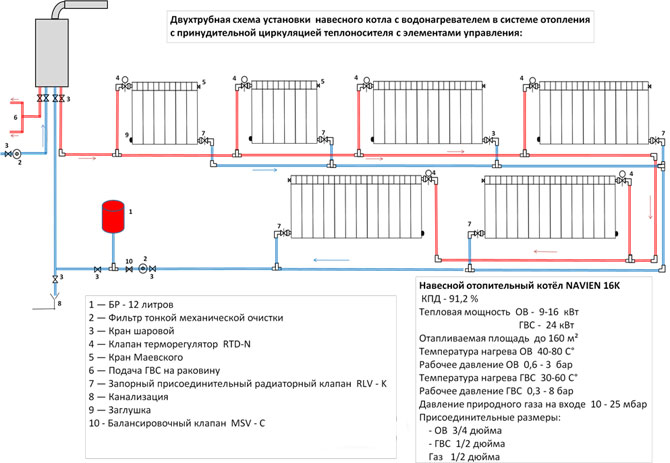
Tying heating radiators with polypropylene is simple and affordable
In recent years, polypropylene pipes have been popular with consumers because they are inexpensive and have proven themselves in operation.
Polypropylene products are distinguished by:
- significant resistance to aggressive environments;
- plaque is not collected on the walls from the inside and solid particles do not settle on them;
- soldering pipes requires special equipment;
- they have a long service life.
Thus, if the heating radiators are bound with polypropylene, there will be no leakage of the liquid coolant in the future. The fact is that in the case when the fitting is installed incorrectly or not fully tightened, when using conventional pipes for tying heating batteries, leaks cannot be avoided.
Like all materials, polypropylene pipes for heating have a number of features. In order not to encounter problems during their installation, you need to know about them in advance.
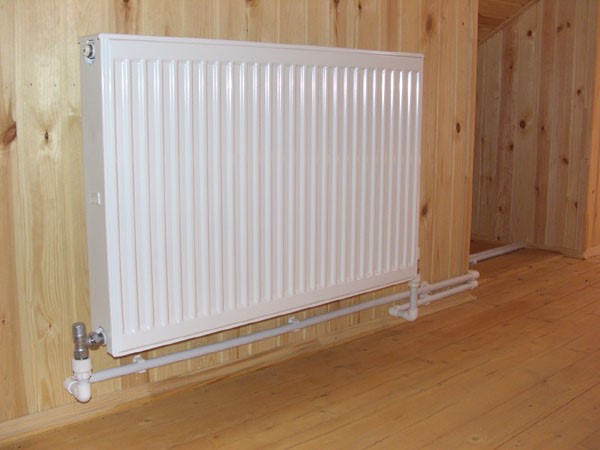
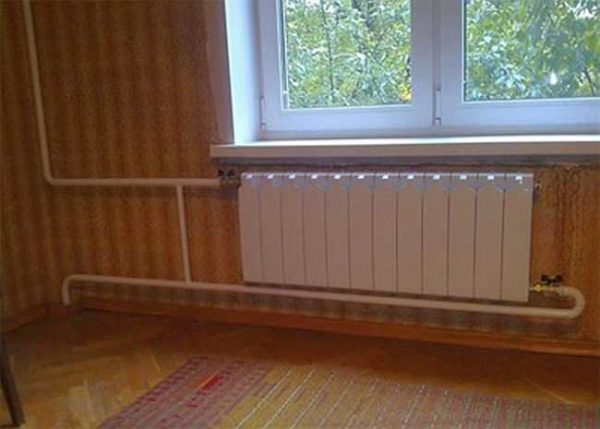
Tying with polypropylene pipes
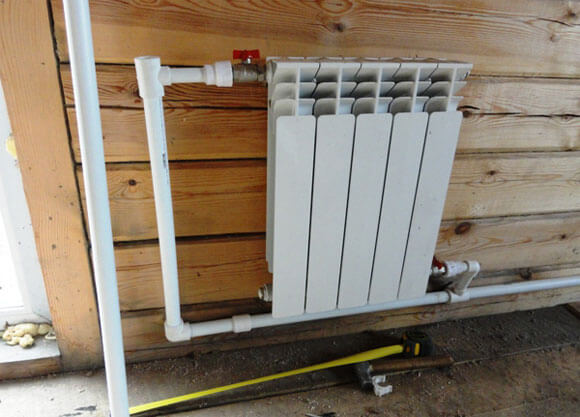
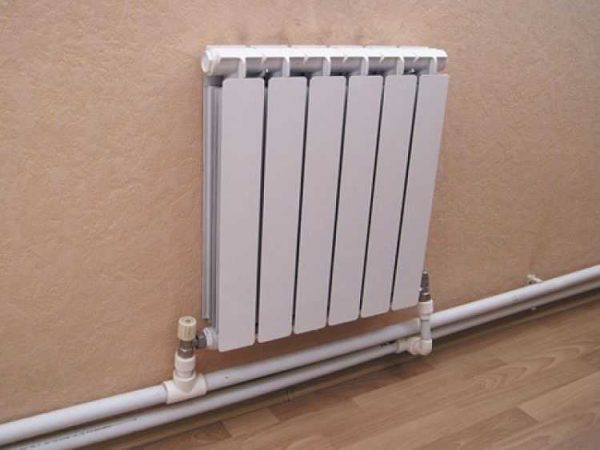
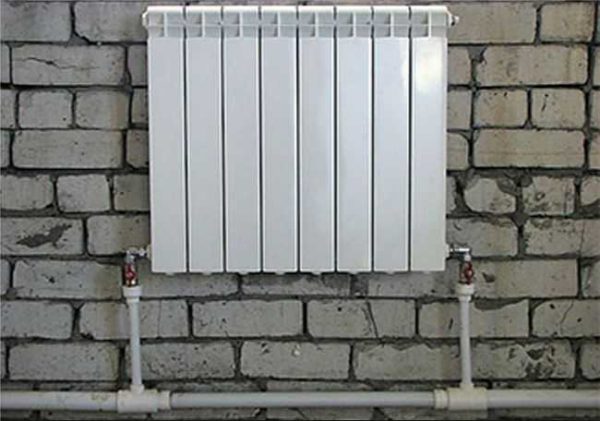
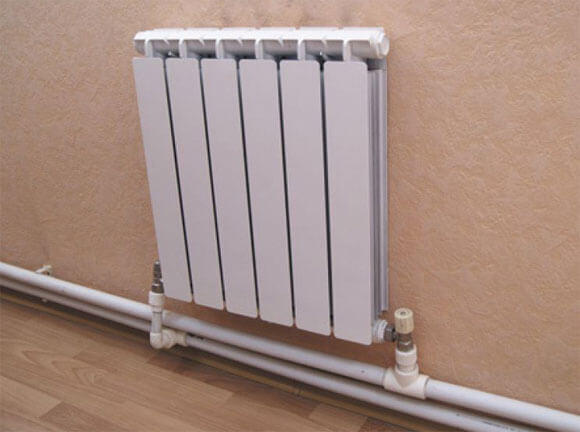
Piping of radiators can be carried out using a variety of pipes, but experts recommend using polypropylene. Ball valves for strapping are also bought in polypropylene, they can be straight and angled, this option is the simplest and most inexpensive. Brass fittings are more expensive, and installation is more difficult.
Polypropylene strapping is performed as follows:
- the coupling with the union nut is inserted into the multiflex, which is easily connected to any outlet;
- the pipes themselves are attached to the walls at a convenient height, they should not fit snugly against the surface, it is better to leave a gap of 2-3 cm. The pipes are fixed with special brackets, which are fixed to the wall with nails or self-tapping screws.
Polypropylene strapping to radiators can also be carried out when pipes are laid into the wall, in which case they come to the surface only at the connection points.
Piping of radiators can be carried out using a variety of pipes, but experts recommend using polypropylene.
Fasteners for batteries can be very different, most often it is a pin connection, which is fixed on the wall surface. Corner brackets can also be used, which also allow you to hang radiators at the required height. For panel batteries, fasteners are supplied in the kit, for sectional batteries, you need to buy separately. Usually, two brackets or pins are enough for one section.
The connection of cranes is carried out in this way:
- the crane is disassembled, a fitting and a union nut are screwed into the radiator;
- the nut is tightly tightened with a special wrench.
As you can see, this process is extremely simple. To perform such work, you only need to purchase a special plumbing key for American women, without which it is unlikely that you can simply install a tap.
The following materials and tools are required for battery installation and piping:
- a set of special keys;
- seals for threaded connections;
- tow and thread paste;
- thread for carving.
