Which heating cable to choose for heating sewer pipes
To resolve this issue, let's compare the advantages and disadvantages of the above wires for heating. Resistive single-wire, two-wire, and zonal can be generalized because of their similarity.
Resistive and zone heating cables
Advantages of resistive (including zonal) heating cables:
- The simplicity of the device;
- Relatively low cost;
- Long-term use resistivity stability;
- Long service life if properly installed.
- The inability to change the length (in zonal this problem is partially solved, but the length changes in steps);
- The need for a thermostatic device;
- If the heating wires are close together, if they are intertwined, and even if the surface is dirty, the insulation overheats significantly. Overheating of the insulation leads to its premature aging and possible short circuit;
- Requirements for installation.
Self-regulating cable
Advantages of a self-regulating cable:
- Does not require a separate thermostat;
- The ability to cut the footage of any length (not less than 1.5 m and not more than indicated in the passport);
- During installation, the approach and crossing of wires is allowed, which greatly simplifies the laying;
- Temperature control occurs independently at each point, along the entire length. This completely eliminates its overheating;
- The surface temperature along the entire length is almost the same.
Compared with resistive, this product has a high cost.
Recommendations of the installation masters
- To increase savings when heating the pipes of the sewerage system with a self-regulating cable, you need to use an additional thermostat to control the ambient temperature.
- It is necessary to ensure a reliable connection of sewer joints, to prevent the passage of moisture.
- It is strictly forbidden to mount cable products with conventional insulation internally.
- The permissible temperature of the pipe material, as well as its insulation, must be higher than the temperature to which the cable will be heated.
- The angles of rotation of the heating cable must correspond to those prescribed in its passport.
- During installation, the air temperature at which the laying is carried out must be higher than the permissible one.
- At the time of the first inclusion of a self-regulating cable in the power grid, its power consumption will exceed the nameplate several times. After that, in a few minutes, the indicator will return to normal.
At first glance, the installation of a heating self-regulating cable to protect the pipes of the sewerage system is very simple, but this requires knowledge of the relevant codes and regulations. By following them, you will be able to mount an efficient and reliable heating system.
In those regions where the ambient temperature can take negative values, piping systems designed to work with liquid media (mainly water supply and sewage systems) need additional means of thermal insulation or heating.
One of the options for protection is the installation of the pipeline below the freezing level of the soil. Another option is insulation with thermal insulation materials. There is an alternative way - the use of a special heating cable, which is especially often used by residents of private houses.
Choosing a cable for a sewer system
The required heating power is directly related to the heat loss of the heated pipe
It is very important to make the right selection of power for the sewer system of the desired diameter and the conditions for its heat transfer.
Important! Incorrect power selection can lead to:
- If the power is too high, overheating, as a result of which the service life of the heating system will decrease.In the worst cases, plastic drains can melt. (When using a self-regulating heating cable, overheating is completely eliminated).
- If the power is too low, the system will not be able to withstand low temperatures, which will lead to freezing of drains.
- To reduce the economic efficiency of heating.
- Increasing the likelihood of electric shock to a person or animal.
- Reduced service life of both the heating system and the sewage system itself.
When you build a sewer with your own hands, design its heating and thermal insulation, you can be guided by the table below. It displays the average heat loss depending on the pipe diameter, insulation layer and temperature difference.
 Figure 6. Selection of specific heat losses of the pipe depending on the diameter and external conditions
Figure 6. Selection of specific heat losses of the pipe depending on the diameter and external conditions
We take the power per unit length equal to or slightly greater than the number that we find at the intersection of the desired thickness and temperature difference. Next, we multiply the length of the pipeline by this number and by a safety factor of 1.3, then divide by the cable power according to the passport - this will be the required length.
Features of assembly and installation of heating cable sections
Before proceeding with the installation of a heating cable, it is worth deciding on the choice of a specific product model, the use of which will be most appropriate in this case.
There are many types of cable available on the market. Their main characteristic - specific power - can vary in the range from 10 to 40 W/m.
