How to increase the heat transfer of a heating pipe with your own hands
The calculation of the heat transfer of the pipe is required when designing heating, and is needed to understand how much heat is required to warm the premises and how long it will take. If the installation is not carried out according to standard projects, then such a calculation is necessary.
What systems need calculation?
The heat transfer coefficient is calculated for a warm floor. Increasingly, this system is made of steel pipes, but if products from this material are selected as heat carriers, then it is necessary to make a calculation. The coil is another system, during the installation of which it is necessary to take into account the heat transfer coefficient.
Steel pipe radiator
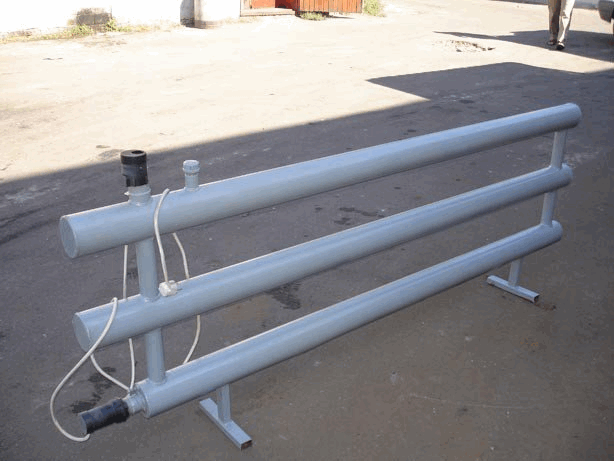
Registers - are presented in the form of thick pipes connected by jumpers. The heat output of 1 meter of this design is on average 550 watts. The diameter ranges from 32 to 219 mm. The structure is welded so that there is no mutual heating of the elements. Then the heat transfer increases. If you correctly assemble the registers, you can get a good room heating device - reliable and durable.
How to optimize the heat transfer of steel pipe?
During the design process, specialists face the question of how to reduce or increase the heat transfer of 1 m of steel pipe. To increase, you need to change the infrared radiation upwards. This is done with paint. Red color enhances heat dissipation. Better if the paint is matte.
Another approach is to install fins. It is mounted outside. This will increase the heat transfer area.
In what cases is it necessary to reduce the parameter? The need arises when optimizing a pipeline section located outside the residential area. Then experts recommend insulating the site - isolating it from the external environment. This is done by means of foam, special shells, which are made from special foamed polyethylene. Mineral wool is also often used.
We make a calculation
The formula for calculating heat transfer is as follows:
- K - coefficient of thermal conductivity of steel;
- Q is the heat transfer coefficient, W;
- F is the area of the pipe section for which the calculation is made, m 2 dT is the temperature pressure (the sum of the primary and final temperatures, taking into account room temperature), ° C.
The thermal conductivity coefficient K is selected taking into account the area of the product. Its value also depends on the number of threads laid in the premises. On average, the value of the coefficient lies in the range of 8-12.5.
dT is also called temperature difference. To calculate the parameter, you need to add the temperature that was at the outlet of the boiler with the temperature that was recorded at the inlet to the boiler. The resulting value is multiplied by 0.5 (or divided by 2). The room temperature is subtracted from this value.
If the steel pipe is insulated, then the value obtained is multiplied by the efficiency of the thermal insulation material. It reflects the percentage of heat that was given away during the passage of the coolant.
We calculate the return for 1 m. of the product
It is easy to calculate the heat transfer of 1 m of a pipe made of steel. We have a formula, it remains to substitute the values.
Q \u003d 0.047 * 10 * 60 \u003d 28 W.
- K = 0.047, heat transfer coefficient;
- F = 10 m 2. pipe area;
- dT = 60° C, temperature difference.
It's worth remembering
Do you want to make the heating system competently? Do not pick up pipes by eye. Heat transfer calculations will help optimize construction costs. In this case, you can get a good heating system that will last for many years.
Increasing the heat transfer of the heating main
Studying ways to efficiently heat rooms of various types, the owners are wondering how to increase the heat transfer of the heating pipe.The main thing in this is the ratio of the volume of the pipe to the entire area of its surface.