Features of connecting radiators
Installation of heating differs in some features:
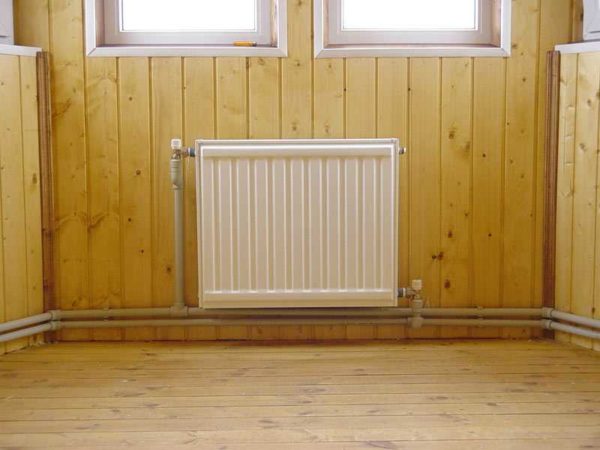
- It is necessary to observe the distance from the radiator to the window sill of 100 mm. If the gap between the batteries and the bottom of the window sill is different, then the heat flow is disturbed, the effect of the heating system will be low.
- From the floor surface to the battery, the distance should be 120-150 mm, otherwise a sharp temperature drop occurs.
- In order for the heat transfer of the equipment to be correct, the distance from the wall must be at least 20 mm.
At the same time, we take into account that the installation method and the efficiency of heating radiators are greatly influenced by the installation method: under the window sill in the open form, the efficiency of the heating system is maximum - 96-97%, in a niche in the open form - up to 93%, in a partially closed form - 88-93 %, fully closed - 75-80%.
The heating radiator can be installed using a variety of methods, its piping is carried out with metal, polyethylene, polypropylene pipes
It is important during installation to correctly position not only the pipes, but also the batteries themselves, to connect in accordance with all recommendations and standards. In this case, the heating system will work very efficiently and will not require repairs.
Share this helpful article:
Heating radiator piping options
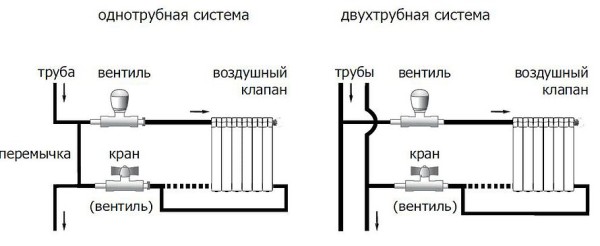
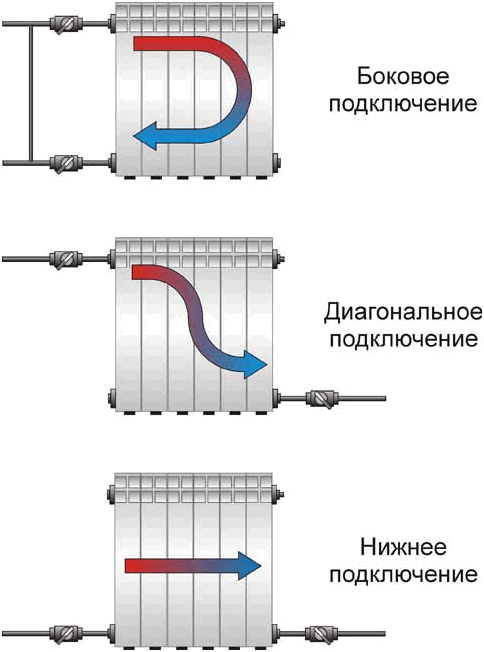
Installation of heating radiators involves their connection to pipelines. There are three main connection methods:
If you install radiators with a bottom connection, you have no choice. Each manufacturer strictly binds the supply and return, and its recommendations must be strictly followed, because otherwise you simply won’t get heat. There are more options with lateral connection (read more about them here).
