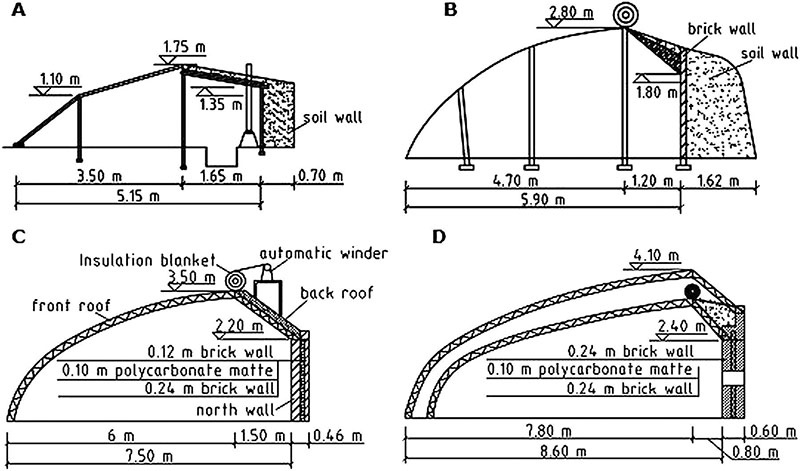
Design features
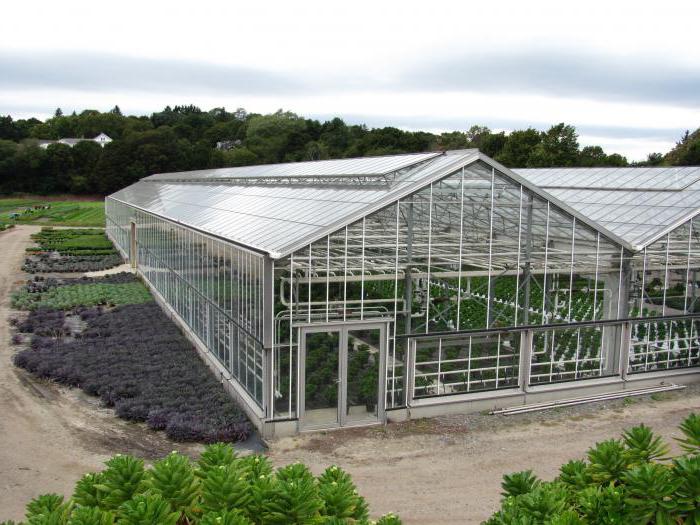
A trench greenhouse is a building with solid walls, deepened to the depth of soil freezing. This feature allows you to use the heat stored in the soil for several cold months.
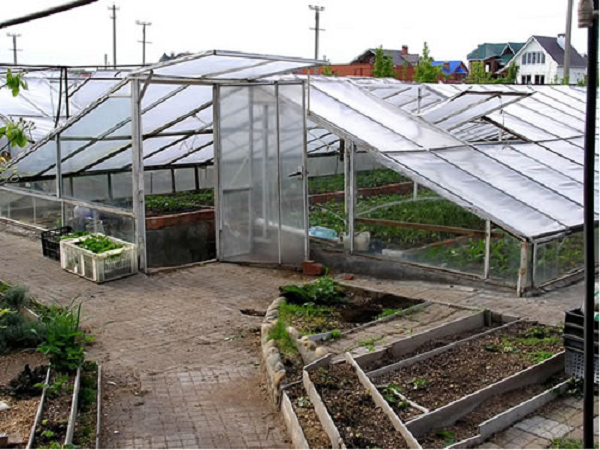

The walls of the greenhouse are made of heat-intensive materials and insulated from the outside to avoid cooling from the upper freezing layers of the soil. Additionally, the soil is protected from freezing with the help of an insulated blind area around the entire perimeter of the greenhouse.
The roof can be of any shape - arched, gable or shed. It is covered with two layers of polycarbonate with insulation of the air space between them or frames with double glazing. When the greenhouse is oriented from west to east, the northern slope of the roof can be sewn up tightly to reduce heat loss.

The entrance to the greenhouse is located from the end and equipped with an insulated vestibule. To descend into the greenhouse, a staircase is made in the vestibule. It can also accommodate heating equipment or a pantry for storing tools and planting material - tubers, cuttings and bulbs.

The recessed greenhouse is equipped with a system of forced supply and exhaust ventilation. For this, plastic pipes and built-in fans are used. When using glazed frames, some of them can be made openable - in summer this will help to avoid overheating.
Fans for forced air exchange in the greenhouse
In the southern regions in a trench greenhouse in winter the temperature does not fall below zero even without additional heating. In temperate latitudes, during frosts, it needs to be heated. As a heating device, you can use a stove, electric heaters or a water boiler.
 Furnace heating of a trench greenhouse
Furnace heating of a trench greenhouse
Efficient heating can be achieved by laying a heating cable or water heating pipes in the ground. The heated soil is able to give off heat to the space of the greenhouse for a long time and warm the air.
 Soil heating scheme using an electric cable
Soil heating scheme using an electric cable
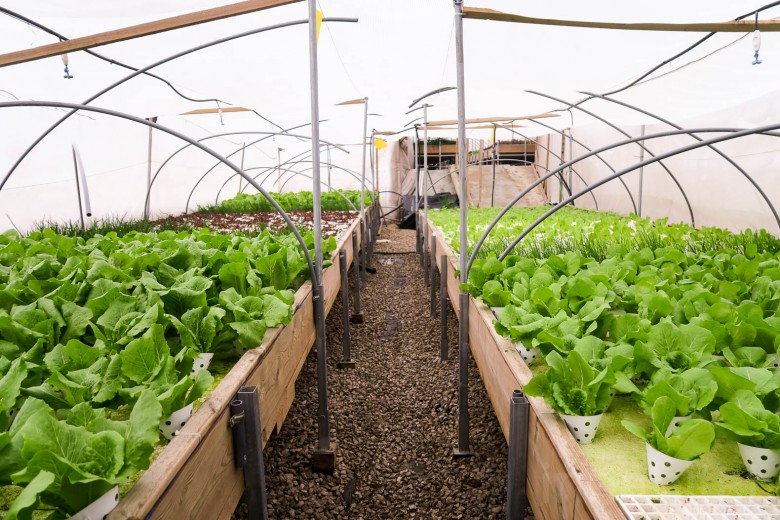
Plants in a trench greenhouse can be placed both on the beds and on the racks. The beds are made of brick or concrete blocks - the walls are an additional heat accumulator. The height of the beds is made in the range of 0.8-1.2 m, so that the plants receive enough sunlight. Fill with organic ingredients to get the effect of a warm bed and additional heating.
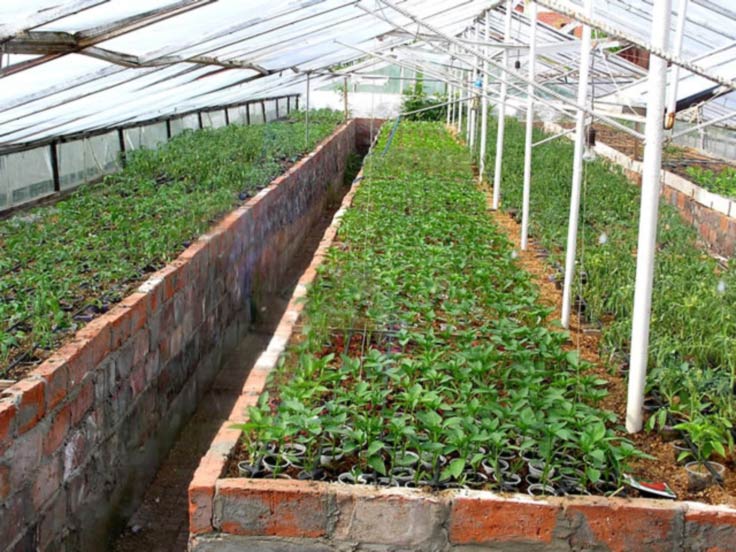

