Strengthening the slopes with a geogrid
In order to strengthen a ditch with crumbling soil or any other slope, a geogrid is used. It is a rigid frame with cells through which plants can grow. The geogrid is more stable than the geogrid because it does not slide down. The advantages of the geogrid are that it is non-toxic, passes water well, does not silt or decompose, and follows the contour of the relief.
You can strengthen a land plot using a geogrid as follows:
- Level the area, remove debris.
- Install anchors 600–900 mm long made of steel in increments of 1–2 meters. Anchors are installed along the perimeter of the geogrid modules.
- The grating is pulled over the anchors. A waterproof geotextile can be placed in the base.
- The geogrid must be filled with crushed stone or soil.
- The grate must be overfilled to provide UV protection.
- Rollers are used to compact the surface. On too steep slopes, this can also be done manually.
What plants can strengthen the slopes and ravines
Today, more and more people prefer to live outside the city. Villages are being actively built, under which new territories are being developed, and often, as a more economical option, lovers of a country lifestyle buy plots on the slopes.
In fact, this turns out to be not cheap at all: steep slopes require complex and expensive construction work, the creation of terraces and retaining walls.
But it is quite possible to try to strengthen the gentle, small slopes with plants, the main thing is to make the right choice.
Loosestripes are great plants to set up a sloping site without spending a lot of effort on caring for it.
Representatives of this genus can decorate both sunny and shady sides of the hill, with wet or dry soils. Spotted loosestrife will prefer southern, sun-drenched slopes, but shady places are not afraid of him either.
It has a long rhizome, branching at the end and forming a whorl of several underground shoots - in this way the plant very quickly conquers new areas for itself, holding the soil together.
The loosestrife will feel good on the shady side of the slope or in depressions where the soil is moist.
Monetary loosestrife is a very unpretentious ground cover plant, resistant even to trampling and undemanding to the place of growth.
Varieties of this group grow rapidly due to root offspring, so it is good to use them to strengthen the slopes. Light-loving roses will like the southern, southeastern and southwestern slopes.
The choice of resistant varieties is great, among them are, for example, 'Bonica', 'Snow Ballet', 'Fairy', and many other cultivars
It’s important to prepare for planting roses!” soil: dig it up to saturate it with oxygen, remove weeds, apply organic fertilizers (garden compost or well-rotted manure), mix with soil, add a handful of bone meal. Do not plant these plants in depressions - cold air stagnates there
Gentle northern slopes with moist soils may well be chosen by rhododendrons.
They have a compact and shallow root system, and in nature they grow under the canopy of trees. Rhododendrons are planted not so much as a slope reinforcement, but for an aesthetic effect as part of compositions of tree and shrub plants, the branched root system of which perfectly holds the soil. The trunk circle of rhododendrons must be mulched.
Decorative throughout the season, styloid phlox is a good choice for decorating the sunny side of a rocky slope. Numerous branching, rooting shoots form a dense carpet from green wintering awl-shaped leaves, decorative from snow to snow.Mix and match several varieties and let them grow freely.
In the spring, an unforgettable sight awaits you: the slope will be painted in pink, white, red, purple tones, depending on the varieties planted. These winter-hardy, low-maintenance plants prefer dry, poor sandy soils, they do not like stagnant water, so they do not need to be planted in lowlands.
The genus Veronica includes several, including mountain spikelets, they are stably decorative and drought-resistant, forming dense turfs of the Incas. It is advisable to use them as part of compositions on a slope, c. spicate has a number of varieties on
choice. Another mountain view filiform - quickly creates a dense light green carpet. This unpretentious plant is rapidly gaining space for itself thanks to creeping shoots that take root when in contact with the soil. Therefore, this type will look good with carpet arrays.
This species and its many hybrids are perfect for slope decoration. The powerful root system of adult specimens can reach 2.5 m in depth. Plants are photophilous, so they should be planted on the sunny side of the slope. Garden forms and hybrids of the river. wrinkled differ in the color scheme of the flowers and the height of the bush. Plants bloom from June and throughout the summer; buds, flowers, and ripened fruits can be observed on the bush at the same time. These roses are stable in central Russia, they winter without shelter. And due to the root offspring, they grow very quickly in breadth.
