Bookmark depth and optimal slope
For pipes with a diameter of up to 50 mm, SNiP recommends making a slope of 3 cm per one meter of laying.
If the pipe cross section reaches 100 mm, then the slope can be reduced by one centimeter. So that the sewer does not become clogged and possible "fatting" does not occur, it is advisable to increase the slope by about half a centimeter for each meter of wiring.
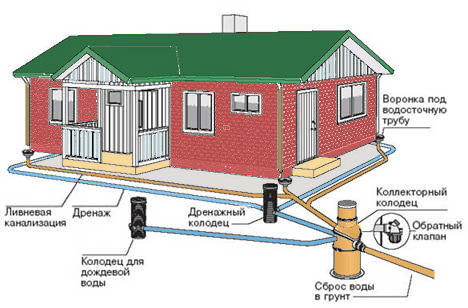
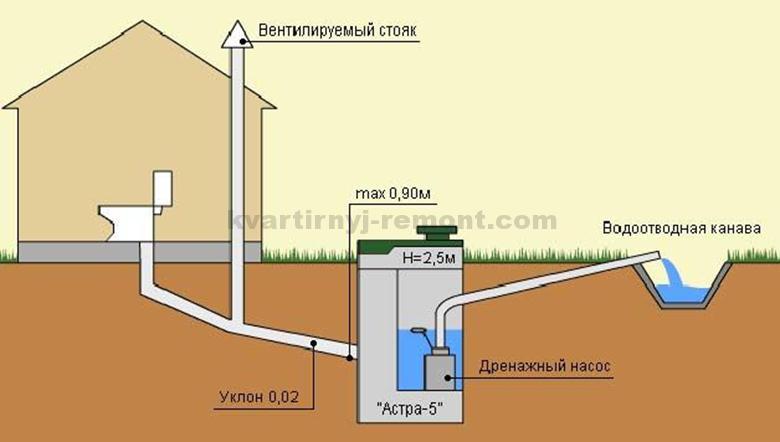
The same values of the angle of inclination are maintained during the laying of pipes in the area near the house. A sleeve is installed in the foundation. Its diameter is 15 cm larger than the main pipe. Thanks to the sleeve, there is a transition to an external sewage system. It is mounted above the soil freezing value by 30 cm.
Then a trench is dug, providing access to the septic tank. Its approximate depth should be no more than one meter.

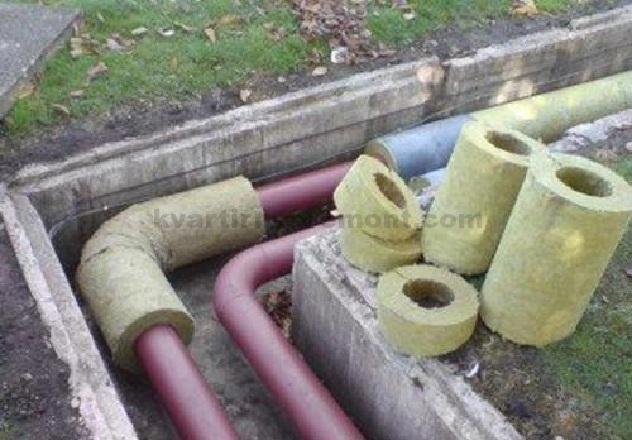
Such work requires additional financial investments, since it is necessary to install additional concrete rings and special high-strength corrugated pipes. They perfectly withstand the pressure of the drain, they do not deform with a large mass of soil.
The usual drain temperature is always higher than in the room, so the pipes do not freeze. Sometimes they are insulated with thermal insulation or a heating cable is laid.
Estimate for storm sewer ways to optimize costs
A typical storm sewer system consists of the following elements - water collectors, drainage pipes, sand collectors, intermediate wells (inspection and drainage) and a wastewater collection tank.
1. Moreover, the best results are shown only by a fully equipped sewer, in the design of which there are all of the above elements. Therefore, saving estimates by excluding any components is far from the best solution.
However, no one prevents us from combining some elements "in one bottle". For example, a manhole with a difference in nozzles can be turned into the same sand collector. And instead of trays - quite expensive products - use a perforated drainage pipe laid in a ditch filled with rubble.
