Best Answers
◆ Cymus ◆:
Bimetal heating radiators
Over time, more and more people are thinking about replacing heating radiators in a city apartment, but are lost in the variety of their types. Bimetallic radiators are the optimal and modern solution to the problem of heating for a city apartment with a centralized heating system.
The prefix "bi" (i.e. "two") in the phrase bimetallic radiators indicates that heating radiators are made of two metals. As a rule, it is steel (inside, in contact with the coolant) and aluminum (outside, in contact with air). The steel inner coating, 2.5 mm thick, makes bimetallic heating radiators capable of withstanding high operating (up to 40 atmospheres) and pressure testing (up to 60 atmospheres) pressure and resist corrosion for decades.
Also, steel does not collapse under the influence of alkali, which is used in the central heating system to remove scale from heating pipes. Thus, bimetallic heating radiators with a steel frame are strong, reliable and durable. The shape, appearance and high thermal conductivity of bimetallic heating radiators are acquired thanks to the aluminum shell, which provides additional heat transfer to heating radiators.
Aluminum radiators The advantages of even the best heating system can be negated by improperly selected or low-quality radiators. And this is obvious - after all, a heating radiator is the device that transfers heat to the right place. No one denies the merits of cast-iron radiators familiar to us since childhood. They are reliable, serve for a long time, but they take up a large amount of space in the house, and because of their weight they are extremely inconvenient when installing the heating system. Another, but far from unimportant claim is made against the hostess' cast-iron radiators - they are very difficult to clean and wash, and painting them with high quality is a total torment! Modern aluminum radiators surpass their cast-iron ancestor in almost all respects. They are light, they transfer heat well into the room, they are small in size and have a flat surface that is easy to clean with standard detergents. Our company, along with other heating equipment, offers aluminum radiators from the best manufacturers. In our stores, the buyer can easily select the necessary thermal appliances made of aluminum. Don't forget to keep in mind that the area of an aluminum radiator should be about three times smaller than that of an old cast iron one - otherwise you will get too hot!
Chairman:
By weight: bimetal radiators are heavier than aluminum ones
Baseboard heating
In shape, skirting heating resembles old-style plate radiators - these are two pipes with a large number of thin plates. The difference is that these pipes are thin, as a rule - copper, have such a small height and width that they are hidden behind a high plinth of a special shape (open at the top). Due to the high heat transfer coefficient of copper, the power of these small radiators is high, it is gained due to the length - even around the entire perimeter of the room.
In addition to invisibility, baseboard heating has another plus - most of the heat is transferred not by convection, but in the infrared range - from heated walls. A stream of warm air rises along the walls, warming them up. When the walls heat up, they begin to radiate heat, which our body perceives as more comfortable. Cons of this system

Baseboard heating is almost invisible
The disadvantages of baseboard heating are the exactingness of the coolant and the thermal regime (it is impossible to overheat), low operating pressure (up to 10 atm). All this suggests that such systems can only work in individual heating, and with boilers controlled by automation.
Coins of the world
The list of bimetallic coins is striking in variety; they are issued on the territory of several countries. Currently, such banknotes are in circulation in 120 countries of the world.
Particular attention should be paid to the money that was minted in France during the reign of Charles I. A farthing with a rose was made from two metals: this was done in order to reduce the number of fakes
When chasing, a brass wedge was inserted into the copper billet. Later, according to the same scheme, pennies were minted from tin with a copper insert.
The penny is a unique coin as it is still in circulation in England. Previously, for such a trifle, you could buy a chicken or 20 eggs.
In 1792, a trial cent was minted in America as part of an experiment. The center of the coin was made of silver, and the ring that surrounded the silver was cast from copper.
Currently, there are a number of banknotes that are minted from two blanks:
- 1 euro, the middle of which is made of cupronickel, and the edging is made of brass.
- 3 euros: brass core and cupronickel edging.
- 5 South American rand. The core of the rand is cast from copper and zinc, and the ring from nickel.
- 2 dollars from Canada: the core of the dollar is made of copper, nickel and aluminum, and the edging is made of nickel.
- 2 dollars, where the core is cast from cupronickel, and the edging is made of brass.