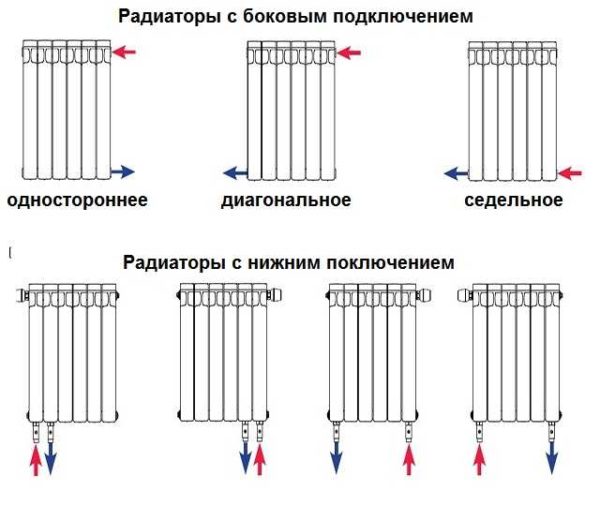
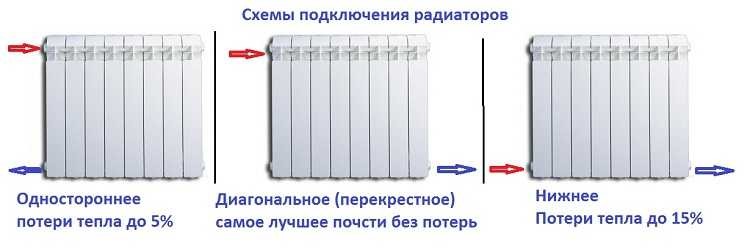
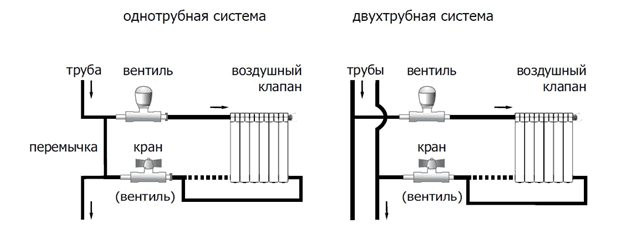
Binding with one-way connection
One-way connection is most often used in apartments. It can be two-pipe or one-pipe (the most common option). Metal pipes are still used in apartments, so we will consider the option of tying the radiator with steel pipes on the spurs. In addition to pipes of a suitable diameter, two ball valves, two tees and two spurs are needed - parts with external threads at both ends.
Side connection with bypass (one-pipe system)
All this is connected as shown in the photo. With a single-pipe system, a bypass is required - it allows you to turn off the radiator without stopping or lowering the system. You can’t put a tap on the bypass - you will block the movement of the coolant along the riser with it, which is unlikely to please the neighbors and, most likely, you will fall under a fine.
All threaded connections are sealed with fum-tape or linen winding, on top of which packing paste is applied. When screwing the tap into the radiator manifold, a lot of winding is not required. Too much of it can lead to the appearance of microcracks and subsequent destruction. This is true for almost all types of heating appliances, except for cast iron. When installing all the rest, please, without fanaticism.
Option with welding
If you have the skills / ability to use welding, you can weld the bypass. This is what the piping of radiators in apartments usually looks like.
With a two-pipe system, a bypass is not needed. The supply is connected to the upper entrance, the return is connected to the lower one, taps, of course, are needed.
One-way piping with a two-pipe system
With lower wiring (pipes are laid along the floor), this type of connection is made very rarely - it turns out inconvenient and ugly, it is much better to use a diagonal connection in this case.
Binding with diagonal connection
Installing heating radiators with a diagonal connection is the best option in terms of heat transfer. She is the highest in this case. With a lower wiring, this type of connection is implemented easily (example in the photo) - supply from one side is at the top, return from the other at the bottom.
With two-pipe bottom wiring
With a single-pipe system with vertical risers (in apartments), everything does not look so good, but people put up with it because of the higher efficiency.
Coolant supply from above
Please note, with a one-pipe system, a bypass is again required.
Coolant supply from below
Strapping with saddle connection
With lower wiring or hidden pipes, installing heating radiators in this way is the most convenient and most inconspicuous.
With a two-pipe system
With saddle connection and bottom single-pipe wiring, there are two options - with and without bypass. Without a bypass, the taps are still installed, if necessary, you can remove the radiator, and install a temporary jumper between the taps - a drive (a piece of pipe of the desired length with threads at the ends).
Saddle connection with one-pipe system
With vertical wiring (risers in high-rise buildings), this type of connection can be seen infrequently - too large heat losses (12-15%).
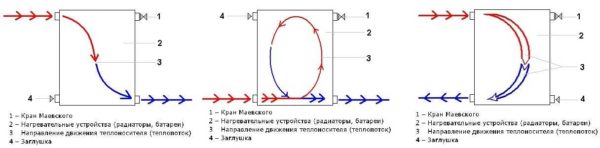
How does the tie-in scheme of the radiator affect its efficiency
Long-term practice of domestic workers in the construction industry has made it possible to identify several types of piping schemes for heat transfer devices. They are dictated by their connection options:
- diagonal bilateral at the top giving;
- one-way when the coolant is supplied from above;
- one-sided with water supply from below;
- double-sided with the connection of both eyeliners from below;
- diagonal bilateral at giving from below;
Experts have developed much more original tie-in options, however, they are far from being so popular.
