Why vibration occurs
The reason for the appearance of vibration can be microdefects in parts and moving elements, uneven distribution of weight, all kinds of distortions as a result of wear. In any fan, as well as in a ventilation unit, there are naturally moving elements that, during operation, create noise in the system and vibration. The main sources of vibration are the fan blades, the electric motor and the motion transmission shaft.
When the fan is new and just installed, it creates little noise, runs quietly and without shaking. After a certain period, the parts of the equipment in operation wear out, bend, which leads to a redistribution of the mass of these parts and inhomogeneity. In this case, it becomes clear that vibration effects appear at a fan blade frequency of 1900 rpm.
As mentioned above, vibration is closely related to noise, moreover, in engineering systems, it is vibration that is the structural component of noise and causes its occurrence in more than 60 percent.
This confirms the importance of acoustic calculations in their projects.
GENERAL PROVISIONS
Upon completion of the main general construction works, the construction site is being prepared for the installation of building elements related to the ventilation device: arrangement of platforms and foundations for ventilation equipment, laying of underground channels, openings in walls, ceilings and partitions for the installation of air ducts or ventilation equipment, intake shafts, rooms for placement of supply and exhaust chambers, etc.
Red marks of clean floors are applied on the walls with indelible paint.
The installation of ventilation devices is started when the object is accepted according to the act for installation. Lifting and transport, installation and rigging devices are prepared according to the project for the production of works before installation. Tools and mechanisms are delivered to the construction site the day before the start of work, based on the number of employed workers in the assembly team. Ventilation equipment and air ducts are delivered to the on-site warehouse before the start of work.
Installation of ventilation devices is carried out from components and parts that are pre-prepared and fully equipped. Air ducts associated with process equipment are mounted after installation of process equipment; air ducts for general ventilation - regardless of the process equipment.
GESN 18-05-002-09
Installation of anti-vibration inserts for pressure pumps: 1.6 MPa with a diameter of 300 mm
LOCAL RESOURCE STATEMENT GESN 18-05-002-09
| Name | unit of measurement |
| Installation of anti-vibration inserts for pressure pumps: 1.6 MPa with a diameter of 300 mm | 10 inserts |
| Scope of work | |
| 01. Fitting and welding of flanges on pipe ends. 02. Installation of flexible connectors with flange connection on bolts and gaskets. |
PRICE VALUES
The price lists the direct costs of the work for the period March 2014 for the city of Moscow, which are calculated on the basis of standards 2014 with additions 1 by applying indexes to the prices of the resources used. Indices applied to federal prices 2000.
The following indexes and hourly rates from the "Union of Estimators" were used:
Index to the cost of materials: 7,485
Index to the cost of cars: 11,643
Used hourly rates:
In parentheses are the wages per month at a given hourly rate.
Hourly rate of the 1st category: 130.23 rubles. at one o'clock (22 920) rub. per month.
Hourly rate 2 categories: 141.21 rubles. at one o'clock (24 853) rub. per month.
Hourly rate 3 categories: 154.46 rubles. at one o'clock (27 185) rub. per month.
Hourly rate 4 categories: 174.34 rubles. at one o'clock (30 684) rub. per month.
Hourly rate of the 5th category: 200.84 rubles. at one o'clock (35 348) rub. per month.
Hourly rate of the 6th category: 233.96 rubles. at one o'clock (41 177) rub. per month.
By clicking on this link, you can see this standard calculated in 2000 prices.
The basis for the use of the composition and consumption of materials, machines and labor costs are GESN-2001
LABOR
| № | Name | Unit Change | Labor costs |
| 1 | Labor costs of construction workers Category 3.7 | man-hour | 59,19 |
| 2 | Labor costs of machinists (for reference, included in the cost of EM) | man-hour | 0,55 |
| Total labor costs of workers | man-hour | 59,19 | |
| Wages of workers = 59.19 x 168.38 | Rub. | 9 966,18 | |
| Salary of machinists = 171.54 (for calculating invoices and profits) | Rub. | 171,54 |
How much does it cost to renovate an apartment. The cost of repairing an apartment per hour.
