Among different types of batteries, bimetallic radiators occupy a special place. The combination of the positive characteristics of two metals - aluminum and steel - allows you to achieve outstanding strength and heat transfer. Consider the device and features of these devices and get acquainted with the rules for choosing and connecting bimetallic batteries.
The device and properties of a bimetallic radiator
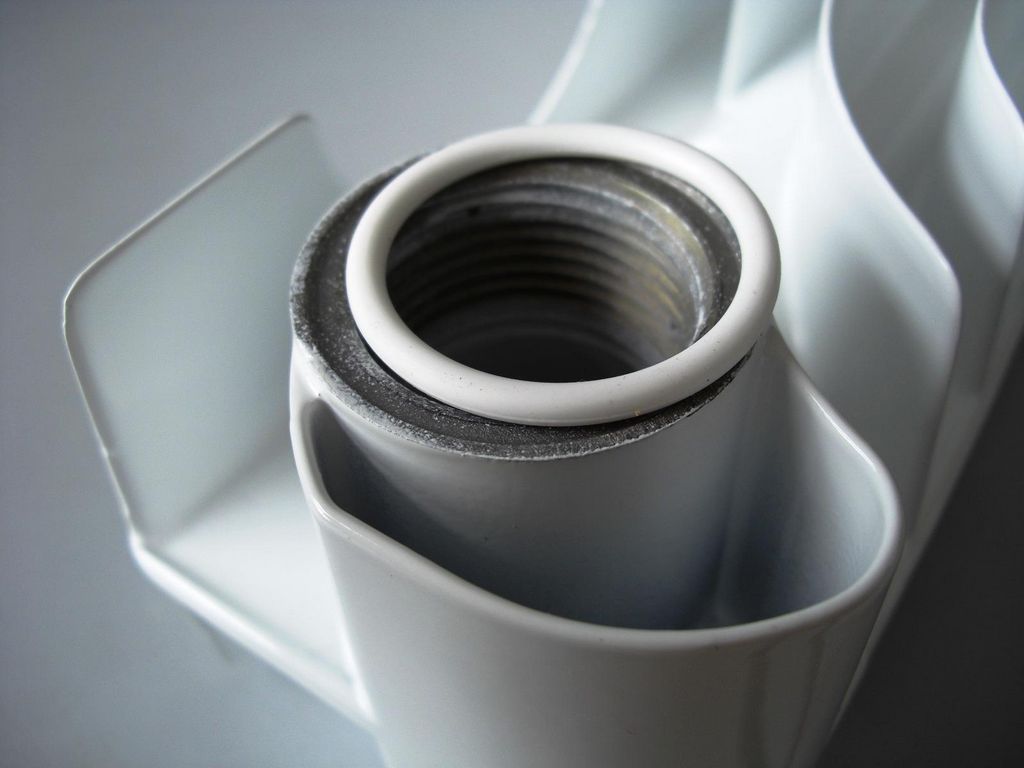
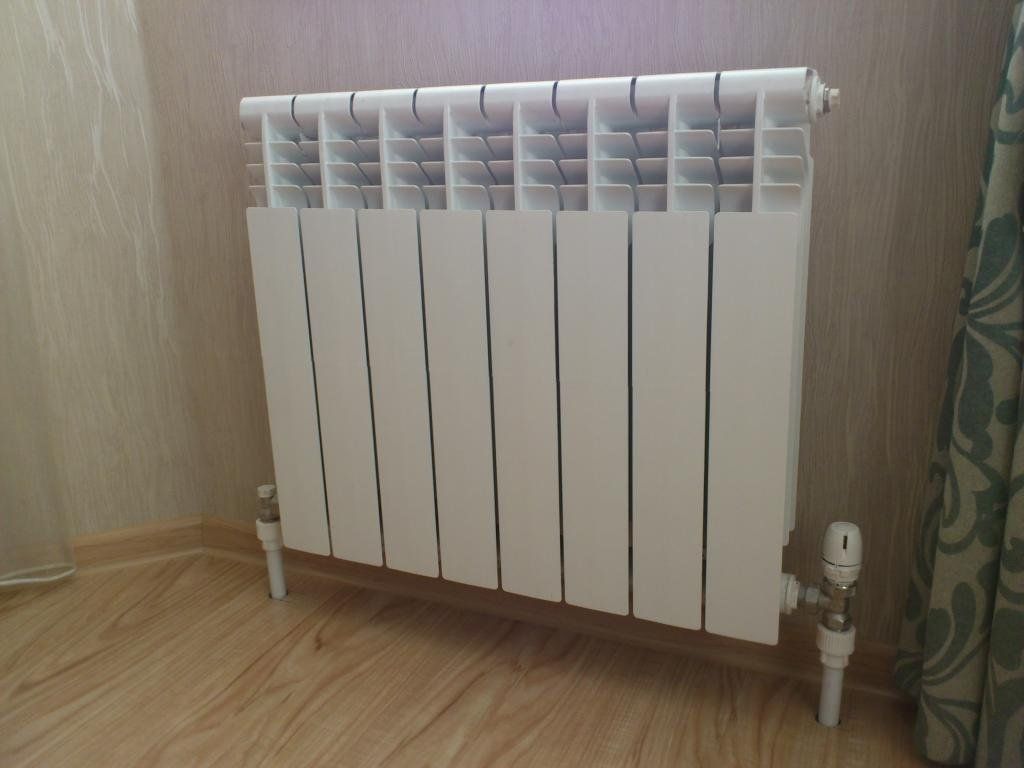
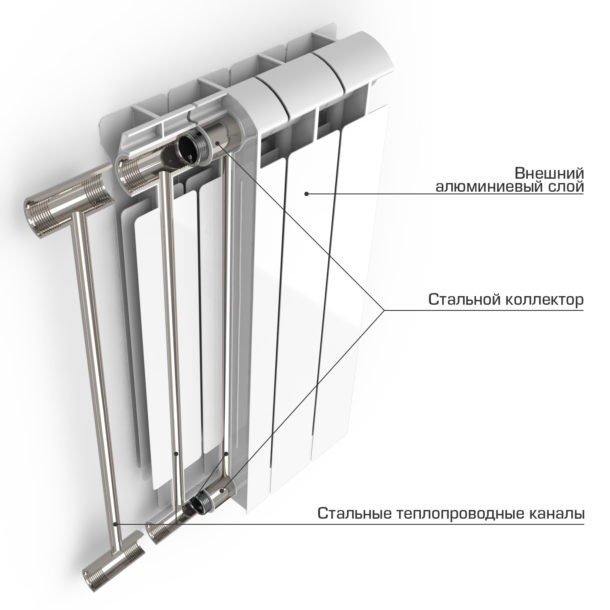
Bimetallic radiators have a combined structure - their inner part, in contact with the coolant, is made of steel; the outer part, which is responsible for the quality of heat transfer, is made of aluminum. This distribution of materials allows you to maximize the positive qualities of both metals, neutralizing their shortcomings.
From aluminum, bimetallic heating radiators received:
- high thermal inertia;
- excellent heat dissipation;
- fast response to battery temperature regulation.
The steel core endowed the batteries with the following characteristics:
- resistance to pressure drops and water hammer;
- resistance to electrochemical influences;
- undemanding to the quality of the coolant;
- durability.
Unlike aluminum radiators, bimetallic batteries perfectly tolerate the conditions of centralized heating systems.
In addition to these advantages, the following positive characteristics of bimetal batteries can be mentioned:
- high limit pressure threshold - 30–40 atmospheres;
- high power with small dimensions;
- efficiency due to the small cross section of the channels;
- the convenience of the design, which allows you to quickly remove individual sections of the device for repair;