Each of these types of connection has its own characteristics and, in particular, disadvantages. The latter must be evaluated in advance and calculate which option will work with maximum efficiency:
- Thanks to a one-way connection, it turns out to significantly increase the efficiency of the entire system and a particular radiator. This is due to the fact that the heating of each individual section of the object is carried out evenly. This option is optimal for buildings with a height of one floor, in which units with a large number of sectional connections are installed.
- The bottom connection is made directly under the floor surface. However, this is not a very effective analogue. This is primarily due to the fact that the heating of the radiator is absolutely uneven.
- The diagonal scheme involves the installation of a Mayevsky crane, as well as a specialized plug. The direction of the heat carrier is set in advance, due to which the level of heat transfer of the object increases significantly.

Heating system options
An autonomous heating system (in a private house, a small cottage) allows you to choose from two possible options for installing a heating system.
This:
- Single-circuit (single-pipe) - classic, which has been used for a long time and everywhere.
- Double-circuit (two-pipe) - more efficient during operation, with the ability to control heat transfer.
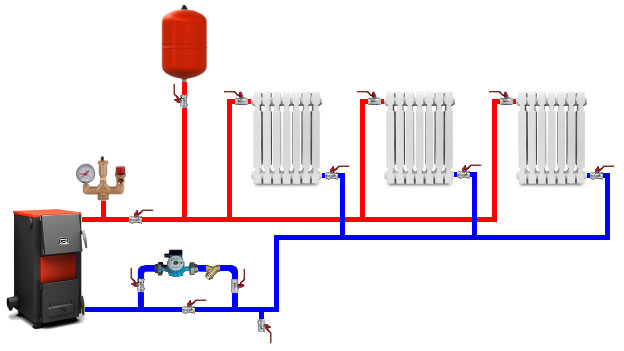
Single-circuit heating system
The radiator is connected to polypropylene pipes in a single-circuit system in series.
Schematically, this type of device is simple:
- A pipe coming from the boiler (supply) is connected to the upper radiator inlet.
- The outlet of the cooled coolant (return) is connected to the lower one.
Supply and return is carried out through one pipe. In a one-story building, this is a horizontal pipe along the perimeter of the system. In apartment buildings, this is a vertical riser pipe.
The subtlety of mounting a single-circuit system is that a bypass must be mounted here.
A bypass is a pipe (crosspiece) built between the supply and return with a valve or check valve. The bypass is necessary to autonomously disconnect one battery from the circuit while the system is running (for example, for repairs).
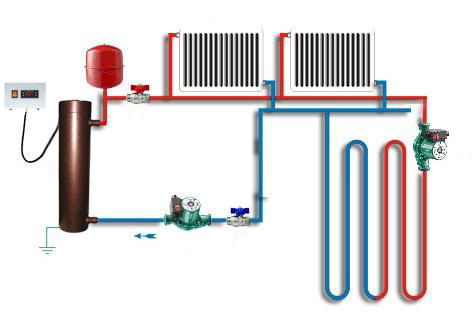
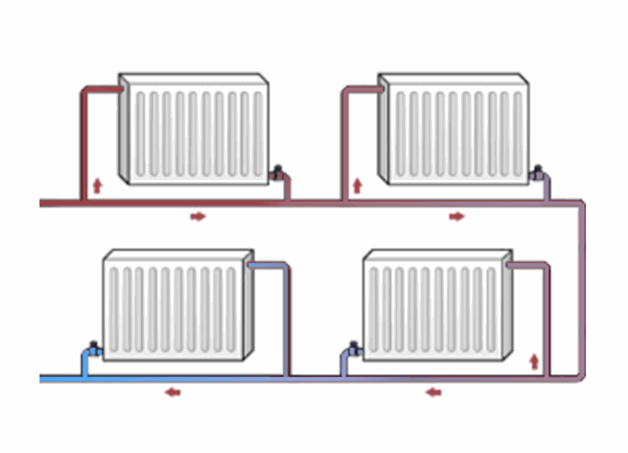
Dual circuit system
With a two-circuit system, the batteries are installed in parallel. The coolant enters from the outlet from the main supply pipe. The reverse return occurs according to the same scheme, through the second (separate) pipe. A separate input for each radiator eliminates the need for additional parts in the form of a bypass. A shut-off valve is mounted on the supply (valve), which shut off the supply in case of need.
A double-circuit heating system is approximately 10% more efficient in terms of heat transfer and is considered more modern.
Brackets or special hooks are required to mount the battery to the wall. For light radiators, 2 supports are sufficient. The number of brackets for heavy batteries is calculated from the need for 1 bracket per three sections.
