Heat transfer resistance of timber of different sections
Insulation of profiled timber of natural humidity:
A beam with a cross section of 100 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 0.73 R, (m2 ° C) / W
A beam with a cross section of 150 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 1.1 R, (m2 ° C) / W
A beam with a cross section of 200 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 1.29 R, (m2 ° C) / W
A bar with a cross section of 250 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 1.85 R, (m2 ° C) / W
That is, even a beam with a cross section of 250 mm does not meet the standards. By the way, this is a fact reflected in the old SNIPs, according to which the thickness of the beam for the North-West of Russia should be at least 500 mm.! Which, of course, is not real - if only to look for a thick forest around the world.
But let's see what happens if we insulate a house from a bar. Fortunately, modern materials are relatively safe and affordable:
Profiled timber of natural humidity with external insulation (basalt or mineral wool)
A bar with a cross section of 100 mm + mineral wool 50 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 1.9 R, (m2 ° C) / W
A beam with a cross section of 100 mm + mineral wool 100 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 3.25 R, (m2 ° C) / W
A beam with a cross section of 150 mm + mineral wool 50 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 2.35 R, (m2 ° C) / W
A beam with a cross section of 150 mm + mineral wool 100 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 3.56 R, (m2 ° C) / W
A beam with a cross section of 200 mm + mineral wool 50 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 2.55 R, (m2 ° C) / W
A beam with a cross section of 200 mm + mineral wool 100 mm has a heat transfer resistance of 3.82 R, (m2 ° C) / W
Bar of chamber or atmospheric drying (importance not more than 20%, GOST):
At the same time, it is interesting that a bar with a section of 140x140 mm is chamber or atmospheric drying !!! (namely, such a bar is subject to external insulation) has a heat transfer resistance = 1.9363 R, (m2 ° C) / W - which is much more than that of a counterpart of natural humidity. Keeping in mind that we need to eventually get walls whose heat transfer resistance will be = 3.16 R, (m2 °C) / W, we must insulate the facade of the house with a layer of basalt slabs equal to only 50 mm!
Conclusion: the best solution for a warm house suitable for permanent residence would be such a cake: a wall of dry timber 140 mm thick + 50 mm basalt slab + windproof film + outer skin imitation timber / block house.
As you can see, the problem of energy saving is easily solved by insulating the facade of a wooden house from a bar.
In our next article, we will tell you how to insulate a house?
Attic, doors and windows
The technology of warming the attic of a wooden house is as follows:
- a vapor barrier layer is laid on the hemmed ceiling of the attic;
- a heater is laid on top - mineral wool or polystyrene foam;
- a layer of waterproofing is laid on the insulator and a crate of boards is mounted.
An ideal option for mounting doors and windows is the use of two-chamber metal-plastic or wooden double-glazed windows and double doors, as well as the mandatory presence of an entrance vestibule. Finally, before choosing a method of thermal insulation of a log house, it will be right to make sure that such a procedure is necessary in principle.
07.05.2017 21:25
Profiled timber attracts many Russians with its affordability and excellent thermal characteristics. However, most of them mistakenly believe that such a house does not have to be insulated. Of course, I want to preserve the unique wooden flavor of the interior and exterior of the building, but comfortable living is more important. In matters of warming a house from a profiled beam, there are some nuances. We will tell about them today.
Warming a house from a bar pros and cons
Today, more and more people are beginning to understand that they are part of nature. And, realizing this simple truth, they refuse to live in brick and concrete houses, preferring life in a wooden house to them.And they are absolutely right, because living in such a house is an incomparable pleasure. And all because wood is a living, breathing material that creates its own special microclimate in the house. Wooden walls are able to remove all unpleasant odors and excess moisture in the air from the rooms. The air in such a house is always clean, saturated with the smells of coniferous forests, which have a beneficial effect on the well-being of people living in the house, especially those who have problems with the heart or pressure.
