Programs for the design of heating systems and water supply. presentation
1 Programs for the design of heating systems and water supply
2 Quick selection of radiators
3 Audytor SDG is needed for quick selection of radiators in different types of buildings No specialized knowledge is required. It is necessary to have information about the size and purpose of the premises, the number of windows and walls outside The size and number of devices in each individual room The general specification of the equipment Estimated heat loads for individual rooms Technical parameters for selected equipment Purpose of the Audytor SDG program What knowledge is needed to work in the Audytor program SDG What data can be obtained as a result of working in the Audytor SDG program
4 Who can benefit from the Audytor SDG program Designers - to quickly calculate the number and size of radiators in a project (for example, at stage A) Customers - to compare and select equipment Sales managers of heating equipment - to be able to quickly select heating devices and calculate the cost Everyone – to select and calculate the size or number of sections of heating devices in your own home
5 GENERAL Object address
6 GENERAL DATA Climatic area
7 GENERAL DATA Wind conditions
8 GENERAL DATA Thermal protection of the building
9 GENERAL These parameters of the heating system
10 GENERAL DATA Exterior wall glazing
11 GENERAL DATA Exterior wall glazing
12 GENERAL Window status
13 GENERAL DATA Default room height
14 GENERAL DATA Distance from window sill to floor
15 GENERAL DATA Default type of radiator
16 GENERAL DATA Radiator default location
17 GENERAL DATA Default radiator protection
18 GENERAL DATA Presence of a thermostatic valve
19 Selecting heaters Room symbol
20 Selecting Heaters Room symbol
21 Choice of heating appliances Room area, m 2
22 Selection of Heaters Room height, m 2 (by default, it is taken from the General data)
23 Selection of heating devices Volume of the room, m 3 Leave the field empty - the program will calculate automatically
24 Selecting Heaters Floor
25 Selection of Radiators Number of walls outside
26 Selection of Heaters Glazing degree Glazing degree is the percentage of the area of windows to the area of walls outside
27 Selection of Heating Appliances Availability and condition of windows Glazing degree – the percentage ratio of the area of windows to the area of walls outside – by default is taken from the General Data
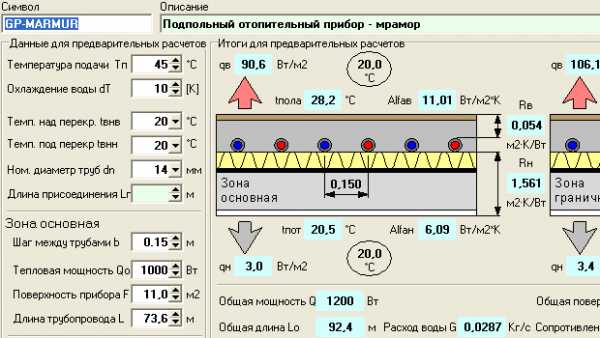
28 Selecting Heaters Required heat output for heating this room, W Leave the field blank – the program will automatically calculate
29 Selecting Heaters Specific heat output for heating this room, W Leave the field blank – the program will calculate automatically
30 Selection of Heaters Distance from the window sill to the floor
31 Selection of Heaters Longest radiator length The field is optional - by default it is taken from the General Data
32 Selecting Heaters Radiator location
33 Selecting Heaters Radiator Protection
34 Selection of Heaters Percentage radiator power The field is optional if there is 1 appliance in the room
35 Selecting Heaters Type of radiator The field is optional — by default it is taken from the General Data F1 — call the catalog of radiators
36 Selecting Heaters Length or number of radiator sections Entering the size of the radiator manually - as needed
37 Selecting Heaters Selected Radiator
38 Selecting Heaters Selected radiator size Length (or number of sections), height, depth
39 Selecting Radiators Actual heating output of the selected radiator
40 Selecting Radiators Information - whether the correct radiator is selected in this room
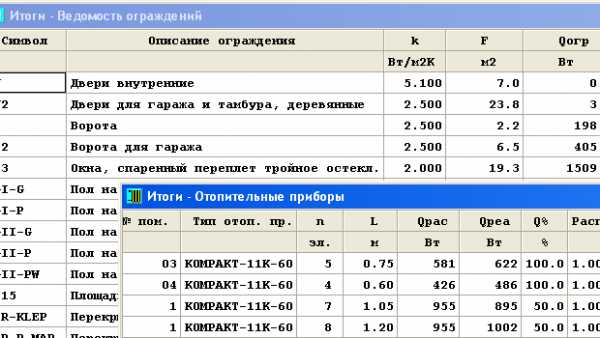
41 RESULTS of the selection list of radiators by rooms
42 RESULTS
43 Preparatory PRINT VIEW
44 CATALOG DATA
46 MANUFACTURER AND PRODUCT DATA
47 Thank you for your attention
How hydraulic calculation calculations are carried out
There are some tasks that need to be solved in order to make a hydraulic calculation of the heating system:
- Determine the diameter of the pipes in all sections of the system (do not forget to take into account the speed of movement of the heat carrier).
