materials
Brick
The laying of the Russian stove is made from. The brick must be well fired and of the highest quality - dense, smooth. A burnt brick (with a dark inside, if broken) is absolutely unusable. Also, a hollow brick is not suitable: the heat will spread poorly over the body of the furnace, its insides will overheat and the entire furnace will soon begin to fall apart.
Especially carefully you need to select bricks for the hearth: they must be even, smooth, exactly the same height. In the old days, stove-makers chose hearth bricks from purchased batches and stored them separately. Nowadays, under can be ironed after laying with a grinder with a bowl-shaped circle. In theory, the oven will not get worse from this, but there is no experimental data.
The lining of the furnace and the upper row of the bench can be laid out of facing bricks on lime mortar. Then the floors will never fail, and finishing the stove will not cause difficulties - laying on clay with widened seams (see
below), although heat-resistant, but not very strong and even, and plaster and tiles do not hold well on it
Solution
For a Russian stove, not quite ordinary; here the combination of heat resistance, high heat capacity and equal to TKR brick is important. The composition of the solution is as follows:
- Carefully sifted the fattest clay that can be found - 3 volume parts.
- Sifted and calcined river sand - 3-5 volume parts.
- Pure water - 1 part by volume.
The solution should also be very greasy - thick, viscous. His condition is checked with two boards; between them squeeze a ball of fresh solution the size of a tennis ball. A lean mortar will crack immediately; average when compressed by about 1/3, and good - by half. Too soft and fluid solution is also not good; sand must be added to it, but not more than 2: 1 relative to clay.
Good clay for laying stoves was once a serious problem. Now the structure of the Russian stove is being simplified: there are ready-made dry mixes for laying stoves on sale and, separately, greasy clay.
When drying, the greasy solution often cracks. In this case, the cracks are covered with a medium or thin clay mortar, but in no case with lime, gypsum or cement.
Traditional and modern Russian stoves
One of the characteristics by which Russian stoves are classified is dimensions. Large structures are considered to be 1500 × 2300 mm, small - 1500 × 1750 mm. There are also furnaces built according to individual projects, their sizes can be any. Depending on the features of the device, traditional and modern are distinguished. They differ in the design of the undercarriage. In the first, the lower part does not warm up, in the second, heated channels are equipped. Furnaces can vary in shape, finish, location, number and functionality of additional elements.
Scheme of the design of a Russian stove with a firebox
The world is changing, people's needs are changing, respectively, new furnace designs and additional opportunities for the implementation of complex technical solutions appear. So, recently models with such improvements have become popular:
- Underfloor and stove. The hob is built into the design of the oven and is a modernized hearth. A Russian stove with a firebox allows you to cook traditional national dishes, dry mushrooms, berries, and fruits.
- Russian oven with a fireplace. The back wall of the stove is brought out through the partition into the next room, a fireplace is equipped. A very convenient option for lovers of open fire. At the same time, the dimensions of the furnace itself change slightly, but there is no need for an additional foundation and a chimney system, and warmth and comfort are guaranteed.
- Topchan and rude. Initially, a large couch, designed for three people, was equipped in the Russian stove. Today, furnaces of such dimensions are rarely built that allow you to make a large stove bench. Instead, they put an attached trestle bed.
- Side heating.Very handy for heating adjacent rooms.
- Bottom heating. The advanced design allows you to heat large areas.
How to make a Russian stove
- The specifics of the laying of a modern Russian stove
- Installation of mandatory appliances for the oven
Russian stove with a firebox By the time of creation, the black Russian stove is considered to be the oldest. It was also called kurna. On guardianship, as they called a kind of elevation, a vault with thick walls was erected. Under it is a crucible (a space located under the arch). Food was placed, then firewood was thrown through a small mouth, in front of which there was a pole resembling a table.

Increasingly, stoves are found in private homes. They are used for heating, cooking and just for beauty.
From this stove, smoke poured first into the hut, and then through the window it found its way out. To permanently remove this drawback, they came up with an overtube (smoke collected there) and a smoke pipe. But even such a modernized stove did not warm the floor. As a result, a device for a new furnace with a firebox was invented. It is similar to the classic one, but there is a stove in the hearth and there is a firebox, and the firebox is separate. From a Russian stove with a firebox, chimneys run along several walls or one at a time. Usually they melted the fire, but in severe frosts they used a crucible to keep it warmer.