The place of radiators in the heating system
The use of radiators in residential heating plays a key role today. Not all residential properties, especially apartments in multi-storey buildings, can be converted to underfloor heating. Therefore, the main work on heating the internal living spaces is performed by radiators or the good old and well-known to us, batteries.
Radiators transfer thermal energy from the coolant to the surrounding space. Heat transfer is carried out due to the large heating surface of the heating device. In modern models, there are a number of technical improvements, thanks to which it has become possible to connect in a variety of ways and with any wiring scheme.
in old cast-iron and steel batteries there was only one upper and one lower branch pipe, through which hot water is supplied and the return flow is carried out.
In modern models, in addition to the main supply and output pipes, there are built-in air vents. This battery design has radically changed the quality of the functionality of the heating system. If there are air pockets in the heating devices, it is enough to open the bleed valve and bleed the air.
In many respects, thanks to modern models of heating batteries, it has become possible to choose the most convenient connection scheme, to install heating devices in those places in the living room in which they are most effective. The quality of the heating water circuit depends on the correct piping. The process is necessary if you are using a pipeline made of polypropylene pipes.
Important! In the presence of metal risers, the strapping is made from other consumables. It can be metal copper pipes or metal-plastic
The use of polypropylene pipes in this case is strictly prohibited.
The reason for the incompatibility of metal pipes with polypropylene products is the presence of a threaded connection. Given the fact that propylene pipes have a high coefficient of thermal expansion, when a hot coolant is supplied, the threaded connection will lose its tightness and stability. Therefore, if you want to connect a heating radiator made of polypropylene pipes, try to use fittings, adapters and couplings made of similar materials.
take into account the difference in diameters of pipes made of different materials
Material selection
The popularity that polypropylene pipes have won. associated with a number of their positive qualities:
- The price for them is much lower than for metal counterparts.
- High durability, due to the fact that the plastic does not rust, moreover, it practically does not deposit sediment.
- Doesn't need painting.
However, it should be borne in mind that not all types of polypropylene pipes are suitable for heating systems. The fact is that they must necessarily have a reinforcing layer that prevents significant thermal expansion of the pipeline.
Reinforced polypropylene pipe
Moreover, it is desirable that the reinforcing layer be aluminum, since fiberglass reinforcement leads to saturation of the coolant with oxygen. This, in turn, causes rusting of the metal surfaces of boilers and other elements of heat supply. Pipes that have aluminum reinforcement and are suitable for heating systems are marked with PN25.
Note! When choosing pipes, attention should be paid to the uniformity of their wall thickness. To do this, you need to look at their cut.
As for the diameter, the optimal parameter is 25 mm.
In this case, it is also necessary to purchase fittings, which include:
Scheme of one-pipe and two-pipe connection of radiators
Scheme of arrangement of the heating system
The main element in every heating system is a heating boiler. In many ways, the wiring diagrams for heating radiators depend on it. If a floor-standing heater is selected, it should not be mounted on top of the heating structure, as such an arrangement reduces the efficiency of the system or can even lead to a malfunction in its operation.
Typically, such boilers do not have devices for venting air, and this often leads to air locks. It must be taken into account that in the absence of an air vent, the pipes of the supply section of the line should be mounted strictly vertically.
It is not difficult to find out if the boiler has an air vent - you need to look at whether or not there are nozzles in its lower part that are intended to connect the heater to the heating system. In this case, the supply line is connected to the return pipes using a special manifold. Usually, pipes are available for wall-mounted gas and electric heating boilers.
Some models of heating units do not have a circulation pump, expansion tank and pressure control device. All these components can be purchased and installed, if necessary, taking into account their location. So it is most reasonable to place a circular pump on the return pipes.
As for the safety group, it is allowed to mount it both on the supply section of the circuit and on the reverse (read: “Safety group for heating - we make the system reliable“).
When tying radiators with polypropylene is done, you need to consider the type of system on which additional components are to be installed. If the design provides for the natural circulation of the coolant, then they are unlikely to be required. In the case when the radiator is piping with polypropylene in a forced circulation design, it will be necessary to additionally use both a circulation pump and other elements. After that, to check the quality of the system, the heating radiators are pressure tested.
In apartments with central heating, it is now customary to install bimetallic radiators, and in private housing construction, piping of an aluminum radiator or a steel heating battery is more common.