The obtained indicators will help to make all the calculations correctly and avoid mistakes. In addition, this issue should be raised even during construction work, since it is more difficult to resolve this issue in a finished facility.
Definition of heat transfer
For the correct selection of the size of registers for space heating in accordance with heat losses, it is necessary to know the heat transfer value of a pipe 1 meter long. This value depends on the diameter used and the temperature difference between the coolant and the environment. The temperature difference is determined by the formula:
∆t= 0.5 (t1 + t2) – tk,
where t1 and t2 are the temperatures at the boiler inlet and outlet, respectively;
tk is the temperature in the heated room.
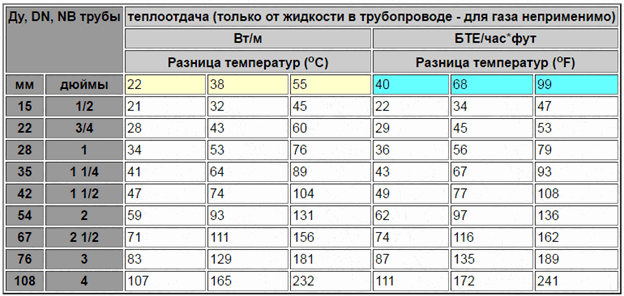
To quickly determine the approximate value of the amount of heat received from the register, the heat transfer table of 1 m of steel pipe will help. Despite the fact that the result is very approximate, this method is the most convenient and does not require complex calculations.
For reference: 1 BTU/hr ft2 oF = 5.678 W/m2K = 4.882 kcal/hr m2 oC.
The table shows what will be the heat transfer of steel pipes in the air at certain temperature differences. Interpolation calculations are made for intermediate temperature differences.
To more accurately determine the amount of heat that a steel pipe gives, you should use the classic formula:
Q=K F ∆t,
where: Q – heat transfer, W;
K is the heat transfer coefficient, W/(m2 0С);
F—surface area, m2;
∆t – temperature difference, 0С.
The principle of determining ∆t was described above, and the value of F is found by a simple geometric formula for the surface of a cylinder: F = π d l,
where π = 3.14, and d and l are the diameter and length of the pipe, respectively, m.
When calculating a section with a length of 1 m, the formula takes the form Q = 3.14 K d ∆t.
Note: when determining the heat transfer of a single pipe, it is enough to substitute the reference value of the heat transfer coefficient for steel when transferring heat from water to air, which is 11.3 W / (m2 0С). For a heater, the value of K depends not only on the material from which the pipes are made, but also on their diameter and the number of threads, since they influence each other.
The average values of heat transfer coefficients for the most popular types of heating devices are shown in the table.
Important! When substituting values into formulas, you must carefully monitor the units of measurement. All quantities must have dimensions that are consistent with each other.
Thus, the heat transfer coefficient found in kcal / (h m2 0С) must be converted to W / (m2 0С), given that 1 kcal / h \u003d 1.163 W.
Of course, the heat transfer table of steel pipes allows you to get a result faster than calculating by formulas, but if accuracy is important, you will have to tinker a little.
To determine the required register size, the required heat output must be divided by the heat output of 1 meter, rounded up to the nearest whole number. As a guide, you can take the average data for an insulated room up to 3 m high: 1 m of a register with a diameter of 60 mm can heat 1 m2 of a room.
Note: As can be seen from the table, the K coefficient for steel pipes can vary from 8 to 12.5 kcal / (hour m2 0C). An increase in the diameters and number of threads leads to a decrease in the efficiency of heat transfer. In this regard, to increase the heat transfer of the register, preference should be given to increasing the length of the elements.
It must also be taken into account that large pipes require an increased volume of water in the system, which creates an additional load on the boiler. The recommended distance between the threads is equal to the diameter of the pipes plus another 50 mm.
If the system is filled not with water, but with a non-freezing liquid, then this significantly affects the heat transfer of the register and requires an increase in its size after additional calculations. This is especially true when using devices with heating elements and oil as a coolant.
The steel pipeline is a fairly strong, durable product with good heat dissipation. Smooth pipe registers can have various configurations, are very easy to maintain and do not require periodic flushing.This allows them to successfully compete with light bimetallic and aluminum heaters, as well as with traditional "indestructible" cast-iron radiators.