2. In a word, there are a lot of options for combining functions. And each promises all tangible savings. In addition, it is possible to reduce the estimate by optimizing the size of sewage conduits or drainage wells. After all, the dimensions recommended in SNiP (200-250 millimeters) are suitable for industrial buildings and for entire blocks of one-story buildings.
3. But for a separate house equipped with a non-pumpable storm well, a 100 mm pipe is enough (a 150 mm pipe can be used to protect against flooding). The result is one and a half, and even double savings only on pipes.
4. Another way to save is the already mentioned non-pumping storm well, buried to the horizon with high permeability. From such a well it is not necessary to pump out water or connect it to the central sewer. The drains will go away on their own, dissolving in sand that conducts moisture well.
As you can see, a creative approach to design gives a real chance for savings.
Really large buildings with a large roof or industrial facilities are best equipped with storm sewers, equipped according to the recommendations from GOST and SNiP. Otherwise, the owner of such facilities may pay a double price for their own indiscretion (and this is without taking into account the cost of dismantling an unsuitable stormwater drain).
You can’t just take and build a rain sewer: at least it will be inefficient, and at the maximum it will flood the site. We need a competent project, the pipeline must be laid correctly. We figure out what the depth of the storm sewer of a private house should be, how to make the right calculation according to SNiP, SP, GOST and common sense.
The current rules state that when developing a rain sewer project, it is necessary to take into account:
- existing cleanup requirements;
- climatic parameters of the area;
- relief of the site;
- geological/hydrological conditions;
- situation with engineering communications;
- other factors (as it is written).
Climatic parameters are contained in SP 131.13330. The rest is individual.
Initial calculations of storm sewers
The main function of the storm sewer is to drain water from the site at a private house or cottage, and in order for the system to work flawlessly, it is necessary to make preliminary calculations.
This will require some data. It is necessary to know the average value of precipitation in a particular area.
This information can be obtained from the local meteorological service or look at the aforementioned SNiP. You also need to find out the total stock area.
In addition, information is needed about the soils located on the site, and the layout of underground utilities.
The design of a storm sewer begins with the calculation of the volume of water to be drained.
Correction factor for areas covered with crushed stone - 0.4, concrete - 0.85, asphalt - 0.95, for roofs - 1.
For more accurate calculations, it is necessary to resort to the formulas in the aforementioned SNiP.
The value of the diameter of the pipes required for the sewerage device is selected according to the corresponding values of the volume of water removed. The necessary tables are also located in the current SNiP.
Pipes for local sewerage
Previously, only metal pipes were used for the construction of sewers. However, due to the susceptibility of metal to corrosion, it is increasingly being replaced by plastic.
An additional argument in favor of plastic pipes is that there is no need to resort to the services of a welder and involve construction equipment for laying, because plastic and metal pipes of the same diameter differ significantly in weight.
When choosing types of pipes for organization, it should be remembered that there are varieties for internal and external sewage.
- Internal sewerage devices include all plumbing items and pipelines located inside the house.
- External sewerage includes pipelines located on the street, as well as storage and treatment facilities for wastewater.
Pipes intended for outdoor use are produced in brown-orange, and those designed for use in the house are light gray.
Professional design
In addition, if the owner of a private residential area has the right to make a mistake, he can design a sewer at his own peril and risk.
To organize even a small enterprise, to draw up plans for the improvement of urban or courtyard areas, carefully calculated, technically sound projects are required that fully comply with all existing sanitary and building standards.
Such design and survey work is carried out by special organizations, having state certification for the implementation of activities of this kind
.
When contacting specialists, the customer presents them with a number of documents that will form the basis of the terms of reference:
- Topographic map of the area from which storm water is to be diverted.
- Geological survey data containing information about the nature of soils at the site.
- General building plan.
-
If you plan to discharge to a centralized collector system
- technical conditions for water utility services for connection. - Sanitary standards for water treatment, if it is supposed to be discharged into natural water bodies or drainage fields.
- Possible wishes of the customer on the organization of the accumulation of collected water.
The result of the work of designers is a package of documents, which includes:
- General information about the area to be equipped and storm sewers.
- A detailed schematic diagram of the storm drain.
- A scaled drawing-plan of the site with reference to the locations of all stormwater elements. In fact, it is a ready-made installation instruction for further work.