- 10 W/m. Suitable for heating plumbing systems with a diameter of not more than 25 mm.
- 16-17 W/m. Can be used in sewer pipelines with a diameter of not more than 50 mm.
- 30-40 W/m. Such power will be enough to heat a large sewer pipeline with a diameter of 110-160 mm.
The assembly procedure itself is very simple and does not require any special skills from the master. Of the tools, you only need pliers for crimping the connecting sleeves, pliers, a building hair dryer for heating the shrink film, side cutters or a knife for stripping insulation, sealant.
The algorithm of actions can be represented as follows:
- The current-carrying cores, the shielding metal braid and the ground are cleaned (not present in all cable models).
- Pieces of a heat-shrinkable tube of the appropriate length are successively put on the individual cores, the cable under the braid and its outer sheath.
- The adjacent ends of the current-carrying conductors are connected in pairs with the help of sleeves.
- A small layer of sealant is applied to the junction, after which heat shrink is crimped.
- A similar procedure is performed with the ground and the screen, if any.
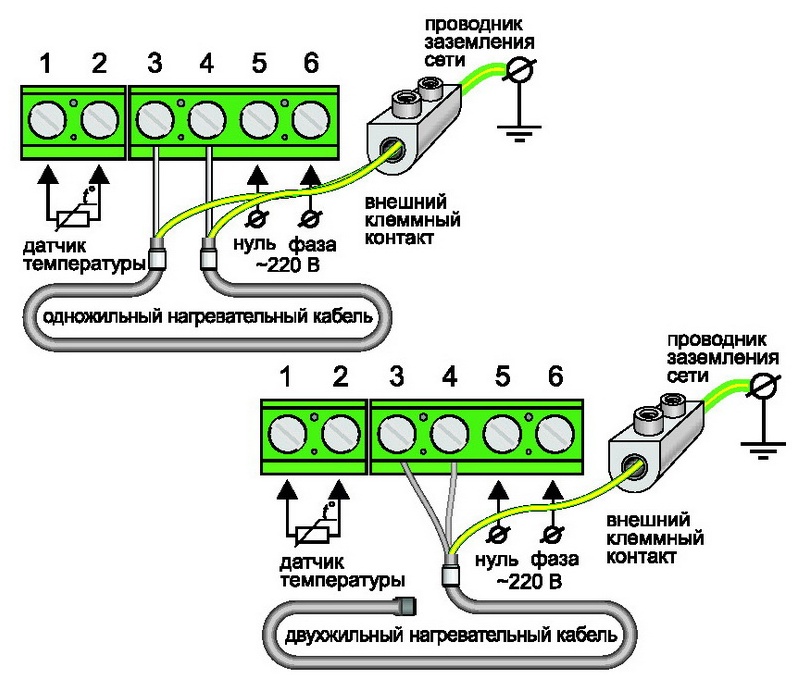
- At the end of the heating cable, the next steps depend on the type of cable. For a resistive two-core cable, the current-carrying conductors are connected, followed by sealing and insulation of the coupling with a jumper. In a self-regulating cable, all the cores at the far end are cut off and separated by a certain distance, to increase resistance in the event of a violation of the tightness of the coupling.
- The free ends of the shrink film are flattened with pliers.
outdoor installation
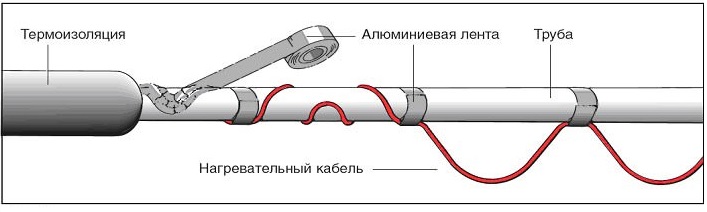
The heating cable is fixed under the pipe with aluminum tape. To improve heat transfer, it should be pressed against the pipe as tightly as possible. Aluminum tape helps to further limit heat loss by partially reflecting infrared radiation.