OPERATION OF MACHINES AND MECHANISMS
| № | Cipher | Name | Unit Change | Consumption | St-st unit Rub. | TotalRUB. |
| 1 | 021141 | Truck-mounted cranes when working on other types of construction 10 t | mash.-h | 0,55 | 1303,9 | 717,15 |
| 2 | 040502 | Manual Arc Welding Machines (DC) | mash.-h | 15,54 | 94,31 | 1 465,58 |
| 3 | 400001 | Cars onboard, carrying capacity up to 5 tons | mash.-h | 0,63 | 1014,92 | 639,40 |
| Total | Rub. | 2 822,12 |
CONSUMPTION OF MATERIALS
| № | Cipher | Name | Unit Change | Consumption | St-st unit Rub. | TotalRUB. |
| 1 | 101-1522 | Electrodes with a diameter of 5 mm E42A | T | 0,023 | 77559,57 | 1 783,87 |
| 2 | 101-2576 | Bolts with nuts and washers for sanitary works with a diameter of 16 mm | T | 0,0224 | 111002,55 | 2 486,46 |
| 3 | 301-1156 | Vibration-isolating inserts for pressure 1.6 MPa (16 kgf/cm2), diameter 300 mm | set | 10 | 12552,34 | 125 523,40 |
| 4 | 507-1008 | Flat welded steel flanges made of steel Vst3sp2, Vst3sp3, pressure 1.6 MPa (16 kgf/cm2), diameter 300 mm | PC. | 10 | 3511,74 | 35 117,40 |
| 5 | 509-0971 | Gaskets made of paronite grade PMB, 1 mm thick, 300 mm in diameter | 1000 pcs. | 0,02 | 114301,19 | 2 286,02 |
| Total | Rub. | 167 197,15 |
TOTAL RESOURCES: RUB 170,019.27
TOTAL PRICED: RUB 179,985.45
You can see this standard calculated in 2000 prices. by following this link
The price was compiled according to the standards of GESN-2001 edition 2014 with additions 1 in prices March 2014.To determine the intermediate and final values of the price, the DefSmeta program was used
Estimate for the construction of a house, for the repair and decoration of apartments - the program DefSmeta
Program rentalThe program provides an assistant who will turn the budgeting into a game.
Causes of vibration
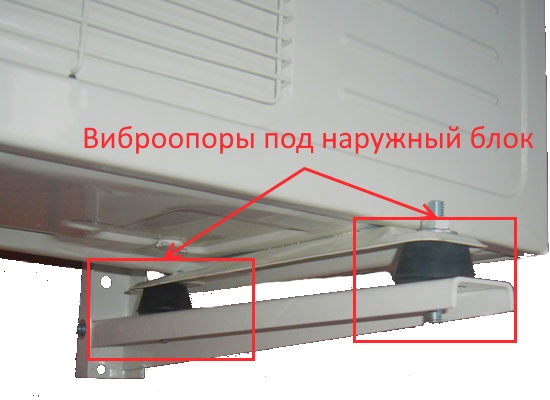

- unbalanced fan impeller;
- loose bolts on the brackets;
- mounting the unit on a weak surface;
- lack of vibration support for the air conditioner.
An increased level of vibration accompanies the work of not only budgetary, but also expensive models. If it is caused by defects in the installation of the outdoor unit, they can be corrected.
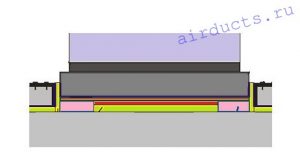
Types of vibration isolators
The main types of methods for reducing vibrations from ventilation installations:
- vibration mounts;
- shock absorbers;
- elastic vibration isolating materials.
These elements are also used in tandem with floating slabs and other design solutions. In addition, an integral element is a vibration-isolating foundation for equipment.
