Pressure in the accumulator and expansion tank
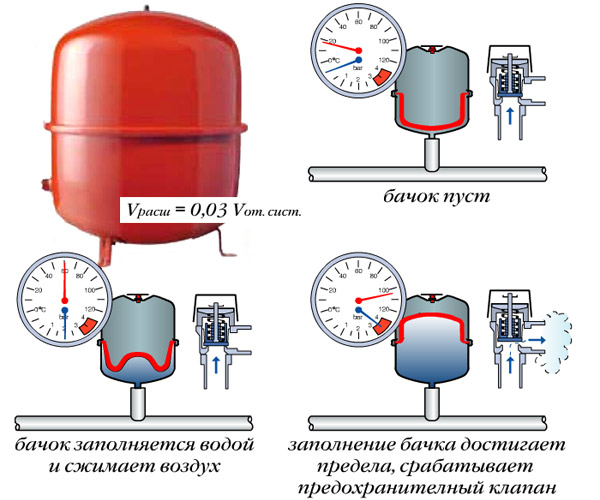
Let the minimum allowable pressure in the system (heating - for the expansion tank, water supply - for the accumulator, when the relay is activated and the pump turns on) is X atmospheres. Then, in the device, the optimal pressure in the absence of water in it (it is empty) should be 90% of X. You need to check the pressure by completely draining the water. Otherwise, measurements will not give anything.
In general, air from accumulators and expansion tanks can gradually escape. But regular checking of air sufficiency is difficult. To carry it out, you need to drain all the liquid from the device, which is not always possible. But there are signs that clearly indicate that the air has escaped. For a hydraulic accumulator, this is too frequent switching on of the pump, for an expansion tank, a strong change in pressure in the system when the temperature of the coolant changes. Therefore, immediately after installing the tank, you need to measure by what percentage the pressure changes when the carrier in the system is completely warmed up, write down this value, and then make sure that this value does not increase too much, pump it up as necessary. For a hydraulic accumulator, you need to measure the time between turning the pump on and turning it off, and also make sure that this time remains constant.
Design differences
First of all, you need to understand that a hydraulic accumulator and an expansion tank, despite the assurances of some unscrupulous managers, are not the same thing. Their design differences are due to the specifics of the application. Installing an expansion tank as a hydraulic accumulator is fraught with unpleasant consequences.
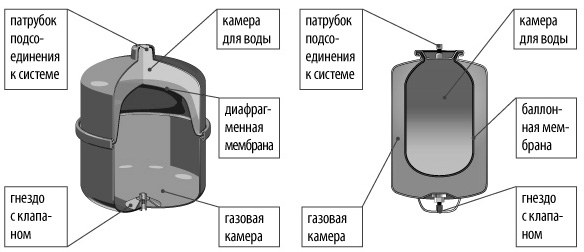
The bottom line is that in the expansion tank for the heating system, the membrane divides the internal volume in half. Initially, air pumped into the lower half creates enough pressure to press the membrane completely against the inner surface. As the temperature of the coolant rises, its volume increases, the pressure increases and water begins to flow into the upper half, squeezing the membrane. Accordingly, the air in the lower half is compressed. The hydraulic accumulator is distinguished by the fact that a balloon membrane is installed in it, entering which water does not come into contact with the inner walls.
Closed expansion vessels: with diaphragm diaphragm, with balloon diaphragm
Considering the difference between an expansion tank and a hydraulic accumulator, it is necessary to understand that they work in different conditions. The change in the volume of fluid in the heating system is insignificant, in addition, it happens slowly, without sudden jerks. However, the temperature can reach 90 °C. Therefore, the first requirement for such a membrane is resistance to prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
For a balloon diaphragm in a cold water accumulator, high temperature resistance is not as important, but the ability to work in the mode of frequent expansion / compression is key
Unfortunately, there is no universal material that is equally resistant to high temperatures and regular stretching. Membranes in modern expansion tanks are made of the following materials:
— NATURAL — can be operated at operating temperature from -10 to 50 °С. Extremely elastic material, however, partial diffusion may occur during use. Natural rubber rubber can be used for both drinking and industrial water; - BUTYL - operation at temperatures from -10 to 100 ° C is possible. More resistant in terms of diffusion, but not as elastic as NATURAL. Synthetic butyl rubber can be used as a hydraulic accumulator membrane; - EPDM - operates at temperatures from -10 to 100 ° C.More water permeable than BUTYL. Synthetic ethylene / propylene rubber is installed in tanks for drinking or industrial water; - SBR - operation is permissible at temperatures from -10 to 100 ° C. Less elastic Used exclusively in expansion tanks of the heating system, not flexible enough for installation in hydraulic accumulators; - NITRIL - operates at temperatures from -10 to 100 ° C. Resistant to active media.