When growing plants on a rack, it is better to concrete the floor, after laying waterproofing and insulation boards under it. Additional heating in this case is best placed under the racks.
 Growing container plants and seedlings in a trench greenhouse
Growing container plants and seedlings in a trench greenhouse
Disinfection save the future harvest
- a whole class of drugs developed against specific types of bacteria: Fitolavin-300 against pathogenic bacteria and rot, Bayleton against gray rot and powdery mildew, Acrobat MC against downy mildew and late blight. The use of these drugs must be preceded by familiarity with the recommendations.
All work is carried out only by hand - this is a guarantee that not a single nuance will be missed
- the covering material is thoroughly washed;
- Nothing will grow by itself. Ultimate calculation, knowledge, work and discipline - that's what the earth loves - these are the components of a good harvest.
- After the entire inner area of the greenhouse is “planted” with invertebrates, give them a little rain by watering the entire plantation with a watering can or hose. If there are still no night frosts on the soil, then watering can be quite plentiful.
However, this is only the simplest preparation of the soil for the next planting, and if you want to achieve maximum results, then you need to additionally carry out a number of preparatory activities.
Underground greenhouses on noble estates
As soon as we decided to build an underground greenhouse in Prosperity, I immediately began to come across various interesting materials on this topic. I will collect the most interesting.
Underground greenhouse of Leo Tolstoy
Now there is a lot of talk about underground greenhouses as a modern invention, but our gardeners had such greenhouses 150 years ago. One of them has been preserved on the estate of the famous vegetarian writer Leo Tolstoy in Yasnaya Polyana. Leo Tolstoy was not only a brilliant writer, but also an excellent gardener, agrarian, beekeeper and teacher.
On his small plot, he grew all the vegetables needed for the family. Almost the same area as the vegetable garden was allocated to Russian greenhouses. In the spring they were stuffed with manure, the benefit of which was accumulated in abundance: there were stables on the estate.
The underground greenhouse (it still operates to this day) was designed and equipped by Count Tolstoy himself in the 70s on the site of a greenhouse that burned down in 1867.
the greenhouses of Prince N. S. Volkonsky. Outside, it is unsightly, with a low ridge and gently sloping glazing. But the snow quickly rolls off the roof and it is quite light in the greenhouse. Inside, the greenhouse is two-level, spacious and high, as it is buried in the soil (almost 2 m). Earthen walls lined with timber retain heat.
At the Tolstoy's, peach and cherry fruits were fruiting in tubs; at Turgenev - pears - in greenhouses and greenhouses. Prince Vyazemsky had about a thousand such tubs, Turgenev also had a solid one: there were winter gardens ... After the abolition of serfdom, more crops began to be planted in open ground.
This, of course, is less laborious - after all, greenhouses need to be heated, ventilated ...
In the museum greenhouse, pomegranates, figs, peaches, and coffee are now growing in tubs. The Tolstoys used to grow coffee, mix it with dried chicory roots, and even take it to Moscow for sale.
What greenhouses, greenhouses and vegetable gardens were in noble estates
In addition to the popular landscape design that many homeowners are now fascinated with, greenhouses and greenhouses with exotic plants used to be an integral part of the noble estate.
The nobles kept hotbeds, conservatories and greenhouses in which fresh herbs, cucumbers, and exotic vegetables were grown to surprise the neighbors. Moreover, many owners of estates did not consider it shameful to work in them.
Greenhouses, as a rule, were built of wood, and stone cellars were built for growing seedlings.
For many nobles, vegetable growing was a serious hobby, and sometimes even one of the few joys in life. As, for example, among the Decembrists exiled to Siberia.
Greenhouse Museum in Tarkhany
Volkonskaya was the first in Eastern Siberia to plant carotelia, dwarf beans, tomatoes, maize, celery, spinach, purslane, and tarragon. She had four types of melons - "dubrovka, real, cantaloupe and Persian."
Moreover, in the courtyard of the Chita prison, Maria Nikolaevna, together with her husband, set up a small greenhouse and taught her friends to “plant a garden”.
The princess sowed cucumbers, and with her own hands, on high manure beds for cucumbers in the yard behind the stables. From frosts, which happened even in July, she covered the crops with “felt and carpets”. “I have,” the princess wrote to her mother-in-law in the autumn of 1829, “I have cauliflower, artichokes, fine melons and watermelons, and a supply of good vegetables for the whole winter.”
Nevertheless, the composer's father tried very hard to diversify the vegetation of the estate in order to somehow distract his French wife from sadness and pamper the children with rare vegetables.
He ordered to arrange a garden, insulate leaky greenhouses and build a greenhouse that would be in harmony with other buildings (a glacier with a pit for storing vegetables, stables, a barn).
The greenhouse was made of logs, with high and rather wide windows for those times for good lighting of plants, had the shape of the letter G and was heated by special stoves. It had a room for a gardener who monitored the heating around the clock.
The owner himself did not work in the greenhouse, but carefully watched the plants. For example, in April 1837, he wrote in his work journal that "cucumbers are already on the fifth leaf." I. Tchaikovsky often visited the greenhouse and brought the children to harvest.
This is a good example of what we should do in an age of natural food shortages and a crisis in the upbringing of our children.
Features of greenhouses for year-round use
For growing vegetables throughout the year, conventional greenhouses covered with foil or polycarbonate are not suitable. The temperature in them in winter frosts inevitably drops below zero, and you can go broke on heating such greenhouses.
Greenhouses for year-round use with heating
The capital greenhouse, in which a stable microclimate can be achieved in winter, has some features:
- capital, usually strip foundation;
- double glazing or covering with cellular polycarbonate with a thickness of at least 6 mm;
- systems that provide the necessary mode of temperature, lighting and humidity.
Year-round greenhouse - photo
The design of the greenhouse can be different, and it usually depends on the region. So, in temperate latitudes and in the south, it is enough to install an ordinary gable greenhouse with double frames on a concrete or brick foundation. Orient it from west to east so that the midday sun illuminates one of the slopes.
In the northern regions, for better thermal insulation and savings on heating, some techniques are used: deepening the greenhouse into the ground, installing a main heat accumulator wall, and a vestibule.
Greenhouse for year-round cultivation of fruits and vegetables
35 underground greenhouses for year-round cultivation
At different latitudes, we have different surface air temperatures, but the air temperature at a depth of 1.5-2.5 m remains unchanged - 10-15 degrees. Your greenhouse will perform better the deeper you plant it in the ground.
This is an underground greenhouse in Spetchley Gardens, UK. The entrance is visible on the right
The underground greenhouse inside can be finished with stone, mud brick (adobe) or any other dense natural material that can absorb a large amount of heat.
Cold weather resistant crops such as lettuce, cabbage and broccoli can be grown here. Glazing creates a "greenhouse effect". You are unlikely to be able to build such a greenhouse if you have a high groundwater level.
Such a greenhouse can be built at least 1.5 m above the groundwater level.
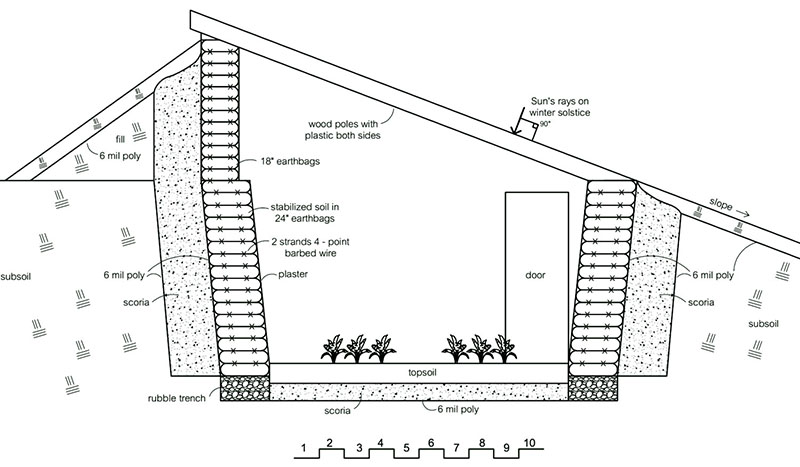
And this is a kind of underground valpini greenhouse, which is built by the Indians in the mountains of South America (translated from Indian, walipini means "place of warmth").
When digging, the top layer of soil is laid on the bottom of the greenhouse, the rest is used as a new shaft on the north side.
The windows are set at 90 degrees to the sun on the winter solstice, this will allow the greenhouse to store the most heat on the days when the sun shines the fewest hours.
This is a diagram of an underground greenhouse made of bags filled with earth. The bags store heat during the day to release at night. A properly designed underground greenhouse naturally heats up on five sides, unlike an above ground greenhouse where only one side, the floor, heats up during the day. Along the walls of such a greenhouse, it is necessary to make a waterproof barrier.
Another representation of underground greenhouses by Barbara and Ken Kern.
This underground greenhouse is made in Mongolia, the performance is during three seasons of the year. As the tracks show, the entrance is on the opposite side.
Inside view.In cold climates, the north, east and west walls should be well insulated. In the north, the ceiling should also be well insulated.
This greenhouse is built on a hill in Tennessee, USA.
This underground greenhouse hole was dug in Texas. The ground here is solid and nothing strengthens it.
You can dig a shallow drainage ditch around the perimeter of the greenhouse to drain rainwater.
Sometimes containers with rainwater are placed in the greenhouse to store more heat.
Pay attention to the vestibule for the entrance on the right. . This valpini greenhouse is made from old windows.
This valpini greenhouse is made from old windows.
Walipini greenhouse in Ladakh, lined with mud bricks, performance year-round in a very harsh climate.
This married couple bought a house with an old swimming pool and turned it into a "city greenhouse".
This clay greenhouse is made in Poland.
The 2 Most Important Factors When Designing an Underground Greenhouse
- a large amount of thermal mass (stone, soil, water),
- positioning towards the sun.
The easiest way to warm up and bring light to the basement. Build an underground mini-greenhouse on the south side of your house.
Underground greenhouse used as a dining room
And if the greenhouse has good acoustics, then you can make a studio
This is the underground greenhouse of the New AIchemy Institute. There is a pond, a compost heap, a greenhouse and a house nearby. Water is dense and holds heat even better than rock, soil is the third best heat retainer. Ponds are used for irrigation of agricultural crops.
Underground greenhouse at an organic farm in Wisconsin. The larger your greenhouse, the more efficient it is, as the temperature inside a small greenhouse can fluctuate quite quickly.
This underground greenhouse of 850 sq.m. lined with straw bales in Wisconsin.
Underground greenhouse Hiroshi Iguchi, Japan. It is obvious that the greenhouse is not completely closed.
Here is another clay and straw greenhouse from New Mexico.
Wall-mounted underground greenhouse.
The semi-basement greenhouse is surrounded on both sides by a stone wall and the earth behind.
Underground greenhouse embedded in a hill
Straw is an excellent insulator (R-value 1.5 to 3 per inch). Manure underground will also help keep the plants warm.
Frame from old windows and straw bales. Put manure or compost on the bottom under a layer of fertile soil, this will help keep warm.published econet.ru
P.S. And remember, just by changing your consumption, we are changing the world together! econet
Kinds
In order to have a crop of fresh vegetables and fruits all year round, use:
- single-sided structures;
- gable;
- arched;
- block structures.
A shed greenhouse can be called the simplest structure. Such greenhouses can often be seen attached to the main residential building.
Shed greenhouses have the following advantages:
- the design is inexpensive;
- has good thermal insulation properties, since the main wall creates an additional source of heat;
- there is no snow cover on the sharp corners of the slope.
Shed greenhouses are used only for home use, where you can grow fresh herbs for the table all year round or equip a winter garden. For industrial buildings they are not used.
Gable greenhouses are located from north to south. They are a separate building with different lengths and widths up to 12 meters.
Such a structure has its advantages:
- used in a small farm, suitable for private use;
- can have different sizes: from 30 to 300 square meters. m, which allows to reduce heat loss in the room;
- building with good thermal insulation and lighting.
The hangar greenhouse is a construction of a gable or arched structure, has a maximum width of up to 25 meters. Due to the fact that there are no racks inside the greenhouse, you can make the most of the space inside the structure.Hangar greenhouses have a large width and a roof slope of up to 30 degrees, which will require additional costs to carry out heating. For coating, reinforced film or polycarbonate is often taken.
Hangar greenhouses have advantages:
- due to its design, plants receive the maximum amount of light;
- there is an opportunity to use mechanics for maintenance;
- there is no need to manually remove snow from arched structures, as it comes off by itself.
Block structures are a series of greenhouses that are connected on the sides. A support post is installed at the junction points, due to which the costs will be lower. The roofs are divided into separate sections with gutters for water runoff. Block structures can have different lengths - sometimes it reaches more than one hectare, so this type of greenhouse is used only for industrial use.
Among the advantages, the following positions can be distinguished:
- the cheapest design for industrial needs;
- has high resistance against wind and snow cover;
- all parts of the greenhouse have excellent illumination;
- it is easy to place all systems for functioning: heating, watering, lighting;
- the greenhouse is easily ventilated through the roof, on which the vents are placed.
The disadvantages of this design can be considered that only up to 70% of the area is used. In addition, melt and rain water begins to accumulate in the recess on the roof, which requires an additional system for melting snow and draining melt water. Block tables are used only for industrial needs - they are not recommended for use in private households because of their size and cost.
If the greenhouse is planned to be built on a small plot of land, underground or recessed buildings are best suited, although for many greenhouses built in the form of a house or arched structure are familiar. If you build structures of this type, then the plants will receive sunlight from 20 to 35%, and when cold weather sets in, they will be quite cold.
Ivanov, a school physics teacher, proposed a different version of the building with a shed roof, which has a slope of 20 degrees and a tightly closed wall at the back, which allows you to use the sun's energy to the maximum. Thanks to this design, you can get a crop much longer.
The construction technology is called Scandinavian, as it began to be used by residents of European countries with a more severe climate. Such a unique design has practically no drawbacks. Its main feature is that due to a certain slope of the roof, the sun's rays do not slide over the surface, but fall perpendicularly - this allows you to harvest much earlier.
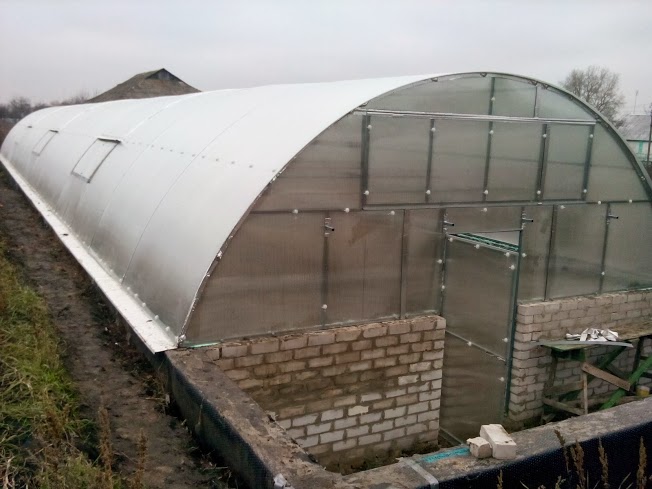
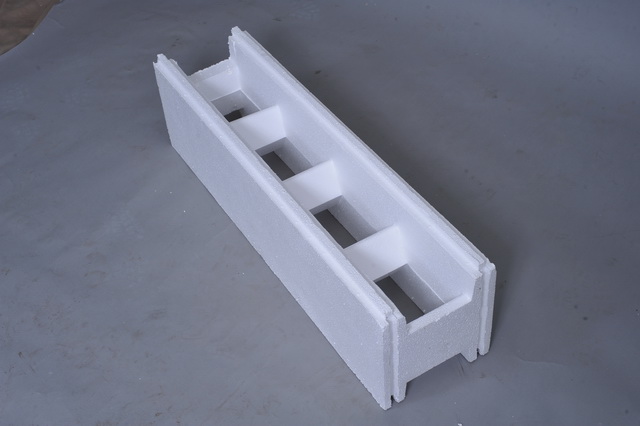
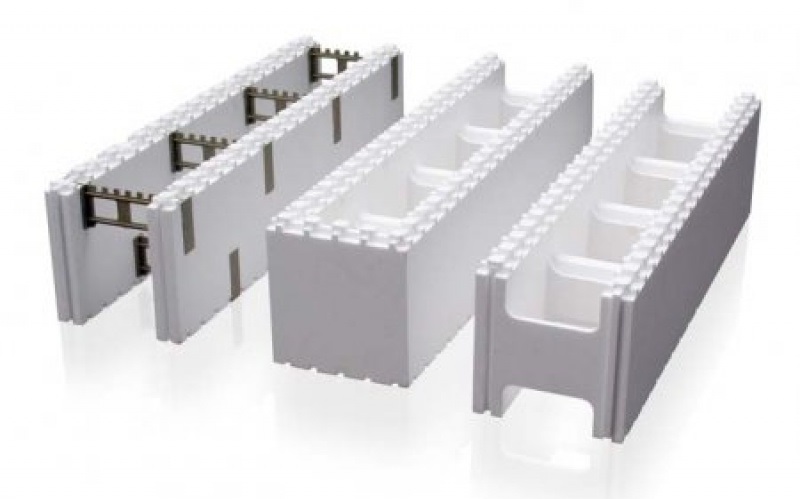
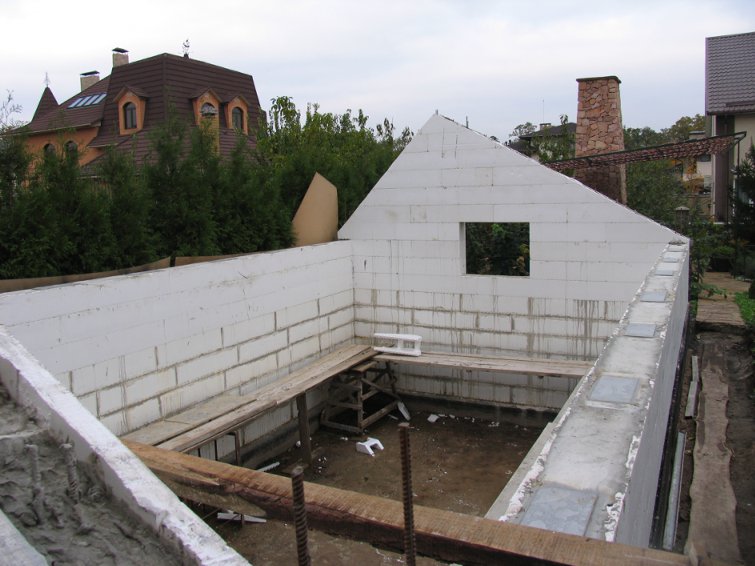
Trench greenhouse from thermoblocks
Thermoblocks are non-removable polystyrene formwork with sufficient rigidity and low thermal conductivity. The blocks are installed on a vertically fixed reinforcement in the form of a wall and poured with concrete. The construction of thermal blocks is carried out quite quickly, and the walls are strong and well insulated.