BASIC RULE FOR STRENGTHENING SLOPES WITH PLANTS: plant plants that form numerous offspring. Here, aggressive growth will not be a minus, but a plus. You need to choose stable, stable species that winter well in central Russia, quickly recovering.
Additionally, a geogrid or geogrid will not interfere.
http://kak-svoimi-rukami.com
Application of geomatites and biomatites
These types of soil cover are used to effectively protect surfaces with a slope of up to 45% or even up to 70% when planting.
For the manufacture of biomats, coconut fibers or straw are used, which are fixed on a layer of cellulose. Geomats are multilayer gratings, for the manufacture of which polypropylene is used.
Since the development of the root system of plants occurs over a certain period of time, in order to instantly stabilize the soil, it is necessary to first lay the retaining structures, and only then plant the plants.
Biomats have the following advantages: their surface becomes green in just 2 months, and the soil is partially fertilized when this material decomposes.
Geomats are a practical and relatively inexpensive material that has many advantages, the main of which are ease of installation, high efficiency and durability.
Roll material is laid on the surface of the slope, fixing all the pieces around the perimeter, and then sowing flowers or herbaceous plants. Due to the loose fibrous structure of the material, the seeds are fixed and germinate, subsequently forming a thick grassy carpet with an invisible reinforcing layer.
Best Answers
Vladimir Petrov:
Buy a plastic net, cover it with earth and plant grass and shrubs. It will help
Sergey Dmitriev:
Hammer the channel 10 - 12
Vasya111:
hire an excavator and clear the hill.
Uncle from the Future...
One option is to arrange something like a Larsen sheet pile in this place. . You just from obathf had something similar. . but in this case, make everything from stronger materials. .
The second option is to arrange a gabion in front of the slope. . what it is and how to do it look on the internet. .And if simplified. . in front of the slope, a mesh box filled with stones or rubble is installed. .
Ho-ho-ho:
if this elevation is on your site, then remove it, but warn your neighbor before that so that he strengthens his fence, well, or there by agreement. After all, you can do planning on YOUR site, and the ground will be poured from a neighbor from above. Therefore, it would be logical to strengthen your site where it crawls away. And they strengthen such places (with a sharp change in altitude) by erecting a monolithic reinforced concrete wall, with a recess in the ground.
Olga:
It is necessary to agree with a neighbor and divert at least surface water during melting. A drainage ditch will no longer fit on your territory
Mona Lisa:
You need an ordinary normal retaining wall, with drainage behind. Planting grass and shrubs will not help, it is only effective on slopes up to 25% and takes time.
Alexey Lomonosov:
ALEK:
The most effective means is the soil surface drainage system .drainage /uslugi/poverhnost/ which will provide protection against groundwater penetration to the surface of the site.
Camila Loginova:
Hello! A very effective way is to use gabions. They sit down so well that they merge and merge into a single whole with the landscape, strengthen the ground. stsgeo /gabioni/ here you can read more and order even for yourself. Gabions can be molded into almost any shape and are not that hard to install! I advise very much! Hope this helps solve your problem!
Geomats
Geomats are used to combat soil erosion and landslides. Geomats support vegetation cover on slopes and slopes.
Geomat is a polymeric material with a permeable structure. It is created by layers of polypropylene gratings superimposed on each other and interconnected by a thermal method. In its structure, the geomat resembles a kind of washcloth with a large number of voids.
The structure of the geomat protects the topsoil and anchors the roots of plants that have sprouted through it. The roots of germinated plants are intertwined with the fibers of the material and together with them form a strong system that strengthens the topsoil on slopes and slopes, protects against hydroerosion, weathering and landslides. There is a wide range of possibilities associated with the use of geomats: sowing with grasses, as well as filling structures with crushed stone, bitumen.