Bimetallic coins are special, among them there are specimens that are minted from precious metals. Their release is most often timed to coincide with a memorable event.
What money is minted from precious metals:
- 10 US dollars. The composition of the alloy includes platinum and gold.
- 10,000 crowns - Slovak coin. It was cast from an alloy containing gold and palladium. Has five corners, minted in 2003.
- In 2003, the Austrian Mint surprised numismatists with the release of an unusual coin. The valuable specimen included niobium and silver. Since then, the Austrian Mint, as a tradition, began to issue one such coin per year.
The cost of such banknotes and their value is determined by experts. Often a coin made from 2 metals at once has not only historical, but also material value.
It is worth noting that today there is money that is minted not only from 2 types of metals. Three and four metals are added to the alloy, calling such specimens trimetallic and quadrimetallic.
In 1992, a significant event happened in France. The public was presented with a coin minted from three metals at the same time - 20 francs, issued in 1992, with the image of the abbey of Mont Saint-Michel. The core of the 20 francs was cast in bronze, the outer ring was made of an alloy of copper, aluminum and nickel, and the inner ring was made of nickel.
20 francs in 1993 were minted in honor of the Mediterranean Games in France, and 20 francs in 1994 in honor of the Olympic Games in Albertville.
The quadrimetallic coin was minted by a private mint in Britain. This event took place in 2006, the copy was made of silver, gold, platinum and polodia.
Which heating radiators are best for an apartment and a house
Now we systematize all the information a little from a different point of view - which batteries are better to choose for an apartment, and which ones for a private house or cottage. First, let's talk about what can be put in apartments. To choose everything correctly, you first need to visit the housing maintenance office or talk to plumbers. You need to find out what pressure is in your heating system and what is the acidity of the coolant and its operating temperature (at least according to the documents).It would be nice to know what jumps in temperature and pressure are. Armed with these figures, you will need to choose a specific model from those types of radiators that are suitable for your situation.
Now about what kind of heating radiators are best for an apartment. Here are your options:
- If you live in a high-rise (more than 12 floors), bimetallic radiators are most likely suitable, if the pressure is not very high, cast-iron radiators can work. When choosing, look mainly at the operating pressure, acidity, and they will withstand the temperature (although only full bimetal will do).
- If the operating pressure in your system is not higher than 14 atm, and Ph (acidity) is not higher than 7-8 and not lower than 5, then steel and aluminum radiators can also be added to cast iron and bimetal. Only for them, when choosing a manufacturer and model, it is necessary to monitor all three parameters - temperature, acidity, pressure.
-
If the system has a high Ph - from 8.5 and above, only bimetallic radiators (full bimetal) will do. They will also be an output at high working pressure (from 20 atm and above).
Once again, we draw your attention to the fact that when choosing a specific model, you must definitely look at the technical parameters. Only in this case, the radiators will work for a long time without repair and replacement.
Now about which radiators are best for a private house and cottage. These systems have a small volume, differ in that in them you control the state of the coolant yourself, you can adjust the acidity, clean the filters. So the selection by acidity in this situation is irrelevant. What needs to be considered is the type of boiler. If there is a solid fuel boiler in the system and there is no heat accumulator in it, which smoothed out temperature fluctuations, cast-iron batteries would be the best choice. They will withstand overheating, and their thermal inertia will smooth out temperature fluctuations.
In all other cases, aluminum radiators are the best choice. They have low inertia, quickly respond to temperature changes. They heat up in just minutes, and a tangible flow of heat comes from them. True, they cool down just as quickly, so that during an emergency stop, the house will be cold quickly.
Heating radiators, by the way, can be very original
Steel radiators will also be good. This is an economical option, but even during normal operation they do not last long - a short service life. For aesthetes, the option with plinth or convector (built into the floor) heating is suitable. Both systems work great with any automated boiler.
