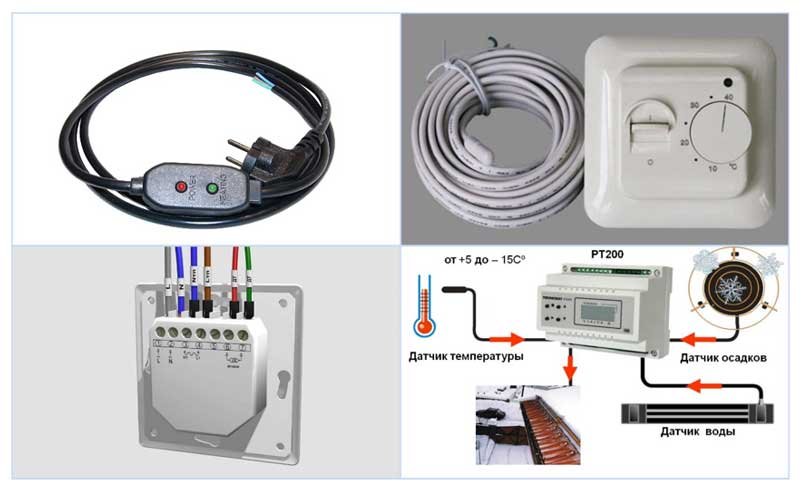
Connecting the heating cable to the network and controlling the temperature
On the market, most often you can find modifications of cable heaters in a set with thermostats, while the length of the cable that is connected to the heating elements through special hermetic couplings does not exceed 3-5 meters.
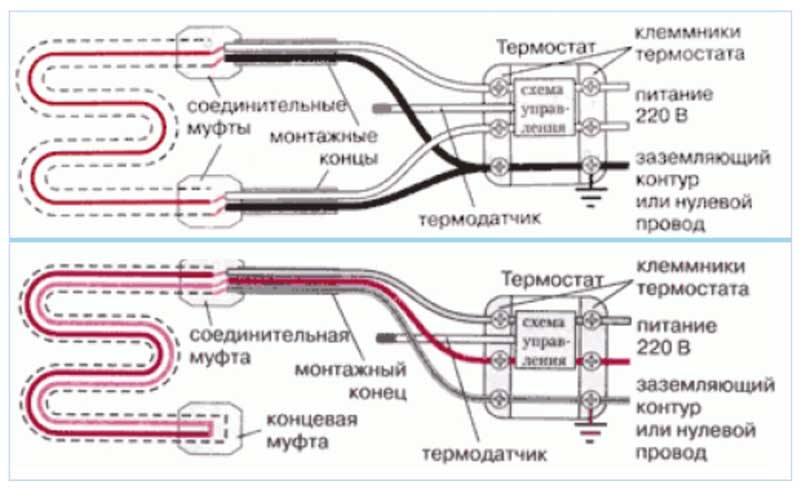
When heating pipelines, the thermostat is installed in a convenient place protected from harmful environmental factors as far as possible (a residential building), while it becomes necessary to tightly connect a short cable to a long wire coming from the house. To do this, use a household hair dryer, special couplings and clamps, installation work is carried out as follows:
- The conductors of the connected cables are cut off at different distances (ladder) and freed from insulation to a length of 10 mm.
- Heat-shrink sleeves are put on each conductor, a common large-diameter sleeve is placed on top of the cable.
- Insert the ends of the wires into the sleeves and clamp them on one side with pliers, after inserting the second ends, the sleeve is crimped on the other side.
- They pull inner sleeves of small diameter onto the wires and heat them with a hair dryer, after compression puts an outer sleeve on the junction and also heat it with a hair dryer.
- In self-regulating cables, it is necessary to seal two end wires, for this they are cut with a ladder, put on top of a special heat-shrink sleeve with a closed end end and heat it with a hairdryer.