- an easily calculated number of sections required for high-quality heating of the room.
- long service life - up to 25 years;
- modern and attractive appearance.
All these advantages are possessed by bimetallic radiators of the STOUT brand. Heating devices are produced at the largest Russian plant "RIFAR", adapted specifically for the operating conditions in our country. Each product undergoes the strictest control at all stages of the technological process of production. The radiator is pressed twice with high pressure - the first time before painting, the second time - after. This guarantees 100% reliability of each instrument.
The available number of sections is from 4 to 14, efficient operation with a coolant up to 135 ° C, withstand pressure up to 100 atmospheres. A well-thought-out logistics system, cooperation with reliable suppliers and partners, as well as a guarantee and insurance directly from the manufacturer make the STOUT brand the best choice.
Tip: since the outwardly bimetallic sectional radiator is practically indistinguishable from aluminum, you can understand which radiator is in front of you, first of all, by weight. A bimetallic device with a steel core is much heavier than an aluminum counterpart.
Possible problems during operation
Bimetal devices have a large number of advantages. Which of their features can be attributed to the disadvantages?
- Despite the possibility of using bimetallic batteries in a system with any coolant, the low quality of the latter adversely affects the service life of the device.
- A different expansion coefficient for the metals present in the battery design can eventually lead to instability of heat transfer, a decrease in the strength of the device.