Geomat is used even on steep slopes. The use of this material allows planting slopes and slopes with an angle of inclination up to 70°. In combination with geotextiles, geomats are used to reinforce and increase the bearing capacity of slopes.
The main properties of geomats:
- UV resistant
- Resistant to aggressive media and water
- Retain properties at temperatures from -30°С to 100°С
- They have a low level of flammability and a low level of smoke
- Non-toxic, can be used in contact with drinking water - on the slopes near the spring, for example.
- Allows you to maintain the natural look of the landscape
- Reduce time and cost of construction due to ease of installation and installation that does not require special skills
Geomat laying:
Pay attention to the fact that before laying the geomats, the slope surface is leveled and debris is removed.
The surface must be compacted if the slope is filled. This is done with hand rollers weighing 20-30 kg.
At the base of the slope at the top and along the bottom edge, an anchor trench should be dug about 30 cm deep
Also make sure that a drainage system has been created - ditches, trays, etc., so that water is discharged down the gutters and pipes.
The upper edges of the geomats are fixed in this trench with dowels or anchor bolts. * (approx. Nagel in construction is a large nail), also the mount can be made of wooden horns, which are driven into the ground with a hammer. Geomats should be laid with the smooth side to the ground. Please note that in the longitudinal direction, the overlap of the geomat sheets should be about 15 cm, and in the transverse overlap of the top sheet of the mat to the bottom one should be 20 cm. The overlap step is 1 meter. If geomats are mounted on a steep slope, then additional anchors are installed in increments of 0.5 meters. Under medium slope conditions, the number of anchors is 2 anchors per 1m2 of surface. (rice.)
It is necessary to roll out the roll and cut it to the desired length.
It is necessary to stretch the roll, straighten the folds and irregularities.Check that the geomats are as close as possible to the slope surface, repeating its profile.
The lower edges of the geomat must be fixed in the lower anchor trench with fasteners (anchors, dowels or spears).
Make sure that after fastening the edges, the anchor trenches are covered with soil and compacted.
Geomats are covered with vegetable soil. Backfill layer 2-5 cm. Check that the entire surface of the geomat is covered. Please also note that if there is a possibility of water descent along the slope, it is necessary to backfill with crushed stone of a fraction of 2-6 mm.
The covered soil is sown with seeds (It is best to sow the seeds at the beginning of the growing season of plants. The approximate consumption of seeds is 40 g per 1 square meter of surface. Two-thirds of the seeds are sown on open geomats or on the slope surface before laying, and one-third after filling the material with vegetable soil).
For anti-erosion protection of slopes, geomats are considered one of the most effective materials in terms of manufacturability and cost of construction.
Improvement of the ravine
In ravine terrain, you can equip a reservoir, a recreation area or a sports ground. An original bridge can be made over the pond. There are many ways to improve the ravine. You need to choose a specific option in accordance with the characteristics of the area. But, in any case, strengthening the slopes is required.
If there is a stream nearby, it is recommended to take it away. To do this, you can build drainage in the form of a pipeline or use backfilling. If the stream is already in the ravine, it is better not to remove it, but to ennoble, equip the banks. Blocking the channel is highly discouraged, it is fraught with serious consequences, up to flooding of the area.
If it is planned to organize a reservoir, the ravine must be cleared of thickets. The bottom should be strewn with a sand or clay layer, followed by careful ramming. Next, you can add water. Fish farming is also acceptable. The resulting banks should be decorated with stones, perennials or decorative elements, including useful vegetation.
The sports ground and recreation area must be equipped on a solid foundation. The latter may be a concrete pavement or special flooring. It is acceptable and simply leveling, followed by tamping the soil.
Volumetric geogrids.
In recent years, to strengthen slopes and slopes, including steep ones, they began to use a three-dimensional lattice, which is a honeycomb structure made of polymer strips welded in a checkerboard pattern. The grid is stretched, evenly laid on the slope surface and fixed with L-shaped anchors or pegs. The cells are filled with crushed stone, soil, etc. (Fig. 5). When laying lawns to strengthen its base, especially when landscaping slopes, another method is also used. Lawn grids are laid on prepared soil, covered with a small layer of fertile soil and sown with grass. Grass roots quickly grow through the cells of the grid, firmly fixing it. The three-dimensional grating also solves such an unusual (important) task as protecting lawns and slopes from moles, which often spoil the grass cover with their molehills. The fine-mesh grating blocks the access of rodents to the surface of the earth, and over time they leave the site.