Cast iron batteries
The oldest of heating appliances. They are distinguished by high reliability, long service life, calmly tolerate overheating of the coolant (up to + 135 ° C), normally respond to water hammer. All because of the fact that they have thick walls. But the large thickness of the metal is not only pluses, there are also minuses. The first is a large mass. Not all modern building materials can support the weight of cast iron. Let today they are far from being as heavy as in the days of the USSR, but still much more massive than all the others. A large mass is also a difficulty in transportation and installation. Firstly, powerful hooks are required, and secondly, it is desirable to mount them together - the mass of a radiator for 6-7 sections is 60-80 kg. But that's not all. A large mass of metal means high heat capacity and significant inertia. On the one hand, this is a minus - until the batteries warm up, it will be cold in the room, but on the other - a plus, because they will cool down for a long time. There is one more minus in high inertia - cast-iron batteries are inefficient in systems with thermostats. All this together leads to the fact that cast-iron heating radiators are not installed very often today.

This is only a small part of modern cast iron radiators.
But they have their own scope - high-rise high-rise buildings.If the number of storeys is higher than 16, high pressure is created in such systems, which only cast iron and some types of bimetallic radiators (full bimetal) are able to withstand. Their properties are also optimal in heating systems of private houses and cottages with conventional solid fuel boilers without automation. These boilers have a cyclic principle of operation, then heating the coolant to a boiling point or even higher, then cooling down. Cast iron normally reacts to high temperatures, and also smooths out temperature differences due to inertia.
Until recently, cast-iron heating radiators had an unattractive appearance - the well-known and long-bored "accordion". Today there are models that look like aluminum or bimetallic ones - with smooth front edges, painted with powder enamel (most often white). There are many designer models, mostly on legs, decorated with cast ornaments. This option is generally available only in cast iron, all the rest have basically a more strict, ascetic design.
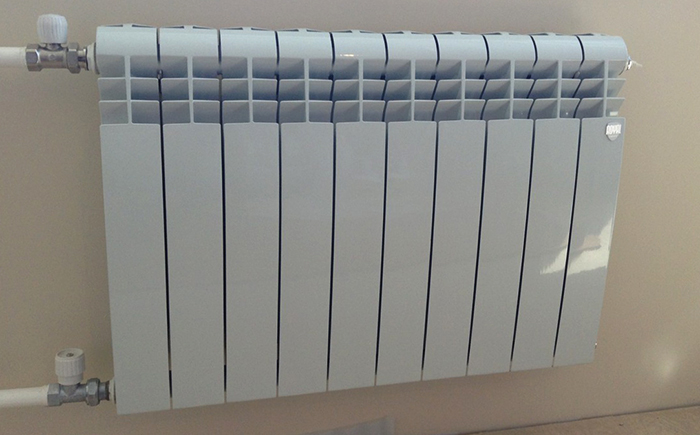
Bimetal radiators
These are two-layer devices. Made of two metals: steel and aluminium. The inner layer is made of stainless steel, the outer layer is a finned aluminum casing. All bimetallic radiators have:
- Long service life.
- Corrosion resistance.
- High-strength, not afraid of water hammer housing.
- Very good heat transfer performance.
- Compact and light weight.
- Ease of installation.
- Beautiful appearance.
Bimetallic devices are of two types: sectional and monoblock. Sectional consist of sections that are interconnected by means of threaded connections. Tightness is ensured by the use of special gaskets. Monoblock radiators are a one-piece welded steel body coated with a layer of aluminum.
The advantages of sectional radiators include high maintainability. If one of the sections fails, it can be easily replaced. The disadvantage is considered to be a rather high risk of leakage between sections, associated primarily with the use of low quality coolant. The use of a monoblock radiator greatly reduces the likelihood of leaks. But its big disadvantage is the high price.
What is common between steel and bimetallic radiators, what are their differences
When deciding on the installation of heating systems in rooms, their owners always have to solve the problem: which heating device is better? To get an answer to the question, you need to know the parameters for choosing these devices.
The comparison table below shows the similarities and main differences between steel and bimetallic heating radiators.