The cable is fixed with short pieces of adhesive tape at regular intervals (at least 30 cm), after which it is also fixed with adhesive tape along its entire length. For additional reliability of fixation, plastic clamps are often used.
It is allowed to place the cable under a layer of insulation, which will not only provide additional thermal insulation, but also help to fix it securely.It should also be borne in mind that, first of all, horizontal sewerage sections need heating, through which drains move much more slowly than vertical ones.
Internal installation
The laying of the heating cable inside the sewer pipes is allowed with some restrictions.
The ring coupling should not be in contact with wastewater passing through the pipes, since they are considered an aggressive environment that can destroy heat shrink in just a few seasons. At the same time, the cable's own insulation is resistant to such influences, and is able to stay inside the pipe for an arbitrarily long time.
Therefore, the ring coupling, as a rule, is taken out of the pipeline. To do this, use special holes in the tee or corner of the structure.
Another indispensable condition is that the cable should be easily removed. Otherwise, in the process of mechanical cleaning of pipes with wire or plumbing cable, the cable will almost certainly be damaged.
Of course, this method of heating sewers cannot be called cheap. However, given that the pipeline will be reliably protected from any temperature fluctuations and will be able to serve properly for many years, the use of a heating cable will be much more profitable than replacing frozen sections of the system.
Heating cables types
resistive
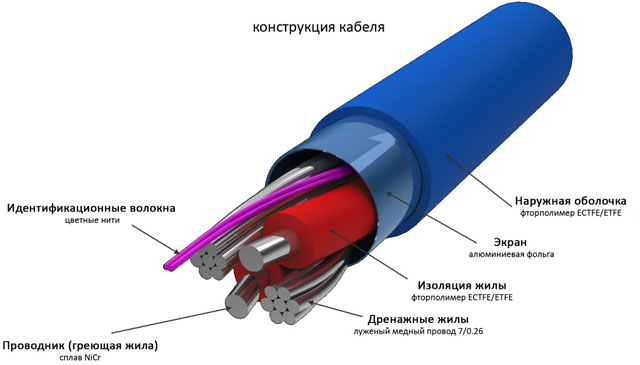
Produced in one- and two-wire versions. The basis of this type of product is a conductive (heating) core, which, when an electric current passes, releases heat according to the Joule-Lenz law. The heating core is insulated, as a rule, with a heat-resistant material (for example, fluoroplastic). Some types use double insulation. Next is a metal shielding braid in the form of a mesh of thin conductors or just foil. This shell protects it from mechanical damage, and is also a screen. The surface of the wire is covered with a heat-resistant sheath.
This cable works as follows. If it is single-core, then the power supply must be carried out from two sides (as shown in the figure below on the left), and the wire should be evenly distributed in a loop along the entire length, which is extremely inconvenient. The problem of two-way power supply is solved in two-core products, although the principle of operation is similar, but it is more convenient to install and connect (in the figure below, on the right). In addition, for both types, it is necessary to use temperature control of its surface using temperature controllers.
Zonal
It is a kind of resistive, or rather a modified version of a two-wire. The modification consists in the fact that short sections of heating spiral wires are added to it, located with a certain step. Now, unlike its predecessor, it can be cut into pieces of the desired length with a certain step.
Figure 4. Construction of a zone heating cable
self-regulating
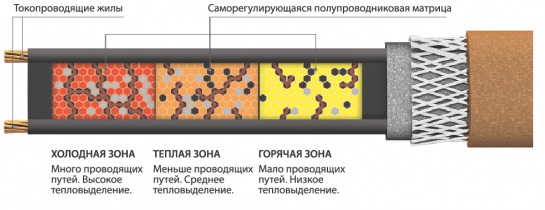
It is a wire with two parallel copper wires, between which there is a semiconductor. This design is covered with protective, electrically insulating and shielding shells. The specific resistance to electric current of a semiconductor is directly proportional to its temperature. That is, the higher its heating temperature, the resistance between the two cores increases and vice versa. As with previous products, heat is released according to the same law (Joule-Lenz), but not in the current-carrying cores, but in the semiconductor separating them. Since its conductivity depends on temperature, the magnitude of the current will also change, and, consequently, the power. In fact, this wire is its own heater and thermostat in any of its sections along its entire length.Accordingly, the amount of heat in each area will be released differently, so that regardless of external conditions, the temperature of its surface will be almost the same at each point.