Features of the device and the principle of operation of the Russian stove
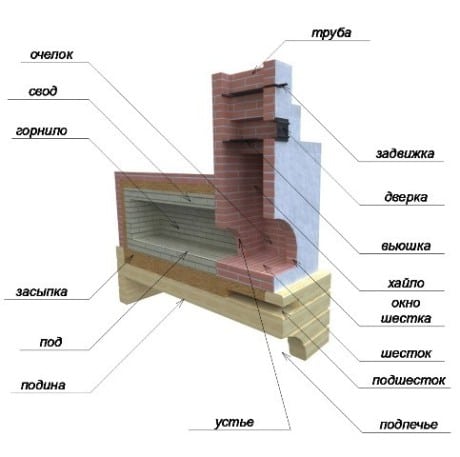
A brick box is not placed on the floor, but raised above its level by 80-100 cm. This ensures the convenience of using the oven for cooking. The chamber under the stove, designed to store household utensils, is called the under-stove. It is covered with boards or equipped with a brick vault and covered with a layer of sand, on which the bottom of the upper chamber is laid - under. For the construction of the hearth, a special brick 25X25 cm is used, which is called the hearth.
The equipment of the hearth is an important stage in the construction of the furnace, because. This part of the structure has to withstand severe loads. During cooking, heavy cast-iron pans, pots of various sizes, etc. are moved along the hearth, so mistakes and miscalculations during its construction can result in unplanned repairs and affect the functionality of the structure as a whole. The surface of the hearth is carefully leveled and polished so that there are no bumps and crevices.
In the front wall of the firebox there is an inlet - a mouth (it is also called a forehead), which is closed by a removable damper. Due to the location of the mouth below the vault of the firebox, it warms up well under. The arch in this case can be of any shape - oval, barrel-shaped or semicircular. A layer of sand on the vault is needed for high-quality heating of the couch.
Outside the furnace, below the hearth, there is a hearth, where pots are placed, burnt coals are raked out. Above the hearth is a closed chamber - an overtube. It got its name because of the location of the furnace pipe above it. The damper for the Russian stove is placed to adjust the draft, and the view is to block the pipe and keep warm. The stove allows you to ventilate the room without losing heat. To do this, close the view and open the door.
How the Russian stove works - diagram
A brief overview of the advantages and disadvantages of the Russian stove
Among the main advantages of installing this type of oven, experts call the uniform distribution and long-term heat transfer, the usefulness and high culinary properties of dishes cooked in the oven at low temperature. Russian brick stoves can serve for decades - 30 years or more, and if they are properly positioned, you can heat fairly large houses consisting of several rooms. A variety of finishes, even a dimensional stove, allows you to organically fit into any style of interior.
Among the shortcomings - low efficiency relative to furnaces with complex smoke circulations and design complexity, the construction of a Russian furnace requires skills and special knowledge, without which it is difficult to do this work.