Vibration mounts
Vibration mounts perform several functions at the same time: they can act as bolts, brackets, fasteners, supports, dampers and, in fact, vibration isolators. The types of vibration mounts are rubber, metal-rubber, also with different design variations: cylindrical, vibration mounts with a plate, “leg” type supports, etc. Such a variety indicates a convenient installation of these elements on the fan frame or ventilation unit.
When choosing this method of reducing the vibration effect, it should be taken into account that such components are most effective in terms of vibration isolation at fan speeds of about 1800 rpm and higher. In other ranges, the efficiency of using rubber vibration mounts drops significantly.
Vibrosprings
Steel springs (shock absorbers) are used in cases with industrial fans with a speed of 1200-1500 rpm. This is due to the fact that such devices pick up the operating frequency with a certain period of time, not immediately, and this creates a fading buildup. The principle of their work is simple and clear. At the same time, their fastening is also not difficult, and their use is possible in many variations.
Vibration Reduction Materials
Another way that is often resorted to is the complete coverage of the foundation with rolled vibration-isolating material. Such materials are made from special porous substances, which are based on polyurethane or elastomer. Thanks to modern production technologies, such “carpets” are both elastic (resistant to heavy loads) and at the same time have a cellular structure, which allows damping vibration effects from ventilation equipment.
The foundation is covered with this material and the ventilation unit is installed from above directly on the "carpet". Due to their properties, such as both rigidity and porosity, elastomers are used not only in the field of ventilation.
Conclusion
The role of damping noise and vibration oscillations in microclimate systems is obvious. If silencers can cope with noise, then in order to remove vibration effects, you will have to resort to more time-consuming methods with lower efficiency. However, with the correct choice of vibration protection methods, it is quite possible to achieve the maximum effect.
Recent trends say that the combination of vibration absorbing materials with vibration springs or other components is most useful.
If you want to measure the actual performance of noise and vibration in rooms, use special devices.
We hope this article was helpful to you. Good luck with your projects!
—
CAUTION 1
|
оÑизонÑалÑнÑй ÑекалÑнÑй наÑÐ¾Ñ Ð¤Ð450 /.| еÑÑикалÑнÑй ÑекалÑнÑй наÑоÑ. a |
поÑа наÑоÑа вÑпоР»Ð½ÐμнР° в виÐ'Ðμ кÑонÑÑÐμйнР°, к Ñл Ð ° нÑÑ ÐºÐ¾ÑоÑого пÑикÑÐμпР»Ðμн коÑпÑÑ ÑпÑоÑÐμнной ÑоÑÐ¼Ñ Ñо вÑÐ ° ÑÑвР° ÑÑим и нР° гнеÑаÑелÑнÑм
a
|
анализаÑионнÑй веÑикалÑнÑй наÑÐ¾Ñ 4ФР- 5м. a |
поÑой наÑоÑа Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð δ °ÑелÑнÑм паÑÑÑбками. RUME ENERGENCE ENERGENCE RUNEMENT ±ÑÑÑ ÑÑÑановлен под Ñглом 90 в ÑÑбÑÑ ÑÑоÑонÑ.
a
Ðлина опоÑÑ Ð½Ð°ÑоÑа Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ поÑадиÑÑна опоÑÑ.
a
|
Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ññðμμðð𲲺º'ðððññμμμ''ð½½ ñ ñ ñð¸ðð¾ ² ñ ñ ñ ñð¸ðð¾²². a |
СÑеÑиÑеÑкиÐμ опоÑÐ°Ñ Ð½Ð°ÑоÑов, моÑнÑÑ Ð²ÐμнÑиР»ÑÑоÑов, Ð'ÑмоÑоÑов, л ÐμÑопиР»ÑнÑÑ ÑÐ ° м, гÑоÑоÑов, ÑÐμÐ'ÑкÑоÑов, гÑÐμÐ ± нÑÑ Ð²Ð ° л ов, пÑокР° ÑнÑÑ ÑÑÐ ° нов и Ð'ñññññññññññññññññññññññññññññññññ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ¶Ð½Ð° неÑооÑноÑÑÑ Ð¿Ð¾ÑадоÑнÑÑ Ð¼ÐµÑÑ.
