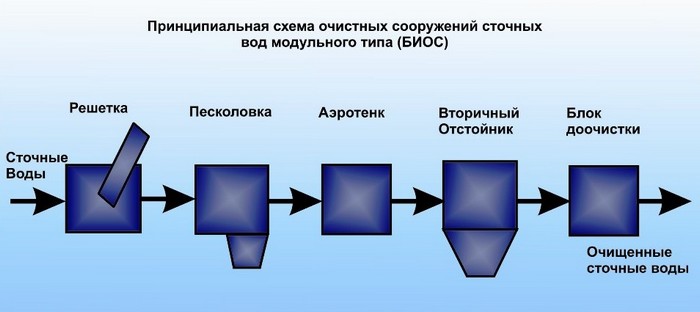
Basic cleansing techniques
 Technological processes for the purification of domestic sewage are very effective. Clarified water after undergoing VOC treatment can be reused for garden irrigation or technical needs.
Technological processes for the purification of domestic sewage are very effective. Clarified water after undergoing VOC treatment can be reused for garden irrigation or technical needs.
The most commonly used methods for cleaning drain liquids are:
- biological;
- mechanical;
- physical and chemical.
For clarification of household and domestic effluents, due to simplicity and efficiency, the first two cleaning methods are usually used.
Mechanical Methods
 During the application of any methods of clarification of contaminated liquids, at the initial stage, methods of a mechanical type are usually used, aimed at separating coarse impurities. The technology of mechanical purification is the simplest and most affordable. For its implementation, the contaminated liquid:
During the application of any methods of clarification of contaminated liquids, at the initial stage, methods of a mechanical type are usually used, aimed at separating coarse impurities. The technology of mechanical purification is the simplest and most affordable. For its implementation, the contaminated liquid:
- uphold;
- filter;
- filter.
The process occurs through the use of coarse filters or in settling facilities by settling heavy components under the influence of gravitational forces. Mechanical cleaning removes approximately 60-70 percent of contaminants from domestic wastewater.
During settling, it is possible to eliminate most of the oil-containing impurities that come through with industrial effluents. Mechanical cleaning is used by owners of car washes and oil refineries.
Clean mechanically and storm drains. For this, sand traps are attached to the highways. The composition of precipitation that is collected from the surface of the earth contains:
- soil impurities;
- branches;
- foliage;
- pebble inclusions.
Sand traps trap large debris, preventing it from clogging storm drains.
Biotreatment methods
 The scheme of operation of a septic tank with aeration
The scheme of operation of a septic tank with aeration
The technological process consists in the use of aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms capable of processing complex organic components in sewage. In this case, they are decomposed into gas and water.
Aerobic microorganisms need oxygen to live. To increase the efficiency of purification, you will need to create suitable conditions by installing an aeration system.
Anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen, so they are able to live in airtight containers. Their by-product is methane. Installations in which purification is carried out with the help of such microorganisms are equipped with a ventilation system.
2 Measures for the sanitary protection of water bodies
1. Legislative
2.
Organization of sanitary protection zones
3.
The device of treatment facilities for
processing of household wastewater.
Industrial waste is usually
cleaned at the factory.
Substances
wastewater are in different
physical state (solid, dispersed,
colloidal, liquid phase) and this allows
break down the entire cleaning process into
several stages:
a)
mechanical cleaning - isolation
suspended solids;
b)
biological treatment - mineralization
organic substances found in
colloidal and dissolved state;
v)
disinfection;
G)
biological ponds.
Types and principle of operation of VOC
 Local treatment facilities for household wastewater contribute to the processing of waste into a relatively safe liquid substance that can be used for technical needs or drained into the soil.
Local treatment facilities for household wastewater contribute to the processing of waste into a relatively safe liquid substance that can be used for technical needs or drained into the soil.
VOCs that are used for bioremediation:
- Septic tanks are sealed chambers into which sewage is discharged. Anaerobic microorganisms live there, processing sediment and contributing to water purification. Liquid after a septic tank requires additional purification, for example, in a filtration well, before it is discharged into a reservoir or soil.
- Septic devices with biological filters. The principle of operation of the biofilter is to seep water through the thickness of coarse-grained material (crushed stone or sand), which is covered with a film of special bacteria. According to this scheme, filtration fields and well installations work. When effluents pass through a biological filter, due to microorganisms, the processes of oxidation and decomposition of organic components are activated.
- Bioponds are artificial water bodies with a depth not exceeding a meter. In them, the contaminated liquid after mechanical cleaning is processed due to the action of bacteria. To accelerate the activity of microorganisms, it is necessary to warm the reservoirs with sunlight: in the Central Russian winter, these ponds have low productivity and are almost never used. Strengthening the activity of aerobic bacteria is also carried out through forced aeration.
- Aerotanks are hermetically sealed installations in which forced aeration is used. In order to process the liquid faster and more efficiently, activated sludge is used, which contains the necessary microorganisms in its composition.
- Deep cleaning stations. The facilities are used for complex clarification of wastewater with maximum effect. After passing through them, the liquid becomes purified up to 98%. Water is driven through several different filters and treatment devices.