- The use of low quality coolant in the system can lead to clogging of channels, corrosion, and deterioration of heat transfer.
Design features
Bimetallic batteries can have two types of designs.
- Cheaper models are distinguished by the presence of a steel core only in vertical channels.Such radiators are sometimes called semi-bimetallic. Despite the fact that they are significantly superior in their characteristics to aluminum devices, they still do not have sufficient strength inherent in full-fledged bimetallic batteries.
- These bimetal heaters have a solid steel frame, which is poured under pressure with an aluminum alloy during the production process.
Separately, we can mention copper-aluminum radiators, which are superior in their characteristics to all existing types of batteries. They have excellent corrosion resistance, excellent heat dissipation and long service life, but high cost has prevented them from being widely adopted.
Battery dimensions
The dimensions of the device matter, because with the necessary power parameters, it must fit in a niche under the window. What sizes can bimetallic batteries have?
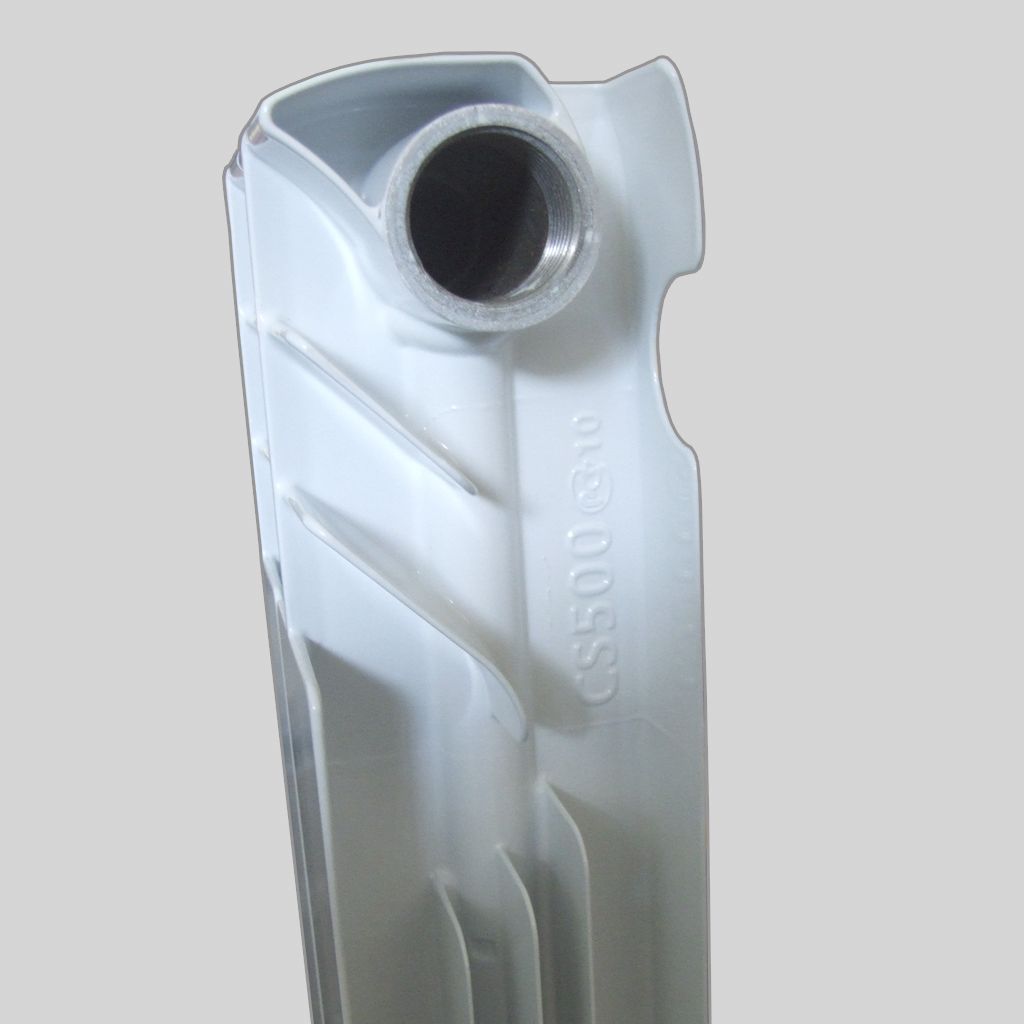
Bimetallic heating radiators are characterized by standard height dimensions. The device has a marking that indicates the center distance of the device - 200, 350 or 500 mm.