Water and gas pipes are widely used in outdoor heating networks with open laying due to their high rigidity and wear resistance. The expediency of using steel pipes for space heating is determined by the operating conditions, financial capabilities and aesthetic taste of the owners. The use of registers is most justified in industrial and technical premises, but in other cases they also have their advantages.
Author (Site Expert): Irina Chernetskaya
Heat flow calculation
For an accurate calculation, it is better to contact the heating engineer of the manufacturer, seller, or calculate the number of radiators on an online calculator. Focus on the size of the room, the number of windows, doors, wall materials, the climate of the location of the house, the power of the heating radiator and other technical characteristics of the devices.
When planning heating, take into account absolutely all factors
A simplified independent calculation of heating radiators by area is as follows.
Calculation of the power of a heating radiator.
For 1 sq. m of the room you need 100 watts, if in a room with a height of 2.8 sq. m 1 window opening and one wall bordering the street.
If 2 walls are external, window 1, 120 watts will be required. For 1 sq. m. rooms.
With 2 windows, 2 walls bordering the street - 130 watts. - 1 sq. m.
It remains to multiply the number of meters and the number of watts. If the ceiling height exceeds the standard 2.7 - 2.8 sq. m., multiply the amount received earlier by 1.1 (correction factor).
How to find out the number of sections?
The dimensions of the structure, the calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators is done in the following way: divide the known power determined for one room by the power of one section of the radiator, announced in its passport. The result of the division is the number of sections. When you receive a non-integer number, for example, 10.6, buy an 11 section device. If the section is 170 - 190 W of power, the room is 18 - 20 square meters. m.
When self-calculating, you need to pay attention to the number of heating tubes in 1 row
It is important to know that horizontal sectional radiators have a heat output that exceeds the heat output of vertical high batteries.
It is important to know that horizontal sectional radiators have a heat output that exceeds the heat output of vertical high batteries.
Manufacturers focused on consumers who are not sufficiently familiar with the technical characteristics often indicate the size of the area of \u200b\u200bthe room in the passport data. This facilitates the selection of suitable parameters, given the standard dimensions of radiators. For original models, entrust the calculation of radiator sections according to the area of the room to the manufacturer's engineer
They will take into account each curly register of the heating battery
WATCH VIDEO
Tubular steel heating radiators are the choice of a prudent owner with a highly developed artistic taste: they are economical, practical, decorative, easy to install, compact and safe in all respects: do not collect dust, exclude accidental injuries. Steel tubular radiators, coated with synthetic protective compounds, do not corrode, externally moisture resistant, when equipped with filters and automation, they work for 20-30 years. Steel tubular heating radiators are very popular in an apartment building.
Decreased heat transfer.
In order to save energy, it becomes relevant to reduce the heat transfer of pipes in those sections of communications that are not used for their intended purpose, for example, when moving from one building to another or in an unheated room.
To do this, there are many options for using thermal insulation materials.Manufacturers present a fairly wide range to choose from, ranging from cheap fiberglass to more expensive types of expanded polystyrene. You can purchase pipes with insulation elements already built into it.
Summing up, we conclude that the use of such calculations helps to significantly save and avoid many technical obstacles in the design of water and heat supply systems.
In fact, you are a desperate person if you decide on such an event. The heat transfer of a pipe, of course, can be calculated, and there are a great many works on the theoretical calculation of the heat transfer of various pipes.
To begin with, if you started heating the house with your own hands, then you are a stubborn and purposeful person. Accordingly, a heating project has already been drawn up, pipes have been selected: either these are metal-plastic heating pipes or steel heating pipes. Heating radiators are also already looked after in the store.
But, before acquiring all this, that is, at the design stage, it is necessary to make a conditionally relative calculation. After all, the heat transfer of heating pipes, calculated in the project, is a guarantee of warm winters for your family. You can't go wrong here.
Methods for calculating the heat transfer of heating pipes
Why is the emphasis usually placed on the calculation of heat transfer of heating pipes. The fact is that for industrial heating radiators, all these calculations have been made, and are given in the instructions for the use of products. Based on them, you can easily calculate the required number of radiators depending on the parameters of your house: volume, coolant temperature, etc.