Membrane bioreactors are increasingly being used to clarify wastewater in enterprises and residential complexes. It combines biological treatment with activated sludge and mechanical membrane filtration. The membrane module is used to separate the sludge mass and is an alternative to the sedimentation of this substance in classical biological treatment plants.
Advantages of bioreactors:
- compact dimensions with high productivity;
- use of old cleaning complexes when upgrading equipment;
- the ability to work with a significant accumulation of activated sludge.
There are two types of biological reactors: with internal and external membrane placement. In the second option, the filter is isolated from the process chambers, and it is necessary to install intermediate pumping equipment.
mechanical cleaning
Mechanical
cleaning takes place on a series of sequentially
located structures, construction
who are destined for detention
different fractions of suspensions.
1.
Lattice
serves to trap large debris
- rags, paper, cotton. She represents
a series of parallel metal
rods fastened together and placed
vertically in the supply manifold
water to sewage treatment plants. gaps
between the bars are 16-70 mm. Removal
waste at large facilities
mechanical rakes. Further dregs
fed into the crusher and then into
digesters or processing is carried out
method adopted for neutralization
solid waste (composting,
plowing, biothermal chambers).
At small stations, they are harvested by hand
rake. Waste contains a lot of organic
substances that easily rot, they
not epidemically safe
and are in need of decontamination. Meaning
grids: frees sediment, falling out
in sedimentation tanks, from coarse impurities,
makes it more uniform
and facilitates its disposal,
prevents clogging of pumps and
sewage pipes
and sediment.
2.
sand traps
designed to hold heavy
mineral suspension (sand) before entering
waste water into a sump. Principle of operation:
the flow of waste water is given a speed
15-70 cm / s is enough to
light organic suspensions did not settle
and yet too small to
prevent heavy sand from settling.
Passing temperature not less than 70C.
Sand traps are settling tanks.
Types of sand traps: 1) vertical - with
circular motion of water 2) horizontal
— with rectilinear water movement 3)
aerated - pass through the bottom
compressed air for cleaning
sand from flakes of organic suspension.
Horizontal sand traps are different
simplicity of the device and high
efficiency. They have 2-3 sections,
each of which can work
on one's own. This allows you to turn off
1-2 sections for low water flow, e.g.
at night. Vertical sand traps more
compact and efficient. Flaw -
construction volume is less than
horizontal, fine sand
don't linger
3.
Settling tanks
—
with sludge treatment
—
without sludge treatment
Settling tanks
with sludge treatment
Are characterized
a large volume of the silt part for
long stay of sediment up to
the end of the fermentation process,
seals of detained suspended
substances (septic tank, two-tier sump,
clarifier-decomposer).
Settling tanks
without sludge treatment
a)
vertical sump - cylinder with
cone-shaped bottom, water enters
through the central pipe and then moves
by the cesspool.
b)
horizontal sump - attached
slope opposite to the flow of the liquid, so that
the sediment slipped or moved with a scraper,
and then accumulated in the silt space.
Depth 1.5-2 m, speed - 7 mm / s.
v)
radial settler - round shape
with a uniform slope of the bottom towards the center,
diameter from 16 to 40 m depth of water layer –
2-2.5 m. Water moves at a decreasing speed
from the center, where it flows from below to
periphery, where it overflows through
holes in the board in the outer circular
gutter. The sediment is removed with scrapers,
attached to a slowly rotating
form. Stay temperature 1.5 hours,
movement speed 7 mm/s. Efficiency
is 60%. The precipitate is converted to
digester where it is fermented.
Methane tanks
- closed tanks that have
at the top of the cap for collecting gas
(70% methane and 30% carbon monoxide), which
used as fuel in
boiler room of treatment facilities. Removal
digested and fresh sludge supply
produced by special pipes.
Sludge is heated hot
steam (100-112C).
There are 2 types of fermentation in digesters:
mesophilic (t-33C)
and thermophilic (t-53C).
Duration of fermentation is 10-20 days. At
thermophilic fermentation lose
viability of helminth eggs and
pathogenic microorganisms of the intestinal
groups. Drying of digested sludge
carried out on sludge sites.
Sites are divided into depth maps
0.7-1m, have a waterproof base
and drainage system for water supply. If
danger of groundwater pollution
ruled out, then the bottom can be natural
priming. The silt is distributed in a layer of 20-70 cm, it
dries up, the water is sent to the biological
cleaning from fresh sludge, or chlorination.
The sludge is used as fertilizer or
sent for biothermal treatment
(composting).
Cleaning rates
Effluent treatment facilities must provide the required degree of purification. The strictest standards exist only for wastewater generated from industrial enterprises. At the same time, the norms stipulate the permissible concentration in purified water of each specific substance.
For domestic sewage, such strict requirements are not imposed. However, the rules still prohibit dumping households. drains without treatment into open water bodies or soil. For this, homeowners can be held accountable.
For sewage of household origin, the concentration of certain substances is regulated by law only if they are discharged into a reservoir.The same applies to wastewater discharged after treatment to the relief, because in this case, sooner or later they will still fall into the reservoir.
There are no such strict requirements for effluents discharged into the ground after the treatment plant, since in this case the owner of the house himself is interested in thoroughly cleaning the liquid. Otherwise, he risks worsening the condition of his site to such an extent that it becomes impossible to live in the house.