The first stage of work in all proposed options is the leveling of the slope surface for laying the grating. The top layer is compacted with a hand roller or vibrating plate. A layer of non-woven geotextile is laid on the ground, which plays the role of drainage for surface water. A geogrid is laid on top. It should be noted that the steeper the slope, the higher the height of the lattice edge should be. The modules are stretched and fixed with L-shaped anchors, checking the uniformity of their tension. Separate gratings are stapled together or connected with U-shaped anchors.
In the upper part of the slope, the geogrid should emerge on a horizontal surface at least 0.5 m from the edge, and then go deep. After fixing the geogrid, the cells are filled with soil, sand, crushed stone or gravel manually or using a loader. Filling is carried out from top to bottom along the slope to the height of the geogrid + 5 cm.
Ceramic blocks, stones
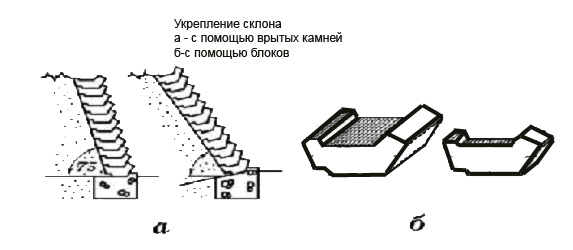
With various slopes, even quite large ones, including on slopes with the possibility of a landslide, a method is used to strengthen the surface with stones and logs dug deep into the mountain. If water flows down the slope, use a special tray to direct it in a certain direction so that it does not destroy the soil (Fig.)
Rice. An example of strengthening a collapsing slope with the help of ceramic blocks: 1 - base soil; 2 - sand and gravel base; 3 - bedrock; 4 - sod layer; 5 - curbstone-lounger; 6 - the direction of slipping mini-mudflow; 7 - direction of water flow; 8 - draining excess mudflow water; 9 - water flow into the drainage tray; 10 - tray; 11 - side stone; 12 - plants.
In some cases, the slope can be strengthened with stones dug into the ground (Fig.) To strengthen it, concrete blocks dug deep into the ground are used (Fig.)
Boards and logs dug across the slope, wooden dies dug into the ground, and so on will also help to keep the soil on the slope. The choice of a particular solution depends both on the style of the garden and on the condition of the surface and soil of the slope.
Geotextiles for strengthening earthen slopes
Geotextile is a non-woven material that is sold in rolls. It is made from polyester and polypropylene fibers. Geotextiles are used to strengthen slopes up to 60 degrees. The material has many advantages:
- frost resistance;
- the possibility of large stretching;
- resistance to aggressive environments, water resistance;
- not susceptible to mold and fungus;
- does not rot and does not tear;
- ease of installation.
Geotextiles increase the bearing capacity of the soil, due to which it does not slip, does not collapse. In addition, strengthening the slopes in the summer cottage with geotextiles prevents the soil layers from mixing when the water drains. The geotextile laying technology is as follows:
- The surface to be reinforced must be leveled.
- It is necessary to take out the soil at a depth of 20–50 cm. Place geotextiles in the recess, pour crushed stone or gravel on top.
- The next layer is geotextile again. Top with sand. Next, you need to lay paving stones or tiles. To do this, you can use a cement mortar.
- To equip the site, which will be above ground level, it is necessary to lay geotextiles, while adhering to an overlap of 20 cm. Formwork should be made around the perimeter. As before, sprinkle sand or stone on the material and lay another layer of geotextile, then sand and tile again.
- Overlapping parts of the geometries must be secured with staples.
