Indicators affecting the calculation of the number of sections
Choosing a radiator for a particular room, you need to take into account the technical features. For example, the calculation will be different for a corner and non-corner room, for a room with different ceiling heights and different window sizes, etc. The most important parameters that are taken into account when determining the required radiator power are:
- the area of your premises;
- floor;
- ceiling height (above or below three meters);
- location (corner or non-corner room, room in a private house);
- whether the heating battery will be the main heating device;
- there is a fireplace in the room, air conditioning.
Other important features must be taken into account. How many windows are in the room? What size are they, and what kind of windows are they (wooden; double-glazed windows for 1, 2 or 3 glasses)? Was additional wall insulation done and what kind (internal, external)? In a private house, the presence of an attic and how insulated it is, and so on, matters.
Pig-iron radiators Conner (China)
According to SNIP, 41 W of thermal energy is needed per 1 cubic meter of space. You can take into account not the volume, but the area of \u200b\u200bthe room. For 10 sq.m of a standard room with one door and one window, one door and an outer wall will need the following heat output of the radiator:
- 1 kW for a room with one window and an outer wall;
- 1.2 kW if it has one window and two outer walls (corner room);
- 1.3 kW for corner rooms with two windows.
In reality, one kilowatt of thermal energy heats:
- In the premises of brick houses with a wall thickness of one and a half to two bricks, or from timber and log houses (the area of \u200b\u200bwindows and doors is up to 15%; insulation of walls, roofs and attics) - 20-25 square meters. m
- In corner rooms with walls made of timber or brick of at least one brick (the area of windows and doors is up to 25%; insulation) - 14-18 square meters. m
- In the premises of panel houses with internal cladding and a heat-insulated roof (as well as in the rooms of an insulated cottage) - 8-12 square meters. m
- In a "residential trailer" (wooden or panel house with minimal insulation) - 5-7 square meters. m.
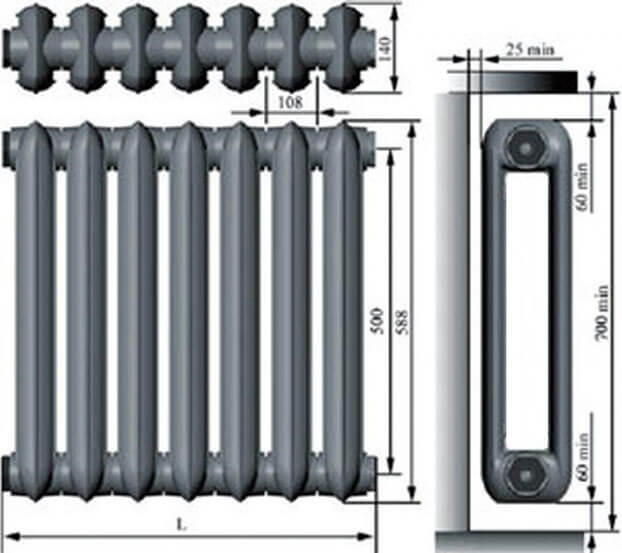
Dimensions and weight of cast iron radiators
The parameters of cast iron radiators using the example of the domestic product MS-140 are as follows:
- height - 59 centimeters;
- section width - 9.3 centimeters;
- section depth - 14 centimeters;
- section capacity - 1.4 liters;
- weight - 7 kilograms;
- section power 160 watts.
On the part of property owners, one can hear complaints that it is quite difficult to carry and install radiators consisting of 10 sections, the weight of which reaches 70 kilograms, but it is good that such work is done in an apartment or house once, so the dimensions of cast-iron heating radiators must be correctly calculated.
Since the amount of coolant in such a battery is only 14 liters, when thermal energy comes from the boiler of an autonomous heating system, then you will have to pay for extra kilowatts of electricity or cubic meters of gas.
Selection, installation and operation of cast iron heating batteries
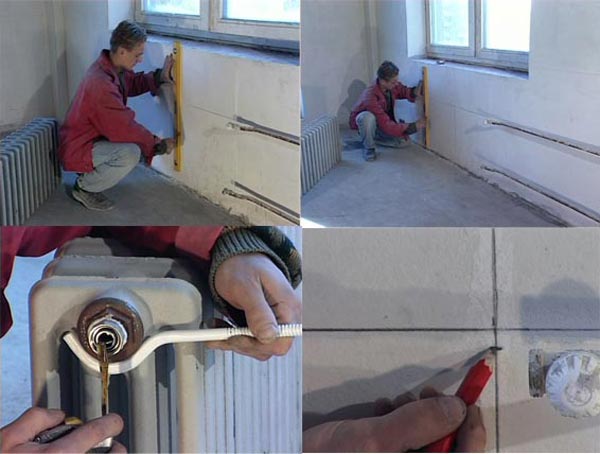
Stages of mounting the radiator to the heating system.