To control the heating temperature, a thermostatic regulator is used, which is placed in a convenient place near the electrical panel; to increase safety, automatic RCD disconnect devices are installed in its circuit, which open the circuit when a short circuit occurs in the line.
Rice. 19 Thermostats to which the heating cable is connected
Temperature controllers and sensors for heating cable
Temperature controllers allow several times to reduce energy costs when using cable heaters, they can be used to set the limits for switching on and off temperatures depending on the application.
Produced thermostats, depending on their purpose, are divided into several groups:
- for warm floors
- de-icing on rooftops
- for heating water supply and sewerage,
- maintaining heat in pipelines with hot water.
The main difference between all types of thermostats is the temperature thresholds, when used in wells, the on temperature is set within +2 - +3 degrees, off - +10 C, to save electricity, the threshold values \u200b\u200bcan be lowered. Thermal sensors with response thresholds from -15 to +5 C are installed in external systems to deal with icing of roofs.
Industrially produced thermal sensors with two wires and a tube at the end differ in the principle of operation, the most popular are resistive and semiconductor types. The principle of operation of the former is based on the change in the electrical resistance of the resistor depending on the temperature; in semiconductor devices, when the temperature regime changes, the characteristics of the p-n junction change.
In both cases, the electric current passing through the resistor or semiconductor changes its value with temperature, and the electrical signal from the sensor controls the operation of the electronic circuit that supplies power to the heating cable.
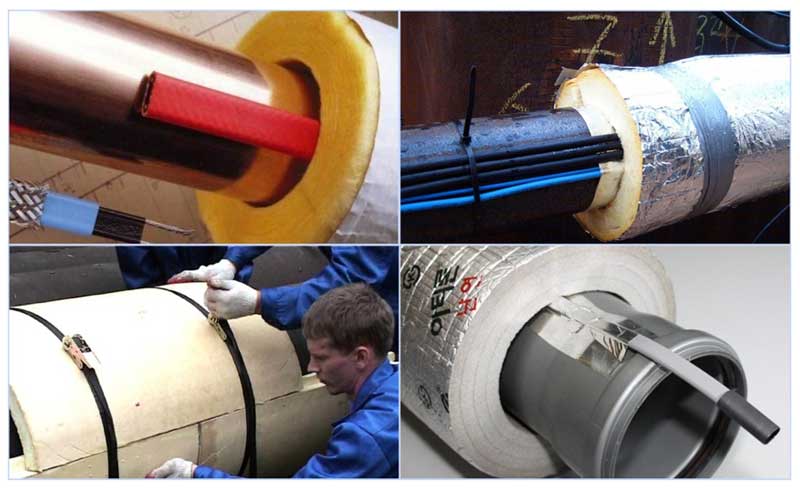
Rice. 20 Ways of thermal insulation
Thermal insulation of heating cables
When laying outside, be sure to use thermal insulation - it prevents the heat from escaping the cable into the environment, thereby increasing the heating efficiency.When immersed in the ground, rigid types of waterproof insulating shells made of foam, polystyrene or polyurethane foam are used.
During the external laying of pipelines, their insulation is not under ground pressure, it is possible to mount a sewer entrance to a heated house using soft materials - foamed polyethylene, all types of mineral wool, glass wool. It should also be borne in mind that the thickness of the protective shell of the insulation for external laying should be greater than the underground version.
Advantages and disadvantages of which cable is better to choose
When choosing a heating cable for pipes, it is important to know the pros and cons of each type on sale. Let's briefly list them
Single-core cable is in demand for the following reasons:
- Inexpensive;
- Durable (10-15 years of operation);
- Relatively easy to install.
The disadvantages include the need to accurately calculate the length, since it has to be laid in such a way as to return the second end to the power source. In addition, as we have already said, working with resistive cables (except for zonal) complicates the prohibition of manufacturers on cutting. For this reason, when buying, you need to know exactly the required length and power.