Table. Comparative characteristics of steel and bimetallic radiators.
| Steel panel radiators | Steel tubular radiators | Bimetal radiators | |
| Design | welded | welded | sectional, monoblock |
| Connection | any | any | lateral |
| Thermal inertia | low | low | low |
| Coolant volume | small | average | small |
| Installation of thermostats | recommended | recommended | recommended |
| Corrosion resistance | average | high | high |
| coolant | water, antifreeze | water | water, antifreeze |
| Permissible coolant temperature (deg) | 110 – 120 | 110 – 120 | 110 – 130 |
| Working pressure (bar) | up to 1 | up to 1 | up to 2.5 |
| Restrictions on the pH of the coolant | 6,5 – 9 | 6,5 – 9 | 6,5 – 9 |
| Corrosive effect of stray currents | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Pressure working / crimping / destruction (bar) | 6-12/9-18/27 | 6-12/9-18/27 | 35/57/75 |
| Use in tall buildings | Not recommended | recommended | recommended |
| Model range | wide | wide | wide |
| Peculiarities | recommended for rooms with high requirements for cleanliness | ||
| Warranty period (years) | 1 | 1 | 3 – 10 |
It should be noted that it is rather difficult for an unprepared person to get an exhaustive answer to the question of which batteries are better.Only a specialist after familiarizing himself with the heating system of a particular house can fully answer it.
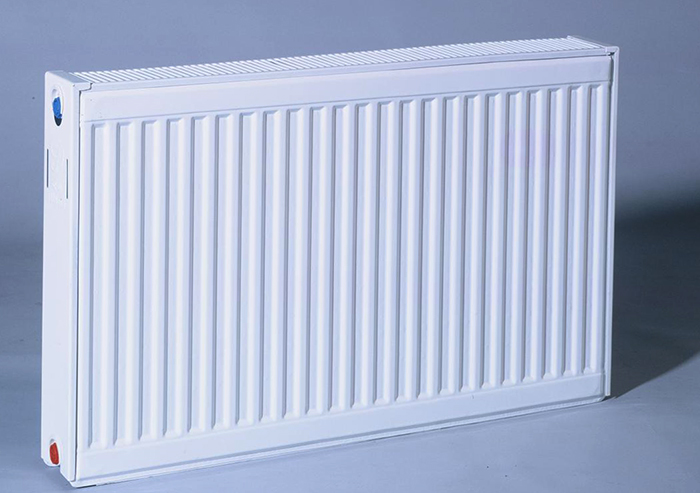
Steel radiators
Steel is an excellent material for heating radiators. Steel radiators according to the principle of the device are panel and tubular. Panel consist of 1-3 panels, tubular from round or shaped pipes.
Structurally, panel radiators are very simple: it is a sealed flat container welded from two steel plates. Panels have a lot of advantages, namely:
- Ease of installation.
- High heat dissipation. The panels are large.
- Profitability. To fill the panel does not require a lot of coolant.
- Safety for children. These devices do not have sharp corners.
- Neat appearance. Installation of decorative lattices is not required.
Along with the advantages, panel radiators also have disadvantages:
Water hammer resistance. Requires a gearbox.
Corrosion resistance. If there are a lot of salts in the coolant, then the inner surface of the heater becomes rusty.
Low strength
Care must be taken during operation.
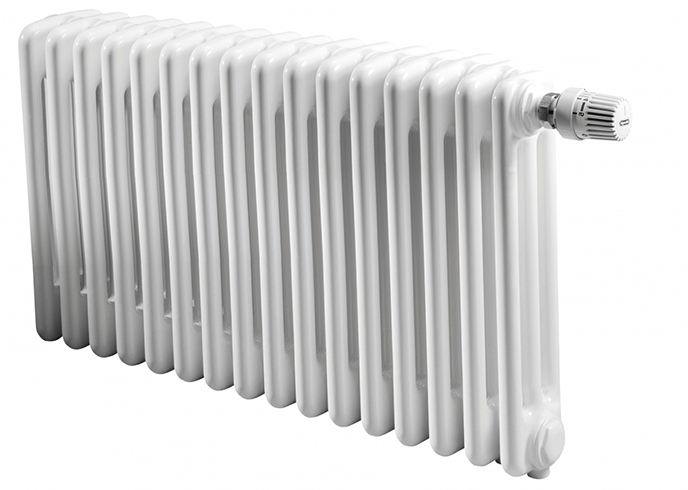
The second type of steel heating appliances is tubular radiators. They consist of several rows of tubes arranged in parallel. Their length can reach 1.5 meters.
tubular type
Outperform panel devices in terms of efficiency. But, due to the higher price, they are less common. Mostly used in private homes. Their advantages include:
- Uniform heating.