- Detailed specification of the equipment required according to technical specifications.
- Full estimate for the purchase of the required materials and construction, installation and commissioning.
The finished storm sewer project is subject to mandatory approval by the water utility enterprises, state technical supervision bodies, the sanitary and epidemiological service, and the environmental control service in charge of the state of water resources.
Only after the full approval of the project in all controlling instances, it is possible to proceed to its practical implementation.
Some design organizations take over the entire process of coordinating the project they have developed.
The design process is complex, but there are no trifles in this matter.
In order for the storm sewer to fully fulfill its functions, so as not to incur penalties for violations of environmental legislation, it is better to entrust the development of the project to experienced specialists whose qualifications are not in doubt.
Is it necessary to lay sewer pipes below the freezing level?
Many non-specialists mistakenly believe that the depth of laying a pipeline for local sewage should exceed the freezing depth. In fact, this is not always possible.
To make it clear, let's look at a specific example. It is generally accepted that in the middle lane the soil freezes to a depth of 1.6 meters. The distance from the house to the first chamber of the septic tank is 15 meters, therefore, if a pipe with a diameter of 100 mm is used, it will be 30 cm.
Thus, the entry point to the septic tank, according to our calculations, will be located at a depth of 1.9 meters (1.6 + 0.3 = 1.9). And if there is an increase in relief in the direction of the location of the treatment plant, then the difference in heights will also need to be taken into account.
Thus, if it was planned to arrange a septic tank of a standard depth of 2.7 meters (from three concrete rings of 0.9 m each), then with such a low entry point, its useful depth will be only 0.8 meters (2.7-1.9 = 0.8), which, of course, is insufficient.
That is, in order to reach the planned usable volume, you will have to dig a pit already under five standard rings. And this is already quite a significant additional cost for materials and digging a pit. In addition, when deciding to build such a deep septic tank, one must also take into account such a circumstance as the level of groundwater.
How to properly equip thermal insulation
In cold regions, it is recommended to supplement the sewer pipeline with thermal insulation. This technique allows you to extend the service life, eliminate the possibility of freezing at very low temperatures. Most often, polyurethane foam is taken for this purpose. If the pipe is wrapped with polyurethane foam, and a polyethylene sheath is made on top, the pipe will not be afraid of frost.
If pipes are laid below the possible freezing point, then the pipes will never freeze. In this case, additional protection is made in case of extreme cold weather.
When performing thermal insulation, special attention is paid to joints and turning points. It is these zones that are rather poorly tolerated by the effects of cold.
So warming the turning points is a must.
In Europe, a more technologically advanced method is used. An electric cable is launched near the pipeline; if necessary, it acts as a heater for the pipe.For many residents of our country, this method is too expensive, because paying for energy is not the smallest item of expenditure. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor the depth of pipe laying. In the central regions, it is better to choose a depth of 1m. And in the northern regions, it is desirable to dig deeper trenches and carry out high-quality thermal insulation. To do this, you can use mineral wool or fiberglass. If the pipes are located above the ground, they are also insulated with similar materials. Since they can fill with water, waterproofing will be necessary for outdoor use.
Types of tanks, their positive and negative sides
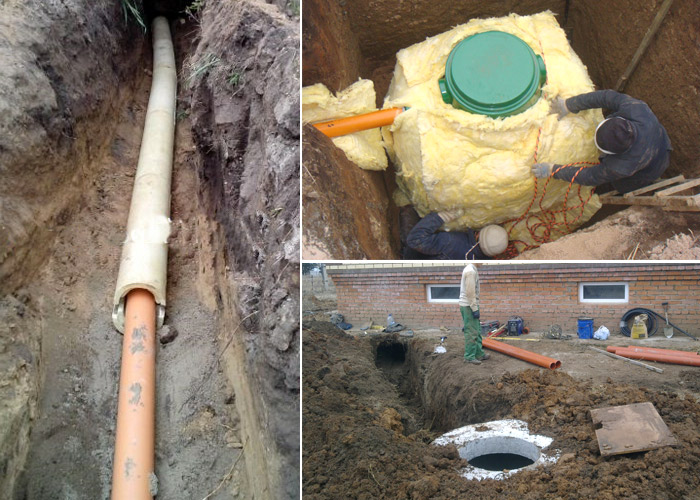
The final part of the system is the tank where the cleaning is carried out. If there is no central collector through which the drains are taken, then autonomous installations are used.