So, strengthening the soil on sloping terrain is a rather time-consuming process. However, if this is not done, the consequences can be dire. Fortunately, the modern market offers many special devices for this purpose. But we should not forget about the old well-known method - planting trees. The best option would be a combination of both methods.
Slope strengthening
It is necessary to strengthen the slopes in almost any case. To prevent a further increase in the ravine, to eliminate the risk of shedding and erosion of the soil, you can resort to the following measures:
- Planting trees, shrubs and grass. The roots of the trees will protect the slopes from collapse and erosion.
- Installation of reinforcing structures in the ground. It is necessary to build a reliable frame for the slopes. Geogrids, volumetric geogrids, biomats and similar materials can be used. All kinds of meshes, gratings and reinforcement mats are commercially available in the form of rolls.The material only needs to be unwound over the surface and slightly deepened into the ground. If the slope is too steep, it is better to use geomats. Such products are made from polymeric materials, respectively, will not collapse during operation. Due to the volume, they better delay erosion. Geogrids can be considered a universal solution. The product is a high-strength canvas with cells of the same size. In the northern regions, it is more expedient to use geomats. They are distinguished by the presence of a multilayer base, which gradually decomposes. Between the layers, soil and seeds are laid that are optimal for steep slopes of vegetation. The design has special polymer elements to retain moisture and prevent soil erosion.
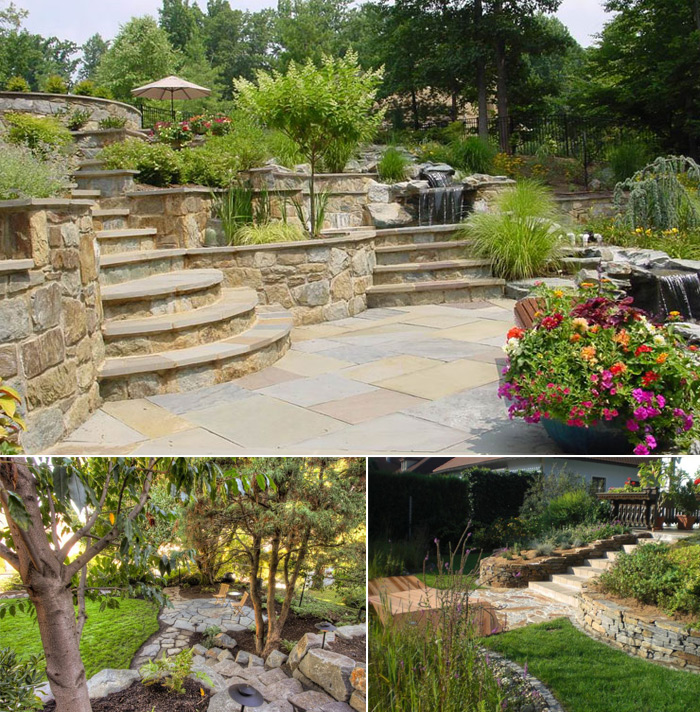
- Terracing of slopes, installation of ledges (in the form of steps) of a horizontal form, strengthening with retaining walls. Various materials can be used: wood, concrete, stone, brick. Terraced not only provides soil retention, but also acts as an element of landscape design.
It is highly recommended to provide drainage in the ground in order to prevent the destruction of retaining walls by water. Regardless of the strength and type of material, constant exposure to moisture always leads to the destruction of the structure.
Retaining walls can have different heights, up to several meters. This is especially true for ravines with excessively steep slopes. Stones and similar materials are very well suited, they provide both reliability and aesthetic appeal.
Beautiful and (or) useful plants should be planted in the gaps between structural elements. High walls are best planted with low-growing vegetation.
It is extremely difficult to make a full-fledged garden in a ravine. Sometimes the best solution is to create artificial beds. They allow you to grow any kind of plants. The beds are connected to the erected retaining walls, due to which both practicality and aesthetics are achieved.
Methods for strengthening slopes
-
Planting trees with a branched root system. The method is effective with slopes up to 8%. Trees can be planted in the cells of reinforcing structures. Roots, intertwined with fasteners, form a reliable protection against destructive processes. In this way, it is possible to prevent not only soil erosion, but also landslides. Plant quince, cotoneaster, elderberry, barberry, wild rose, climbing roses within the slope of the garden - singly or in groups, but not too close to each other.