- High energy efficiency.
- Easy installation and maintenance.
- Precise adjustment of heat transfer with a thermostat.
- A variety of models in appearance.
- Low injury risk.
Of course, steel tubular radiators have some disadvantages:
- Corrosion resistance.
- High price.
- Instability to mechanical stress.
Main selection criteria
You have to solve the problem of choice, both when building a new house, and when repairing an old one. Heating radiators, as well as electricity, water, sewerage, are an essential part of engineering communications in any room. When choosing heating appliances, experts take into account four main indicators.
House type. When choosing a radiator, first of all, it is necessary to take into account the type of house. If the apartment is located in a high-rise building, then it is not recommended to install steel panel devices in it.
It is worth paying attention to bimetallic models. If the house is low-rise, then both types of radiators can be installed.
Appearance
The modern design of the device is not only a tribute to good taste, but also a testament to quality. Responsible manufacturers devote a lot of effort and money to developing optimal shapes that not only give a beautiful appearance, but also improve the thermal performance of the radiator.
Correct calculation of power. Underheating or overheating of the room means a loss of comfort. To avoid this, it is necessary to correctly calculate the required thermal power of the device. It is calculated according to a simple formula: the power (in watts) should be equal to the area of \u200b\u200bthe room in square meters multiplied by 100. If the room is well insulated and has metal-plastic windows, 200 watts are subtracted from the resulting figure. If the room is angular, or it has several large windows, then the power of the radiators is increased by 25%.
The right choice of manufacturer. Often in life, the pursuit of cheapness turns into problems. This fully applies to heating devices. A radiator made by a semi-handicraft method may not have the characteristics that are stated at all. After a couple of heating seasons, it may begin to leak and require replacement.
How to make the right choice? There can be no single answer. Everyone wants to have beautiful heating appliances that combine the advantages of both steel and aluminum.Of course, such a choice is not an easy task, but still feasible even for non-specialists. It is only necessary to have a minimum understanding of the subject of purchase and adhere to a few of the above simple criteria.
Only four of these simple indicators will allow the owner of a house or apartment to choose the optimal configuration of the radiator, its type and cost, and which will last a very long time.
Convectors
Recently, floor-to-ceiling glazing has become increasingly popular. Really beautiful, but what about the heating .... question. You can put low radiators on legs, but then all the chic is smeared. That's when floor convectors are used. Under them, a niche is made in the floor and the device itself is installed on the floor, closing it with a grate. In order to increase heat transfer at the same time (necessary for a period of cold weather), fans are built inside. The solution is aesthetic, but such systems cost decently. There is another nuance - fans, even the quietest ones, are noisy. This noise does not annoy someone, it bothers someone very much. In any case, there are more and less noisy models.

Floor convector - output for heating floor-to-ceiling French windows and glass doors
So, if you need to heat a French window from floor to ceiling, the best option is a convector built into the floor.
Aluminum
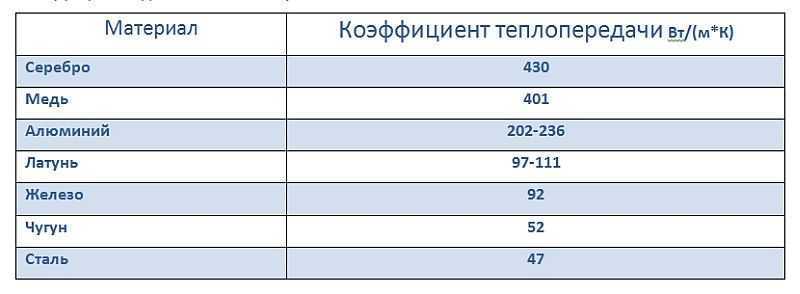
Aluminum heating radiators are not made of pure aluminum, but of an alloy based on it. This metal was not chosen by chance, as it has one of the highest heat transfer coefficients - 4-4.5 times better than cast iron and 5 times better than steel.