Another limitation for all resistive systems is the inadmissibility of crossing sections of the cable line. In this case, the temperature rises sharply at the contact points, which can lead to melting of the insulation and burnout of the wire.
A two-core resistive system is easier to install than a single-core one, but at the same time it is more expensive. When laying such a cable line, it is not necessary to pull it back to the outlet. It is enough just to fix it on the pipe and close it with a heat insulator on top. In terms of durability and protection against external influences, single-core and two-core versions of pipe heating are the same.
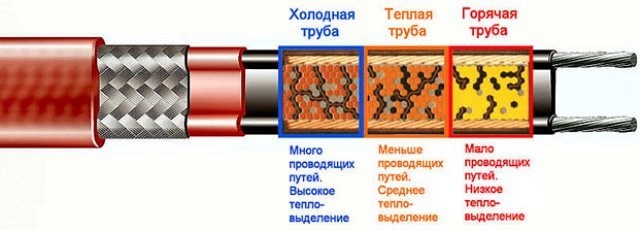
A self-regulating heating cable (SGK) is devoid of the disadvantages of a resistive one, but its cost is much higher. The high price is partly offset by simple installation, the ability to cut and shorten, as well as profitability. If the water supply goes underground below the freezing mark, then you just need to purchase a small piece of SGK cable and put it on the most critical section - the transition of the pipe from the ground to the house.
The overlap of the current-carrying turns of the "smart" line is not terrible. There will be no overheating at the contact points. The semiconductor matrix will automatically lower the temperature there. In addition, during the operation of a self-regulating cable, the coldest areas heat up more, while the temperature in others is maintained at a lower level. Due to this, energy savings are achieved, in contrast to resistive traces operating at full power along the entire length.

What to look for when choosing a heating cable
When choosing a heating cable for pipes, the following factors are taken into account:
- Operating principle. The disadvantage of resistive cables is their uniform heating temperature along the entire length. In order to save energy, it is better to use a self-regulating cable on underground pipes. In addition, its design, in the absence of a remote sensor, is convenient for location inside pipelines, and the minimum power of the device is 10 watts. per linear meter is enough for its linear placement underground in a heat-insulating shell.
- Power. For outdoor heating, devices with high power are used; linear-cable modifications with a spiral winding of the heating wire inside have the best performance.
- Insulation. For internal location in water pipes, devices with food grade plastic insulation should be used, it is better to choose modifications with a copper screen - the presence of the element reduces interference and protects the user from electric shock in case of damage.Also, the braid of tinned copper wires contributes to a more intensive heat removal from the heating conductors or matrices.
- Manufacturer. A wide range of models of heating cables from various manufacturers is presented on the market, products from Raychem, Nelson, Lavita, Ensto, Devi are well-known among foreign suppliers, a wide range of heating cable products from a domestic manufacturer, a company from the Moscow region, is sold on the construction market. .

Rice. 21 Table of dependence of heater power on pipe diameter and insulation thickness
The use of a heating cable for sewerage and water supply is the most effective method of dealing with icing, because any thermal insulation does not heat the pipeline, but only increases its freezing time. Self-regulating cables that have recently appeared on the construction market are slightly more expensive and more efficient than resistive devices, they are the best option when lowered into the water supply.
Heating cable power for water supply
It is rather difficult for a user even with an engineering education to determine exactly how much power is required for the efficient operation of a resistive or self-regulating heating cable - the calculation formulas are too cumbersome and the calculation takes a long time. The task is within the power of only qualified specialists, and its solution in everyday life was carried out by manufacturers and distributors of heating electrical cable products.
For domestic HDPE plumbing with a standard diameter of one or one and a half inches, the optimal thickness of the insulation shell is 30 mm; when using sewerage, you will need a higher power cable of about 20 W per meter or spiral winding, with a heater thickness of 50 mm.
For outdoor heating, the power of the heating cable is linearly related to the ambient temperature and the state of the heated elements, for pipelines its average value is about 20 W per linear meter, on roofs and in downpipes powerful resistive electric cables up to 60 W per linear meter are used.