What is needed for installation
Installation of heating radiators of any type requires devices and consumables. The set of necessary materials is almost the same, but for cast-iron batteries, for example, the plugs are large, and the Mayevsky tap is not installed, but, somewhere at the highest point of the system, an automatic air vent is installed. But the installation of aluminum and bimetallic heating radiators is absolutely the same.
Steel panel ones also have some differences, but only in terms of hanging - brackets are included with them, and on the back panel there are special shackles cast from metal, with which the heater clings to the hooks of the brackets.
Here for these bows they wind up hooks
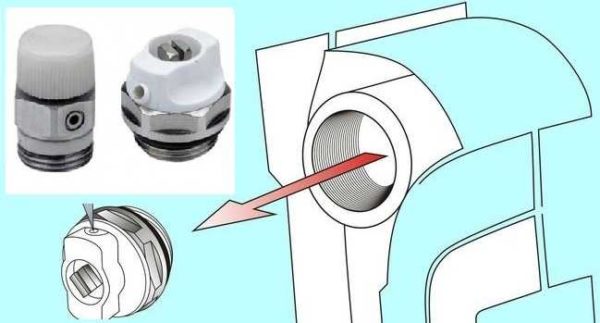
Mayevsky crane or automatic air vent
This is a small device for venting air that can accumulate in the radiator. It is placed on a free upper outlet (collector). It must be on every heater when installing aluminum and bimetallic radiators. The size of this device is much smaller than the diameter of the manifold, so another adapter is required, but Mayevsky taps usually come with adapters, you just need to know the diameter of the manifold (connecting dimensions).
Mayevsky crane and method of its installation
In addition to the Mayevsky tap, there are also automatic air vents.They can also be placed on radiators, but they are slightly larger and for some reason are only available in a brass or nickel-plated case. Not in white enamel. In general, the picture is unattractive and, although they deflate automatically, they are rarely installed.
This is what a compact automatic air vent looks like (there are bulkier models)
There are four outlets for the radiator with lateral connection. Two of them are occupied by the supply and return pipelines, on the third they put a Mayevsky crane. The fourth entrance is closed with a plug. It, like most modern batteries, is most often painted with white enamel and does not spoil the appearance at all.
Where to put the plug and the Mayevsky tap with different connection methods
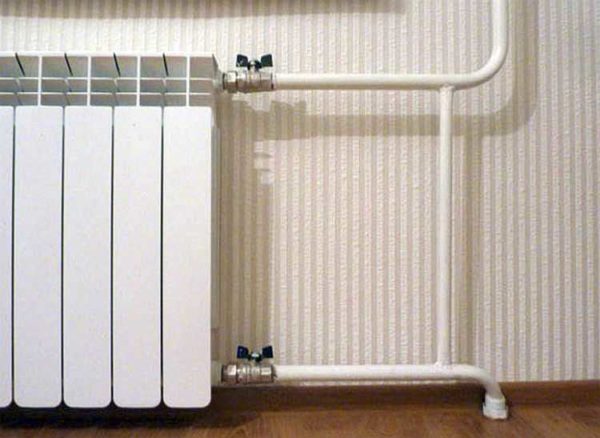
Shut-off valves
You will need two more ball valves or shut-off valves with the ability to adjust. They are placed on each battery at the input and output. If these are ordinary ball valves, they are needed so that, if necessary, you can turn off the radiator and remove it (emergency repair, replacement during the heating season). In this case, even if something happened to the radiator, you will cut it off, and the rest of the system will work. The advantage of this solution is the low price of ball valves, the minus is the impossibility of adjusting heat transfer.
Taps for heating radiator
Almost the same tasks, but with the ability to change the intensity of the coolant flow, are performed by shut-off control valves. They are more expensive, but they also allow you to adjust the heat transfer (make it smaller), and they look better outwardly, they are available in straight and angular versions, so the strapping itself is more accurate.
If desired, you can put a thermostat on the coolant supply after the ball valve. This is a relatively small device that allows you to change the heat output of the heater. If the radiator does not heat well, they cannot be installed - it will be even worse, since they can only reduce the flow. There are different temperature controllers for batteries - automatic electronic, but more often they use the simplest - mechanical.
Related materials and tools
You will also need hooks or brackets for hanging on the walls. Their number depends on the size of the batteries:
- if the sections are not more than 8 or the length of the radiator is not more than 1.2 m, two attachment points from above and one from below are sufficient;
- for every next 50 cm or 5-6 sections, add one fastener at the top and bottom.
Takde need a fum tape or linen winding, plumbing paste to seal the joints. You will also need a drill with drills, a level (a level is better, but a regular bubble one is also suitable), a certain number of dowels. You will also need equipment for connecting pipes and fittings, but it depends on the type of pipes. That's all.