The greenhouse shown in the illustrations is oriented from west to east, has a gable roof with different sizes of slopes. The northern slope is sheathed with OSB sheets and soft tiles, the southern one is made of 10 mm cellular polycarbonate. To improve the illumination in the greenhouse, additional lighting with HPS lamps is provided.
Step 1. Mark out the site and dig a foundation pit for the greenhouse using the technology described above.
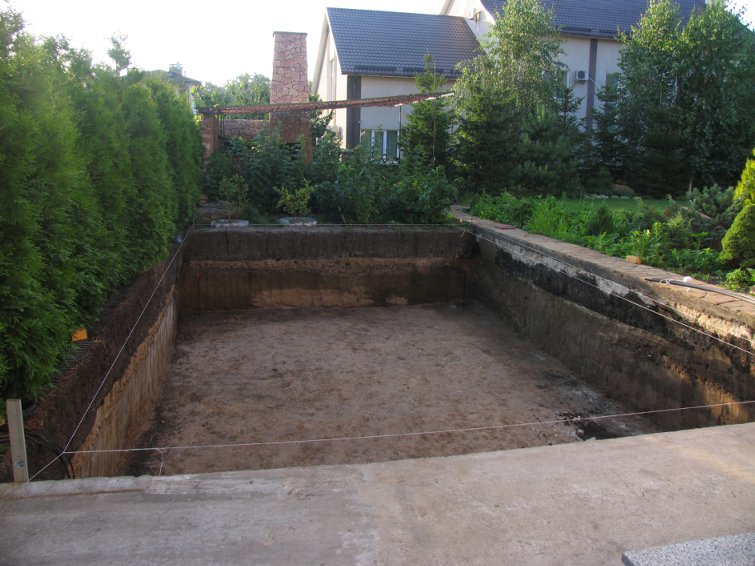