If the choice (lightweight or cast iron radiators) is made in favor of the latter, then it is necessary to calculate the number of batteries in the room and the number of radiators in each of them. To do this, you need to know the technical characteristics of a particular model, first of all, the amount of heat generated. Another important task is to determine the place for installing batteries and the method of mounting: wall or floor. Based on this, a specific sample is selected. Almost most of the cast-iron heating radiators photos can be found on the Internet. Cast iron radiators have a different external volume, including they can be quite voluminous or completely flat, and have different heights and widths.
A common place in a living room where a battery can be installed is a niche located under the window sill. Its parameters dictate the size of the battery. The technical characteristics of this battery should provide 1 kW of heat per 10 m² of room area.Moreover, if the volume of the room is larger than usual due to the high ceiling, or it has a second window, then 1.2 kW of heat is needed for the same area. If the room occupies a corner position, it makes sense to add a few extra sections, since there is more heat loss there.
The mounting method dictates both the weight of the battery and the strength of the wall near which it is placed. If it is hung on the wall, then it is worth remembering that at least three brackets are required for each of the batteries. Today, floor mounts are often used for cast iron batteries, and many models have ready-made legs. If the wall is made of wood, then you should use corner mounts. Next, you need to carefully bring the pipes supplying the coolant and screw them, ensuring the tightness of the thread as much as possible. At the same time, do not overdo it in the application of force, so as not to disrupt it, otherwise water will begin to leak.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=8l2cyQIMvMQ
Repair of a cast iron battery most often consists precisely in eliminating leaks at the junctions with pipes. The question arises: how to wash the radiator from the inside? It also has an uncomplicated, albeit time-consuming, solution. It is disconnected from the battery, and then with the help of a flexible brush and a hose with high water pressure, all accumulated dirt is easily washed out. Like repairs, this procedure is best left to a specialist. Independent steps can be quite successful, but they can also lead to damage.
Cast iron batteries will become an uninterrupted and trouble-free source of heat for you, your children and grandchildren.
Aluminum radiators
Aluminum appliances have a higher heat transfer than other types of heating batteries. They also have a large flow area. Thanks to these features, they provide quick heating of the room and make it possible to control the temperature. They are also light in weight.
These radiators are made of aluminum alloy and covered with powder enamel. Most often they are used in private houses with an autonomous heating system, since they serve for a long time only with a small working pressure and a clean coolant. For houses connected to the central highway, aluminum batteries are not suitable due to the fact that sudden pressure drops occur in such systems. Aluminum is a lightweight material, so it can not withstand high pressure and simply burst.
But for private buildings, such radiators are ideal. To make the house cozy and warm, and the heaters last for a long time, you just need to monitor the purity of the coolant and the pressure in the system. To maintain a comfortable temperature, it is recommended to install special thermostats.
If water is used as a coolant, then aluminum radiators must be washed once a year with running water under pressure. This problem does not arise if the heating system was created from plastic pipes with quick couplings. In this case, the radiator is easily removed, washed and then installed back into place. Aluminum batteries look great. The front end seems flawless, smooth and beautiful. Despite the fact that irregularities always occur during the casting of a section, they are not visible on the finished product. Judging by the appearance, it may seem that the batteries are made of plastic. The sides of the sections are also evenly painted. The back and interior are covered in one thin layer, but because the composition is of high quality, the paint does not peel or peel off.
The main difference between these two types of aluminum radiators lies precisely in their appearance, the performance characteristics are almost identical.
What is heat dissipation and power of radiators
The power of cast-iron heating radiators and their heat transfer are among the main characteristics of any device that provides space heating.Usually, manufacturers of equipment for heating structures indicate this parameter for one section of the battery, and their required number is calculated based on the size of the room and the required heat transfer from cast-iron heating radiators.
In addition, other factors are taken into account, such as, for example, the volume of the room, the presence of windows and doors, the degree of insulation, the characteristics of climatic conditions, etc. The heat transfer of heating radiators depends on the material of their manufacture. It should be noted that cast iron loses in this matter to aluminum and steel. The thermal conductivity of this material is 2 times lower than that of aluminum. But this disadvantage is compensated by the low inertness of cast iron, which gains heat and gives it away for a long time.