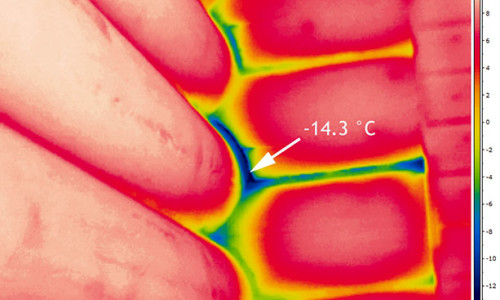
The heat loss of a house from a bar usually falls on various slots and joints.
But life does not stand still, and construction technology too. Today, more and more often you can find houses built from timber - a tree processed using a special modern technology, thanks to which, in the end, an excellent building material is obtained, durable, having a beautiful appearance, low cost, easily and quickly mounted. But a house built from this material has one significant drawback - it is necessary to insulate a log house.
Although this question is not so unambiguous, because the thickness of the walls of a house under construction from a wooden bar is usually selected taking into account the thermal conductivity of the tree and the characteristics of the local climate. Usually, the thickness of the walls from the timber is enough to maintain a comfortable temperature inside the house. The standard thickness of a wall made of timber is 30-32 cm, which is comparable to the effect of a 10-15 cm ball of insulation, such as mineral wool or fiberglass. And the idea that any insulation will lead to a change in the appearance of the facade of the house, makes many owners of houses built from timber to abandon their insulation.
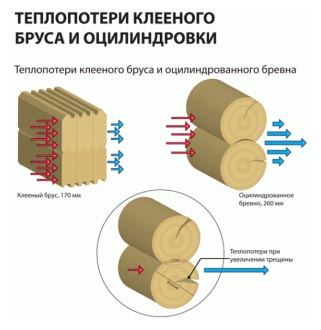
Heat loss of glued laminated timber and cylindering.
But there is one very significant counter-argument to all these arguments. If you do not make thermal insulation of a house built from timber, this can lead to cracks in the bars, gaps between them, as well as to skew and depressurization of windows. After all, there is no guarantee that the sealant located between the bars will provide high-quality permanent protection for the entire period of operation of the house. And poor thermal insulation will lead to the fact that, due to blowing and freezing, the temperature regime of the walls is violated, and the wood will rot, significantly reducing the life of the house.
Yes and no
Wood has a very low thermal conductivity - on average, 3.5 times lower than that of a brick. Thus, where a brick wall of half a meter thickness is needed, a bar of 150 x 150 mm can be dispensed with.
If we are talking about a building that is not intended for permanent residence (country house), or when building in a warm region, a house made of profiled timber does not need additional insulation. The thermal insulation properties of the material itself will be sufficient to provide a comfortable microclimate even in the event of some frosts. Provided, of course, that the thickness of the timber is correctly selected.
If construction is carried out in a region with a harsh climate, and permanent residence in the house is also implied, then insulation can be considered quite appropriate, if not necessary. Warming will solve the following problems:
- Preservation of a comfortable microclimate even at extreme temperatures;
- Increasing the energy efficiency of heating by reducing heat losses;
- Reduced wear of wall structures.
It is also highly recommended to insulate during the construction of baths, regardless of the region.
Warming methods
The preferred method of insulating a house from a bar depends largely on the specific project.
The main feature of the use of profiled timber in comparison with log materials is that there is no need to insulate the interventional space. The reason is obvious - there is practically none, since the timber has a square (rectangular) cross-sectional shape.
Otherwise, the insulation of houses from a bar is carried out with standard prims.
Traditionally, they are divided into external and internal. External insulation of wooden houses is practiced only if you did not count on maintaining the "traditional" appearance. Usually, the warming procedure is not much different from similar actions in relation to a brick house.
The only thing worth noting is the need for high-quality ventilation of the space between the wall and the insulation (achieved by mounting the insulation on the frame with some indentation). Otherwise, wall structures will be adversely affected by excess moisture.
Before starting external insulation, you should decide on further finishing. For example, if you plan to use siding or lining, then one frame can be used both for laying insulation and for installing finishes.
Internal insulation also implies the loss of a colorful design, but there are a number of other subtle points:
- Internal insulation reduces the usable area of the premises, so it is advisable to use panels no thicker than 30 mm;
- One of the key points when choosing a heater is the ability of the material to pass excess moisture;
- The insulation must be unattractive to rodents;
- Since we are talking about a wooden building, the insulation must be chosen completely non-combustible.