The scope of application of compensation tanks is not limited to heating systems and water supply, they are successfully used for storing fire extinguishing liquid in automatic fire extinguishing systems, as well as as part of a powder fire extinguishing module.
Regardless of the type, a hydraulic accumulator and an expansion tank are an integral part of any life support system and provide a high level of comfort and safety.
The choice of accumulator, expansion tank. Service. Exploitation. Repair. (10+)
Hydraulic accumulator, expansion tank. Features of choice
A hydraulic accumulator and an expansion tank are designed for slightly different purposes, but are arranged in almost the same way, so I combined them in one article. The hydraulic accumulator is designed to accumulate water in the autonomous water supply system, to protect the system from overpressure, and to prevent frequent switching on of the pump. The expansion tank is installed in the heating system. It protects it from overpressure, which can occur when water (or other coolant) expands from an increase in temperature. The key difference between a hydraulic accumulator and an expansion tank is that the expansion tank must operate at a sufficient temperature, such requirements are not imposed on a cold water accumulator. But on the other hand, for most accumulators, there are high requirements for the quality of the membrane material, since they are used in the supply of water that can be eaten. For an expansion tank, such requirements are less critical.
Design and purpose of devices
Expansion tank
- The main purpose of the tank is to compensate for the expansion of the coolant. When heated, water increases in volume, and quite strongly (+0.3% for every 10 degrees Celsius). In this case, the liquid practically does not shrink, so that the heated coolant will exert significant pressure on the pipe walls, junctions and valves.
- To compensate for this pressure, as well as to minimize the effects of water hammer, an additional tank is built into the system - an expansion tank. The first tanks had a leaky design, but today pneumatic-hydraulic models are almost universally used.
- Inside such a tank is a membrane made of an elastic material. Since the membrane is in contact with a heated coolant, it is made of polymers that are resistant to high temperatures - EPDM, SBR, butyl rubber and nitrile rubber.
- The membrane divides the tank into two cavities - the working one (the coolant enters it) and the air one. When the pressure in the system increases, the air chamber decreases in volume (due to air compression), and this compensates for the load on pipes and valves. Approximately the same thing happens with water hammer - but here the process goes at a faster speed.
- When the temperature of the coolant decreases, the volume of water decreases, and the air, exerting pressure on the membrane, displaces an additional volume of hot water into the pipes of the heating system.
Hydraulic accumulator
The accumulator, at first glance, practically does not differ in design from the expansion tank:
- The base is the same container made of corrosion-resistant steel, only painted blue.
- There is also a membrane inside the tank - however, it is somewhat different in shape from the membrane of the expansion tank.
- The internal volume is also divided into two chambers, only in hydraulic accumulators the water chamber is located inside the membrane, i.e. liquid contact with the metal walls of the tank is completely excluded.
Yes, and the design functions according to a similar principle, although they use it for a different purpose:
- When the pump is turned on or water is supplied through a centralized water supply system, the chamber is filled with liquid under a certain pressure.
- If the pressure drops for some reason, the air chamber increases in volume, and water from the working chamber enters the system. Thanks to this, the pressure in the pipes is stabilized, and the equipment (washing machines, dishwashers, etc.) works without failures.
- The second aspect of the operation of the accumulator is the protection of the pump from frequent switching on. As long as it is possible to compensate for the withdrawal of water from the system due to the reserve in the tank, the pressure switch will not work and the pump will not start pumping water. Thus, the equipment will turn on less often, which means it will work longer.
- A large accumulator (for 50, 100 or more liters) is also a supply of water. Yes, you won’t last long on such a supply, but with economical spending it is quite possible to survive a water supply accident or a power outage that will make the pump impossible to work.
- In addition, the accumulator, like the expansion tank, compensates for water hammer.
Required volume of accumulator and expansion tank
It must be clearly understood that the volume of these devices, which is given in the specification, is the volume of the tank itself. Less liquid is placed in it. The volume of a liquid depends on the pressure.
Determining the volume of the expansion tank is quite simple. You need to understand how much water (or antifreeze) will be in your heating system. We take the coefficient of thermal volumetric expansion of water with a margin of 6E-4. Thus, the volume of water when heated from zero to 100 degrees will increase by 0.06 times, that is, by 6%. If there are 100 liters of water in the system, then the excess volume will be 6 liters.