Table with thermal conductivity coefficients of different metals
Therefore, aluminum radiators are distinguished by high power (180-190 W per section), at least a high heating rate and low inertia. It is they who work very effectively in tandem with thermostats, allow you to maintain a stable temperature with an accuracy of one degree. The advantages of aluminum radiators include their low weight (one section weighs 1.5-2 kilograms), which facilitates delivery and installation. Another positive point is that the shape is designed in such a way that it has a large cross section of the channels for the coolant (slightly smaller than that of the cast-iron "accordions"). This is good, since there is a low probability that these channels will become clogged and the radiator will stop heating.
Now about the disadvantages of aluminum radiators. They are related to the properties of aluminum. As you know, it is a reactive metal. It actively interacts with most of the chemical table, and reacts especially violently with copper. And in modern heating systems, copper parts are common. Such a neighborhood threatens the rapid exit of the copper parts of the system and system, as well as increased gas formation. They learned how to deal with gases - they put automatic gas vents (valves) in the systems, and they save copper by not putting it close to aluminum appliances. The process, of course, still goes on, but not with such intensity.
Aluminum radiators look modern
The chemical activity of aluminum is also manifested in the demands on the quality of the coolant. Not in the sense of its contamination, but in the sense of its acidity. Aluminum radiators work normally in systems with a coolant acidity not higher than 7 (Ph 7).
The softness of aluminum is not very good for the operation of the heating system. In the alloy, from which heating radiators are made, there are additives that increase its rigidity, but, anyway, they do not work in high pressure networks. Typical working pressure is 8-16 atm depending on the type and manufacturer.
Based on the foregoing, an area looms where aluminum radiators will be the best. These are individual heating systems with boilers controlled by automation. They also feel good in apartments, but only in low-rise buildings (up to 10 floors), in which a coolant with Ph 7-8 circulates.
Steel panel and tubular radiators
There are two different types of steel radiators, with different characteristics and very different looks. These are tubular and panel. Some are made from steel pipes, others from steel sheets. Both of them have a relatively low price, which is what attracts them. But steel in heating systems does not “live” for a very long time, so these are also the most short-lived heating devices. Of course, there are exceptions - some manufacturers cover pipes or sheets with a protective layer, due to which the warranty period is estimated at a decade or even more. But the price of such steel radiators is also far from small.

These are tubular radiators. They can be both high and narrow, and low and wide.
Of the other characteristics - a small thermal inertia, exactingness to the coolant. Moreover, both in acidity and in the presence of foreign particles. Panel models are especially demanding - thin channels are formed in them through which the coolant moves. They are even thinner than bimetallic ones, so inlet filters are strictly required. If we talk about the acidity of the coolant, then the highest rate at which steel radiators work is Ph8. Working pressure - about 10-16 atm.
With power, the spread is very large. The design of both panel and tubular radiators is such that they can be of different sizes. Serially produced panel radiators are from 30 cm to 90 cm high, from 40 cm to 3 m long. There are special models that are elongated in height. Their maximum height is 2.7 meters (on special order they can do even higher, only there will be problems with transportation).
Panel radiators can be of different configurations and power
The variation in the size of tubular radiators is even greater. They can be from 19 cm to 3 m high, from 10 cm (two sections) to 3 meters wide, from 6 cm to 21 cm deep. The power of these radiators depends not only on the number of sections, but also on the number of columns (pipes in one row). Columns can be from two to six. Two or three columns can be hung on the wall, wider ones are often placed on the floor. Unlike all others, the sections of tubular radiators are one-piece, that is, they cannot be grown or reduced. They are welded together. On the one hand, there are fewer leaks, but on the other, less mobility. But this is compensated by their high plasticity - tubular steel radiators can be curvilinear - at least install them around columns or wrap large containers with plants (there is a minimum bending radius). There are, by the way, models in the form of benches or tables.
Which radiators are more suitable for which systems
1. Now, having examined and compared the main characteristics of radiators, we can draw conclusions. First, let's find out which heating radiators are better - aluminum or bimetallic - for an apartment in a multi-storey building. It uses central heating.
- The pressure in the system can change dramatically, reaching exorbitant values. Water hammer is possible.