Cesspool
Perhaps this is the cheapest option. The hole is easy to dig in the right place. However, it cannot always cope with large volumes of stocks. Dirt can be a source of unpleasant groundwater odor.
septic tank
Such a structure can be laid out of brick and poured with concrete. You can also install standard reinforced concrete rings. If the septic tank is well made, it can be used for many years, as it is characterized by increased strength. The disadvantage of this design can be called a long installation and large financial investments.
Stand-alone installation, industrial type
Of course, such a design is always much more expensive, but all costs are fully covered due to the rapid construction and very high quality. Such installations will work for a very long time with virtually no breakdowns.
Biological treatment system
About such a system, you can safely say "the most expensive." For its operation, it is necessary to bring a constant electrical supply. However, it has high performance and high-quality cleaning.
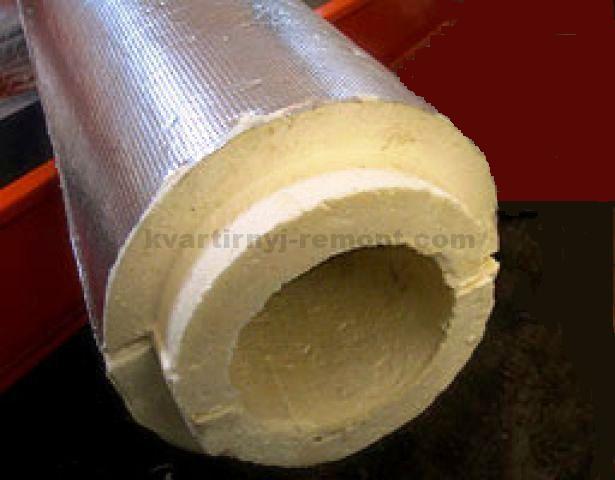
Why is it important to insulate the sewer pipe

The insulation of sewer pipes is no less important than choosing the correct laying depth and the required diameter. This operation is necessary and also has a protective function.
Freezing of pipelines is a frequent occurrence in winter, especially if they were laid a long time ago. This leads to very sad consequences, the elimination of which requires a sufficient amount of time, effort and money. Freezing of sewage can lead to their expansion, as a result of which the sewer pipe bursts and requires major repairs with digging a trench and replacing the affected area.
It is enough to lay the pipe 10 cm below the freezing depth and additional insulation is not required. But this can be more expensive than the purchase of special materials that also protect pipes from freezing. Therefore, it is more profitable to purchase thermal insulation materials, which are available in large quantities on the construction market.
Materials that are most often used for sewer insulation:
- Mineral wool. This option is most often used in construction, but is expensive, since additional purchase of waterproofing is required. If you do not carry out waterproofing, then mineral wool, after getting wet, loses all its properties.
- Polyurethane foam. A very easy-to-use material that is moisture resistant and ideal for insulating sewer pipes. It is often produced in the form of two half-cylinders, which have special grooves that allow you to cover the pipe on both sides and fix it. In addition to ease of use and quality of the structure, polyurethane foam has an affordable pricing policy and is therefore very common when laying pipelines.
- Penoizol. It is very convenient if special spray equipment is available, since penoizol is produced in liquid form.To insulate the pipe, its surface is treated with several layers of material, which hardens after some time.
There is also a popular option for heating pipes, which requires additional consumption of electrical energy. On top of the water pipe, or inside it, a heating cable is laid, which is available both with the possibility of self-adjustment and without it. Self-regulating heating cable consumes less electrical energy, heats only the necessary places. A conventional cable works constantly and with the same power, because of this, its consumption is somewhat higher.
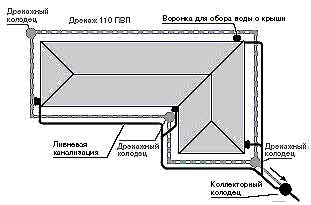
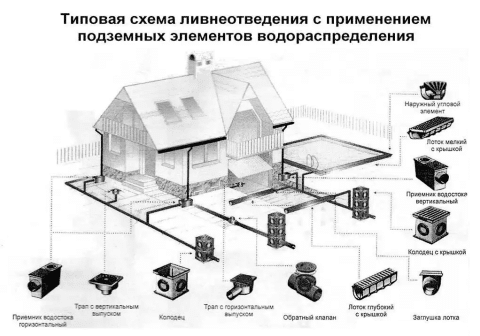
Storm sewer elements
As a rule, the following elements are included in the sewerage network:
- Storm water inlets. This is one of the important elements of the system, the main function of which is the local collection of water from the surface of the earth.