In closed heating systems with forced circulation, the efficiency of aluminum batteries will be much greater, but subject to the presence of an intense coolant flow. As for open structures, cast iron has more advantages with natural circulation. The approximate power of one section of a cast-iron radiator is 160 watts, while for aluminum and bimetallic appliances the same parameter is within 200 watts. Therefore, under equal operating conditions, a cast iron battery must have a large number of sections.
Coolant for cast iron radiators
One of the significant advantages of cast iron models is insensitivity to various coolants. There is no need to monitor the acidity of the circulating fluid. The width of the channel makes it possible to freely pass and not allow impurities to accumulate inside, which are in abundance in central heating systems.
Cast iron radiators do not enter into chemical reactions with antifreeze, water or other liquids containing antifreeze additives. However, this does not mean that water treatment can be forgotten. Indeed, in addition to batteries, the coolant flows through pipe lines, inside the boiler and other installed equipment.
Technical characteristics of cast iron radiators ms 140
At the moment, in our country, cast-iron heating radiators ms 140 can be called the most common model of heating devices. These devices are manufactured in accordance with GOST 8690–94. Depending on the distance between the axles, there are five standard sizes of ms 140 batteries: 300, 400, 500, 600 and 800 mm.
Previously, all standard sizes were used quite widely, and they could be seen not only in residential apartments, but also in administrative and industrial buildings. At the moment, cast-iron radiators ms 140 500 and 300 are most often used. Other modifications are extremely rare and, as a rule, they are made to order.
In view of the popularity of ms 140 500 batteries, the technical parameters of this model should be considered. For heating cast iron radiators brand ms 140, the characteristics are given for one section, since this is a purely sectional model. By choosing the right number of sections, you can create the optimal temperature in the room.
The main characteristics of heating radiators ms 140 500 are as follows:
- pressure. Working pressure is up to 9 atmospheres, and pressure testing - up to 15 atmospheres;
- heat transfer is low and equals 175 W;
- each section has two channels;
- section dimensions: height - 50 cm. width - 9.8 cm;
- the capacity of one section is 1.35 liters of water;
- the radiator is able to withstand coolant temperatures up to +130 degrees.
It is worth considering the device of a cast-iron heating battery model ms 140 500. Gray cast iron is used for production. The nipples are made from ductile iron. Gaskets are installed between sections. For the production of gaskets, heat-resistant rubber is used.
We calculate the power of a cast-iron radiator
You can calculate the number of sections for cast iron heaters using a variety of methods. In specialized books, there are methods that include a large number of factors, including the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, the location of windows and doorways, the material and structure of the walls, technical indicators of batteries, etc.
However, you can get the desired value using a simpler formula: multiply the area of \u200b\u200bthe room by 100 and divide by the power of one section.
The result obtained should be corrected as follows:
- In rooms with a height of more than 3 m, 1-2 sections are added to compensate for heat losses
- It is necessary to add several sections for rooms in which two walls border the street
- In rooms with two window openings, radiators are installed under each of them, dividing the number of sections found equally. This is necessary in order to form air barriers under the windows for cold through flows from outside.
- A fractional value is always increased in a positive direction
Classic cast-iron radiators differ little in appearance. However, the development of the market for heating appliances and the constant change in the style features of the interior forced manufacturers to come up with something new, more elegant and extravagant.
Today, the market offers models of various color palettes (gilding, silver, copper, bronze, etc.). There are radiators with artistic casting, on which ornaments are applied.
However, the external design significantly affects the cost. Decorative models are much more expensive than classic, modern aluminum, steel or bimetallic ones.
Video instructions for assembling sections
Having considered in more detail the features and technical characteristics of cast-iron heating radiators, you can get your own idea of \u200b\u200bthese heaters. However, it is impossible to assert their great superiority over other models. The reason is that each of the proposed options has its pros and cons.
Due attention should be paid to cast iron models when designing a heating system. They can be purchased for savings in a used condition and do not worry that they will soon fail.
Advantages over other batteries
- The indisputable advantage of a cast-iron radiator over modern aluminum, steel, bimetallic batteries is its durability. The half-century anniversary of the cast-iron battery is a ubiquitous phenomenon. In some cities, those batteries that were cast in the century before last have survived and continue to work properly.
- The cost price of a cast-iron product can only please the future owner - not everyone can afford European prices for trendy aluminum or bimetallic batteries. In addition, buying a large number of sections promises significant benefits.