Tables.
This is the quintessence of all the necessary parameters, collected in one place. Today, a great many tables and reference books are posted on the Web for online calculation of heat transfer from pipes. In them you will find out what is the heat transfer of a steel pipe or cast-iron pipe, the heat transfer of a polymer pipe or copper.
All that is needed when using these tables is to know the initial parameters of your pipe: material, wall thickness, internal diameter, etc. And, accordingly, enter the query "Table of heat transfer coefficients of pipes" into the search.
In the same section on determining the heat transfer of pipes, one can also include the use of manual Handbooks on the heat transfer of materials. Although they are getting harder and harder to find, all the information has migrated to the Internet.
Formulas.
The heat transfer of a steel pipe is calculated by the formula
Qtp=1.163*Stp*k*(Twater - Tair)*(1-pipe insulation efficiency),W where Stp is the surface area of the pipe, and k is the heat transfer coefficient from water to air.
The heat transfer of a metal-plastic pipe is calculated using a different formula.
Where - temperature on the inner surface of the pipeline, ° С; t
c - temperature on the outer surface of the pipeline, ° С; Q-
heat flow, W; l
— pipe length, m; t
— coolant temperature, °С; t
vz is the air temperature, °C; a n - coefficient of external heat transfer, W / m 2 K; d
n is the outer diameter of the pipe, mm; l is the coefficient of thermal conductivity, W/m K; d
v —
pipe inner diameter, mm; a vn - coefficient of internal heat transfer, W / m 2 K;
You perfectly understand that the calculation of the thermal conductivity of heating pipes is a conditionally relative value. The average parameters of certain indicators are entered into the formulas, which may and do differ from the real ones.
For example, as a result of the experiments, it was found that the heat transfer of a polypropylene pipe located horizontally is slightly lower than that of steel pipes of the same inner diameter, by 7-8%. It is internal, since polymer pipes have a slightly larger wall thickness.
Many factors affect the final figures obtained in tables and formulas, which is why the footnote "approximate heat transfer" is always made.After all, the formulas do not take into account, for example, heat losses through building envelopes made of different materials. For this, there are corresponding Tables of amendments.
However, using one of the methods for determining the heat output of heating pipes, you will have a general idea of \u200b\u200bwhat kind of pipes and radiators you need for your home.
Good luck to you, builders of your warm present and future.
Assortment of water and gas pipes
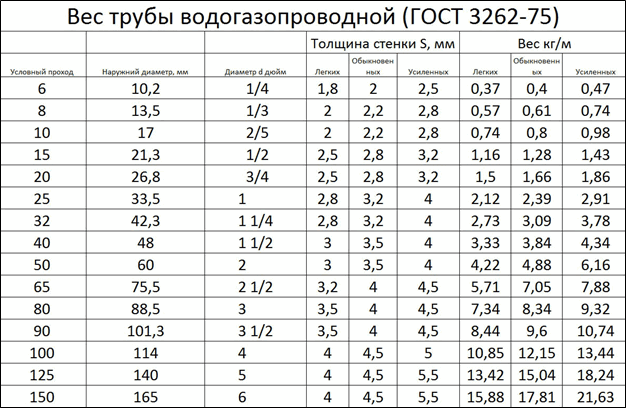
Water and gas pipes are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of the state standard - GOST 3262-75. It has been operating for more than 40 years and regulates all sizes and technical requirements.
There are 3 types of pipes in the assortment:
- Lungs;
- Ordinary;
- Reinforced.
The type of pipe is determined by the wall thickness. It can vary for different diameters from 1.8 to 5.5 mm. Reinforcement of the walls allows products to withstand more pressure and provides a longer service life. At the same time, of course, the consumption of metal for manufacturing, cost and weight increase.
The table of weight of steel water and gas pipes given in GOST allows you to determine the mass of 1 linear meter depending on the type and diameter.
Important! The mass determined from the table is theoretical, the actual value may differ by 4-8%, which can be noticeable with large batches. Galvanized products are always heavier by about 3-5%
As can be seen from the table, a steel water and gas pipe can have a nominal bore from 6 to 150 mm, which corresponds to an interval from ¼ to 6 inches. Inch sizes are often used for marking fittings and valves.
