effect.
Whether the thickness of the heat insulator for external walls is correctly calculated depends on the durability of the structure and the microclimate in the room: if the thickness of the heat insulator is insufficient, the dew point is inside the wall material or on its inner surface, which causes condensation, high humidity, and, then, the formation of mold and fungal attack.
The method for calculating the thickness of the insulation is prescribed in the Code of Rules “SP 50. 13330. 2012 SNiP 23-02-2003. Thermal protection of buildings”.
Factors affecting the calculation:
- Characteristics of the wall material - thickness, design, thermal conductivity, density.
- The climatic characteristics of the building zone are the air temperature of the coldest five-day period.
- Characteristics of materials of additional layers (cladding or plaster of the inner surface of the wall).
The insulation layer that meets the regulatory requirements is calculated by the formula:
In the "ventilated facade" insulation system, the thermal resistance of the curtain wall material and the ventilated gap is not taken into account in the calculation.
Wall thickness calculation example
The thickness of the insulation of a frame house for permanent residence on the example of the Moscow region (such a calculation was given above) was 150 mm when mineral wool with a density of 50 kg / m 3 was used. Since most manufacturers produce this insulation with a thickness of 50 and 100 mm, you will have to put insulation either in three layers with a thickness of 50 mm, or in two 100 and 50 mm. From this, the coefficient of thermal conductivity will not change.
OSB 12 mm thick with 50 mm air gap and 5 mm plaster was chosen as the outer skin.
The interior is sheathed with gypsum board 13 mm.
Total: 150 + 12 + 50 + 5 + 13 = 230 (mm).
Now, focusing on these data, it is now possible to calculate the foundation, but you need to understand that this is just a mathematical calculation and it does not take into account the problems that may arise during the installation of the structure.
To make sure that there is no draft anywhere in the house, the design is checked with a thermal imager.
The thickness of the foam for insulation
Penoplex is a derivative of the extrusion of expanded polystyrene, a higher quality type of foam, in which improvers are added when punching through the mold. There are quite a few brands of foam plastic, and the choice of a suitable material for insulating a house outside or inside depends not only on the properties of a particular class of foam plastic - the functional purpose of the room, the thickness of the foam plastic, and installation parameters, and many other factors will play a role here. To navigate the properties of this insulation, you should study its characteristics.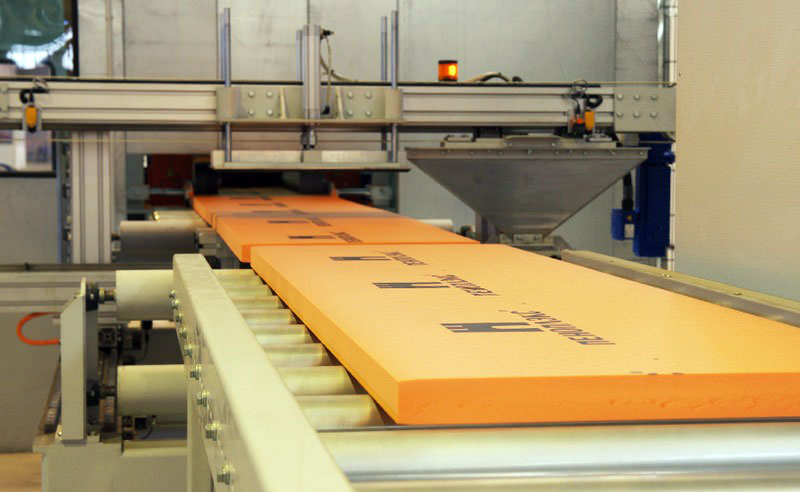 
How to calculate the thickness of the insulation
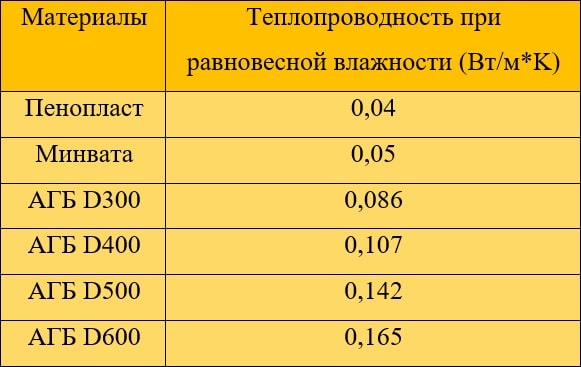
- The required total thermal resistance (R) is 5.28.
- R aerated concrete wall 400 mm from D500 - 2.6.
- R insulation should be: 5.28-2.6 = 2.68
Now you need to use the table, according to which the thermal conductivity of heaters is located, in our case, mineral wool.