- Another advantage of cast iron is the absence of any requirements for the coolant. Water of any quality is poured into the heating system.
- The thickness of the cast iron sections allows it to withstand the highest operating pressures. starting from 9 atm and above. In addition, cast iron perfectly tolerates water hammer, so it is he who is given the advantage in centralized heating systems.
Recommendations for choosing heating batteries
Externally, bimetallic radiators resemble aluminum ones, it is difficult to distinguish them. If there is no specific knowledge, visual differences are not easy to see. However, with regard to performance, bimetallic batteries are much better than aluminum ones.
The best radiator is currently bimetallic. It is durable and withstands high pressure, so it can also be installed in multi-storey buildings with a centralized heating system. As for aluminum products, they can not always be used.
It is not recommended to use them in cases where:
- There is high pressure in the heating system. Since aluminum is a brittle metal, if the maximum allowable pressure is exceeded, the product may not withstand and leak. For this reason, aluminum radiators are not used in high-rise buildings connected to the central highway.
- Non-freezing liquids that are incompatible with aluminum are used as a heat carrier.. In the case of contact of such a coolant with this metal, a chemical reaction occurs, leading to the destruction of the heater.
- The boiler has a copper heat exchanger. Copper and aluminum are incompatible materials, since they form a galvanic pair, between which an electric current occurs, which destroys both elements. Aluminum suffers the most, as its ions are attracted to copper. As a result, over time, the walls of the heater will become thinner and may leak. However, such a problem will not arise if metal-plastic or polypropylene pipes were used when creating the heating system - in this case, galvanic steam is not formed.
Panel steel radiators are used exclusively in autonomous heating systems. These batteries can be used with any coolant and even with copper heat exchangers. Steel radiators are quite durable, but they are prone to rust.
All types of heating radiators have certain advantages and disadvantages, so the choice depends on the specific situation. As for the characteristics and operating conditions, bimetallic radiators are the best, but not every family can afford to buy them.
Details about the types of heating batteries on the video:
Recommendations for selection and installation
The selection of this type of battery comes down to determining the required number of sections for heating a particular room and a suitable size. To do this, you should know the required thermal power or approximately calculate it by quadrature, and take heating radiators with some margin. If we take as a basis that 100 W of thermal energy is needed for each m2 of area, then 1 kW of heat will be needed for a room of 10 m2, and sections of the MS 140 500 - 1000 / 160 = 6.25 device, 7 pieces are taken.
For the northern regions, an increasing coefficient from 1.5 to 2 must be applied to the value of the thermal power, and for the southern regions, a decreasing index equal to 0.7.
Installation of radiators is carried out to the outer wall in accordance with the scheme.
For fastening batteries MS 140, 2 types of brackets are used: steel and cast iron.
There are paired strip-welded brackets that are best used when mounting on a wall made of porous materials. They can be attached to the surface at several points.
External design features
Cast iron radiators are produced only in the factory, for these purposes they use mainly a gray grade of cast iron. The radiator is made up of separate sections or “cloves”, each contains a round or oval channel through which the coolant will move. Sections can be single-channel and two-channel. Next, the sections are assembled into a single battery, they are joined together, heat-resistant gaskets are laid for tightness. The size of the battery will depend on the number of sections.
The size of cast iron heating batteries can be different, various models with different section parameters are now being produced. The size is selected individually depending on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, insulation and the number of window and door openings in the house. The size of radiators can vary from 50 to 140 centimeters in depth, from 35 to 150 centimeters in height, the width is chosen based on the number of sections.
Batteries are made using the casting method. therefore, the design is tight, reliable.Cast iron perfectly accumulates and gives off heat, suitable for autonomous and central heating systems. Cast iron batteries have a high wear resistance and service life. well withstand pressure surges, the operating pressure in the battery is nine atmospheres. They are also picky about the coolant, fine sand and scale during the movement of hot water cannot cause significant damage to the channels inside the sections. For central heating systems, where the coolant “acquires” a good supply of chemical elements during the journey, cast iron is also suitable, since the metal does not react and does not rust.
Calculation of heat transfer
First of all, it is recommended to pay attention to the existing technical passport, which is attached to each product of this type. In it you can find the necessary information regarding the thermal power of one section of the product
These figures need significant adjustment. The heat dissipation of bimetallic heating radiators, like aluminum ones, have excellent power ratings, while the judgment is based on the well-known fact that copper products have an excellent level of heat dissipation, as well as aluminum ones. They have a high thermal conductivity, while heat transfer depends on many other factors.