- The temperature will also not be stable, sometimes changing greatly during the heating season and even during the day.
- The composition of the coolant is not clean. It contains chemical impurities, as well as abrasive particles. It is hardly possible to speak of a pH not exceeding 8 units.
Based on all this, you can forget about aluminum batteries. Because the central heating system will destroy them. If electrochemical corrosion does not eat, then the pressure will be finished with temperature. And the water hammer will make the last, “control shot”. Therefore, choosing from two types of radiators (aluminum or bimetal), stop only at the latter.
2. Now consider the heating system installed in a private house. A well-functioning boiler produces a constant low pressure, not exceeding 1.4 - 10 atmospheres, depending on the boiler and system. Pressure surges, and even more water hammer, are not observed. The temperature of the water is also stable, and its purity is beyond doubt.It will not contain any chemical impurities, and the pH value can always be measured.
Therefore, aluminum batteries can also be installed in such an autonomous heating system - these devices will work perfectly. They are inexpensive, have excellent heat dissipation, and their design is attractive. In stores you can pick up batteries made in Europe. It is preferable to choose models made by casting. Bimetallic batteries are also suitable for those who live in their own house. If you have the desire and enough funds, you can put them.
Just remember that there are many fakes on the market.
And if a model (whether aluminum or bimetallic) has a suspiciously low price, then you can already be wary. In order not to get into a mess, check that each section and the packaging (high-quality and full-color) have the manufacturer's marking
Russian coins
Bimetallic coins appeared in the days of the Soviet Union. It happened in 1991, minting continued in 1992 on behalf of the USSR. 10 rubles are considered special because their minting marked the collapse of the Soviet Union. It is also noteworthy that the state emblem was removed from the money.
Goznak of the USSR also issued 5 rubles, which were made of two metals, the Red Book series.
Later, the minting of money from two blanks was resumed, but this happened only in 2000.
Russian coins were minted in two types. Bimetallic coins made of precious metals were minted in a limited series, which is dedicated to the cities of the Golden Ring. There are only 12 pieces in the series, which are made of gold and also have silver inserts. Similar banknotes were minted in the period from 2004 to 2008.
From 2004 to 2011, banknotes were minted in denominations of 3 and 25 rubles. Their uniqueness lies in the fact that money made of silver has inclusions of gold, which are visible only on one side on the reverse.
It was possible to buy money cast from gold and silver at the Savings Bank of Russia.
In the Russian Federation, there is money that was minted from base metal alloys. But they are also classified as bimetallic:
- 10 rubles 1992.
- 50 rubles 1992.
- 100 rubles 1992.
- 5 rubles 1993.
- 30 rubles 1994.
After the collapse of the USSR, the Bank of Russia took up minting coins of the Red Book series.
At present, the number of series and money minted from two types of metal is much larger.
After a long break in 2000, bimetallic coins were minted. They are dedicated to the anniversary of the end of the Great Patriotic War. A circulation of 20 million is also considered unique - this distinguishes this series from others. 10 rubles were minted not only in honor of the 55th anniversary of the Great Victory, but also in honor of other significant events: the 200th anniversary of the formation of the ministry in our country, the 40th anniversary of the first flight of Yuri Gagarin into space. There is also a series visited by the ancient cities of Russia.
The circulation of a particular series ranged from several thousand to several million copies. So, for example, a series visited on the 60th anniversary of the Great Victory came out with a circulation of 60 million copies.
Kazakhstan and Ukraine are significantly behind Russia. In these countries, similar banknotes were issued much later.
Ukrainian 5 hryvnia
Since 2006, banknotes made of silver and tantalum with a face value of 500 tenge have been minted on the territory of Kazakhstan, which are included in the Cosmos series.
In 2003, for the first time on the territory of Ukraine, a coin with a face value of 5 hryvnia was minted, which was cast from two blanks. 5 hryvnias were issued in a limited edition, despite the fact that they were made of non-precious metal.
10 rubles
Recently, 10 rubles, made from two different blanks, have been popular among numismatists. Collecting leads to the fact that there are fewer and fewer coins in circulation. As a result, they turn into a rarity, and their value increases.