- Door pallets. This is an analogue of storm water inlets, which are installed in front of the entrance groups of the house or at the gate.
- Trays or gutters. Elements installed in ditches to divert water. So that water can move along them by gravity, a slight slope of the storm sewer is provided, directed to the collector.
- Pipes. This element performs the same function as the trays, but is not laid in surface trenches, but underground.
- Sand traps. These are filter elements that prevent debris and soil particles from entering the drainage system.
- Viewing wells. Elements necessary to control the operation of the system.
Energy saving device
Point and line stormwater drainage
A point-type sewer is created to collect rainwater from the roof of a house in several places.
In this case, water through drainpipes enters orderly located water inlets, which supply it to a common main.
A storm sewer device of a linear type differs from a point one in that the surface protected from erosion is larger.
The linear system is a network of trays or gutters, the layout of which allows you to cover a large area.
This is a suitable choice for a country house or cottage with concrete or asphalt paths and other areas.
In order for drainage to take place without failures, it is necessary to make a slope. This is provided for in SNiP 2.04.03-85.
These elements are installed under downpipes for local collection of water.
To protect the entire system from debris, it is required to install gratings on each of them. In this case, the cleaning of storm sewers will be carried out less frequently.
The next important element is door pallets. They perform the function of water inlets, but install them in front of doors and gates.
Trays and gutters are also important components placed in ditches to facilitate the removal of water from the site.
Video:
https://youtube.com/watch?v=2lnlbpiI6JE
For closed-type sewerage, not trays are used, but pipes, the laying depth of which depends on the specific area.
So that cleaning the storm sewer in a private house is not too laborious, a sand trap should be provided, this is also mentioned in the SNiP.
In this case, all debris and sand will be filtered, preventing clogging of the drainage system.
What problems may arise during the installation of a sewage system, how to solve them
In some cases, the depth of sewerage during installation in a cottage depends on some external factors.

The only way out of this situation will be the thermal insulation of the pipes.
Before starting the installation of the structure, it is necessary to wrap the pipeline with several thick layers of insulation, and then lay it to a depth of no more than 30 cm. It will be possible to create heating of the pipe, for which it will be necessary to lay a heating cable under the pipe.
outside line
To install the sewerage of an individual house, it is necessary to carry out a diagram drawing taking into account the surrounding landscape. Professionals recommend that the septic tank be located as low as possible, and the pipes should have a slight slope.
To determine which treatment system should be taken as the basis, to what depth the pipes will lie, it is necessary to pay attention to the following factors:
- groundwater;
- Soil type;
- Freezing depth.
The construction of external sewerage is usually begins with laying the pipeline from the foundation.
Drains should be discharged towards the cesspool made. Any turn of the pipe must be equipped with a special revision, in the form of an adapter equipped with a cover. Through it, it will be possible to easily eliminate the blockage.
An inspection well is mounted on the outside, a ventilation umbrella is installed.
The exit is through a riser with an installed one. Since there will always be a very strong unpleasant smell in it, such a pipe should be installed as far as possible from windows or next to the smoker.
It is forbidden to combine a fan pipe with an ordinary ventilation shaft.
The umbrella can be replaced with a special vacuum valve installed at the top of the riser. Remember that it has nothing to do with the check valve.
Calculation of storm sewers
There is a whole array of numbers and formulas in the calculation of storm sewers, but if we simplify everything utterly, several parameters are important:
- system performance (volume of drains);
- pipe slope;
- pipe diameter;
- depth of the pipeline and collectors.
The efficiency of surface runoff removal depends on the diameter of the pipes. The diameter, in turn, depends on the amount of precipitation in the area and the area of the service area (including the drainage system, if one collector is used). All the necessary numbers are in the regulatory documentation, and they are enough if you follow the rules.