The original decoration of the Russian stove allows you to fit it into any style of interior
Building an oven
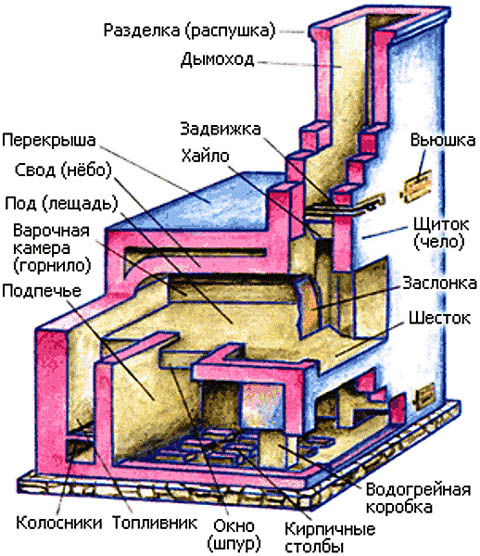
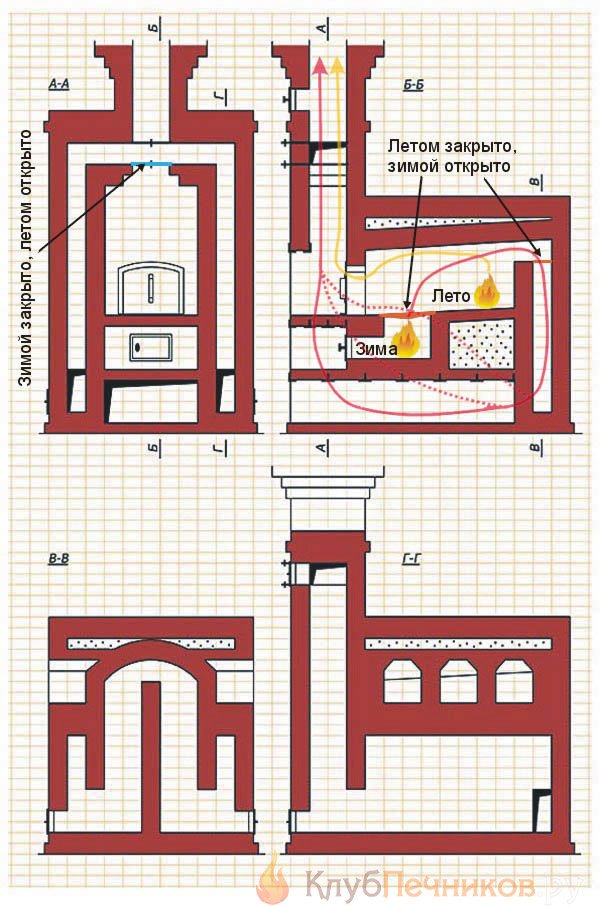
A complete diagram of the Russian stove is shown in the figure below, with a list of positions. To the above, there is an addition - a stuffing box. This is a gas-air heat exchanger: smoke circulation through the wall heats the air that is taken in from below. The vent of the air vent opens into the room above, then there is a damper, and behind it the mouth of the air vent opens into the chimney above the view.
In summer, the damper is open, and the air flow in the ventilator brings out the excess heat of the flue gases, while at the same time ensuring good ventilation of the room. For the winter, the damper is closed; heated air enters the room and heats it.
The air vent is the easiest and most reliable way to get bottom heating from the stove without overly complicating its design.

- Underfurnace;
- undercoat;
- Six;
- Dusnik;
- Chelo;
- gate valve;
- Chimney;
- Overlapping;
- damper;
- Mouth;
- cutting;
- Warm stove;
- hot stoves;
- threshold;
- backfill;
- The vault of the furnace;
- crucible;
- Cheek;
- Porsok;
- Sub-baking;
- Arch underlay;
- pharyngeal arch;
- Hailo;
- mouth arch;
- masonry ledge;
- Dust channel;
- The mouth of the chimney.
What is ordering?
The oven is laid out in horizontal layers of bricks - in rows. A set of instructions for laying each row is the order. Sometimes orders are called rows (first order, we lay out orders, etc.). This is, generally speaking, false.
For each type of furnace, the order, of course, will be different. Modern orders are accompanied by drawings. You can start building a furnace only if its order is absolutely clear.
Is it worth it
Does it make sense to take on such a difficult job on your own? How much does the work of an experienced and reliable stove-maker cost? If 100% of the cost of materials, as is customary in general construction work, then it is still not that expensive.
By no means twice against the material. You can meet offers to lay down the oven for 20,000 rubles, but this is an obvious nonsense. Let's try to figure it out ourselves.
The stove-maker works in the middle latitudes for half a year, and always with an apprentice assistant. Considering their employment in 100% of working time, the salary of the master at 25,000 rubles, and the assistant at 15,000 and the time to complete the work 7 working days (this is a completely real time), we get that a simple stove will cost no less than 45,000 rubles, and a Russian stove with a stove and a water heater (see Fig.) at 55,000-60,000 rubles.
But in a week it will be possible to heat. There is only one condition: the master must tell where, when and to whom he has already laid the stoves, and they must be examined personally. Good masters are sure to stock up on recommenders, and if they twist and mumble, it’s better to turn to another.