- Calculate the pressure loss.
- Solve hydraulic balancing.
- And, of course, the flow rate of the coolant.
What free programs exist for this?
As you might guess, this program is designed to quickly perform the necessary calculations. First, you need to make all the appropriate settings and select the most suitable items of equipment. Thus, it is possible to create completely new schemes. Moreover, a ready-made scheme can be adjusted as necessary.
This software harmoniously combines both options, allowing you to create original designs and adjust old ones. The program has the widest possibilities regarding hydraulic calculations, from the flow rate of the coolant to the selection of pipes of the required diameter. All the results of your work can be imported into the operating system in any form.
This program is freely available. It allows you to calculate everything you need for systems, regardless of the number of pipes. The essential difference of "Hertz", which favorably distinguishes it from other analogues, is that you can create various projects, both in new buildings and in reconstructed buildings, in which the glycol mixture is the coolant. The program was certified by OOO TsSPS.
Data entry is very convenient, as it is carried out graphically. The results of calculations are visualized in the form of diagrams.
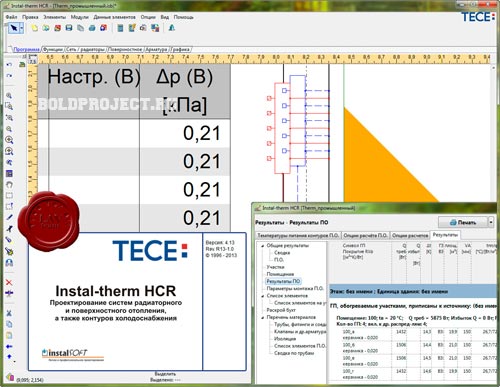
With it, you will calculate the surface or radiator. It consists of a special set of four similar programs. So, let's look at the possibilities of the program:
- Selection of the pipeline depending on the diameter.
- Selection of suitable radiators.
- It determines the height at which the pumps must be placed.
- Various kinds of calculations of heating surfaces.
- Determination of the most suitable temperature.
Unlike the previous options, you can download for free only a trial version of the program, which, of course, has some limitations. First of all, in the vast majority of options, you will not only be able to import an image into the operating system, but even print it. In addition, in each individual application there is a kind of limit: three completed projects per one. However, you can modify it an infinite number of times, this is not prohibited. And, finally, finished projects will be saved in a special format, no other version will be able to read such an extension.
As a result, I would like to note that the hydraulic calculation of the heating system is an integral part of the modern control system.In order to choose control valves without having an idea of what is happening on the market at the moment, you will have to make calculations over the entire area of \u200b\u200bthe structure, it is advisable to use the richest possible library. The operation of the entire system will depend on how correct your data will be.
Calculations and work to be done in advance
Hydraulic calculation is the most time-consuming and complex design stage.
- First, the balance of heated rooms and premises is determined.
- Secondly, you need to choose the type of heat exchangers or heaters, as well as arrange them on the plan of the house.
- Thirdly, the calculation of the heating of a private house assumes that a choice has already been made regarding the configuration of the system, types of pipelines and fittings (regulating and shut-off).
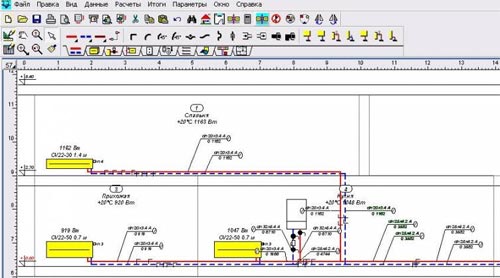
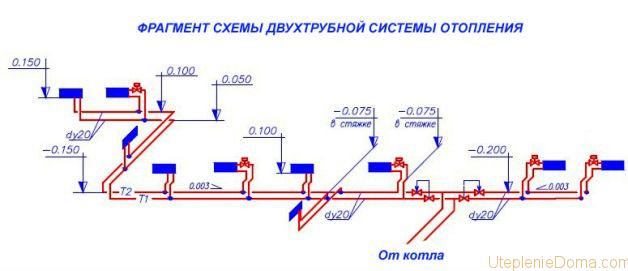
- Fourthly, a drawing of the heating system must be made. It is best if it is an axonometric diagram. It should indicate the numbers, the length of the calculated sections and thermal loads.