Otherwise, the insulation technology is standard, and depends on the method of subsequent finishing.
Shrinkage of a house from a profiled timber of natural moisture
Glued laminated timber - pros and cons
Stages of warming a house from profiled timber
All elements of the house need insulation. Therefore, it is worth taking a responsible attitude to each of them. Otherwise, the event will be useless.
Foundation
There are two ways to insulate the foundation:
Internal insulation is highly undesirable and is recommended only if, for some reason, external insulation is not possible.
External insulation has several advantages:
- materials for it are cheaper than for internal insulation;
- allows you to avoid freezing and, as a result, a sharp temperature drop, which lead to the destruction of the structure;
- allows you to save the internal area of \u200b\u200bthe basement.
The most preferred material for insulation of the foundation is polyurethane foam.
It is more expensive than polystyrene, and has the following advantages:
- its installation does not take much time;
- there are no seams and gaps;
- no cold bridges.
For laying such material, special equipment is used. The thickness of the insulation layer should not be less than 5 centimeters.
A little less often they use a heater - extruded polystyrene foam. It has only a couple of advantages:
- low price;
- absolute immunity to moisture.
The floor, laid out with boards, will sooner or later be covered with gaps and cracks. And this means that the thermal insulation of the room will drop sharply. To prevent this from happening, they also provide floor insulation. Moreover, it is desirable to do this at the stage of building a house in order to avoid problems with laying boards in the future.
Thermal insulation of the floor covering implies not only the laying of insulation, but also hydro and vapor barrier. What materials are required is best agreed with a specialist, since the choice depends on many factors, such as the material of the boards, the ventilation system in the house, and so on.
In order to insulate the floor, logs are installed in the foundation. Then shields are nailed to the timber and a hydro- and vapor barrier, a heater and again both insulations are installed.
This method is not the only one, but is more common in its execution.
Walls
There are only three options for wall insulation:
The last option for those who care about the aesthetics of the room.
As a rule, the following materials are used for thermal insulation of walls:
- natural insulation: linen, sheep wool, lnovatin and more. Such materials are suitable for interventional styling;
- foam or any cotton material is ideal for external insulation;
- for the inside - exclusively cotton insulation.
In addition to thermal insulation materials, a vapor barrier will also be required, which will not allow the insulation to absorb moisture.
Also, do not forget about the ventilation system.
In order to avoid misunderstandings related to the thermal insulation of the room in the future, it is better to immediately familiarize yourself with all the rules for laying materials. If you do not have sufficient experience in this area or are not confident in your abilities, then it is better to contact specialists.
Features of the Russian climate - strong wind, heat and frost, rain - one way or another, require home insulation. Consider how to insulate a house from a bar in accordance with the regulations and standards for heat saving.
In general, insulation should be started even during the manufacture of a log house, laying an interventional sealant after each row of logs. Wood is a natural material that dries and shrinks over time. And therefore, a year later, after the walls of the log house have dried and shrunk, repeated work on glazing and thermal insulation is carried out.
Types of insulated glued beams
There are several types of insulated timber, which differ in the type of heat-insulating material, as well as in the type of timber construction itself.
Thermal insulation material
Polyurethane foam (PPU insulation).
This material has not a bad set of positive properties. So, for example, a fairly low coefficient of thermal conductivity. When using it, the entire volume of the timber frame is filled, and the possibility of the formation of cold bridges is also reduced. But along with the advantages, there is also a disadvantage. This material has low vapor permeability, because of this, when designing a building, you need to take care of an effective ventilation system.
Ecowool (cellulose).
The advantages of this insulation lies in its rather high thermal insulation characteristics, as well as in relative cheapness, which affects the cost of the insulated timber itself. But when using this material, the possibility of exposure to rodents increases. It is also necessary to use special equipment, which increases the time of construction work.