Combined system (stormwater and drainage)
The volume of effluents is calculated by the formula:
- Q is the volume of stocks.
- q20, l/sec., per ha — precipitation intensity factor.
- F is the area of the serviced territory (recalculated in hectares; roof slopes - in a horizontal projection).
- Ψ is the coefficient of absorbency of coatings.
The q20 value is obtained from the local meteorological center. Ψ standard:
- 1.0 - roof;
- 0.95 - asphalt;
- 0.85 - concrete;
- 0.40 - crushed stone (rammed);
- 0.35 - soil (including turf, lawns).
For each storm water inlet, a separate calculation is made. Then the obtained figures are summed up and the diameter of the pipes is determined.
Normative documents
The set of rules regulates the smallest diameter of pipes. For gravity networks, it is 150 mm (and it goes as acceptable, and desirable - 200 mm). Using other pipes, violate the provisions of the joint venture. In production networks, the use of 150 mm pipes requires justification.
Parameters valid for pipes 150 mm:
- calculated highest speed: for metal pipes - 10 m / m, for non-metallic - 7 m / s;
- calculated filling of rectangular channels and pipes of cross section - full;
- the smallest slope (the need for a smaller slope should be justified): for 150 mm pipes - 8 mm / meter, for 200 mm pipes - 7 mm / m;
- connection slope - 2 mm/m;
- the slope of individual trays is 5 mm/m;
- the smallest dimensions of trapezoidal cuvettes, ditches: along the bottom - 30 cm, along the depth - 40 cm;
- between the outlet and attached pipes, an angle of at least 90 degrees is required, otherwise a well is installed, and in it - a riser with the connection of storm water inlets with a drop;
- require a well device: long straight sections (every 35 m - for private households), turns, drops, turns on collectors, connected pipes of different diameters;
- the radius of the turning curve of the trays must be at least 1 pipe diameter;
- the radius of the turning curve on the manifold from 120 cm (inclusive) must be at least 5 pipe diameters, manholes are needed both at the beginning and at the end of the curve;
- collector diameter for pipes up to 500 mm - 1000 mm (1000x1000);
- installation of a collector with a diameter of 700 mm for pipes of 150 mm is permissible;
- the depth of the collector with a diameter of 700 mm should not exceed 1200 mm;
- the diameter of deep wells (from 3 m) should be at least 1500 mm;
- the minimum design speed of the movement of wastewater through pipes and channels is 60 cm / s.
It is impossible to rely on the given figures using pipes of a smaller diameter: already 110 mm need a minimum slope of 2 cm / m. In each case of violation of the rules, you will have to make an individual calculation of storm sewers.
Programs for calculating storm sewers
There is advice to use AutodeskBuildingSystems, but it's like hammering nails with a microscope. Theoretically, it is possible to calculate storm water in any program that, in principle, can design engineering networks, but in practice we do not recommend it. Firstly, this kind of software is never free (except perhaps the trial version, but it is always cut off). Secondly, it is difficult for an ignorant person to understand professional software. Thirdly, such software is not needed for our small task.
You can calculate rainwater drainage on specialized resources that provide calculators or programs that work in a browser (we launch and count). Most (maybe all) of them do separate calculations:
- hydraulic,
- surface runoff from the territory,
- volume of water from the roof,
- collector capacity,
- pipeline slope,
- network depth.
If these parameters help to build a stormwater… good luck.
We painted the rules and regulations, formulas and figures, based on SNiP and SP, but according to common sense, the calculation of rainwater drainage should be entrusted to specialists - no matter how trite it may sound. Yes, all the figures are given, but the main factor was, is, will be the climatic parameters, although they are indicated in the joint venture, but not completely. The joint venture does not know what kind of soil is on your site: sand passes water instantly, clay does not pass at all. Calculation error = flooded area with all the consequences.
Method for calculating the depth of a pipe connected to a storage tank
The value of the outlet of the pipe in the room increases by the length of the outer line, multiplied by a coefficient, the value of which is selected according to the diameter of the pipe:
- D 50 mm - 0.03;
- D 110 mm - 0.02;
- D 160 mm - 0.008;
- D 200 mm - 0.007;
The calculation is carried out according to the formula:
h2=h1+l*k+g
,
h2 is the depth of the point from where the exit and connection with the storage tank is carried out;
h1 - the value of the exit from the premises. 1.4 m is taken;
l is the distance from the foundation to the storage well. Usually 10 meters.
k - coefficient, always equal to 0.02;
g is the natural slope of the surface. Usually does not exceed 0.3 m.
h2=1.4+10*0.02+0.3=1.9 m.