- Fifthly, the main circulation ring is installed. This is a closed circuit, including successive pipe sections directed to the appliance riser (if a one-pipe system is considered) or to the most distant heater (if a two-pipe system takes place) and back to the heat source.
HERZ calculation program HERZ official website of HERZ Armaturen in our country
We also inform you that the database of HERZ fittings in the RAUCAD program has been updated. For questions about obtaining a new database, please contact the engineer of the technical support group of the department of internal engineering systems of the LLC REHAU company, Moscow, tel.: (495) 663-33-88 (ext. 203).
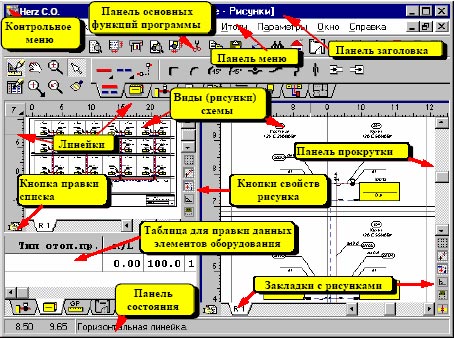
HERZ C.O.
HERZ C.O. is needed for hydraulic calculation of single and heating systems with two pipes and cooling, during the design of new systems, as well as for regulating existing ones in buildings under reconstruction (for example, after building insulation), it has the ability to calculate systems where the heat carrier is glycol mixtures.
The program makes it possible to perform all hydraulic calculations of equipment, within which:
diameters of pipelines are selected;
the water consumption in the designed equipment is analyzed;
pressure losses in the equipment are determined;
the hydraulic resistances of the circulation rings are determined, taking into account the gravitational pressure associated with the cooling of water in pipelines and heat consumers;
the settings of the pressure difference regulators are selected, installed in the places selected by the designer (the base of the risers, branches, etc.);
the required authorities of the thermostatic valves are taken into account;
excess pressure in the circulation rings is reduced by selecting preset valve settings;
the need for equipping an appropriate resistance in terms of hydraulics of the area with the heat consumer is taken into account.
The program uses many solutions that facilitate and improve the work. The most important of them are:
- graphical data entry process;
- presentation of the results of calculations on the scheme and floor plans;
- a developed context-sensitive help system that calls up information about both individual program commands and a hint regarding the input data;
- multi-window environment, it allows you to simultaneously view many types of data, totals, etc.;
- normal cooperation with the printer and plotter, the function of previewing pages before printing and output to the plotter;
- luxurious diagnostics of errors and the function of their automated search, both in the table and on the diagram;
- quick access to the catalog data of pipes, radiators and fittings.
HERZ OZC program
The HERZ OZC program is used to determine the calculated heat loss of individual rooms in a building, as well as the entire building. The calculation is carried out in accordance with the relevant standards. The program does:
- calculation of heat transfer coefficients for walls, floors, roofs and ceilings between the upper floor and the attic;
- calculation of heat losses for individual premises;
- calculation of heat loss of the entire building.
The program uses many solutions that facilitate and improve the work. The most important of them are:
- advanced help system;
- luxurious catalog of building materials;
- the function of automated determination of resistance to heat transfer, resistance of air layers of ceilings between the upper floor and the attic, soil resistance;
- the function of automated creation of the next floors, copying of rooms, and also the choice of rooms, for example, if during the input of data about the room it will be necessary to call another room;
- the option of automated distribution of heat losses from a room with a small need for heating capacity (for example, a corridor) to adjacent rooms, which makes it possible to directly transfer the calculation results to the HERZ C.O.
The program provides an opportunity to calculate the heat loss of huge buildings.
The following are data restrictions:
Limit number of defined fences: 16300 Limit number of layers in one fence: 16300 Limit number of rooms: 16300 Limit number of fences in one room: 16300
The results of heat loss calculations are the output data for the HERZ C.O program used to design district heating systems.