Inductive
Such a heating cable consists of an insulated conductive core wound around a ferromagnetic core, which is a pipe. Alternating current creates an alternating magnetic flux, which induces eddy currents in it, and they heat it up.
Such heating is considered obsolete and is now used extremely rarely. This is due not only to low efficiency, but also to the fact that it can only be used for metal pipes.
Purposes of application
The use of a heating cable for heating piping systems can be justified in the following situations:
- Large depth of soil freezing. If the ground freezes more than 4-6 meters, installing a pipeline below this level can be a very labor-intensive undertaking.
- Complex types of soils. Rocky rocks in the area where the sewerage is supposed to be laid.
Of course, all these phenomena should be discussed only in relation to regions in which there is a periodic or constant presence of negative air temperatures that can provoke damage to the sewer.
It is worth noting that the use of an internal heating cable for sewerage systems is not without some drawbacks.
So, due to the presence of an additional element, the throughput of the pipeline decreases. Also, the risk of blockages increases and the tightness indicators deteriorate, since it is necessary to additionally mount the tee. For extended sewer systems, this option may be unreasonably expensive.
But for private courtyards, where sewer systems of a sufficiently large cross section and short length are operated, an internal cable is the best fit.
For sewerage systems based on PVC, concrete or asbestos-cement pipes, the internal heating of the pipeline may even be the only one available. These materials have very low thermal conductivity, so it is very difficult to effectively heat them from the outside.
Advantages of sewer heating
Heating sewer pipes with a heating cable from the inside has a number of advantages:
- Wires that warm up from the inside make it possible to maintain the desired temperature level so that the liquid in the system does not freeze.
- High security of cables drawn from the inside and their regulators.
- Such devices can be used not only from the inside, but also on the outside of the highway.
- Simple and convenient application.
- The ability to save electricity due to the automatic regulator.
The only drawback of devices installed from the inside is the dependence on the supply of electricity. For these reasons, additional sources have to be installed on important pipelines, which will come to the rescue in case of interruptions in the operation of the main source.
The main stages of laying the heating cable
In private homes and in production, installation of heating is carried out at the stage of insulation of sewer pipes. It is necessary to securely seal the joints to avoid moisture seepage. The cable can be laid on the outside of the pipeline (under thermal insulation) or inside it.
Internal installation
This method of heating the sewer system has many more disadvantages:
- Increased risk of blockage
- The heating cable is constantly exposed to the aggressive environment of drains (accordingly, you need to fork out for a purchase with a more stable outer sheath);
- It is extremely difficult to apply this method on extended communications;
- An additional tee is required.
However, the method of laying inside the pipe can sometimes be the only possible solution. Advantages:
- It is possible to heat pipes with low thermal conductivity or old systems with significant deposits on the walls;
- It is convenient to heat partially in places where the sewerage passes through the foundation;
- It is convenient to heat water pipes and drains without thermal insulation.
The main stages of installation:
- In order to introduce the cable into the sewer, a special coupling-nipple is installed.
- If there is no tee or inspection hole, you can cut a small section, and then mount an adapter of the desired diameter.
- Insert the cable to the required depth.
- The sewer pipe must be sealed. It is necessary to screw the nut with the nipple and check the tightness.
- Connect the cable to the mains. To do this, it is necessary to provide a power socket nearby or a circuit breaker in advance.
 Figure 7. The main stages of installation of a heating self-regulating cable inside a pipe
Figure 7. The main stages of installation of a heating self-regulating cable inside a pipe
outdoor installation
When installing a heating cable outdoors, there are two ways - this is laying in a "wave" ("spiral") or along the pipe. Regardless of the method, it fits along the entire length. A higher concentration of laying should correspond to places with a higher probability of freezing. Further, it is displayed in a warm place, and only then an electrical connection is made.