Step 2. Install the formwork under the foundation and reinforce it using a corrugated bar Ø12-14 mm. The reinforcement is placed in two horizontal rows at the level of the foundation and installed vertically to the height of the walls. Reinforcement crossings are knitted using annealed wire. The foundation is poured with concrete and left for 15-25 days to gain strength.
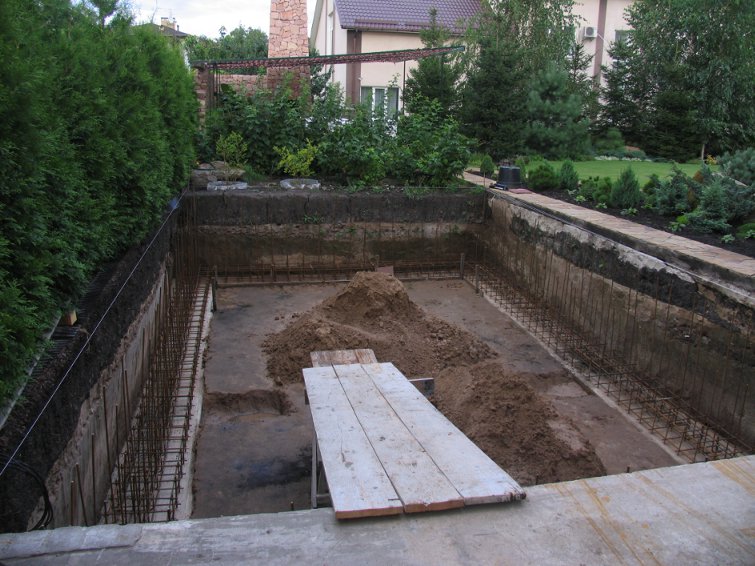

Step 3. The foundation is treated with liquid bituminous waterproofing in several layers. Fill the bottom of the trench with sand and level it.
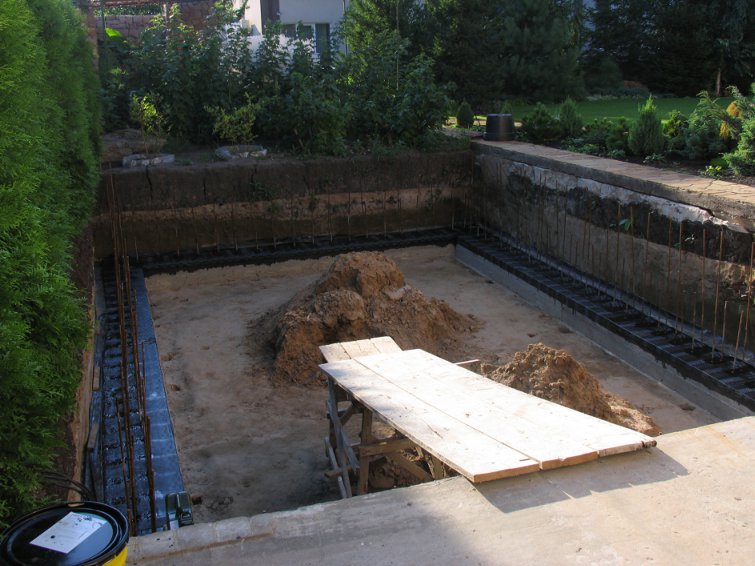

Step 4 Install the first row of thermoblocks and pour them with concrete. The joints of the blocks, when cracks appear, are coated with cement mortar.
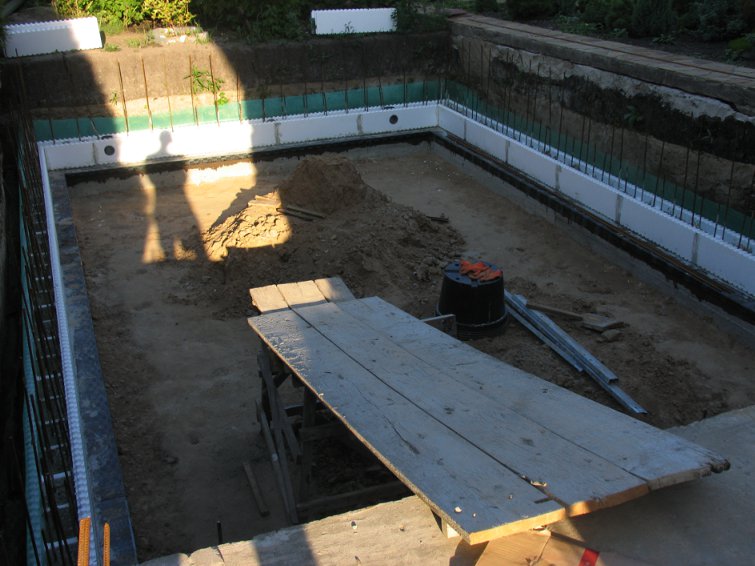