Now we need to determine the permissible pressure of the coolant in the heating system. Let the minimum value be X1 and the maximum X2. Usually it is 1.8 atmospheres and 2.4 atmospheres. If the pressure in the empty expansion tank is 90% of the minimum allowable for the coolant (let it be X0), then [Required expansion tank volume, liters] = [0.06] * [Volume of coolant in the system, liters] / (([X0, liters] + [1]) / ([X1, liters] + [1]) — ([X0, liters] + [1]) / ([X2, liters] + [1]))). For our case with 100 liters of carrier, we get 36 liters. In this case, more is not less. You can take with a margin, but this volume will be enough.
The volume of the accumulator depends solely on the maximum peak water flow. If one tap can work in the house at the same time, then the volume of the accumulator should be about 30 liters, if two taps - 60 liters, if 3 - 90, and so on.
Connecting the accumulator to the system
Typically, the water supply system of a private house consists of:
- pump;
- hydraulic accumulator;
- pressure switch;
- check valve.
In this scheme, a pressure gauge may also be present - for operational pressure control, but this device is not necessary. It can be periodically connected - for test measurements.
With or without 5-pin fitting
If the pump is of a surface type, the accumulator is usually placed near it. In this case, a check valve is installed on the suction pipeline, and all other devices are installed in one bundle. They are usually connected using a five-pin fitting.
It has leads with different diameters, just for the devices used for tying the accumulator. Therefore, the system is most often assembled on its basis. But this element is not at all necessary and everything can be connected using ordinary fittings and pieces of pipes, but this is a more time-consuming task, and there will be more connections.
With one inch outlet, the fitting is screwed onto the tank - the branch pipe is located at the bottom. A pressure switch and pressure gauge are connected to the 1/4 inch outlets. A pipe from the pump and wiring to consumers are connected to the remaining free inch outlets. That's all the connection of the gyroaccumulator to the pump. If you are assembling a water supply scheme with a surface pump, you can use a flexible hose in a metal winding (with inch fittings) - it is easier to work with it.
As usual, there are several options, you choose.
Connect the accumulator to the submersible pump in the same way. The whole difference is where the pump is installed and where to supply power, but this has nothing to do with installing a hydraulic accumulator. He puts it in the place where the pipes from the pump go. Connection - one to one (see diagram).
How to install two hydraulic tanks on one pump
When operating the system, sometimes the owners come to the conclusion that the available volume of the accumulator is not enough for them. In this case, a second (third, fourth, etc.) hydraulic tank of any volume can be installed in parallel.
There is no need to reconfigure the system, the relay will monitor the pressure in the tank on which it is installed, and the viability of such a system is much higher. After all, if the first accumulator is damaged, the second one will work. There is another positive point - two tanks of 50 liters each cost less than one of 100. The point is a more complex technology for the production of large containers. So it's also more cost effective.
How to connect a second accumulator to the system? Screw a tee onto the input of the first one, connect the input from the pump (five-pin fitting) to one free output, and the second container to the remaining free output. Everything. You can test the circuit.
Repair
Common malfunctions are: breakage of the air check valve (nipple) and damage to the membrane. The check valve can be replaced by putting it from a car tire. They are suitable for most accumulators and tanks. Damage to the membrane can only be repaired in repairable (collapsible) devices. I've done it successfully myself a couple of times. It is necessary to disassemble the tank, remove the membrane, thoroughly wash and dry it, find the place of damage, degrease, seal or vulcanize it
When choosing an adhesive, be sure to pay attention to whether it is waterproof, elastic, whether it can be used at elevated temperatures (for an expansion tank), whether it can come into contact with food (for a hydraulic accumulator)
Unfortunately, errors occur periodically in articles, they are corrected, articles are supplemented, developed, new ones are being prepared. Subscribe to the news to stay informed.
My question is - is it possible to use a container with one input as a hydraulic accumulator. Will the water compress the air inside the container and thus act as a damper? I mean, there is no membrane in the design. Read the answer.
Heating system with forced circulation. Organization of forced circulation of the coolant in the circuits of the heating system.
We fill in the coolant. How to replace antifreeze in the heating system. How to properly fill the heating system with coolant, choose between water and.
Pipe heating system so that the winter plumbing does not freeze. With your hand. Do-it-yourself plumbing. External, non-freezing. Laying of water pipes
Gas in the house autonomously. Is it real? Personal experience. Review. Installation errors. Review of the experience of autonomous gasification, installation of a gas tank for liquefied gas. T.
Sealed threaded pipe connection. Plumbing adhesive - sealant. How to properly connect a pipe thread in a pipeline? Ensuring tightness.
Personal experience in selecting a gas burner for heating according to the characteristics of k. How to choose the right gas burner for heating. Advice. Personal experience. Review.