Important! When choosing a radiator, it must be taken into account that the center distance is the gap between the inlet and outlet holes of the battery, which does not correspond to the entire height of the case. To find out the actual height of the device, you need to add 80 mm to the value of the center distance.
The total height of the device with different markings:
- marking 200 - real height 280 mm;
- 350 - device height 430 mm;
- 500 - height 580 mm.
The width of the heating device will depend on the number of sections, which is calculated based on the parameters of the room and the power of a separate section.
Attention! When choosing the size of the radiator, do not forget that, in accordance with technical standards, the device must be installed at a distance of at least 10 cm from the windowsill and 6 cm from the floor.
Calculation of the number of sections of bimetallic batteries
How many sections of a bimetal radiator can fully heat a room? The calculation of bimetallic radiators requires knowledge of two parameters:
- how many square meters is the area of the room;
- power of one section of the device.
According to building codes, approximately 100 watts of power is required to heat 1 square meter of living space. To find out the total power required for space heating, the area value is multiplied by 100. The result is divided by the power of the section of the selected radiator.
We will find out how many sections of the device will be needed for a room of 25 square meters. m. when using a bimetallic device, the power of one section of which is 170 watts.
- 25 x 100 \u003d 2500 W - the required power.
- 2500: 170 \u003d 14.7 - rounded up to 15 - we get the required number of sections.
Given the fact that system parameters may change due to equipment wear or blockages, a 20% margin can be added. More sections may be needed to heat a corner apartment, a room with a large number of windows, high ceilings. For regions with a harsh climate, the required number of sections will be 1.5–2 times more.
Important! Since batteries with more than 10 sections do not warm up efficiently enough, it is advisable to install several radiators with fewer sections.
What to look for when choosing
Let's find out what characteristics of a bimetallic radiator you need to study when buying.
- Operating pressure. A bimetallic sectional radiator must withstand a constant load of 15 atmospheres; for a centralized heating system, it is better to choose a device with a maximum operating pressure.
- The rated power of the section is needed to calculate their number.
- Dimensions. For standard window sills with a height of 80 cm, a model with a center distance of 500 mm is suitable.
- The thickness of the steel tabs.The thicker the walls, the stronger the device and the longer it will last.
- Price. Bimetallic radiators are at least 20% more expensive than aluminum ones. If the price is lower, most likely it is a "semi-bimetal" of low quality.
Installation of radiators
Which pipes are best for bimetallic batteries? Experienced craftsmen advise combining bimetallic heating radiators with reinforced polypropylene pipes. It is allowed to use steel and metal-plastic pipes on collet joints, however, in this case, you need to be prepared for leaks and blockages. Due to its reliability, the optimal connection method when connecting is the spot welding method.
Traditionally, it is customary to place the radiator under the window strictly in the center. This allows the device to create a thermal curtain that creates an obstacle for the penetration of cold air flows through the window.
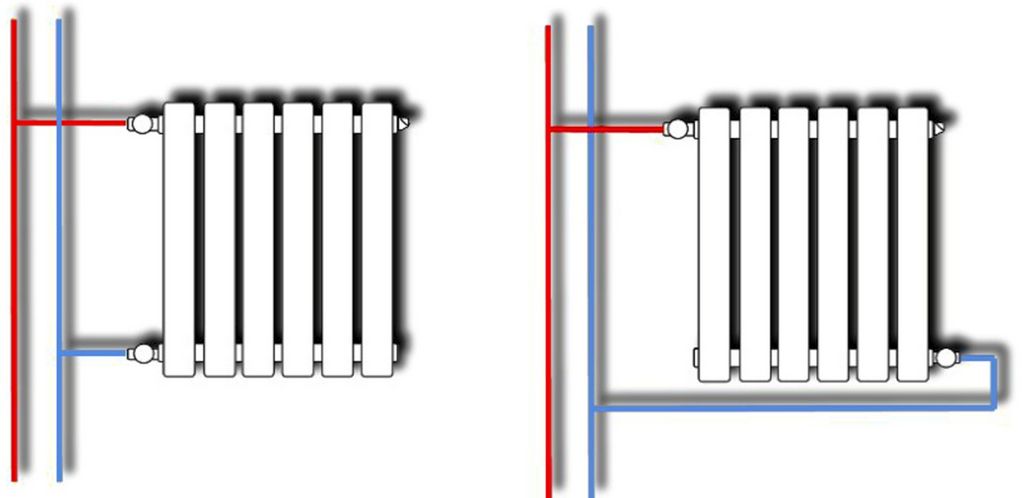
What are the options for connecting a bimetallic radiator?