Step 5. Every three rows it is necessary to perform horizontal reinforcement with corrugated bars. They are placed on special guides in thermoblocks.
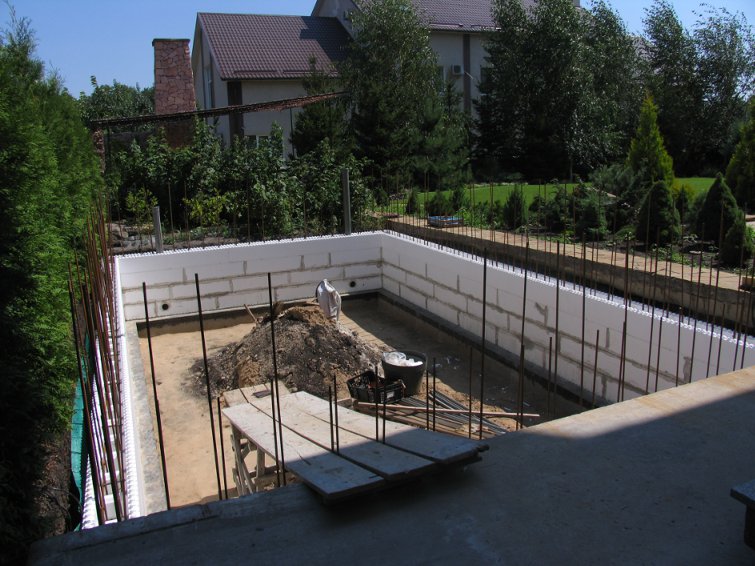

Step 6. Upon reaching the ground level, the outer side of the masonry is wrapped with rolled waterproofing, covered with sheets of flat slate and the soil is backfilled.
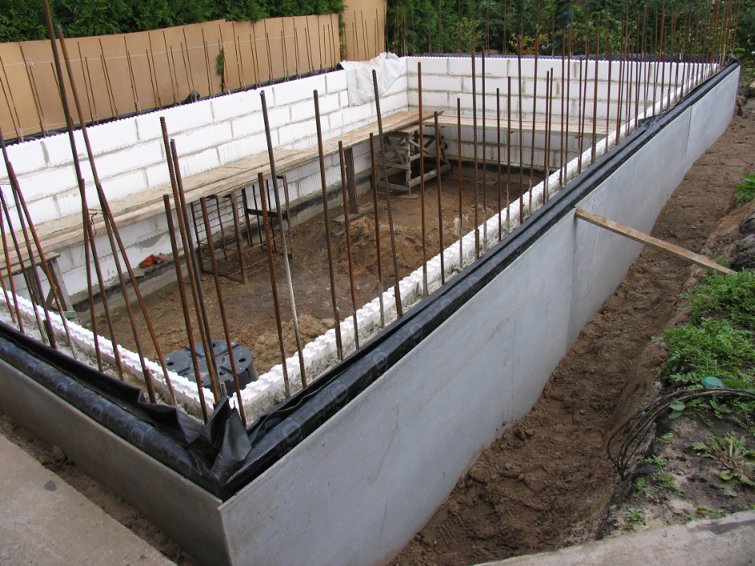

Step 7. Continue laying the above-ground part of the walls using the same technology. Perform door and window openings.
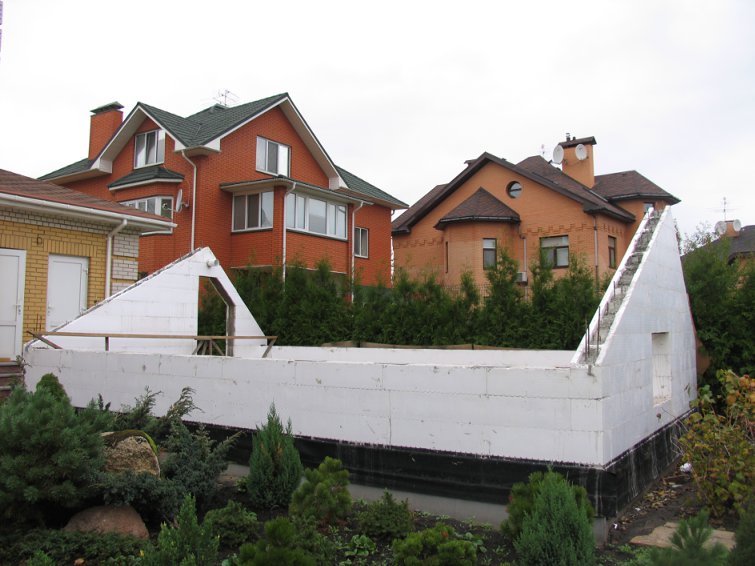

Step 8. Fill in the side ends of the greenhouse. Thermoblocks for them are cut to size according to the template.
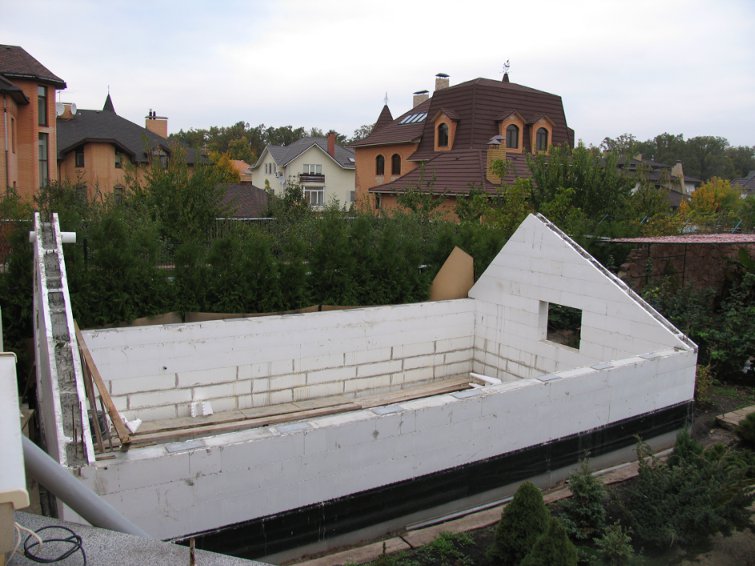

Step 9 The top row of masonry is reinforced with horizontal bars. After pouring and hardening of concrete, the excess part of the vertical reinforcement is cut off, the upper edge of the walls is leveled with a cement-sand mortar.