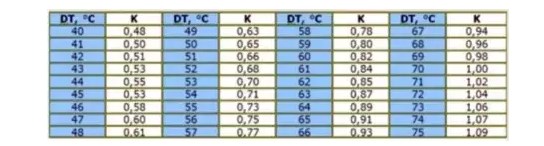
The heat output of the heating radiator is multiplied by a correction factor taken depending on the value of DT
The figure indicated in the passport is correct only if the difference between the supply and processing temperatures is 70 ° C.
Using the formula, calculations are performed as follows:
The instruction may have different designations. Often only a difference of 70°C is mentioned and nothing more.
How to calculate heat transfer and power of radiators
In order to always maintain a comfortable temperature in the room, it is necessary to correctly calculate the heat transfer of heating devices and select them in accordance with the required characteristics.
This is the only way we can correctly calculate the heating radiators so that in cold weather it is warm and comfortable in the room.
The thermal power of the heater is indicated in its passport. However, this parameter may vary depending on actual operating conditions. The calculation of the heat transfer of the radiator is determined based on the value of the temperature difference - the difference between the average temperature of the coolant and the air in the room:
where Тin is the temperature of the coolant at the inlet;
Тout – coolant outlet temperature;
Troom - the air temperature in the heated room (a value of 20 degrees is considered comfortable).
In the technical specifications, the temperature regime is referred to as Tin / Tout / Troom. and the temperature difference as Tnap. If the heating system has indicators that differ from the values \u200b\u200bspecified in the passport, then the heat output of the radiator should be calculated using the formula:
where k is the heat transfer coefficient of the heater (indicated in the passport);
A is the area of the heat transfer surface of the radiator (indicated in the passport);
Tnap - temperature difference.
Having calculated the power of the heating battery, you can determine the required number of batteries or select a certain type of heater that has sufficient heat output to heat a particular room.
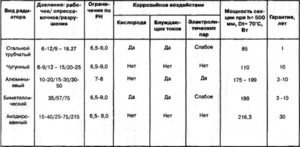
Explanation of comparative values of heating appliances
From the data presented above, it can be seen that the bimetallic heating device has the highest heat transfer rate. Structurally, such a device is presented by RIFAR in a ribbed aluminum case. in which metal tubes are located, the entire structure is fastened with a welded frame. This type of batteries is installed in houses with a large number of storeys, as well as in cottages and private houses. The disadvantage of this type of heating device is its high cost.
Important! When this type of battery is installed in houses with a large number of floors, it is recommended to have your own boiler station, which has a water treatment unit. This condition for the preliminary preparation of the coolant is associated with the properties of aluminum batteries.
they can be subject to electrochemical corrosion when it enters in a poor quality form through the central heating network. For this reason, aluminum heaters are recommended to be installed in separate heating systems.
Cast iron batteries in this comparative system of parameters lose significantly, they have low heat transfer, a large weight of the heater. But, despite these indicators, MS-140 radiators are in demand by the population, which is caused by such factors:
The duration of trouble-free operation, which is important in heating systems.
Resistance to the negative effects (corrosion) of the thermal carrier.
Thermal inertia of cast iron.
This type of heating device has been operating for more than 50 years, for it there is no difference in the quality of the preparation of the heat carrier. You can not put them in houses where there may be a high working pressure of the heating network, cast iron is not a durable material.
Comparative conclusions
The heat transfer of aluminum radiators is slightly lower, although they are lighter and cheaper than bimetallic ones. In terms of test and operating pressure, aluminum devices can also be installed in buildings of any number of storeys, but on condition: there is an individual boiler room with a water treatment unit. The fact is that aluminum alloy is subject to electrochemical corrosion from low-quality coolant, characteristic of central networks. Aluminum radiators are best installed in separate systems.
Cast iron radiators differ sharply from others. the heat transfer of which is much lower with a large mass and capacity of the sections. It would seem that with such a comparison, they will not find application in modern heating systems. Nevertheless, the traditional "accordions" MS-140 continue to be in demand, their main trump card is durability and resistance to corrosion. Indeed, gray cast iron, from which MS-140 is made by casting, quietly serves up to 50 years or more, while the coolant can be anything.
In addition, a conventional cast-iron battery has a large thermal inertia due to its massiveness and spaciousness. This means that when the boiler is turned off, the radiator remains warm for a long time. As for the working pressure, cast iron heaters cannot boast of high strength. It is risky to purchase them for networks with high water pressure.