To give a more complete picture of the complexity of the work, we will briefly consider how to lay out the simple furnace described above. Just for example; detailed ordering of the Russian stove is a rather voluminous brochure.
ordering
1-6 rows
We do not make a screed for waterproofing the foundation, we put it dry - sweating is excluded. We start from the left front corner (pos. a-1 in the figure). In the corner - a 3/4 brick with a poke out. From it - a row of 12 full measures to the corner a-2. Seam - widened up to 13 mm; this will be everywhere in the first 3 rows, because in the 4th row, a masonry ledge will be formed.
In the corner a-2 - two poke 3/4 and a double row of full measures to the corner a-3. We come to the corner a-4 in the same way as a-1 - a-2. Row 1 is completed by two full measures, forming an opening of 540 mm. We check the masonry with the rule and diagonals.
In the second row (pos. b) on the sides of the poke of the 1st row are covered with spoons. In the corners - 2 three-fours, stacked with spoons. The full size frames framing the opening are covered with 3/4 pokes with dressing of the seams. The third row (pos. c) is identical to the first.
4 row - according to the positions of the brace. The location of the bricks is as in the 2nd row. We narrow the seam to 5 mm to get a ledge of 25 mm on the sides. We check the masonry level.
5 row - according to pos. e. In d-2 and d-3, two 3/4; between them - two spoon rows. The side walls are bonded. We squeeze the walls of the opening under the furnace under the heel of the arch.We install it on props and circle it and lay out the 6th row identically to the 4th.
First arch
When laying out the arch, in addition to the above, the following must be observed; for subsequent arches/vaults too:
- There should not be a single untied seam across the arch from heel to heel (on the left in the figure below).
- The seams from the top to the heels gradually thin out from 13 to 5 mm.
- Circles with formwork are removed only after the mortar has dried.
7-10 rows

7th row is laid out as the 5th; 8 - like the 6th (on the left in the figure). In the sidewalls from the inside, the butts are hewn under the heel of the arch. On the 8th row, we begin to lay out the undercoat: three rows of full length butt measures, counting deep from the brow. The middle poke from below needs to be hung under the arch under the stove. We put the 9th row as the 7th, but lay out the 2nd row of the undercoat with spoons. We lay out the arch of the podpechka.
10 row - special, in fig. right: corners from 3/4, sides from full length spoons; rear of poked full lengths. From the brow inward - 3 rows of full-length butt sizes. In a row - 7 pieces laid flat. This will be the hearth with the hearth of the gag.
bedding
We make the filling of the crucible from broken bricks on clay mortar. We tamp and stretch, as indicated by the arrow. It’s better to do it yourself with a break and not try - not every stove-maker can do it.
11-17 rows
Even rows are laid out as the 10th. In odd numbers on the sides there are tychkovye rows; behind - spoon. The 15th and 16th are hung under the heels of the arches. Upon completion of the 17th row, the masonry of the walls around the furnace is interrupted until the entire front of the furnace is laid out, up to a vertical plane passing along the back wall of the mouth.
Zev, zagnetok, mouth, crucible
Arches and vaults are erected along the circles of the arches with formwork. The side walls of the cap will go into the brick; forehead and mouth - half a brick. The heel of the arch of the pharynx will fall on the 15th row; the heel of the arch of the mouth - on the 16th. It will be especially difficult for a beginner to iron the inner walls of the hail: from above you can’t see what you are doing, and from the inside dust and crumbs fly into your eyes. Therefore, hail must be processed from above, aligning with a template.
18 and above
We put odd rows as 1 or 11; even - like 2 or 10, see fig. If the floors are stacked on clay, then starting from the 19th row, the bricks from the inside are pressed in place to the arch of the furnace. But this does not always save clay floors from falling through, so the best craftsmen erect a box around the crucible, make a backfill of brick chips on clay, level it and ram it, and let a continuous lining of spoons framed by sticks with three-fours at the corners. In order for the floor to hold forever and not push through the vault, the further depends on the prosperity and generosity of the customer: either a wooden shield-flooring, or a row of facing bricks on lime with bandaging of the seams.
The last method is far from being as simple as it seems: the vault is tilted forward. Therefore, a row of bricks is laid flat on its locks lengthwise and with dressing of the seams relative to the locks. Then they are cut into a wedge so that such a cross member is flush with the walls.