AGB - autoclaved aerated concrete
The thermal conductivity of mineral wool at equilibrium humidity is 0.05.
The thickness of the insulation is determined quite simply: the required thermal resistance of the insulation is multiplied by its thermal conductivity, that is
2.68 x 0.05 = 0.134 meters.
Conclusion: we need mineral wool with a thickness of 134 mm. But mineral wool slabs are sold with a multiplicity of 50 mm, which means that the insulation layer will be 150 mm.
Important! The economically justified thickness of mineral wool for wet facades is from 100 mm. Since during the installation of insulation (wet facade) it is necessary to use several layers of plaster, mesh, facade umbrellas, other fasteners, there will not be much savings between the insulation thickness of 50 and 100 mm
And the cost of work and consumables for the installation of heaters of different thicknesses is almost the same
Since during the installation of insulation (wet facade) it is necessary to use several layers of plaster, mesh, facade umbrellas, other fasteners, there will not be much savings between the insulation thickness of 50 and 100 mm. And the cost of work and consumables for the installation of heaters of different thicknesses is almost the same.
Also note that 100 mm of insulation, in 90% of cases, shifts the dew point from the wall to the insulation. That is, moisture will never freeze in the wall, therefore, the service life of such a wall will be almost infinite.
Characteristics of various materials
Table 1

The value of the normalized resistance to heat transfer of the outer wall depends on the region of the Russian Federation in which the building is located.
table 2
The required layer of thermal insulation material is determined based on the following conditions:
- the outer building envelope - a solid ceramic brick of plastic pressing with a thickness of 380 mm;
- interior finish - plaster with cement-lime composition 20 mm thick;
- exterior finish - a layer of polymer cement plaster, layer thickness 0.8 cm;
- the coefficient of thermal engineering uniformity of the structure is 0.9;
- thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulation - λА=0.040; λB=0.042.
What is penoplex
Heat loss through the walls of a building can range from ¼ to 1/3 of the total. An increase in thermal resistance due to the inclusion of special coatings in the design of external walls makes it possible to reduce its thickness and reduce the consumption of other building materials.
Wall insulation is necessary not only to prevent heat from escaping the house in the cold season, but also to excessive heating of the room in summer, so the right choice of a heat insulator determines the financial costs not only during construction, but also during operation (heating, air conditioning).
Differences from other options
In the name of this insulation, attention should be paid to the word "extruded", since a different production technology distinguishes it from ordinary polystyrene. Molten polymer under high pressure is passed through small nozzles, resulting in solidification of a dense foam plate with a thickness of 20 to 100 mm.
The molten polymer under high pressure is passed through small nozzles, resulting in a solid foamed plate with a thickness of 20 to 100 mm.
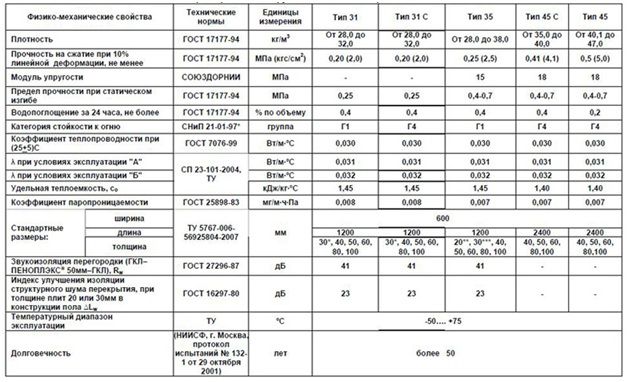
Technical characteristics of various brands of penoplex are presented in a summary table:
Of the presented types, only 45 are used for paving, the rest - for the insulation of residential buildings.