In order for the pump not to turn on every time a tap is opened in the house, a hydraulic accumulator is installed in the system. It contains a certain amount of water, sufficient for a small flow. This allows you to practically get rid of short-term switching on of the pump. Installing a hydraulic accumulator is not difficult, but a certain number of devices will be required - at least - a pressure switch, and it is also desirable to have a pressure gauge and an air vent.
What should be the pressure in the accumulator
Compressed air is in one part of the accumulator, water is pumped into the second. The air in the tank is under pressure - factory settings - 1.5 atm. This pressure does not depend on volume - and on a tank with a capacity of 24 liters and 150 liters it is the same. More or less may be the maximum allowable maximum pressure, but it does not depend on the volume, but on the membrane and is indicated in the technical specifications.
Pre-check and pressure correction
Before connecting the accumulator to the system, it is advisable to check the pressure in it. The settings of the pressure switch depend on this indicator, and during transportation and storage the pressure could drop, so control is very desirable. You can control the pressure in the gyro tank using a pressure gauge connected to a special inlet in the upper part of the tank (capacity of 100 liters or more) or installed in its lower part as one of the piping parts. Temporarily, for control, you can connect a car pressure gauge. His error is usually small and it is convenient for him to work. If this is not the case, you can use the regular one for water pipes, but they usually do not differ in accuracy.
If necessary, the pressure in the accumulator can be increased or decreased. To do this, there is a nipple at the top of the tank. A car or bicycle pump is connected through the nipple and, if necessary, the pressure is increased. If it needs to be bled off, the nipple valve is bent with some thin object, releasing air.
What air pressure should be
So the pressure in the accumulator should be the same? For the normal operation of household appliances, a pressure of 1.4-2.8 atm is required. To prevent the tank membrane from tearing, the pressure in the system should be slightly higher than the tank pressure - by 0.1-0.2 atm. If the pressure in the tank is 1.5 atm, then the pressure in the system should not be lower than 1.6 atm. This value is set on the water pressure switch, which is paired with a hydraulic accumulator. These are the optimal settings for a small one-story house.
If the house is two-story, you will have to increase the pressure. There is a formula for calculating the pressure in a hydraulic tank:
Vatm.=(Hmax+6)/10
Where Hmax is the height of the highest draw point. Most often it is a shower. You measure (calculate) at what height relative to the accumulator its watering can is, substitute it into the formula, you get the pressure that should be in the tank.
If the house has a jacuzzi, everything is more complicated. You will have to select empirically - by changing the relay settings and observing the operation of water points and household appliances. But at the same time, the working pressure should not exceed the maximum allowable for other household appliances and plumbing fixtures (indicated in the technical specifications).
How to choose
The main working body of the hydraulic tank is the membrane. Its service life depends on the quality of the material. The best for today are membranes made of isobutyl rubber (it is also called food grade). The body material matters only in membrane type tanks. In those in which a “pear” is installed, water is in contact only with rubber and the material of the case does not matter.
What is really important in tanks with "pears" is the flange. It is usually made from galvanized steel.
In this case, the thickness of the metal is important. If this is only 1 mm, after about a year and a half of operation, a hole will appear in the metal of the flange, the tank will lose its tightness and the system will stop working.Moreover, the guarantee is only a year, although the declared service life is 10-15 years. The flange usually deteriorates after the end of the warranty period. There is no way to weld it - a very thin metal. You have to look for a new flange in service centers or buy a new tank.
So, if you want the accumulator to serve for a long time, look for a flange made of thick galvanized or thin, but made of stainless steel.
Expansion tank
Heating water is designed to transfer heat from the boiler to the radiators. It is known that when heated by 10 ° C, the volume of water increases by about 0.3%, from which it follows that heating to the prescribed 70 ° C will give an increase in volume by about 3% of the original. It is known from the school physics course that liquids are practically incompressible, therefore even such a seemingly insignificant increase in volume can lead to a rupture of the pipeline or leaks at the joints. In order to prevent this from happening, an expansion tank is installed in the heating system.
Initially, such containers were open, which led to certain problems:
- the liquid in them constantly evaporates, you have to monitor the water level and replenish it regularly; - an open expansion tank must be installed in the upper part of the system and insulated to prevent freezing of the coolant and, as a result, an increase in the cost of the structure; - constant access of oxygen contributes to corrosion; - pressure regulation with an open circuit is difficult.
Modern materials and, in particular, the durable and elastic material of the membrane, make it possible to equip a closed system, without access of oxygen to the coolant. This also allows for a constant water level and the ability to adjust the pressure. Another advantage of the closed tank is the ease of installation and maintenance. It can be installed anywhere in the heating system and, if necessary, can be easily dismantled and connected elsewhere.