According to the calculation, a sewer trench is created.
We insulate sewer pipes

If there are joints or a lot of turns, it is very important to insulate them. It is in these places that problems always arise.
In Europe, electric cables are used to insulate pipes. It is laid along the entire length of the pipe.
In our country, in the southern regions and central regions, the pipe is laid in a trench one meter deep. In the north, where there are always great colds, the depth of the sewers is even greater. Such pipes especially need thermal insulation.
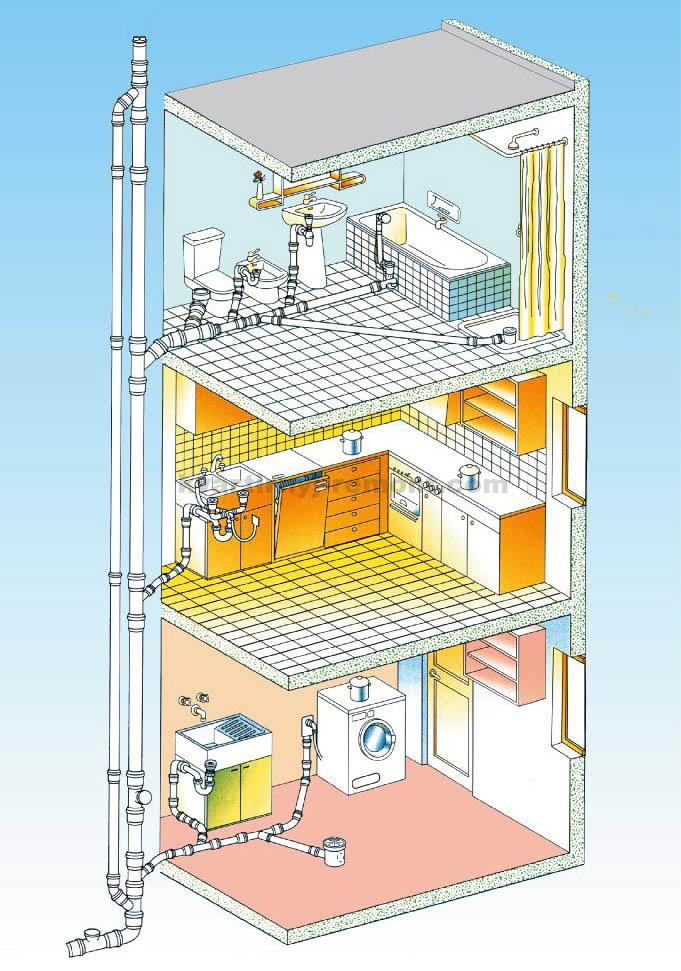
When the sewer pipe is laid inside the house, some additional technological operations are performed. It is possible to create a large number of turns, all kinds of bends.
According to professionals, it is not worth abusing such opportunities.
It is very important to make the system as simple as possible. It won't cost a lot of money, and it will be much easier to maintain it.
The internal sewerage in the house must have a natural drain. The ideal option is to lay the pipe directly under the floor. If the diameter of the outer and inner pipes have large differences, you can use the connections. For such purposes, a knee with an angle of 30 degrees is best suited. This will improve water runoff.
The arrangement of the sewer system requires the most scrupulous attitude to all stages of the process, including depth, slope, and reliability of connections. Each of these factors has a great influence on the quality of the entire system. Negligence is unacceptable here, if there is no self-confidence, it is better to turn to professionals.
The external part of the sewer system of a private house
The main requirement is to ensure proper bias. The only correct drain is gravity. Too low a speed will cause blockages. Too fast movement of effluents - to accelerate the destruction of pipes.
The sewerage laying scheme in a private house includes a characteristic of the features of the pipe exit from the room. The rules for removing a pipe from a house depend on the type of foundation. With a strip foundation, the output is arranged on the side. With slab - the pipe is laid from top to bottom, for this a pipe section and a 45 ° elbow are used. To equip the sewer, a pipe-sleeve is laid in advance in the foundation, through which the main pipeline is then removed. Such a base is needed to protect the pipeline from excessive pressure and potential destruction.
