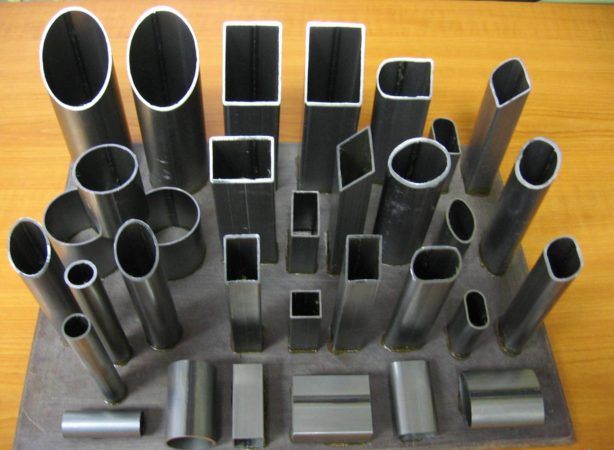
Description of the technological process
The starting material for the pipe-rolling complex is hot-rolled round billets with an outer diameter of 140 and 160 mm and a maximum length of 9600 mm.
Continuously cast billets with an outer diameter of 200 mm (maximum length also 9600 mm) in combination with hot rolled round billets with an outer diameter of 140 mm can be used to increase productivity and improve yield. The items come from the warehouse.
In billet saws, the raw material is cut to a length of max. 4.200 mm and fed into the ring furnace.
After heating to the required temperature, the workpiece is transported to the piercing mill.
At the outlet of the piercing mill, the hollow billet is injected with nitrogen-assisted anti-oxidation powder, and the hollow billet is then conveyed to the PQF rolling line.
The insertion of the mandrel into the hollow billet is carried out inside the line in the axis of the PQF rolling mill. The mandrel circulation system is designed to cool the mandrels and lubricate them with graphite.
On the inlet side of the PQF continuous rolling mill, a descaling system is provided on the outside of the sleeve.
The pipe is rolled on a 4-stand PQF mill with a hollow billet reduction stand.
The hollow billet reduction stand, located in front of the first PQF stand, is designed to calibrate the outer diameter of the hollow billet and reduce the gap between the hollow billet and the mandrel.
The PQF process is based on the principle of continuous rolling in a series of 3-roll stands on a mandrel that moves at a constant speed throughout the rolling phase.
The speed of the mandrel is calculated according to the deformation scheme; it is lower than the speed of the sleeve exit from the first stand. Therefore, the material moves faster than the mandrel and the friction forces between the material and the mandrel are directed in the rolling direction. Minimizing the cross flow towards the deformation zone and removing the pipe from the mandrel in line allows the use of a very small inter-stand distance.
Optimum material flow allows rolling at higher speeds.
Directly in line with the PQF mill, there is an extracting and calibrating mill, consisting of 3 stands, respectively 3-roll type, designed to remove the sleeve from the mandrel.
After rolling, the mandrel is retracted, removed by means of rotary arms and fed into the mandrel circulation system.
After leaving the extraction and sizing mill, the sleeve on the transverse conveyor is sent to the preheating induction furnace.
The finishing rolling of the heated sleeve is carried out on a stretch-reducing mill equipped with the Carta automation system for tube rolling with optimized setting data.
The pipe coming out of the stretching and reducing mill is cooled in a walking beam cooler. In batch cutting saws, the pipe is cut to length.
In the pre-finishing line, the pipes pass through a straightening machine, an eddy current testing system and a pipe marking machine.
In accordance with the required standards, the pipes pass through the required Finishing Line.
engineering and bearing pipes
packaging, weighing and labeling
boiler pipes
chamfering, hydraulic testing, non-destructive testing
packaging, weighing and labeling
oilfield and gas pipes
heat treatment
chamfering, hydraulic testing, non-destructive testing
packaging, weighing and labeling
Continuous Furnace Welding of Metal Pipes
A strip of rolled metal used as a blank for a future product (also called a strip) is pulled through a special furnace in which the metal is heated to a temperature of 1300 ° C (the exact temperature depends on the steel grade).After heating in the furnace, the edges of the strips are blown to remove scale and local temperature increase.

After that, the edges are subjected to additional blowing, which helps to increase the temperature to values that allow welding. In this state, the metal billet is rolled through the compression rolls, in which the final welding of the pipe takes place. Rolled pipes manufactured in this way are classified as hot-worked products.
Application area
"Seamless Pipe Defect Classifier" establishes terms and definitions, possible internal and surface defects of the surface of hot rolled seamless carbon and alloy steel OCTG pipes. The illustrations given give a clear idea of the nature of the considered defects.
The terms established by this "Seamless Pipe Defect Classifier" are mandatory for use in all types of documentation being developed.
There is one standardized term for each concept. The use of synonymous terms is not allowed. Synonyms that are unacceptable for use are given in the standard as a reference and are marked with the mark "Ndp".
Standardized terms are printed in capital letters, and invalid synonyms are printed in lower case.