The backfill will turn out to be two-sided, and the floors will lie on the wedge and walls. What is the point here? Recall building mechanics: the vault is much more difficult to crush from above than to break through from the side. The load from the beds will be transferred to the lock, and from it through the vault to the cheeks of the furnace. The arch of the vault will work only for compression and, if the legs fail, it will remain intact, and the legs are easy to restore.
If, however, the bricks of the upper rows are hewn, then the load from the decks will give a lateral shear load on the roof. Shear building materials hold up poorly. If the floors failed, the vault will fail, and the stove needs to be shifted.
Evolution
The development of the Russian stove went along four intertwining branches: bottom heating, stove, economy, compactness. A huge contribution to it was made by I. S. Podgorodnikov, who developed the Housekeeper and Teplushka series of stoves, which are still widespread today. The scheme of "Teplushka" Podgorodnikov is shown in the figure. It was improved by IV Kuznetsov; - in fig. left below.
The bottom line is that the firebox and the cooking chamber are separated, and the oven is sealed.Flue gases through the borehole descend into the furnace (on which a second low bench is equipped, convenient for the old and small, and the furnace works in the most natural way and like a stove. The accumulation of soot in the furnace is excluded due to the careful calculation of the structure. What kind of work it cost in the age of adding machines and slide rulers We better not guess.
However, such a stove took up a lot of space and acquired an increased fire hazard: the fire burned close to the mouth of the furnace. Further improvements until the 90s were of little use - the furnace became too complicated. The following figure shows a sectional view of a compact housekeeper from the 70s and 80s. Its efficiency is above 80%, but not every stove-maker will undertake to fold such a labyrinth, and even a heat engineer with a diploma, not like an ordinary housewife, will not be able to figure out the purpose and procedure for using all these doors and dampers at once. In addition, there are nooks and crannies that are inaccessible for inspection and cleaning.

With the development of computer modeling, the Russian stove took the path of qualitative improvement: all creative abilities could be turned into ingenuity and ingenuity. In the following figure (on the right) is a successful modern Russian stove. The “highlight” of the design is that instead of backfilling under the bakery (where, as it turned out, it still does not work as intended), they arranged a winter firebox. The increase in the height of the undercoat made it possible to bring the volume of bedding under the crucible to the optimum.
There is only one drawback to such a furnace: to switch “winter - summer”, you need to move not one, but two dampers, and in addition put / remove a heavy plate that closes the mouth of the winter furnace. If you still come up with something with this stove, then such a stove can already be automated for the winter: a winter firebox can run on gas.
Installation of mandatory appliances for the oven
Devices that any Russian stove must have are installed and fixed as they are laid. When heated, metal heats up more than brickwork. Therefore, when producing a furnace firebox, one should not be surprised at the deformation of the metal frames of the doors. Outcome - the frame expands and simply falls out. To avoid this, the frames of the doors for the firebox are fixed with a gap (4-5 mm) between the masonry and the frame, which must be filled with a cord with asbestos. For reliability, the frames are reinforced with paws. Paws are placed between the bricks and fixed using brick and mortar. The frame with the cord should be inserted as tightly as possible into the opening. There should be no voids between the masonry and the frame.
The hole needed for the firebox can be blocked by various methods. If the length of the brick exceeds the width of the hole, brickwork is carried out in a strong lock. In the opposite situation - a jumper.
Having finished the laying of clay bricks, it is worth doing the facing of the furnace. The walls must be rubbed with dry red brick. This will help get rid of dried clay residue. Next, the seams are embroidered: they take a wooden spoon and give them the appearance of a semi-roller. The unlined plane of the Russian stove has the best heat transfer, but it looks sloppy and rough. Dust gradually accumulates in the seams. Therefore, the oven should be covered with tiles.
Ordinal description of the RP masonry with a fireplace.
Once again, I want to remind you that the order of the furnace is not an engineering drawing and only shows the laying order, the location of the valve channels and other elements of the furnace. Competent dressing is done by the stove-maker himself on the spot each time in different ways, depending on the location of the stove in space, the dimensions and deviations of the bricks and seams, on the choice of the shape and size of the stove fittings and the method of finishing the stove.