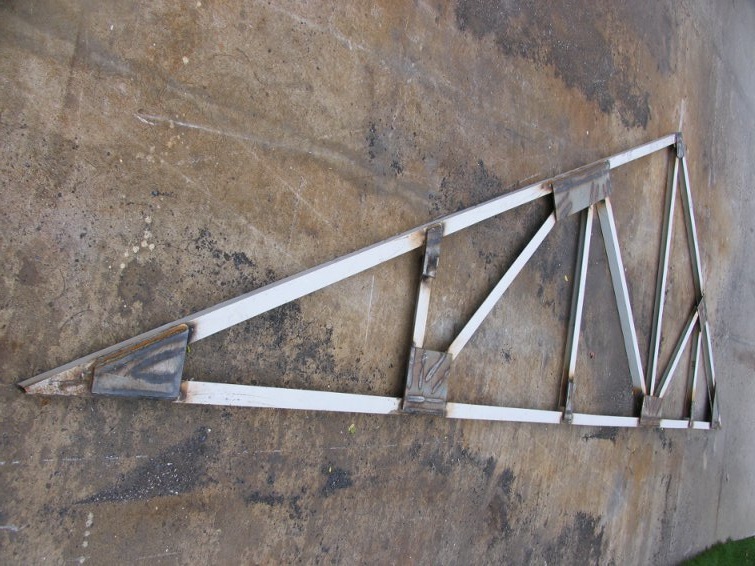
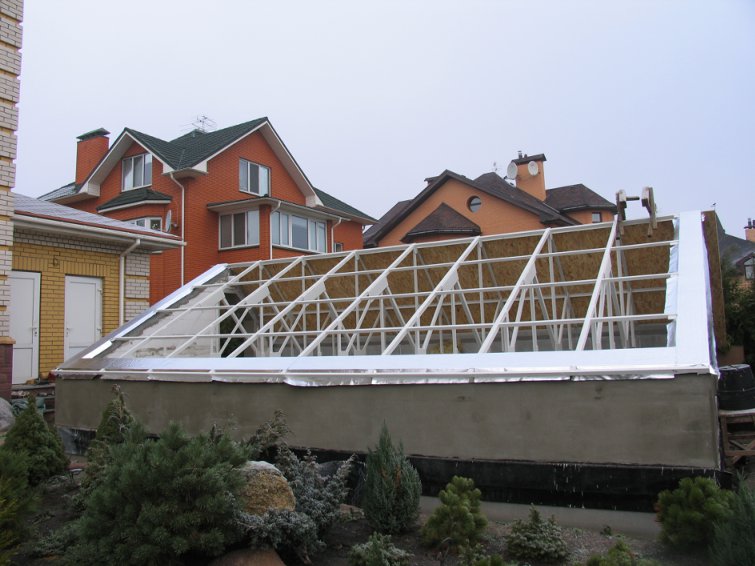
Step 10. According to the sketch, roof trusses are made from a metal corner 50x50 mm. They clean the welding spots and cover the trusses first with a primer, and after it dries, with light-colored metal paint.

Step 11 Install the trusses in place, fixing them to the anchors in the concrete pouring of the thermoblocks.
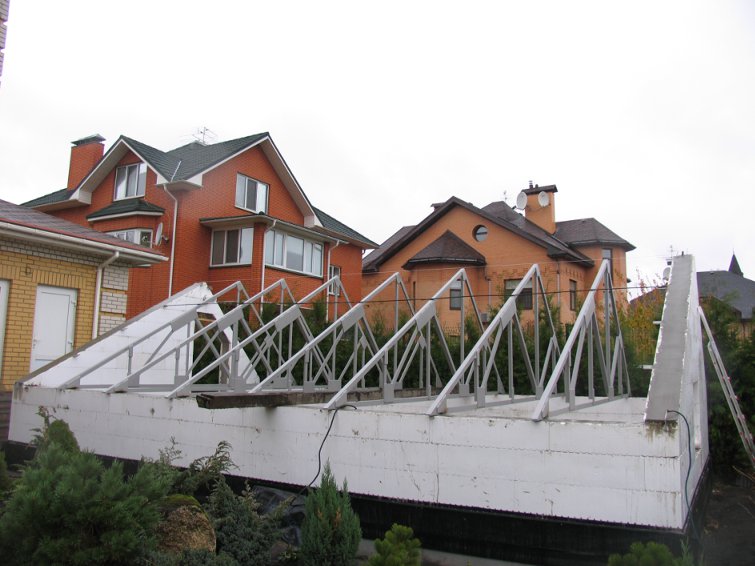

Step 12 With the help of transverse bars, the roof trusses are connected into a single structure. For screeds, you can use a metal strip 20-30 mm wide.
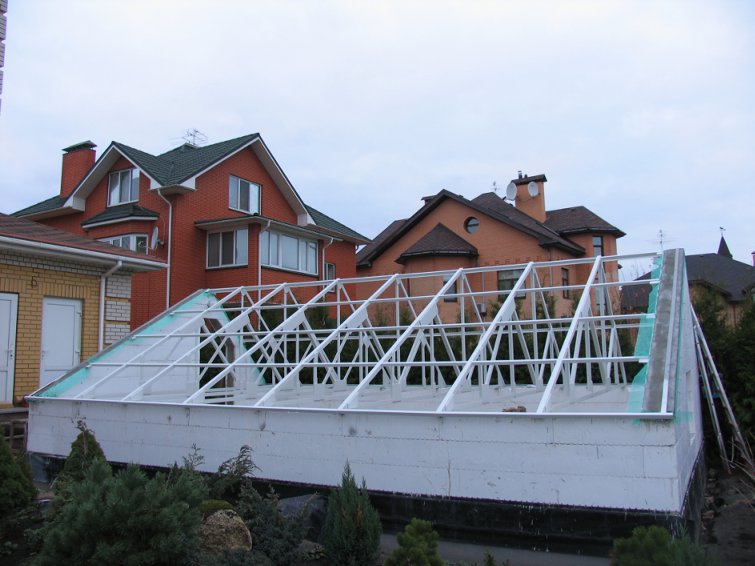

Step 13. The northern slope of the greenhouse is sewn up with a moisture-resistant OSB-plate.

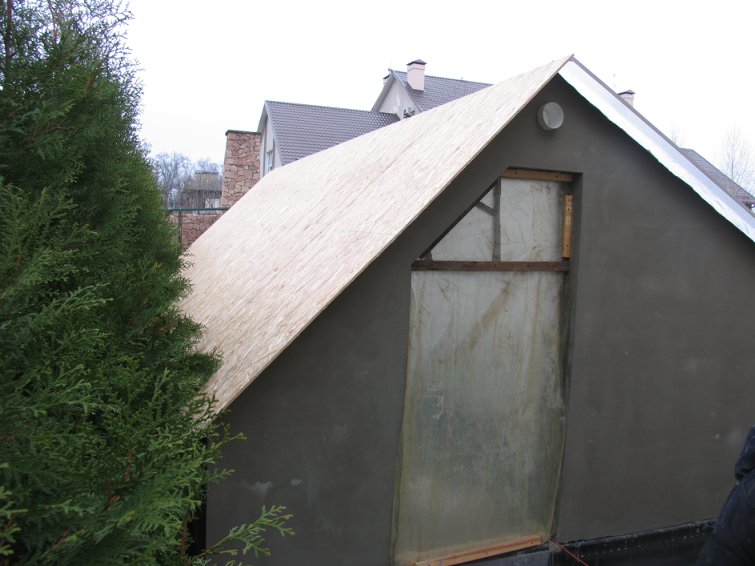
Step 14. The walls of the greenhouse are plastered and, if desired, painted with weatherproof paint.

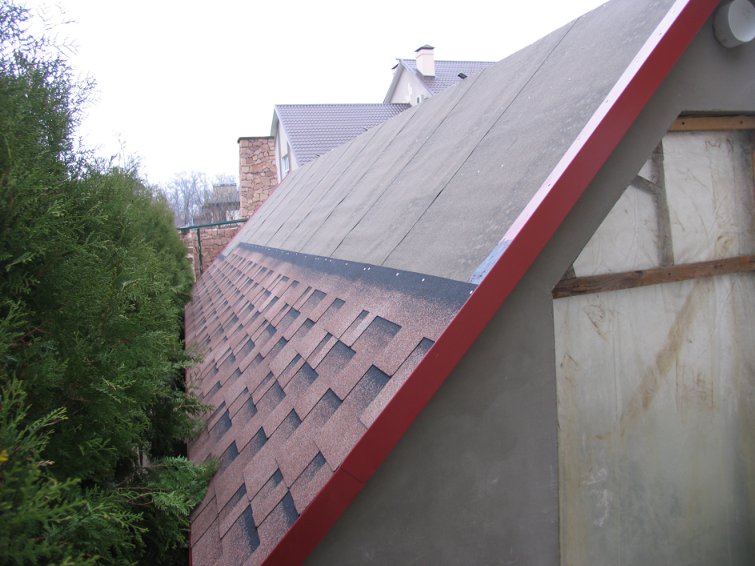
Step 15 Sheathe the OSB-slab with flexible tiles. Install wind and cornice strips.