ABBREVIATIONS:
| TMK | – | OJSC Pipe Metallurgical Company. |
| VTZ | – | OJSC "Volzhsky Pipe Plant" |
| Sintz | – | OAO Sinarsky Pipe Plant. |
| STZ | – | JSC "Seversky Pipe Plant" |
| TAGMET | – | JSC "Taganrog Metallurgical Plant" |
| VMZ | – | OJSC "Vyksa Metallurgical Plant" |
| CHTPZ | – | OJSC Chelyabinsk Pipe Rolling Plant |
| PNTZ | – | JSC "Pervouralsk Novotrubny Plant" |
7 Solidity of metal
6.7.1 Pipes of supply group B, as well as supply groups A and E (in
case of rationing of temporary resistance) must withstand the test
hydrostatic pressure calculated according to the formula given in GOST 3845,
at allowable stress in the pipe wall equal to 40% of the tensile strength
for the specified steel grade, but not exceeding 20 MPa.
The manufacturer can guarantee the ability of seamless
cold-formed pipes to withstand the test hydrostatic pressure
without testing. The ability of the pipes to withstand the test hydrostatic
pressure is provided by the production technology of seamless
cold worked pipes.
Instead of hydrostatic pressure testing of welded
of cold-formed pipes, the manufacturer can carry out a continuity test
metal pipes by non-destructive methods.
Cold rolling fabrication
The technology for the production of steel pipes by cold rolling consists of two stages:
- initial processing;
- calibration.
initial processing. The hollow sleeve is cooled after piercing on the mill. Its temperature drops to values at which the metal loses the plasticity necessary for forging or piercing. In this state, the product undergoes final processing by pulling through the forming rolls. The metal billet cannot be called cold, since its temperature is quite high due to the deformation loads to which it is subjected in the rolls of the rolling mill.
Calibration. Before this operation, the pipe is subjected to annealing (the metal is heated to a state of recrystallization). This is done in order to remove the stress that appeared in the metal after rolling on the mill. Thanks to annealing, the steel acquires the plasticity and toughness necessary for calibration, all microcracks are eliminated, and the structure of the pipe walls becomes homogeneous.
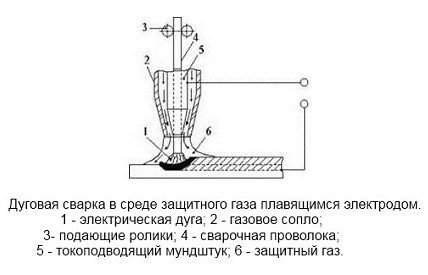
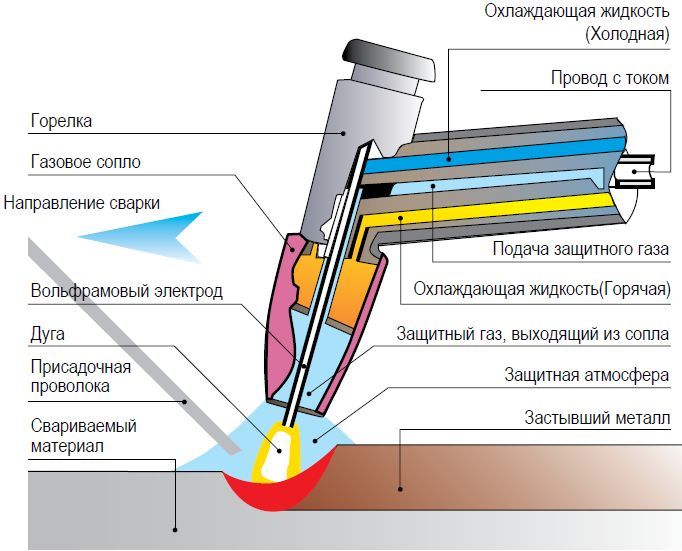
Gas-shielded pipe welding
Most often, this method is used for welding high-alloy steel products or in the manufacture of stainless pipes. In the process of welding such a metal in the usual way, the alloying elements are destroyed, which significantly degrades the quality of the weld.
Rolled pipes, in the production of which welding in a shielding gas or electric arc welding is used, refers to products manufactured by cold deformation.
Classification
Product classification is carried out according to three main parameters:
- Sleeve production method;
- Technology of rolling a sleeve into a pipe;
- Method for the final formation of the diameter and profile wall thickness of the product.
Technology of rolling a sleeve into a pipe
At the same time, the method of rolling the sleeve to the fullest extent characterizes the production process. Depending on it, the name of the production shops and pipe-rolling units is given.
Ways to get a sleeve
Various methods can be used to obtain a sleeve. Among them are piercing on a press, piercing on a cross roll mill, press roll piercing, combined piercing on a press and a cross roll machine.
Sleeve rolling technologies
To date, in the production of hot-rolled pipes according to GOST 8732-78, the most common technology is the use of automatic rolling mills.
Their use provides the following benefits:
- Variety of assortment of finished products;
- High performance;
- Automation of the production process;
- High level of mechanization of production.
Variety of pipes
With the help of such production equipment, it is possible to obtain pipes of small (up to 150 mm), medium (up to 250 mm) and large (400 mm and more) diameters.