The Russian stove never went out at all. It slowly glimmered in its corner during industrialization, electrification, gasification, and has always been the object of close attention of specialists due to its remarkable qualities.Now the Russian stove is experiencing a rebirth; a significant role in this was played by its economy, omnivorousness and the ability to build with your own hands - expensive materials and sophisticated industrial equipment are not required. Why is it good, what are its secrets, where can and where it can not be built?
We increase the efficiency of the Russian stove due to the lower heating
As I drew your attention earlier - the lower firebox in the Russian stove
This is a modern update. At the bottom of a modern Russian stove
passes the chimney channel, which serves to heat the lower part of the furnace
This is a huge contribution to reducing the amount of fuel burned. Moreover, if you heat a Russian stove with a stove bench
only through the main firebox, then the feet will simply be cold and you will have to walk around the house in warm shoes. But the lower heating of the Russian stove solves this problem easily and simply! This is how it looks in the photo of a Russian stove with a lower firebox
.
Thus, we double the area of the heating source! Therefore, in order to heat the same room to the desired temperature, you will need half as much firewood as in the case when you would have classic russian oven
. Well, now let's turn to the solution of the second problem - fast food preparation. This decision follows from the first thesis.
Russian oven with stove
- here is the best solution for cooking in such an oven. After all, it is worth throwing a few firewood into the lower firebox, and after 15 minutes the stove of the Russian stove will be hot to heat water or heat up food. Unlike the classic version, when it is necessary for the firewood in the hearth of the Russian stove to burn out, only coals remain. This will take at least an hour. And such Russian oven with stove
— the most effective solution in 2017!
Russian stove for a summer residence
. Now let's talk about sizes. I specifically want to post a photo where we design the dimensions Russian oven with hob
. This is a photograph of the same Russian stove No. 180,
If we take any option Russian oven with stove bench
- then such a design in depth (due to the bed) has a size of at least 2.5m! It is not easy to imagine a country house with dimensions of 5x5, that is, 25 squares, where a stove occupies 3.5 squares, because there is not much space ... and most importantly, a huge amount of bricks and firewood goes into the couch, which is not always possible to pay for the owners of small houses. In our case, the customer and I came to the conclusion to completely abandon the couch
which would take up a lot of space.
The size of my Russian oven with a hob and a firebox
came out: 7 bricks x 6.5 bricks, or 1.7 meters x 1.6, which is quite acceptable for any small house.
Of course, my work is only a private solution for a specific customer. Here is another one of mine Russian oven with a bench and a stove, and a lower firebox
. I built this stove at the beginning of 2010, and no photo of the stove bench has been preserved, but the design turned out to be huge. I hope you enjoy my work, only the price of such a Russian stove will be much higher due to the large amount of work. Russian stove number 182
If you are interested in my approach to work, then I am always ready to help solve any of your tasks in the field masonry of Russian stoves
, especially since there are not many stove-makers in St. Petersburg with such real experience and their own photographs. And there are many factors: firstly, this is not the most common task. For example, for the whole year, 10-12 people can contact me with a request for masonry of a Russian oven with a stove
. And many Russian price
the oven is just annoying. The price of work on a Russian stove
ranges from 180,000 - 350,000, the same variation in materials, depending on the volume and type of brick.
To give some kind of assessment of my work and the necessary materials, I need to understand the task to the utmost. To do this, call me directly, I will identify all your needs, describe all the parameters for myself and I can make an estimate for your Russian stove.
Building a Russian stove with your own hands
For construction, you will need refractory and ceramic bricks. Refractory is used for laying the furnace part, ceramic - for the rest of the structure. It is also necessary to prepare templates for arches and vaults, steel strips. In addition, we need such cast-iron elements:
- furnace, blower, cleaning, ventilation doors;
- grate;
- view;
- damper;
- stove and two burners;
- hot water box.
Masonry mortar: features of preparation and quality control
Masonry mortar can be purchased at a hardware store in the form of a dry mix, or you can cook it yourself. To do this, you need refractory clay, sand, and for fireclay bricks - also fireclay powder. Brick pipes in the attic space are placed on a cement-sand mortar.