Meaning of indicators
The finely porous structure of foam plastic (100 - 200 microns) makes it a fairly light but durable material. Its characteristic qualities are:
- resistance to mechanical stress (when laying on a flat surface);
- low vapor permeability (thickness 20 mm is comparable to 1 layer of roofing material);
- moisture resistance allows it to be used on the outside of walls, in baths, bathrooms, basement levels without heating;
- an insignificant coefficient of thermal conductivity expands the possibilities of application in thin partitions created by oneself: balcony railings, walls of a veranda, extension or garage;
- light weight does not lead to a significant increase in the load on the base when sheathing already designed structures (insulation of individual apartments in a multi-storey building);
- the density of the polymer allows the use of conventional cutting tools to fit sheets to size when performing work;
- chemical resistance to most compositions used in construction (exceptions: gasoline, diesel fuel, acetone, enamels, oil paints, formaldehyde, acetate-based solvents). For more information about the qualities of the material, see this video:
What to compare

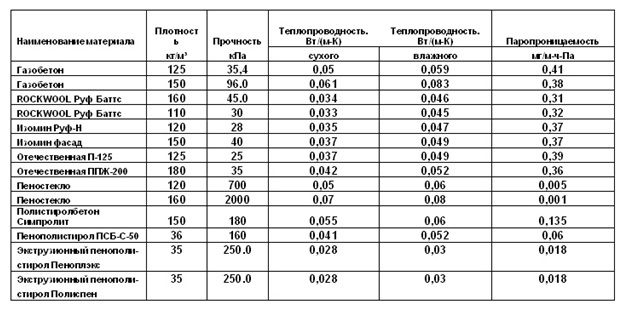
The ratio of technical characteristics can be seen in the reference tables of materials:
Variety and features of heaters
Modern manufacturers offer a wide range of materials used as heaters and meet all existing requirements and standards:
- Styrofoam;
- basalt or stone mineral wool;
- penoplex;
Before making the final choice, it is necessary to familiarize yourself in detail with the features and benefits of each of them. Having studied the technical characteristics of various materials, we can safely say that the leaders in their main qualities are mineral wool or basalt insulation boards, as well as wall insulation boards.
The basis for the choice is the data on the thermal conductivity, thickness and density of each material:
- stone wool - from 130 to 145 kg / m³;
- expanded polystyrene - from 15 to 25 kg / m³;
- penoplex - from 25 to 35 kg / m³.
The density of basalt wool reaches 100 kg / m³, which makes basalt insulation one of the most sought after and popular. This does not mean that consumers should abandon the use of mineral wool as an insulating material used in the course of finishing work before facing the facade walls of a brick building.
Choose a thermal insulation material based on the most significant characteristics of each. Having decided to choose polystyrene as a reliable and effective heat insulator, it is necessary to clarify the dimensions of the plate, its density, weight, vapor permeability, resistance to moisture. Despite the many positive qualities, this wall insulation has some negative features:
- susceptibility to destruction by rodents;
- high degree of flammability.

This forces consumers to select other materials, among which mineral wool is the most popular for wall insulation. It is characterized by high density, low weight, low thermal conductivity. Its vapor permeability ensures a normal level of humidity. In addition, mineral wool is one of the fire-resistant materials.
Extruded polystyrene foam is in demand among consumers. These plates are characterized by a high degree of resistance to mechanical damage. EPPS is not subject to rotting, the formation of fungus and mold, and is resistant to moisture. It is used for insulation of the basement and load-bearing walls. In the latter case, plates are installed, the density of which is 35 kg / m³.
Frame house projects
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 42² Total area
- 6 x 7m Building area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 28² Total area
- 5 x 4m Building area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 170² Total area
- 11 x 8m Building area
- 3 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 127² Total area
- 10 x 7m Building area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 200² Total area
- 9 x 13m Building area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 140² Total area
- 12 x 9m Building area
- 3 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 127² Total area
- 9 x 8m Building area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 130² Total area
- 10 x 10m Building area
- 3 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 83² Total area
- 10 x 9m Building area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 30² Total area
- 7 x 6m Building area
- 3 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 156² Total area
- 11 x 9m Building area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 140² Total area
- 8 x 9m Building area
- 4 rooms
- 2 bathrooms
- 120² Total area
- 8 x 10m Building area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 35² Total area
- 5 x 9m Building area
- 2 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 42² Total area
- 6 x 9m Building area
- 2 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 72² Total area
- 12 x 6m Building area
- 2 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 74² Total area
- 7 x 6m Building area
- 3 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 110² Total area
- 13 x 9m Building area
- 3 rooms
- 1 bathroom
- 75² Total area
- 9 x 7m Building area
- 1 room
- 1 bathroom
- 45² Total area
- 6 x 9m Building area
With a fairly low price, the quality of materials used in frame housing construction is growing every year. It is not surprising that this type of buildings is becoming more widespread in all regions of Russia. And depending on the climatic zone, the same project will have different requirements for heat saving, therefore, what should be the thickness of the walls of a frame house must be determined in each case separately.
There are several subspecies of frame technology - if the general principle of building houses is the same, then the nuances, among which the thickness of the walls, may differ
What materials are used for insulation
Mineral wool is one of the common heaters, which is characterized by good thermal insulation, but has a significant drawback: a high rate of moisture absorption. In this case, it is recommended to protect the wool with hydro- and vapor barrier.
Fiberglass is a good thermal insulator. The material is resistant to high temperatures and does not rot. Mineral wool can be used not only to insulate the outer walls of a brick house, but also to insulate a chimney in a boiler room or bathhouse.