Step 16. The southern slope is sewn up with polycarbonate 10 mm thick with a reinforced structure. When laying polycarbonate sheets, special profiles and self-tapping screws are used. The ends must be insulated with adhesive tape and an end profile.
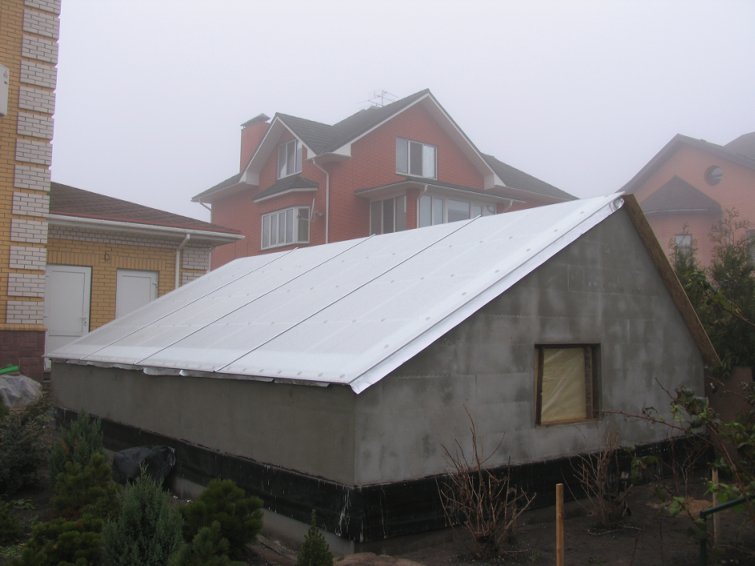

Step 17. Due to the large number of blank walls, the illumination in the greenhouse during the winter months is insufficient for most crops. Therefore, it must be equipped with a backlight based on gas discharge or LED lamps.
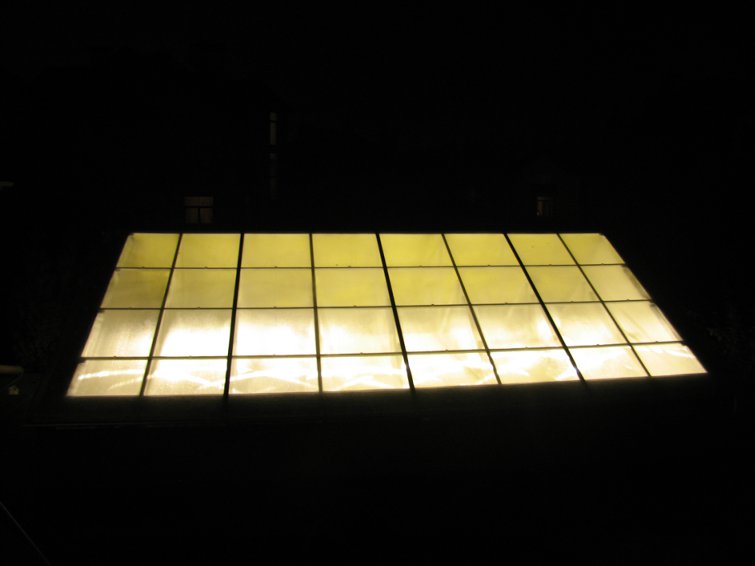

Video - Buried greenhouse
A trench greenhouse is an expensive construction, but with active use it pays off in two to three seasons. In it, you can grow not only the usual vegetables and herbs, but also southern fruits - citrus fruits, persimmons, pomegranates, pineapples. Such a greenhouse is also suitable for growing seedlings, breeding rare flowers and ornamental plants.
Shed structures with wooden walls
This construction option is more economical than greenhouses with a gable roof. The frame of the building consists of three rows of wooden posts placed in the pit. On the north side, the first row is 20 cm below the average and is upholstered with a croaker. Eighty centimeters from it there is a middle row, sheathed to the height of the ridge. In the resulting notch, I have biofuel sprinkled with earth (10-15 cm). Above these racks, a roof is built into the cavity of which sawdust is poured.
Racks from the south are made 30 cm above ground level, completely upholstered with croaker. On both sides, the walls are sprinkled with earth. On the north side, they also cover the roof covered with tar paper with it. In the working area, a chimney is built on the floor.And above it, a flooring is laid, on which racks with earth are placed, leaving space for free access to them. Such a greenhouse can be used all year round. In the absence of heating, it can be operated from the first months of spring until the onset of frost.
What do tomatoes grow on?
Here is another spring version of the "pie" for tomatoes:
If you are not a supporter of the mineral fertilizer of greenhouse soil, and you also don’t want to apply manure or chicken before planting tomatoes (at least for fear of becoming infected with helminths later), then consider the option with green manure. This green manure is planted in early spring, long before you bring the first seedlings.
And here are the ideal predecessors of greenhouse beds for tomatoes:
- The price of an exact solution to the issue of how to cultivate the land in a greenhouse in the spring, here is a crop that will justify all spring worries
- - this well-known drug shows itself perfectly against pathogens of powdery mildew, late blight, rot, scab, curl and bacteriosis. The use of copper sulphate negatively affects plants, therefore it is available for use only in autumn. Do not use concentrations above 10%. Copper sulfate is part of the Bordeaux mixture
- Temperature Method
- If you are lucky with the sun, then the following actions can help:
- It is not enough to build a greenhouse on the site, get an unusual seedling and place it in the soil, waiting for the harvest. The earth requires constant care, whether it is outdoors or in a greenhouse.
- Gently put a worm in it,
- Humus is poured onto its bottom, which has been waiting for this procedure for at least 3 years. It must be remembered that it should not contain any straw or hay, as this significantly increases the time it takes to decompose in the ground.
- Fertilizers are applied, depending on the variety (a professional sales assistant should explain to you in detail how, how much, and when).
- Step 1. Put reeds and long rotting branches in the bottom layer.
Green manure quickly form a green mass and are often grown in a greenhouse only to go as an organic fertilizer with valuable nitrogen. As a result, only 3 kg of green mass will replace 1-1.5 kg of manure for you! These are beans, peas, seradella, mustard, lentils, soybeans, rapeseed, phacelia, colza and broad beans.
polycarbonate greenhouse
When using polycarbonate as a material for sheltering the frame of a wall-mounted polycarbonate greenhouse, the following rules should be remembered:
- carefully measure the material;
- make holes at a distance of 4-5 cm from the edge. Polycarbonate will not be able to crack at the drilling site;
- use reinforced tape to close all joints and cavities. This approach will make it possible to insulate and preserve the microclimate even in winter;
- use thermal washers;
- do not overtighten the fasteners. The polycarbonate sheet should not sag under the influence of the fastener.
- seal the remaining cracks with foam or plaster;
- conduct electricity and other systems;
Features of the construction of an in-depth greenhouse
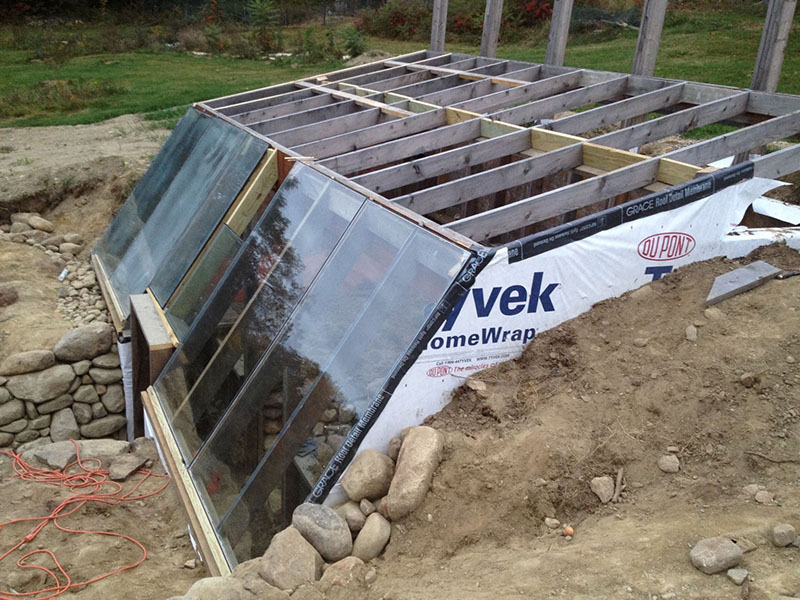