Therefore, it is very important to correctly operate with these units of measurement when completing the system.
Note: if there is no table at hand, you can independently recalculate the diameter. To do this, it is enough to know that 1 English inch corresponds to the average thickness of the thumb of an adult male and is equal to 25.4 mm. All calibers are easily identified by dividing the bore by 25, rounded up to the nearest standard value.
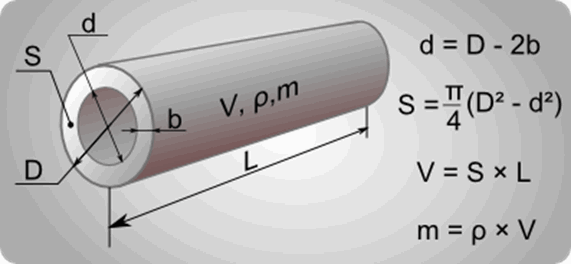
The mass of the pipe can also be found manually using the simple geometry and physics formulas shown in the figure below. With large volumes of calculations, it is convenient to use a special online calculator that allows you to automate the process.
The following designations are used in the figure:
d is the inner diameter of the pipe;
D - outer diameter;
b is the wall thickness;
S is the area of the metal in cross section;
V is the volume of metal;
m is the mass of the product;
ρ is the specific gravity of steel, equal to 7.85 g/cm3.
Important! It should be borne in mind that the inner diameter and nominal bore are not the same thing. Pipes with different wall thicknesses have different inner diameters with the same nominal bore
A conditional passage is understood as a certain standard value in the assortment line, which is only approximately equal to the value of d. Bringing pipes of different types to the same nominal diameter greatly simplifies the selection of fittings and other components.
It should be noted the high strength characteristics of steel pipes. They have the rigidity characteristic of a metal rod of the same diameter. It is also much easier and cheaper. So, the product of the heaviest type will have a weight of 30-40% less than all-metal rolled products.
Due to this, the water and gas pipe is widely used not only for transporting various media of any temperature, but also in construction and engineering for the construction of various structures.
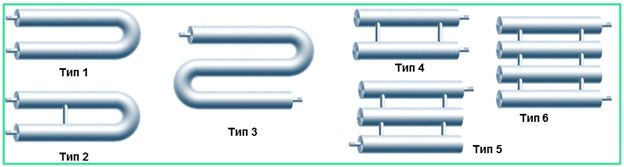
Types of heating registers
Steel heating registers are water-gas or electric-welded pipes, which are connected by welding into devices for space heating. They can be of different configurations. In accordance with the shape of the devices, the following varieties are distinguished:
- Serpentine;
- Sectional.
The figure shows some of their design options.
Sectional, in turn, are divided into types depending on the method of connection: thread or column. In the first case, the heated liquid passes sequentially through each pipe, moving along the device, as in a coil. In the second, the coolant enters each subsequent pipe from two sides in parallel, as shown in the figure above.
Sometimes similar structures are used from a metal profile of a rectangular or square section. They are somewhat more expensive than round ones, but can be convenient for self-production if the source material is available.
Despite the unattractive appearance, steel registers are quite popular in technical premises. They can often be found in garages, workshops, production halls, and sometimes in public buildings. Some homeowners prefer pipe registers because of the relative cheapness of the product and the possibility of making a device of the desired length and shape with your own hands.
In terms of their ability to give off heat, such devices are somewhat inferior to radiators of the same length, but at the same time they have a lower cost. An important advantage of smooth tube registers is their ease of maintenance. It is the convenience of regular cleaning that determines their frequent use in medical institutions.
To increase the heat transfer of a steel pipe, plate fins are used. They significantly increase the area of contact with the surrounding air, and also improve convection. The efficiency of such heaters is about 3 times higher than smooth-tube ones. The disadvantage of finned registers is only the difficulty in removing dust that accumulates between the plates.
There are also more complex modern designs of vertical registers. They can be both straight and arched in plan, repeating the outlines of the most complex architectural forms. There are options for the arrangement of columns in one or two rows. Such registers are very convenient for large high rooms and give freedom to bold design solutions.