Comprehensive calculation of heating systems, water supply and drainage according to GOSTSNiPSP RAUCAD Official website of REHAU
RAUCAD is a professional CAD program based on AutoCAD for the design and calculation of internal engineering systems. The new, integrated software assistant has everything you need from project management to order specification and quotation. Thanks to the intuitive interface, you will step by step design both 2D and 3D pipeline networks for heating, water supply, drainage and drainage for water drainage, as well as axonometric diagrams, calculate them simply and quickly. Thermal disinfection of circulation networks and hydraulic balancing in the heating network of pipelines are also included in the capabilities of the RAUCAD program.
(Installing RAUCAD requires AutoCAD 2010/2011/2012/2013/2014 versions)
- Graphical calculation of heating and water supply pipeline systems according to SNiP 41-01-2003, SNiP 2.04.01-85*;
- Graphical calculation of drainage systems according to SNiP 2.04.01-85*;
- Graphical calculation of heating systems and low-temperature heating systems;
- Assistant for designing in AutoCAD with a base of conventional graphic symbols GOST (SPDS);
- Schematic generator;
- Calculation module for water supply systems with "loop wiring" to eliminate stagnant zones, dangerous from the point of view of the possibility of growth of legionella bacteria.
Heating system design
- Drawing plans for heating systems in AutoCAD;
- Drawing schemes of heating systems in AutoCAD, including specialized features for drawing axonometries;
- Automated calculation of heating systems with the choice of pipe diameters, with hydraulic adjustment and the choice of balancing adjustment according to SNiP. Detailed custom specifications.
Design of water supply systems
- Drawing plans for water supply systems in AutoCAD;
- Drawing schemes of water supply systems in AutoCAD, including specialized features for drawing axonometries;
- Automated calculation of water supply systems with the choice of pipe diameters according to SNiP. Detailed custom specifications.
Design of drainage systems
- Drawing plans for drainage systems in AutoCAD;
- Drawing schemes of drainage systems in AutoCAD, including specialized features for drawing axonometries;
- Automated calculation of heating systems with the choice of pipe diameters according to SNiP. Detailed custom specifications.
REHAU Quote and Order Specification Program
- Preparation of specifications for orders from the warehouse;
- Preparation of REHAU commercial offers;
- Export to a file for uploading to the electronic ordering system.
- Preparation of specifications in the form of GOST;
- Printing on A3 sheets;
- Reunification of several specifications into one;
- Ability to manually enter and adjust specifications.
Regarding preliminary work.
Due to the fact that the hydraulic calculation requires a lot of time and effort, we need to first perform some calculations:
- Determine the balance of rooms and rooms that are heated.
- Decide on the type of heating equipment and heat exchanger. Arrange them according to the general plan of the building.
- Before proceeding with the calculation, it is necessary to select pipelines and decide on the configuration of the heating system as a whole.
- It is necessary to make a drawing of the system, preferably an axonometric diagram. In it, indicate the length of the sections, the numbers and the magnitude of the load.
- The circulation ring should also be installed in advance.
Important! If the calculation concerns a wooden house, then there are no differences between it and brick, concrete, etc.
will not be.
Hydraulic calculation methods
As we have already said, hydraulic calculation can be done on an online calculator, using a special program, or in an Excel spreadsheet. The first option is suitable even for those who do not understand anything in heat engineering and hydraulics. Naturally, this method can only obtain approximate values, which cannot be used in large and complex projects.
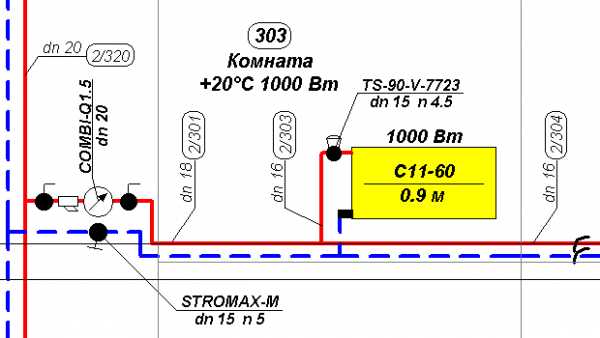
An example of an axonometric diagram.
The software is very expensive and it makes no sense to buy it at a time, but you can make a spreadsheet in Excel without investment. You can perform the calculation using different formulas:
- theoretical hydraulics;
- SNIP 2.04.02-84.
But the calculation method may also differ: specific pressure losses or resistance characteristics. The latter cannot be used for gravity systems with natural coolant circulation. When installing small two-pipe forced circulation heating circuits, it is enough to follow a few simple rules. The main lines are made of polypropylene pipes with an outer diameter of 25 mm. The outlets to the radiators are made of 20 mm pipes. And we wrote about how to choose a pump.