a
92 опоÑа наÑоÑа, Α Ð Ð Ð Ð μñðññððμμ½½ðññññððμμμ½½ððññð ° ° м / ñ2, ññÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ññððμ. о Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ² »Ðµ. СР»ÐμÐ'овР° ÑÐμл Ñно, имÐμнно Ñ Ð½Ðμго нÐμоР± ÑоÐ'имо нР° ÑинР° ÑÑ Ð¾ÑÐμÑÐμÐ'ной пÑоÑиР»Ð ° кÑиÑÐμÑкий: - ÑÐμÐ¼Ð¾Ð½Ñ Ð°Ð³ÑегаÑа.
a
|
ÐÐ ° кÑимР° Ð »ÑнÑÐμ Ð · нР° ÑÐμÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ð¾ÐºÑÐ ° внÑÑ ÑÑовнÐμй кол ÐμÐ ± Ð ° ÑÐμÐ »Ñной ÑкоÑоÑÑи Ð'л Ñ ÑÑÐ ° нÐ'Ð ° ÑÑнÑÑ Ð¿Ð ° ÑовÑÑ Ð½Ð ° ÑоÑов. a |
Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ РРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРопоÑÐ°Ñ Ð½Ð°ÑоÑа Ð ² Ðμн½ððððððºððð½½½½ð¼¼¼¼½½½½½½¼¼¼½½¾¾ð½½½½ðñ½½½¾ð𸸽¸¸ððððð ° ° ° ° Ð
a
Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μl , опоÑÑ Ð½Ð°ÑоÑа, Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐ Ð Ð Ð ÐμÐμμñ½½ °μμμμμμμμμμμ
a
|
100% a |
ÐÑÑокиÐμ ÑÑÐμÐ ± овР° Ð½Ð¸Ñ Ðº ÑÐμÑÑÑÑÑ ÐÐ|Ð, коÑоÑÑй в Ð · нР° ÑиÑÐμÐ »Ñной мÐμÑÐμ Ð · Ð ° виÑÐ¸Ñ Ð¾Ñ ÑÐ ° Ð ± оÑоÑпоÑоР± ноÑÑи Ð¾Ð¿Ð¾Ñ Ð½Ð°ÑоÑа, Ð ° ÑÐ ° кжÐμ нÐμÐ'оÑÑÐ ° ÑоÑнР° Ñ ÑоÑноÑÑÑ ÑÐμоÑÐμÑиÑÐμÑкого ÑÐ ° ÑÑÐμÑÐ ° Ð'ÐμÐ »Ð ° ÑÑ Ð¾Ð ± ÑÐ · Ð ° ÑÐμл ÑнÑм пÑи пÑовÐμÐ'ÐμниР¸ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ðμ дейÑÑвÑÑÑÐ¸Ñ Ð½Ð° опоÑÑ.
a
Equipment Ð ÐμвРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРδÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ² опоÑÑ Ð½Ð°ÑоÑа нвðð''ññ¸¸¸¸ððÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ² Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ° Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð - 0 30 Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð μ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð δ его коÑпÑÑа.
a
ÐÐ ° ÑÐ¾Ñ Ð²ÑоÑого конÑÑÑÐ ° (ÑиÑ. 5.41) ÑÐ ° ÑпоР»Ð¾Ð¶Ðμн в вÐμÑÑнÐμй ÑоÑкÐμ пÐμÑл и в Ð ± ÑÑÐμÑной ÐμмкоÑÑи 4, вÐμÑÑний ÑÐ »Ð ° нÐμÑ ÐºÐ¾ÑоÑой Ñл ÑÐ¶Ð¸Ñ Ð¾Ð¿Ð¾Ñой наÑоÑа. Ð ¥ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμñÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð ÐμñÐ Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð Ð ² РРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРРн °ÑоÑÐ°Ñ Ð¿ÐµÑвого конÑÑÑа.
a