Using a more efficient model
In some situations, the efficiency of batteries can be improved only radically by replacing them with new ones. Note that even high-quality heating systems after two decades of operation need to be updated due to the fact that their resource is being depleted. Technology does not stand still, which means that older-style radiators use less efficient and energy-intensive materials.
Another important argument in favor of replacing old batteries with new ones is the improved design of the latter. In modern models, the heat transfer area is much larger, in addition, manufacturers have developed innovative radiator parts to increase their performance. We are talking about convection windows in the upper part of the device and vertical ribs.
Summing up, we note that the advice of experienced craftsmen given in this material will help raise the temperature in the apartment by 2-4 degrees. If you can’t cope with the problem of heating with your own hands, then you will have to resort to the services of professionals. We will talk about how to calculate the power of the heating system and organize its installation in one of the following articles. Stay tuned for site updates and see you soon!
In accordance with applicable law, the Administration disclaims any representations and warranties, the provision of which may otherwise be implied, and disclaims liability in relation to the Site, the Content and its use. ttps://seberemont.ru/info/otkaz.html
Was the article helpful? Tell your friends
Heating and ventilation
Heating and ventilation
Heating and ventilation
Heating and ventilation
Heating and ventilation
Estimated indicators
In order to calculate the power of heating equipment, as well as to find out the scale of heat loss during the transportation of the coolant, it will be necessary to perform heat removal from the pipe at certain temperatures of the liquid inside it and the air outside. The thermal insulation layer serves as an additional parameter.
The formula for calculating the heat transfer of a steel pipe looks like this:
Q=K×F×dT, in which:
Q is the desired result of the heat transfer of the steel pipe in kilocalories;
K is the thermal conductivity coefficient. It depends on the material of the pipe, its section, the number of circuits of the heating equipment, as well as the difference in temperatures between the outside air and the coolant;
F is the total surface area of the pipe or several pipes in the instrument;
dT is the temperature head, that is, ½ of the total temperature of the liquid at the inlet and outlet of the pipe minus the air temperature in the room.
If the pipes are additionally wrapped with a layer of thermal insulation, then its efficiency in percentage terms (the amount of heat passed through it) is multiplied by the obtained heat transfer rate.
For example, let's calculate the heat transfer of a register of three pipes with a cross section of 100 mm and a length of 1 m. The temperature in the room is 20 ℃, and the coolant cools down from 81 to 79 ℃ when passing through the pipe.
According to the formula S=2pirh, we calculate the surface area of the cylinder:
S= 2×3.1415×0.05×1=0.31415 m2. If there are three pipes, then their total area will be 0.31415 × 3 = 0.94245 m 2.
Indicator dT = (79+81):2-20 = 60.
The value of K for a register of three pipes with a temperature difference of 60 and a cross section of 1 meter is taken equal to 9. Therefore, Q \u003d 9 × 1 × 60 \u003d 540. That is, the heat transfer of the register will be 540 kcal.
Thus, we considered the concepts of heat transfer, as well as ways to minimize the heat loss of a steel pipe for certain cases. There is nothing very complicated about this. The main thing is to approach the issue responsibly.
Heat transfer is the heat exchange between two media separated by a surface. Its intensity is characterized by a coefficient. When installing a heating main, the problem of energy saving should be taken into account. Therefore, old heating mains are being replaced by new ones, which use pipes equipped with thermal insulation, which makes it possible to reduce heat losses by almost 80%.
In everyday life, the need to determine the heat transfer coefficient arises in two situations:
- if you need to calculate heating devices;
- if it is required to estimate heat losses in the pipeline.
In both the first and second cases, it is necessary to determine how much heat a steel pipe for a heating main gives off to space, if the temperature of the coolant and the temperature of the medium are known. An additional parameter is the absence or presence of thermal insulation.
Simple ways to increase the heat transfer of radiators
We improve air circulation. Batteries transfer heat to the air, which, when heated, rises, and then, when cooled, falls down. This is how air circulates, and the room becomes warm as much as the heat transfer of the battery and the speed of the air flow allow. Therefore, in order to increase the temperature inside the room, first of all, it is necessary to ensure good air circulation. To do this, free up the space around the battery to the maximum: remove the protective screen, raise the curtains, move the furniture, and so on.