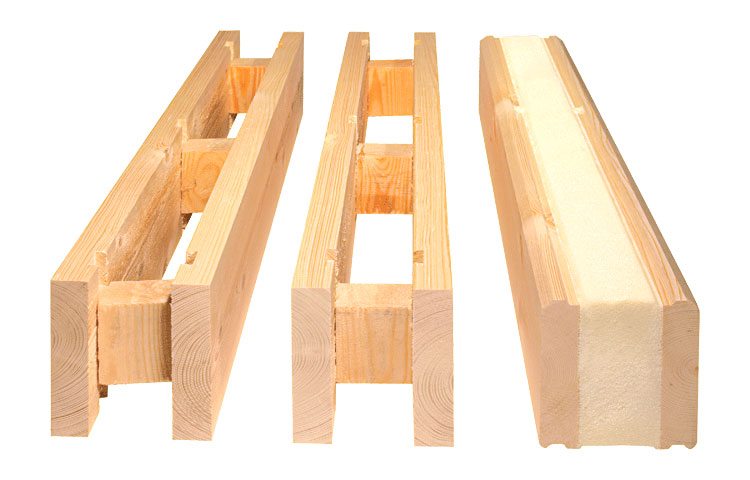
The design of the insulated profiled timber
Single chamber timber
The design of such a bar consists of two boards, which are connected by jumpers every 500 mm. The frame of this type is in most cases filled with polyurethane foam, which ensures the "solidity" of the used timber.
Photo of a single-chamber timber
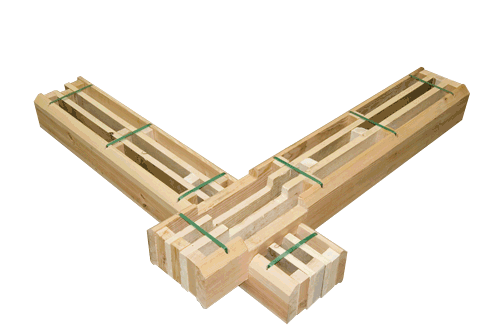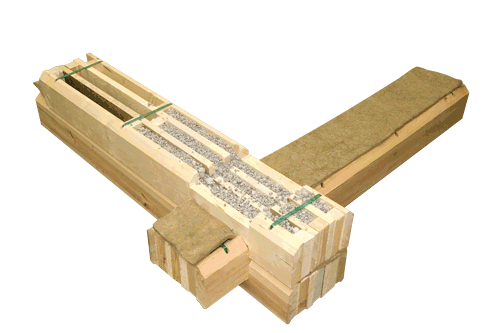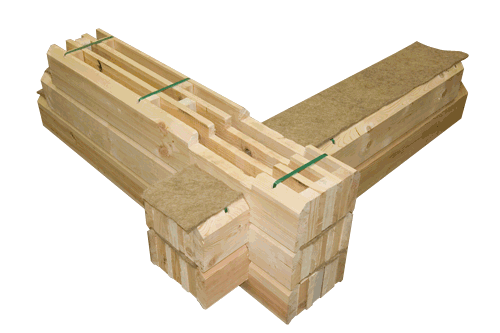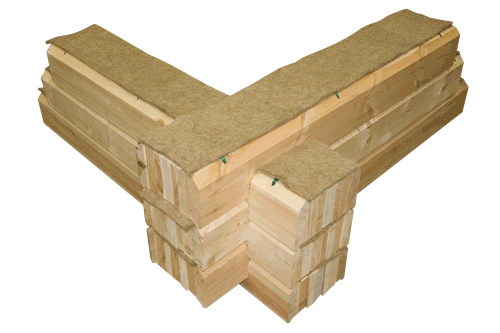
Packet timber
This type of construction is in many respects similar to the design of a single-chamber timber.
But there is an important difference. Its frame is separated by longitudinal bridges, in addition to horizontal ones, which form separate honeycombs closed on all sides.
They are filled with the selected insulation. This type of construction device significantly increases the characteristics of a single-chamber beam, but at the same time the cost of such a material also increases.