In addition, the gardener must consider:
- Direction of the wind. Air masses create a draft, which is why you have to spend a lot of money on heating an underground building.
- Relief. Many farmers are building a recessed greenhouse with their own hands on the slopes of the hills. Thus, they save on walls as well as heating.
- Lighting.Trees should not grow near the building, which, with their shadow, prevent the penetration of sunlight.
A universal type of earthen greenhouse is a gable greenhouse with brick walls. The depth of pouring the foundation is 80 cm when using a strip base. The walls are erected in one brick, smearing all joints with waterproofing mortar. In parallel with this, they are reinforced with vertical metal devices. The optimum angle of inclination of the roof is 25˚. It is constructed from glass or polycarbonate. In such a thermos greenhouse, even garden crops can be grown.
The project of a shed recessed greenhouse
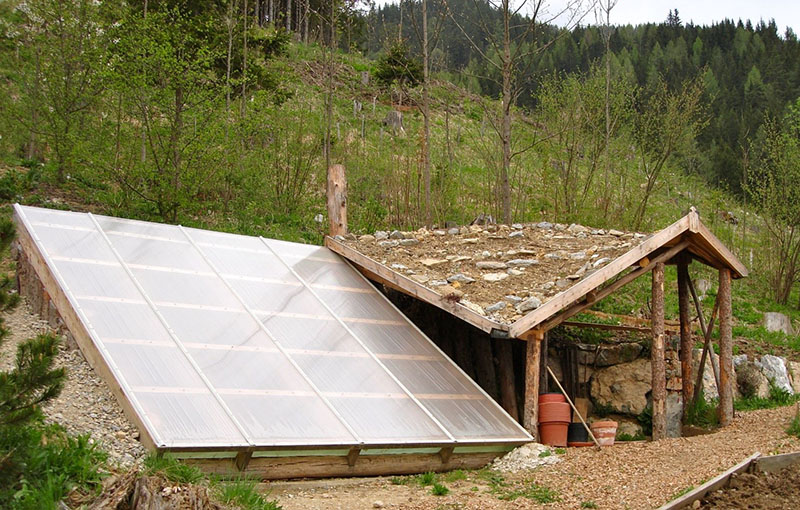

The frame of the greenhouse is made of three types of material:
- wooden bars;
- profiled pipes;
- PVC profile.
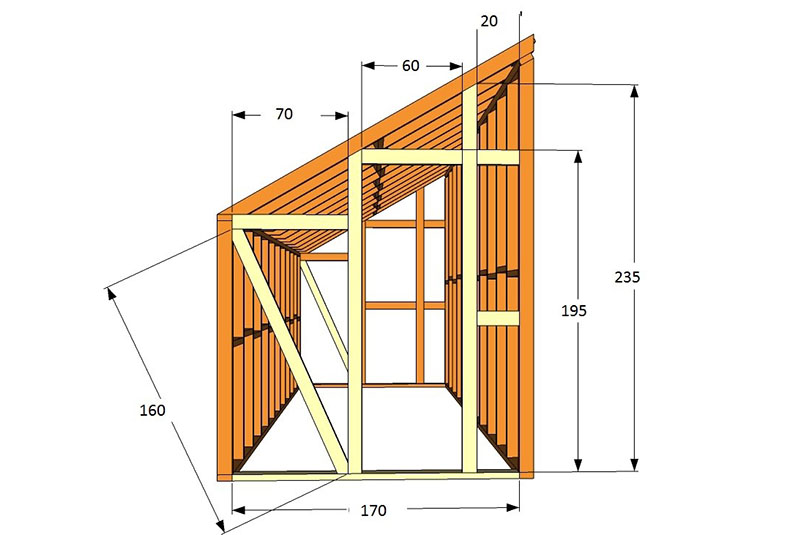
In such a complex process, diagrams and drawings of the building will become assistants to the gardener. The exact dimensions of a sunken single-pitched or double-pitched greenhouse will help the farmer build a reliable and practical building that he will use for decades.
underground greenhouse
It implements the idea of preserving the heat of the earth itself. After all, it is no secret that at a certain depth the average temperature indicator practically does not change throughout the year, remaining virtually unchanged there in winter and summer.
The introduction of this factor in the construction of the greenhouse allows you to get a huge savings in funds that are spent on heating in the winter, such a greenhouse means ease of maintenance and a measured local climate in its internal space.
The underground structures should be oriented east-west according to their ability, in this case one of the sides of the greenhouse will be very sunlit, while the reverse side must be painstakingly insulated with the introduction of mineral wool or polystyrene foam.
Biovegetarian and underground greenhouse
Despite the deepened base, the upper part will still be made according to the general rules for the installation of greenhouses. The owner will also face the question of choosing a rational option for shelter.
Which greenhouse is better - made of polycarbonate, film or glass? The 1st method works best in full-fledged traditional-looking structures, the film, as previously mentioned, is the most affordable option, and glass can become an intermediate version suitable for objects with increased requirements for thermal insulation.
Depending on the scale of the planned greenhouse economy, the dimensions of the recess are determined. The standard parameters of such structures are 1.5 x 2.5 m. With all this, the depth can reach 1 m
It is important to take into account the location of the object on the territory of the site.
Depending on the size of the year-round underground greenhouse, the method of organizing the base for the frame and, accordingly, the parameters of the pits is determined. After arranging niches for pillars, they should be lightly covered with rubble or gravel, and then filled with water.
Bearing elements are installed according to the type of conventional foundation, in other words, using cement mortar. When the mixture completes polymerization, you can proceed to the construction of the frame.
Mixed planting of vegetables in the garden, in the greenhouse, schemes, videos

Check Also
Spring and autumn planting of irises in open ground It is irises that look incredibly beautiful in a garden or in a flower bed from perennial flowers, planting and leaving in ...
Autumn is the time when many trees shed their leaves. Some earlier, others later. The apple tree is no exception. However, our columns, and the neighboring full-fledged apple tree ...
Spathiphyllum - home care. How to care for spathiphyllum (“female happiness”) Flower growers often breed spathiphyllum or “female happiness” - an unpretentious indoor plant, with an interesting ...
Created on 03/12/2013 11:20 am Spider mites on plants. Control measures. Photo. If indoor plants live in your house, then get ready for a long fight with spider mites. …
How to grow a lemon at home from a seed so that it bears fruit? Fans of exotic plants are always wondering how to grow a lemon at home so that the tree is healthy, beautiful and ...
Snapdragon needs no introduction as it is one of the most famous ornamental plants. Moreover, it has such pronounced decorative properties that any ...
from diseases, pests Fruit rot of an apple tree. Affected fruits with conidiospore pads and a mummified fetus. For the control of weeds, diseases and pests of cultivated plants, ...
Natalya Kombarova • 03/02/2018 Rhododendrons are beautiful ornamental plants of the heather family. They are difficult to grow in our climate. Homeland - subtropics, so they love warmth and ...
Money tree (fat woman): home care. The desire of people to enrich themselves is boundless. To do this, they resort to the most unexpected actions, which sometimes plunge others into shock. One…
The term floribunda means gratefully blooming or blooming profusely. This is a variety obtained by crossing hybrid tea and polyanthus. This was first done by the breeder Poulsen in 1924. Then it started...
TO EVERYONE WHO CARES FOR THE FATE OF RUSSIAN AGRICULTURE AND FOOD SECURITY OF RUSSIA. TO EVERYONE WHO WANTS TO WORK ON FERTILITY LANDS WITHOUT NEEDING LOANS. Nikolai Ivanovich Kurdyumov, FERTILITY ...
Fittonia is a herbaceous plant of the acanthus family. It is native to the tropical forests of Peru. Phytonia has about 10 species. Perennial creeping plant with pubescent shoots, which serves ...
Ficuses are the most popular indoor decorative leafy plants. Their large shiny leaves attract both experienced flower growers and beginners in this exciting, but sometimes difficult business. …
Let's continue our conversation about gooseberries. In a previous article, we learned about what a useful gooseberry is, as well as how to choose seedlings and ...
What useful, healing properties does cypress have? Energy of cypress. What is the use of cypress? Healing properties of cypress. Cypress belongs to the cypress family, which has significant differences from other representatives ...
How to care for indoor jasmine at home? + PHOTO Introducing indoor jasmine (sambac, polyanthus) and home care: watering, top dressing, pruning, reproduction, ...
If there is gloxinia in the grower's home collection, planting a tuber is a mandatory step in growing this amazingly beautiful houseplant. When, after mass flowering, decorative ...
Flower POTS for indoor plants: types + TIPS! Introducing pots for indoor flowers. Consider the types of flower pots for indoor plants, their advantages and disadvantages. Let's share…