From the exit point to the septic tank / cesspool, the pipe is laid evenly, without bends. In the septic tank, the drain pipe is inserted at the top. This is done to provide a place for the accumulation of waste.
In order not to be mistaken in the depth of laying the pipe, you need to find out how things are with the neighbors who have already equipped their own drain. If they have problems with pipe freezing, you need to dig your pipe deeper. No matter how deep the pipe lies, in any case, a slope is needed. Usually they make 2 - 3 cm per linear meter.
- First, you should make a detailed layout of the piping inside the house. This will reduce time and financial costs by providing all the best options.
- Pipes are carried out towards the riser or to the septic tank, sharp corners are excluded.
- The riser on each floor must be equipped with a tee designed to service the sewer system for quick cleaning.
These articles are usually viewed as well.
There is a lot of controversy about this on the construction forums. Although in paragraph 4.8 of SNiP 2.04.03-85 “Sewerage. External networks and facilities "everything is said quite clearly
Here is the wording "depth of penetration into the soil of zero temperature
»
, and this is nothing more than the depth of freezing of the soil.
You can find out the depth of freezing from many regulatory documents. Closest to engineering networks SNiP 2.01.01-82 "" Construction climatology and geophysics ". And although a new SNiP 23-01-99 * "Construction Climatology" has already been released to replace this document, the map of freezing zones remained only in the old Soviet SNiP.
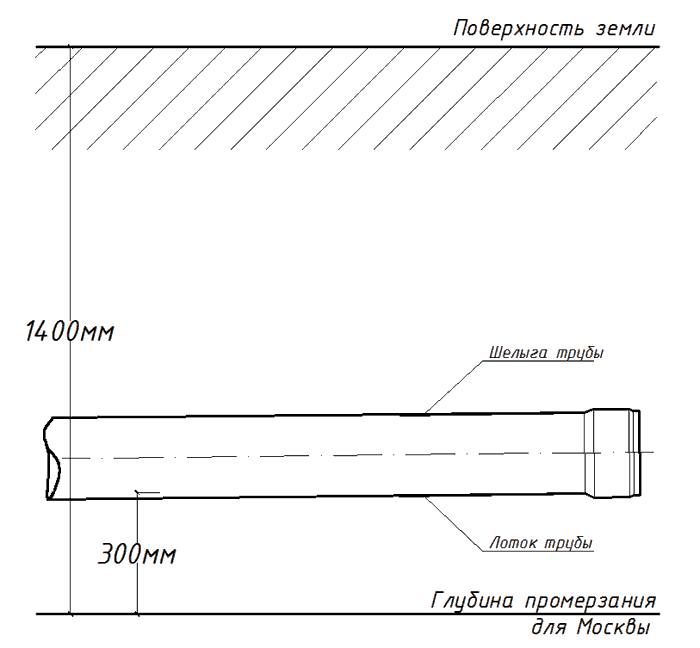
For the hero city of Moscow, the freezing depth is 1.4 meters, for St. Petersburg - 1.2 meters, and for Sochi - less than 80 centimeters. Let's take a "small" pipe with a diameter of 200 mm. For it, you need to subtract 0.3 meters from the freezing depth. Having made a simple arithmetic calculation, we obtain the minimum depth of the sewer pipe tray Du200 - 1.1 meters. For Moscow. Visually - in the drawing:
This is how pipes should be laid.
Now about the sad. About how pipes are actually laid. If it concerns some capital objects, then everything is fine.State or non-state expertise is obligatory, and projects for serious objects are made by serious designers.
Whether it's a private house. In almost all instructions for small treatment facilities such as Topas, Biofluid, etc., it is written in black and white - the sewer pipe from the house should exit at a depth of 0.5 meters. Otherwise, the pipe simply will not fall into the inlet of the treatment plant. SNiP also provides for such cases of laying - with mandatory insulation.
In practice, sewer pipes are rarely insulated or heated. Installers say that nothing will freeze, refer to their vast experience and global warming. Therefore, in winter, the Internet multiplies with numerous questions and detailed instructions on what to do if the sewer pipe is frozen.