Packet timber
An example of assembling a box from a profile insulated beam
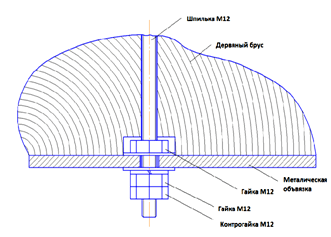
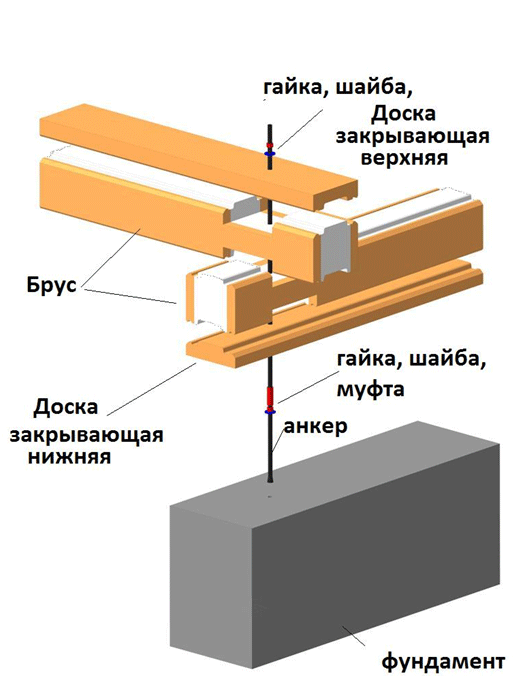
Having selected and installed the foundation according to the project, we install anchor bolts at a given distance.
For a foundation of screw piles, anchor bolts are attached as shown in the diagram:
Type of fastening to the foundation on screw piles.
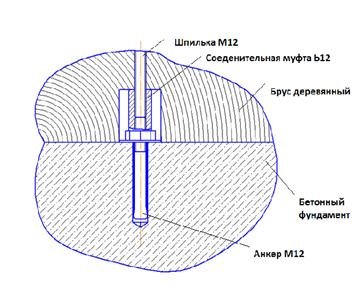
If a strip foundation filled with concrete is used, the anchor bolts are fastened as follows:
Method of fastening to the strip foundation.
- After installing the anchor bolts, we lay the insulating material on the foundation.
- Then we screw the sleeve onto the anchor, into which the stud is screwed.
- The next step is to install the bottom layer of profiled, lining boards that are put on studs.
- The beam with grooves lies on the board, while the pin is the guide.
- The next one is installed across the installed beam, then the box is assembled in the same way.
- The upper beam of the box is also covered with a profile board, after which it is attracted by a nut with a washer.
Scheme of assembling a box from a profile insulated beam
On our website, you can learn about the insulation of the loggia (also find out how to insulate the roof of the house).
Distinctive features of the insulated beam
In order to find out what the superiority of this beam over others is, it is enough to find out what the wall thickness is required from one or another building material in order to achieve the requirements of SNiP II-3-79:
- insulated profiled timber 150 mm;
- glued laminated timber 350 mm;
- brick wall 1700 mm;
- foam concrete wall - 880 mm;
- wooden wall - 450 mm.
In addition, this building material is much more energy efficient, since for comparison it is almost 2 times lighter than a beam from an array. Thanks to this, the work of builders with their own hands is facilitated, the process of installation work is accelerated. It also allows you to save money by using a not very deep foundation. The reinforced concrete foundation can be replaced with a foundation using screw piles, which also affects the timing and cost, since its price is rather low.
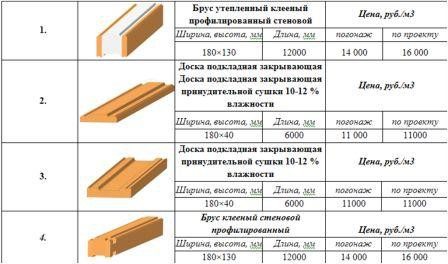
Comparative characteristics of products
Savings are also expressed in the reduction of heating costs, almost 3 times, but at the same time the walls are vapor and breathable, which favorably affects the atmosphere of the whole house.
The method of construction is also simplified. Since all elements of connections and selections for doors, windows and openings are made directly at the factory. As a result, the customer has a designer and instructions for assembling a house. The instruction is quite simple, so qualified construction teams and special equipment are not required, but only 2-3 people are enough.
There is no need for additional work on the interior and exterior of the house. Since the wood is processed on special woodworking machines at the manufacturer's factory.