Willow hedges can also provide erosion control. Cut willow branches (about 70 cm long). Plant them crosswise along the perimeter of the slope, water the future trees abundantly.
- Strengthening with reinforcing elements. Stones, logs, geogrids, biomats are implanted into the ground in order to create a frame and fastened with anchor bolts.
- Terracing is the creation of retaining walls. This method was quite popular in Europe in past centuries. Retaining walls are not only durable and simple, they serve as a kind of garden decor. For a small slope, a support up to 0.5 m high is erected. A layer of soil is removed from the slope, then drainage and flat stones are placed along the hill. If the height of the slope is more than 0.5 m, a foundation is laid at the base of the slope, and only then concrete blocks or natural stones. The foundation must really be strong, because it is it that gives stability and prevents destruction. To ensure that water does not accumulate at the base, it is necessary to take care of drainage. To build a retaining wall, you need to develop a project and choose the right material.
- Brick walls are laid in such a way that the vertical seams of one row do not coincide with the seams in the higher and lower rows.
-
The wall made of natural stone looks decorative. Lay stones of different sizes on top of each other (the gaps between them should be filled with earth, later plants can be planted in them).
- The concrete wall is connected to the metal, and then lined with artificial or natural stone.
- Wooden props, although less durable, are attractive enough to be used in a garden or park.
- Artificial stone blocks are often used for retaining walls. Of these, you can also build a barbecue, pergolas, containers for flowers.
- The slope is a great place for rock garden. However, keep in mind that a rocky garden needs regular watering. Build ledges at the base of the slope, the layer of soil will not be washed out.
Engineering and geological expertise
To determine “by eye” the presence of groundwater in the ravine, as well as the tendency of the soil next to it to erode, is the surest way to be at the bottom of this very ravine, along with all the buildings and without funds for repairs. Therefore, if you decide to buy a plot next to a ravine, then the first to launch into the territory is not a cat, but a team of engineers.
It is they who will be able to find out the geo- and hydrodynamics at the site. From their report, you should understand whether the ravine will expand and at what rate, whether it can be filled in or limited in growth and what this will require, as well as how deep the groundwater is under the bottom of the ravine and how high it rises during the rainy season . Only after receiving answers to all these questions, it is worth considering the option of acquiring this site.
Plants to strengthen the slope
This method of strengthening the slope is suitable if there is no desire to spend money. The essence of the method is that plants with a powerful root structure fix the earth and prevent it from crumbling. There are many plants with such properties. Suitable for this purpose will be ground cover and cereal lawns. Grasses will only be effective if the slope angle is no more than 8%.
Among the trees and shrubs, there is also a large selection. Great for:
- juniper;
- lilac;
- rose hip;
- Pine;
- hawthorn;
- blackberry;
- quince;
- sea buckthorn;
- tree peony.
For plants planted on a slope, frequent watering is necessary, especially for beds on a slope. The fact is that the water does not linger in the upper layer of the slope and goes down. But to achieve a beautiful even lawn in such an area will not work. An uneven place can be used for a more practical thing than a vegetable garden and beds. For example, a playground, a glade for recreation.
Slope Safety Measures
To avoid the risk of a landslide, every three or four terraces down the slope they build a main wall in the form of a gabion or rubble-cement masonry 60-80 cm wide. Such a wall allows you to effectively strengthen a slope 10-15 m long. A stone wall must have a bundle, for example, cement, lime, clay mortar, or, as in the case of a gabion, a steel mesh. Often, masonry is reinforced by arranging piles of asbestos-cement pipes, this allows you to seriously strengthen the barrier and reduce the size of the masonry.
In the broken terraces, safety paths must be equipped. In fact, these are ordinary paths or stairs leading down or up the slope, the base of which is reinforced with geogrid, gravel and anchor rods.