Speed up air circulation with a fan. The faster the air moves, the more heat energy it can take from the battery. On the coldest days, you can turn on the fan, directing it to the center of the battery to capture as much area as possible. To ensure the autonomy of such a system and ensure its quiet operation, you can place computer fans. They are quiet, low power, and when placed directly under the battery do not disturb the natural direction of air movement in the room.Fans will allow you to raise the temperature in the room by 3-10 degrees, and their low consumption makes it possible to blow the battery all winter round without significant damage to your wallet. Calculate for yourself: the power of conventional fans is about 40 watts, computer fans - no more than 5. Total consumption: 40 * 24 (hours) * 30 (days) \u003d 29 Kilowatts \u003d about 95 rubles per month. In the case of computers, even less - about 23 rubles per month. when connecting 2 at once.
Installing a heat shield. The heat from the battery radiates in all directions, and in order not to heat the walls, but to direct the heat energy into the room, you need to install a heat-reflecting screen behind the battery. For these purposes, you can use foil isolon (foamed base with foil on one side), gluing it to the cleaned wall behind the battery with any suitable means (tile glue, universal glue 88, silicone, etc.). Ideally, the area of the heat-reflecting screen should be larger than the area of the battery.
If the battery is cold, you need to bleed the air. To do this, you need to unscrew the usual or Mayevsky tap at the battery.
It will not be superfluous to keep a container or a towel under the valve, because as soon as the air comes out, water will flow in a thin stream. Once this happens, the valve can be closed. The procedure should be repeated for each battery in the house.
Heat loss through pipes
In a city apartment, everything is simple: both the risers, and the supply to the heating devices, and the devices themselves are located in a heated room. What's the point in worrying about how much heat the riser dissipates if it serves the same purpose - heating?
However, already in the entrances of apartment buildings, in the basements and in some warehouses, the situation is radically different. You need to heat one room, and bring the coolant to it through another. Hence - attempts to minimize the heat transfer of the pipes through which hot water enters the batteries.
thermal insulation
The most obvious way how the heat transfer of a steel pipe can be reduced is the thermal insulation of this pipe. Twenty years ago, there were two ways to do this: recommended by regulatory documents (insulation with glass wool wrapped with non-combustible fabric; even earlier, external insulation was generally made solid using gypsum or cement mortar) and realistic: pipes were simply wrapped with rags.
Now there are a lot of quite adequate ways to limit heat loss: here are foam linings for pipes, and split shells made of foamed polyethylene, and mineral wool.
In the construction of new houses, these materials are actively used; however, in the housing and communal system, the limited, politely speaking, budget leads to the fact that the pipes in the basements are still just wrapping ss ... um, torn rags.
Welcome to the twenty first century
What are
Heating registers are made of different materials, they have different shapes. Each has pros and cons.
What are they made of
If we talk about materials, then the most common is steel, or rather, steel electric-welded pipes. Steel does not have the best heat transfer, but this is offset by a low price, ease of processing, availability and a large selection of sizes.
It is very rare to find stainless pipes - decent power requires a large number of pipes, and how much stainless steel products cost, you have an idea. If they did, it must have been a long time ago. They also use “galvanizing”, but it is more difficult to work with it - it will not work to cook.
- requires a neutral and clean heat transfer fluid, free of solid particles
- the presence of other metals and alloys in the system is undesirable, except for compatible ones - bronze, brass, nickel, chromium, therefore all fittings and fittings will need to be sought from these materials;
- carefully performed grounding is mandatory - without it, in the presence of water, electrochemical corrosion processes begin;
- the softness of the material requires protection - casings, etc. are needed.
There are registers made of cast iron. But they are too bulky. In addition, they have a very large mass, under them you need to make no less massive racks. Plus, cast iron is brittle - one blow, and it can crack. It turns out that this type of registers also needs protective covers, and they reduce heat transfer and increase the cost. Moreover, installing them is a difficult and hard job. The advantages include high reliability and chemical neutrality: this alloy does not care what coolant to work with.
In general, copper and cast iron are not easy. So it turns out that the best choice is steel registers.