The main difficulties arise with the choice of clay. It can be of different structures, and the task of the stove-maker is to find the right proportions for mixing sand and clay. Check the plasticity of the solution by rolling a small flagellum out of it and bending it. The better it bends before cracking, the better the solution. Another old-fashioned way: the ball from the solution must be compressed with two planks until cracks appear. A good mortar will crack when compressed to a third of the diameter.
When preparing a masonry mortar, it is important not to make a mistake with the proportions. In any case, it's better to make it fatter than too lean.
Foundation and masonry of the Russian stove
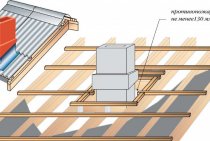
It is better to design the foundation for the furnace together with the house; later it will be difficult to build it in the finished building. Experts recommend choosing an independent slab foundation for a Russian stove and building it using standard technology. The protrusion between the edge of the foundation and the masonry (cut-off) is made at least 0.5 m. When the structure is ready, a two-layer roofing material is laid on it as a waterproofing material.
Furnace masonry must be airtight. To achieve this, you need to choose strong bricks without cracks and make thin seams (up to 5 mm).
The stove is placed in a brick, in half and a quarter of a brick. It is better to lay the outer walls in brick, and the inner walls in half a brick. Ligation of seams - bonder and spoon masonry alternately. In the lower part, an under-furnace is left and covered with brick or concrete slabs. Masonry seams are processed and plastered, coated with cement, external surfaces can be finished with ordinary plaster for interior and exterior use. After that, a fine finish is performed, and the furnace is ready.
The process of laying a Russian stove: the construction of an arch
The special value of the national home lies in the spiritual enrichment of an urbanized society. In many ways, the return to the origins of furnace construction is due to a tribute to fashion, because there are more modern and relevant models of heating devices. Folk style, appeal to traditions is a natural process for a civilization whose life is far from the way of life of their ancestors. The Russian stove in the interior of the house is a symbol of the restoration of the lost connection between generations. A beautiful, functional, efficient stove not only heats the house, but heals the soul and body.
The process of finishing a mini oven
Incorrectly selected solutions may not immediately crack, or even crumble the next day, but they will still not last long.
Building a stove with a firebox and a fireplace is a rather long process. Often people look forward to its completion. The most time-consuming and lengthy part of the work is brickwork. However, even after the last brick has been laid, it will be too early to consider the matter finished. You will also need to complete the finishing that the mini-heater needs.
If the mini stove is very neatly built of beautiful facing bricks, has a smooth front face and right angles, you can do without additional finishing.However, a fairly large number of people have their own prejudices about the fact that brickwork should not be in the house at all. Consequently, the caravan is often provided plastered and whitewashed.
The traditional way is to simply smear with clay mortar.
This is done without the use of any special tools - clay is thrown in and smoothed with a moistened palm.
The surface after such a finishing process may not be completely smooth, with traces of handicraft. It should be understood that today this technique is widely used in order to create something unique in interior design.
Modern technology for applying plaster involves the use of special tools. among which there will be trowels that will be needed to apply the solution, a trowel to level the applied solution, a grater, with which the solution is compacted and the surface is leveled in a circular motion.
The heating pad can be plastered only when it is 100% dry. Before proceeding to this process, it should be heated. The mortar will consist of clay and sand in a ratio of two parts sand to one part clay.
List of materials
Brickwork is a classic version of the furnace device, as the material warms up evenly and slowly.
- single red brick M-200 - 1600 pcs;
- fireclay brick Sh-8 - 250 pcs;
- wedge-shaped fireclay brick Sh-44 - 100 pcs;
- smoke damper 26x26 centimeters - 2 pcs;
- smoke damper 13x26 centimeters - 3 pcs;
- damper (dimensions are determined locally) - 1 pc;
- two-burner hob (dimensions are determined along the way) - 1 pc;
- grate 20x28 centimeters - 5 pcs;
- furnace door 21x25 centimeters - 1 pc;
- blower door 14x25 centimeters - 1 pc;
- cleaning door 7x13 centimeters - 2 pcs;
- steel corner 60x60x5 millimeters - 1.5 m;
- steel strip 50x5 millimeters - 20 m;
- chamotte clay - 100 kg;
- sand, ordinary clay - the amount is determined by the need for the material.