What can be the binding of polypropylene pipes
The piping for a home heating system can be very different. The thing is that the consumer is always trying to reduce the amount of consumables, while trying to equip radiators in all heated rooms.
It should be said right away that these are relics of the past. Unlike expensive metal pipes, polypropylene consumables are much cheaper and easier to install. therefore, saving on the length of the pipeline is not worth it. Choose the type of strapping that will bring the most benefit in your case. The only factors that may influence the choice of type of strapping are the following factors:
- what heating scheme is used (one-pipe system or two-pipe);
- what type of radiator connection you have chosen (diagonal, side or bottom).
As a rule, when using any heating scheme: one-pipe or two-pipe, any type of connection for heating radiators can be used.
according to experts, the laying of the pipeline is necessary to minimize the number of bends.A smooth highway remains resistant to hydrodynamic loads. The pipeline will reduce the number of zones in which air can accumulate.
For tying a single-circuit and double-circuit heating system using polypropylene pipes, there are some peculiarities.
- usually in such a system a serial connection of radiators is used;
- a bypass is always mounted in front of the battery, connecting the supply pipe and the return pipe. During normal operation of the heating system, the bypass is not activated. During preventive maintenance or in the event of an emergency, the water supply to the radiator is stopped. The coolant circulates freely through the bypass.
- both parallel and series connection of batteries is used;
- both radiator pipes are connected to different pipes. The upper one is connected to the supply pipe, the lower branch pipe is connected to the return. Usually in two pipe systems there is a parallel connection of radiators, so the installation of bypasses is not required.
Tying polypropylene pipes with radiators is carried out in two ways: by soldering and using fittings. Installation of radiators and their connection is carried out using a soldering iron and plumbing keys for an American.
The first option is a one-pipe system
As a rule, schemes of this category are resorted to as part of the construction of multi-storey buildings. Each heat transfer device is inserted into a kind of gap in a single pipe for the entire system. Through this pipe, the coolant moves along the entire line, and the return water is also carried out through it. The batteries are connected in a certain sequence, namely, in the one in which they are installed in the riser structure. Due to the specifics of the series connection design, it is obvious that the first radiator in the system will always heat up better and, accordingly, it will also heat the rooms an order of magnitude stronger, while the last element of the circuit will give the least amount of heat energy.
The installation can be slightly upgraded to improve the performance of the heating system as a whole. So, experts in the construction industry offer two main options for organizing the heating of multi-storey buildings, namely, the supply of coolant at the top and bottom:
- So, speaking of the top supply, it must be said that the water moves inside a straight pipe, reaching the top element in the riser. After reaching the so-called “top”, the coolant goes down, simultaneously filling and heating the radiators, of course, starting from the top one.
- In order to save money, consumables and general labor costs for construction, quite often designers prefer a scheme that provides for water supply from below. As part of such a piping scheme, heat exchange devices are connected to a pipe that goes to the top floor; there are also batteries on the downstream line.
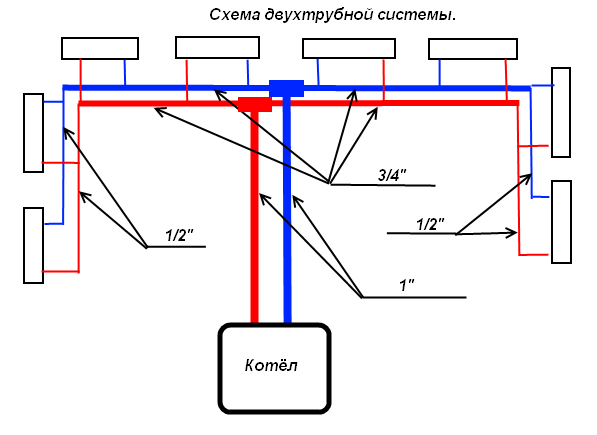
 A two-pipe system will not save much, but will provide heat
A two-pipe system will not save much, but will provide heat
The single-pipe system is the optimal and therefore the most commonly used option for private country houses, the height of which is not more than one floor. This is understandable, because it is the single-pipe scheme that allows you to save money both during the construction process and during the heating season. In addition, it will be much easier for the owner of a house in which such a construction is carried out to determine in which direction the water moves in the pipes.
This is important, because when connecting radiators to the main, you need to clearly understand which hole will receive the coolant, and which one will give water an outlet
It is worth noting that this scheme has a huge number of shortcomings and often does not meet the requirements of the residents of the house.