- Side or one-way connection has maximum efficiency, but only with a small number of sections (up to 12 pieces). With a larger number of sections, the section remote from the supply pipe will not warm up well.
- The bottom connection is less efficient in terms of heat dissipation and is used only in case of a specific system configuration.
- Diagonal connection is used for radiators with 12 or more sections and allows you to achieve uniform heating of the device.
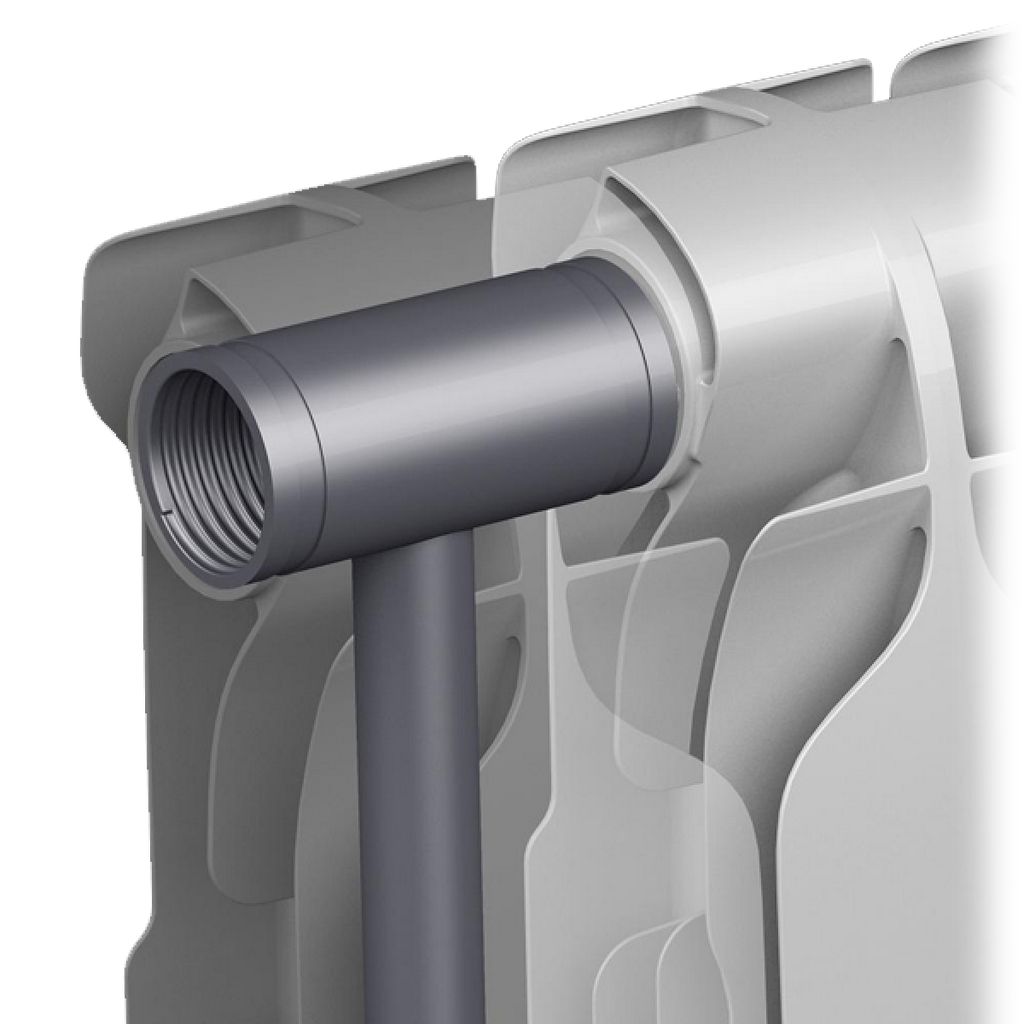
Before connecting to each bimetallic battery, an air bleed valve or a Mayevsky valve, as well as adapters for connecting to pipes, must be installed.
Radiator connection procedure:
- After dismantling the old equipment, using the building level, marking is made for the installation of a new device, holes for the brackets are drilled.
- Brackets attached to the wall with dowels and cement mortar.
- The battery is connected to the supply lines, a faucet or thermostat is placed at the junction.
Important! Since the bimetallic sectional radiator has narrow internal channels that are very easily clogged with debris from the heating system, it is imperative to install a coarse filter before connecting to each battery.