Spiral laying
This is the most versatile and probably the most effective way. Of course, for this you need to spend time and have the relevant experience in reserve. But this method allows heating the sewer with the possibility of further modifying it at low cost.
- For short lengths, the cable is laid in a spiral wound around the pipe. (calculated length is distributed over the entire pipeline).
- For long distances. We divide the route by the number of sections, a multiple of two (approximately).
- With a margin in length, we fasten the pre-cable product.
- We wrap the resulting loops around the pipe in the opposite direction, one from one.
- We wind the coil in increments of 30-50 cm.
It is attached to the pipe with adhesive or aluminum tape in increments of 0.5-1m or along the cable along the entire length. The aluminum tape is sealed to ensure complete cable sealing.
Laying along the pipe
This is an easier installation method, but slightly worse in terms of heating efficiency. The principle of such laying can be seen in the figure below. With one (left) and two (right) heating elements. Fastening the cable product to the pipe through 0.5-1m or along the entire length is similar to the previous method.
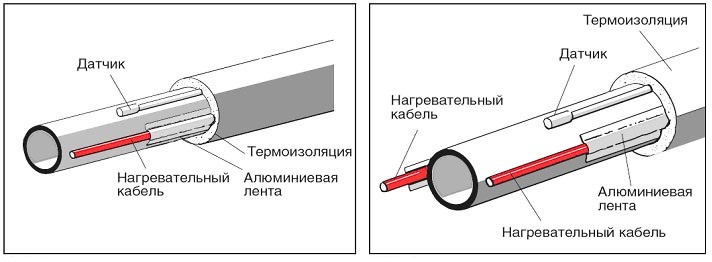
When laying a sewer pipe system in the ground, the same insulation and additional heating are required. In addition, it is recommended to use an outer protective shell. It is recommended not to stick the heating self-regulating cable with a strip of foil, but wrap it completely around the pipe, as shown in the figure below.
 Figure 11. Installation of a self-regulating cable with a full winding
Figure 11. Installation of a self-regulating cable with a full winding
Types of pipes to be heated
It is necessary to arrange the heating of sewer pipes with your own hands, if they pass over the surface, are located in unheated basements or at a shallow depth in the ground.
In constant winter heating need:
- External sewerage (at the exit from the house) and laid above the freezing level of the soil. Pipelines leading to the receivers of treatment systems. Connecting pipes of multi-stage septic tanks. Flushing filter outlets.
Fixing the heating cable on the pipe
If freezing occurs in the pipe at any of these stages, the ice plug will clog the passage and the system will stop working.Then you will have to look for where the problem arose, and master the emergency heating of pipes with a cable with your own hands.
Reliability of the heating cable
The reliability of a self-regulating cable directly depends on the quality of the heating matrix (semiconductor material between current-carrying cores). The lower the quality, the faster it ages - as a result, the specific heat release and self-regulation decrease. The service life of such a low quality matrix is 3-4 years.
Proven manufacturers who care about their reputation, such as Fujikura, Pentair, Devi, Hemstedt, use quality materials for production. This, of course, translates into a higher price, but its work throughout the entire service life (15 ... 20 years) is worth it.
Varieties
Industrial enterprises produce several types of heating cable:
- Self-adjusting. Able to independently adjust to the current weather conditions and control the intensity of heating. As the ambient temperature rises, the cable resistance automatically decreases. This leads to a decrease in current and power. This option is somewhat more expensive than its counterparts, but more than pays off in terms of energy savings.
- Resistive. The resistance and heating power of such a product do not change, which has a positive effect on its cost, but negatively on indicators of durability and efficiency. To increase efficiency, temperature controllers and sensors are additionally installed on the resistive cable.
- Zonal. According to the principle of operation, it is similar to resistive, but it does not function over its entire length, but only in predetermined areas. Such a cable is often used for the insulation of metal containers.