Production of thick-walled seamless pipes
For the manufacture of thick-walled pipes, the rolling method on a pilgrim mill is used. The main area of use of products produced in this way is the oil refining and oil industry.
The range of rolled products of this type is represented by the following types of products:
- Small profile pipes (wall thickness from 2.5 to 4 mm, diameter - no more than 114 mm, product length - up to 60 m).
- Medium (length - up to 40 m, thickness - 5-8 mm, diameter - up to 325 mm).
- Large (length - up to 36 m, thickness - 6-10 mm, diameter - up to 700 mm).
Longitudinal rolling on a continuous mill
Continuous rolling is considered to be the most efficient method for manufacturing seamless hot rolled tubes. It can be used for the production of rolled products with a diameter of 16 to 350 mm and a wall thickness of 2 to 25 mm. Most often, for the production of rolled steel in accordance with GOST 8732-78, low-alloy and carbon steels are used, less often - high-alloy ones.
Helical rolling
Screw rolling is used on the piercing, rolling and calibrating rolls of the pipe rolling unit. Such machines are characterized by high maneuverability, but at the same time they are inferior in productivity to equipment with a continuous mill.
When using this method, there is no need to replace rolls when switching to the production of hot-rolled shaped pipes of a different diameter, which greatly simplifies the process. This technology is mainly used in the manufacture of hot-rolled steel pipes for bearing rings.
Production at rack mill
With this method of production, the glasses are pushed with a mandrel through a series of roller cages. This technology is used to produce seamless hot-rolled tubes from square billets.In this way, pipes of small wall thickness are obtained, with a diameter of not more than 245 mm. Modern equipment of foreign manufacturers allows high-strength products with a length of up to 12 meters and a wall thickness of 2.5-10 mm.
The choice of production method is determined by the required characteristics and purpose of the finished product. Modern equipment makes it possible to obtain high-quality products, ensure compliance with GOST 8732-78 and, at the same time, reduce cash costs for the production of hot-rolled and cold-rolled steel pipes.
Varieties of pipe metal
Metal pipes can be classified according to the conditions of use, production technology and corrosion protection method.
There are two main applications: general purpose and specialized. Steel pipes for special purposes are divided into the following types:
- for heating, water and gas pipes used in settlements;
- metal pipes for gas transportation and oil pipelines, designed to work under high pressure;
- products for drilling rigs;
- for the chemical industry (must have high resistance to corrosion);
- metal products with a rectangular or shaped cross section;
- bearing.
By production technology:
- electric-welded pipe rolling with a straight seam;
- welded steel with a spiral seam;
- seamless cold rolling;
- seamless hot rolling.
According to the method of corrosion protection:
- stainless steel rolling;
- galvanized metal (on one or both sides);
- with polymer coating.
Related video: Pipe rolling
https://youtube.com/watch?v=bJlMDTRYvBY
A selection of questions
- Mikhail, Lipetsk — What discs for metal cutting should be used?
- Ivan, Moscow — What is the GOST of metal-rolled sheet steel?
- Maksim, Tver — What are the best racks for storing rolled metal products?
- Vladimir, Novosibirsk — What does ultrasonic processing of metals mean without the use of abrasive substances?
- Valery, Moscow — How to forge a knife from a bearing with your own hands?
- Stanislav, Voronezh — What equipment is used for the production of galvanized steel air ducts?
Electric arc welding of rolled pipes
The manufacturing technology using electric welding makes it possible to produce products with a minimum wall thickness and a large diameter. Most rolled pipes, in particular, for laying gas pipelines and water supply networks, are produced by arc welding with flux. The process of manufacturing electric-welded pipe-rolling includes several stages:
- rolled sheet metal is given the necessary shape by pulling it through the profile rolls of rolling mills;
- as a result, steel billets prepared for welding are obtained;
- the profiling process is carried out using roller rolling.
Polishing is more preferable for the production of straight-seam pipe than compression molding, which is used mainly in the manufacture of large rounded products.
Unlike metal products with a straight seam, the profiling of spiral tubular products is carried out on sleeve or wolf-straightening mills. After forming, the edges of the steel blanks are welded using electric arc welding. Depending on the type of product, a straight or spiral weld appears on the surface, which must be cleaned of the grant and cooled.
The cooled product is calibrated. After that, it is examined, ultrasonic scanned and tested for resistance to possible loads. Further, a final check is carried out, and if no defects are found, the products are sent for sale.
Manufacturing standards
The production technology and characteristics of finished products must meet the requirements of regulatory documentation.The following standards apply in this area of production:
- GOST 8731-74 - regulates the properties of hot-rolled general-purpose rolled products from alloyed and high-carbon steels;
- GOST 9567, GOST 8732 - establish pipe sizes and acceptable parameter deviations;
- GOST 8732-78 - defines the assortment of hot-rolled seamless shaped pipes;
- GOST 21945-76 - regulates the characteristics of hot-rolled seamless pipes made on the basis of titanium alloys.
Pipes based on titanium alloy
There are also other regulatory documents that define the characteristics of hot and cold rolled products manufactured using a particular technology.