On the obverse of 10 rubles there is a hidden designation of the face value, it is enclosed in the number 0, you can see it, but for this you need to alternately change the viewing angle. Also in the number 0 you can find the inscription RUB.
On the yellow ring there is the inscription "Bank of Russia" and the year of minting the coin, the ornament is also decorated with two branches that go over to the white core.
10 rubles 2013 issue
With the reverse, everything is more complicated, it has changed several times and depends on which series the banknote belongs to.
In 2015, three coins with a face value of 10 rubles were minted:
- dedicated to the 70th anniversary of the Great Victory;
- dedicated to the end of the Second World War;
- dedicated to the liberation of the world from fascism.
It is noteworthy, but every coin of Russia, which was minted from an alloy that does not include precious metals, fits the concept of “bimetallic”. The reason is that money is clad with an alloy of copper or nickel.
But numismatists mean by this concept specimens that were minted from two types of blanks. At the same time, alloys for the production of coins must be made from various metals. Only in this case can money be called bimetallic in the view of numismatists.
Not all money minted from 2 billets at the same time are in demand among collectors. But there are also some that are quite expensive. If a marriage was allowed during minting or the exhibit has other features, numismatists can pay quite a lot for them. The most valuable are the banknotes of the Roman Empire and the first cents of the 17th century, cast in the USA as an experiment.
Expert answers
Paul Acc:
Aluminum heatsink:
1. Working pressure - 16 bar. 2. Crimping pressure - 24 bar. 3. Safety margin - 60 bar. 4. The maximum temperature of the heat carrier is 120°C
Bimetal radiator:
1. Maximum coolant temperature -110 C 2. Maximum operating pressure - 20 bar 3. Crimping pressure - 30 bar 4. Heat dissipation of 1 section - 171 W 5. Inlet - 1″
BABY:
Heat exchange during heating.
Maria Leon:
Bi is more expensive. And everything is Chinese.
Alexey Fedorov:
Bimetal is better. Withstands heavy loads and longer service life.
The Scarlet Flower:
Probably only the price, but they heat the same. I recently did heating, the master advised me to take aluminum ones, he said that they have better heat dissipation, they heated the winter normally, it was hot.
vnemugI:
For an apartment, bimetal is better because it is less susceptible to damage from aggressive components in water and holds more pressure than aluminum. Aluminum for a private house will be fine, where the system is filled with special antifreeze. In general, you know that there is nothing more reliable and better than cast iron. You can find out more here - .glavteplotorg /scat/cat36
vikont.X:
no difference at all. let's say the boiler gives +50 degrees. , then the heat exchanger will be +50 degrees. even if it's made of gold. the only difference is…. if you turn off the gas, some will cool faster than others. the same thing happens when they are heated, some quickly heat up others more slowly. everything goes to zero. buy affordable. advice: cast iron should be checked with a dosimeter, a lot of this junk is brought to us secretly from Chernobyl.
Yuri Uncovered:
I join the opinion that bimetal is definitely better, and even for a private house.
Alex Mishin:
In my apartment, aluminum radiators have been ideally serving for 12 years - domestic ARRPZ, now, alas, they are very difficult to find on sale. Imported models are worse because they have thinner internal channels through which the coolant flows.
Bimetallic radiators come in two fundamentally different designs. In some, a steel tube from the radiator fin goes into an aluminum manifold, and a galvanic couple is obtained that is in contact with water. Corrosion of aluminum in this place is, of course, extremely intense. In the second case, the water flows completely through the labyrinth of steel tubes. The tubes are covered with aluminum from the outside.In this case, it is not at all clear - why then aluminum? !
Why were bimetallic radiators invented at all? Yes, simply because it is easier for the manufacturer to take ready-made steel tubes than to form channels directly in aluminum! And the marketing of what happened as a result is designed to ensure the eloquence of advertisers ...
Sergey Arefev:
The site offers all different types of radiators and not only. s.a-lpha
Shura Blum:
Magnet.
Sergey Pomotov:
by passport
Valckhall:
by weight, in bimetallic radiators inside a welded frame made of steel pipes, due to it they hold more pressure than aluminum ones, but because of it they are much heavier.