Rice. 12 Connection diagram for single-core and two-core cables
How does a heating system with a heating cable work?
Heating of pipelines with a heating cable, which is connected to an AC 220 V electrical network, is carried out by two main methods:
1. The cable is placed outside the pipe. With this method, an already laid highway or sewer pipes are insulated, while the wire fits snugly against the outer surface of the pipe. Pipes with a ready-made channel for placing a heating cable are sold on the construction market - this allows you to reduce heat losses, and to save electricity, they use additional insulation of underground pipelines with foam plastic (foam) or polyurethane shells.
An electric cable is laid along the pipeline; spiral winding is used to increase the heating temperature along the entire length or in critical nodes.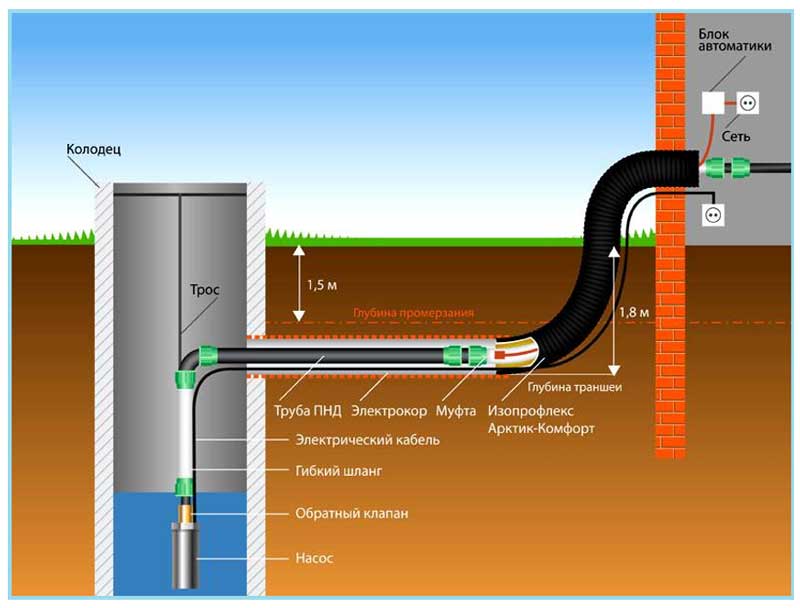
2. Heating inside pipes. The main disadvantage of external insulation with an electric cable is low efficiency - most of the heat goes into the environment and you have to additionally install insulation, which leads to an increase in the cost of work.
Therefore, in water lines it is better to lay the heating cable inside the pipes - this applies to water mains. In the sewer system, the presence of foreign objects inside can cause blockage.
It is unprofitable to lay wires inside pipes along the entire length - the cable is quite expensive and will increase hydraulic losses, reducing the useful cross section of the pipeline. Therefore, it is more rational to install it in the zone of the borehole head in front of the water supply system and pressure pipe supplying water to the house. In this case, warm water will prevent freezing in the well, automatic devices and surface pumping station, also heated water will flow into the water supply going to the house.
The main difficulty in the internal installation of an electric cable in a pipeline is to choose a mounting method and a sealed fitting for joining it with a pipe when the wire is immersed.
System Benefits
The heating cable for plumbing inside the pipe has a lot of advantages for communications. If there is such a heater inside the networks, the system will be durable and reliable. In this case, plumbing communications can be mounted above the level of soil freezing.
When choosing a quality product, the owner of a private house can count on a long service life of the system. Condensation will not form on the pipes. Therefore, their surface will not be subjected to rapid destruction. The service life of a self-regulating wire reaches 40 years. At the same time, it consumes a minimum amount of electricity. It starts working only when the ambient temperature drops. If it is above +15 ° С, the wire itself stops functioning. Therefore, you can forget about interruptions in the water supply system.