This solution allows you to make terraces of unlimited length without the risk of soil slipping. In addition, drainage trays are installed on the paths, discharging water down the slope of the summer cottage. Of course, paths and stairs can be made in the form of a snake or a broken march, this will only strengthen the slope.
A good addition would be to plant low-growing shrubs along the edge of the terrace, such as gooseberries or currants, this will strengthen the edge and prevent the terrace from shedding.
Expert answers
Nelya Guseva:
Concrete steps with reinforcement, or lay stone in steps Peculiar terraces, up to 3 meters wide
Alexander Dmitriev:
Piles hammer, and then the scribe.
Peter Sidorov:
better do this, plant a bush with offspring possibilities in front of the ravine and on the slope ....and you can also try to dot the slope with seeds of perennial plants ... even a dandelion
Andrey:
dig a well or a deep trench - this is a plus to plant piles and shrubs on a ravine and sow other grass every year so that the walls of the ravine do not erode further - all this was given to you at school in the third grade in a natural history lesson
Tatyana:
Plant willows or willows along the very edge, and drive piles or stakes into the ground deeper in front of them.
bakhtiyar irgashev:
drainage must be done and all sorts of willows should be planted from the side of the ravine so that the roots hold the soil and drainage is not difficult to do, only money is needed, you need to take asbestos-cement pipes to make holes on one side and pour crushed stone into the trench, put these pipes with holes down from above, fill them up again and by gravity the water in these pipes will leak out and lower the water level in the ground
Natalia Begisheva:
The easiest and cheapest way to fix ravines is to line the bottom and walls of the ravine with brushwood. Brushwood is placed clods down, against the flow of water. Any brushwood is suitable here - willow, aspen, pine, and if there is an opportunity to choose, then one should give preference to the one that is more gnarled. They lay it in a layer from 0.3 to 0.7 m thick, strengthen it from above every 1.5 - 2 m with transverse slabs, which are tied with wicks to clogged stakes. Streams of water running down the ravine, filtering through brushwood, leave earth, sand and silt in it; thus little by little the brushwood is filled with drifts, which are then covered with grass and turf, and the surface of the ravine becomes permanently fixed. If one layer of brushwood is not enough, then when it is filled with earth, a second layer is laid on it, etc. It is useful to add some part of living willow brushwood to dry, dead brushwood; it is also good to take willow stakes. In this way, with one or two bundles of brushwood and a few willow stakes, small ruts and gullies can be fixed.
Inna Alekseeva:
We have a plot with a house on the mountain. Crawled hard. They made a retaining wall at the bottom of the site, concrete terraces. Now let's crawl a little. If the neighbors did the same, it would be even better. True, at the bottom we have a road and then a cliff. Shrubs and grasses - right. We also planted irises along the terraces (they keep the soil well). In the upper part of the site and in the dacha, the terraces were made of rebar (instead of piles) and slate.
P()m@}-{:
hammer stakes along the edge. horizontally fill boards on them and finish with slate from the inside of the site, hire a taji - let them grind off a high edge and pour from the edge of the slope until leveling along the perimeter of the site on a sand cushion in three fingers, dig asbestos pipes 20 cm (fine gravel inside up to half, the top of the pipe - with holes .)
Mirage Mirage:
Drive piles)
Alya Dichko:
We just dug up logs.
mark trukhanovsky:
Drive piles along the border of shedding to a depth of freezing point + 15%. But it would not have turned out to be more expensive than a house. While the shrub will grow, you will leave with it.
Stalin:
Plant trees and shrubs.
Paul:
To start, make beds in wooden boxes. To strengthen the house, it is necessary to install piles that have entered the bedrock for half a meter
Granny Tanya:
Make a retaining wall at the border of the site so that the bulk soil does not slip. To do this, drive reinforced concrete piles or a metal profile (channel, I-beam), drive so that the piles enter the mainland soil, then the wall itself is made of monolithic reinforced concrete, the base must be wider than the thickness of the wall at the top, install the reinforcement from the inside, where the soil will press, the wall will also reach the mainland soil. Expensive but reliable.