The principle of operation of a self-regulating cable is based on the properties of certain polymers that can contract and expand with temperature changes. Placed between conductive wires, the polymer expands under the action of heat, moving away neighboring conductor particles and weakening their electrical contact. This leads to an increase in resistance, a drop in current strength and, accordingly, a decrease in heating of the corresponding section of the cable.
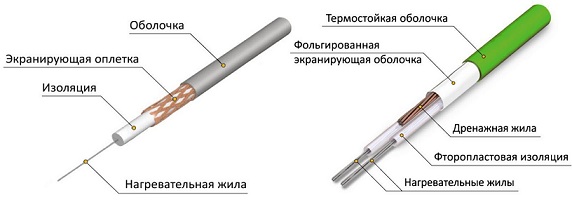
Resistive cable, in turn, can be classified by structure into two groups:
- Single core. The cable is a single metal conductor protected by a layer of insulation and shielding material. A current flows through this conductor, as a result of which the metal is heated. The laying of a single-core cable is carried out in loops so that both ends can be brought out to one point for connection to the network. Such a cable is not used for laying inside pipes, since it will be difficult to control its location there, and when the cable sections overlap each other, it can quickly burn out.
- Two-wire. In this design, one of the cores (having high resistance) is used only for heating, while the second one is used as a current conductor. Such a cable does not need to be led to one point - it is powered from one side, while a jumper between the cores is simply mounted at the other end.
How to carry out installation work
In order to carry out the arrangement of electric heating of the sewer system with your own hands, you will need the following tools and devices:
- heating cable for water supply and sewerage pipes;
- roulette;
- forceps;
- stationery knife;
- marker;
- scissors;
- double sided aluminum foil tape.
Installation of a heating cable for heating a sewer pipe 110
The work is carried out in the following sequence:
- Wrapping the pipe with special tape.
- Applying markup. Wire laying lines are drawn, places of its attachment are marked.
- The imposition of the heater on the line in accordance with the markings.
- Fixing the device with aluminum foil tapes.
- Wrapping the line with insulating material.
If a heating cable is laid in a sewer pipe, then a tee must be installed beforehand. The clamping sleeve is already fixed in it. When laying on straight sections, pushing the wire is allowed without additional devices. Its cut must be well insulated.
In case of difficulties, a cable or a telescopic handle is used. With their help, the device is pulled into the pipe from the side where it is more convenient to do it. You can tie a tennis ball to the heater and wash it off with strong water pressure. When laying the cable, it is not allowed to twist or bend it more than the minimum radius specified by the manufacturer.
Heating inside the system
The heating cable inside the sewer pipe has been used for a long time. By its structure, it is an electric cable, where the resistance regulates the temperature regime inside the network. It uses a well-known property of metal conductors, this is heating when electricity passes through itself. At the same time, as the resistance increases, the heating level rises.
From the foregoing, it becomes clear that the heating cable for sewer pipes must be equipped with good waterproofing, because it is constantly in the water.
The cable that is laid inside is arranged as follows:
- metal conductor for heating;
- cores enclosed within heat-resistant insulation;
- another layer of PTFE insulation;
- copper screen;
- outer layer of insulation.
In addition, the broach inside the drain structure contains a temperature controller. It prevents overheating on the mechanism and saves energy.
Constant heating cables for a private house
When choosing a heating cable, it is required to calculate the heat loss of sewer pipes in winter. After that, the thermal power of the heater is selected so as to block them with a margin of 20-60%.
Their installation is simple and you don’t even need to pull a separate branch from the electrical panel. It is enough to supply heating cables with a plug for a home outlet - it's the same as connecting a heating element in a water heater. Heating pipes of autonomous sewerage in a private house is relevant in our time.
Two types of constant wattage heating cables are used:
Resistive - can be one- or two-wire.
It does not provide for the ability to regulate heating during operation and requires constant monitoring. Zonal - like a resistive cable for heating sewer pipes, works on the principle of constant resistance. But not along the entire length, but in cyclically repeating zones. Suitable for steel pipelines.