Cellulose wool is used mostly for interior work. The material has good characteristics, with the exception of a high degree of moisture absorption and low resistance to mechanical stress. Note that this heat insulator is environmentally friendly.
A good option for insulating brick walls from the outside or from the inside is polyurethane foam, which is resistant to mold and does not rot. The material can be used without any problems when insulating a brick house with your own hands.
Such insulation as expanded polystyrene (polystyrene) is also widely used, which is characterized by low cost and high thermal insulation performance. It should be borne in mind that the material does not absorb moisture, but at the same time it is endowed with high flammability. It is not recommended to use it in residential buildings, however, often the internal insulation of brick walls is carried out with foam plastic.
Extruded polystyrene foam has similar characteristics. Of the positive features, it is worth highlighting the low vapor throughput and high strength index. The characteristics of the material are maintained even at high humidity levels. It can be used not only for insulating a brick house from the inside or outside, but also for the construction of an insulated blind area, since this design has a longer service life.
What data is needed to calculate the thickness of the insulation
The size of the insulation layer depends on the thermal resistance of the material. This indicator is the reciprocal of thermal conductivity. Each material - wood, metal, brick, polystyrene or mineral wool - has a certain ability to transfer thermal energy. The thermal conductivity coefficient is calculated during laboratory tests, and for consumers it is indicated on the packaging.
If the material is purchased without marking, you can find a summary table of indicators on the Internet.
Material name
Thermal conductivity, W/m*K
Concrete
silicate brick
foam concrete
Tree
Mineral wool
0,07-0,048
Extruded polystyrene foam
polyurethane foam
0,041-0,02
Styrofoam
0,05-0,038
Foam glass
The thermal resistance of the material is a constant value, it is defined as the ratio of the temperature difference at the edges of the insulation to the strength of the heat flow passing through the material. The formula for calculating the coefficient: R=d/k, where d is the thickness of the material, k is the thermal conductivity. The higher the value obtained, the more effective the thermal insulation.
Why is it necessary to calculate the thickness of the insulation
Comfortable living in the house involves maintaining the optimum temperature in the room, especially in winter. When erecting a building, you should remember about thermal insulation, you should correctly select and calculate the thickness of insulation for walls, roofs, floors and attics. Any material - brick, wood, foam block or mineral wool has its own value of thermal conductivity and heat resistance.
A warm home is the dream of every owner
Thermal conductivity is the ability of a material to conduct heat. This value is determined in laboratory conditions, and the data obtained are given by the manufacturer on the packaging or. The thermal resistance of a material is the reciprocal of thermal conductivity. A material that conducts heat well has low heat resistance and requires insulation.
When erecting a building, one should remember about high-quality thermal insulation. If mistakes were made in the walls of the house or in other structures during construction, then cold bridges may appear - areas along which heat quickly leaves the house. Condensation may occur in these places, and in the future, mold may form, if not taken during the warming measures.
Calculation of the thermal insulation layer formulas and examples
In order to be able to accurately calculate the amount of insulation, it is necessary to find the heat transfer resistance coefficient of all materials of the wall or other section of the house. It depends on the climatic indicators of the area, therefore it is calculated individually according to the formula:
tv is an indicator of the temperature inside the room, usually 18-22ºC;
tot is the value of the average temperature;
zot is the duration of the heating season, days.
Values for counting can be found in SNiP 23-01-99.
When calculating the thermal resistance of a structure, it is necessary to add up the indicators of each layer: R = R1 + R2 + R3, etc. Based on the average indicators for private and multi-storey buildings, the approximate values of the coefficients are determined:
- walls - at least 3.5;
- ceiling - from 6.
The thickness of the insulation depends on the material of the building and its size, the lower the thermal resistance of the wall or roof, the greater the insulation layer should be.
Example: a wall made of silicate brick 0.5 m thick, which is insulated with foam.
Rst. \u003d 0.5 / 0.7 \u003d 0.71 - thermal resistance of the wall
R- Rst. \u003d 3.5-0.71 \u003d 2.79 - value for foam
Having all the data, you can calculate the required insulation layer using the formula: d = Rxk
For foam plastic, thermal conductivity k=0.038
d \u003d 2.79 × 0.038 \u003d 0.10 m - foam plates 10 cm thick will be required
Using this algorithm, it is easy to calculate the optimal amount of thermal insulation for all parts of the house, except for the floor. When calculating the base insulation, you must refer to the soil temperature table in the region of residence. It is from it that data is taken to calculate the GSOP, and then the resistance of each layer and the desired value of the insulation are calculated.