OD categories
Metal pipes are produced with outer diameter from 10 mm to 1420 mm. According to the value of this parameter, they are conventionally divided into three categories:
1. With an outer diameter of 10 mm to 108 mm, pipes are classified as small diameter products. They are used for laying plumbing systems in apartment buildings and private houses;
2. With an indicator from 114 mm to 530 mm - to pipes with an average diameter. They are used in crude oil collection systems and in the construction of urban water pipelines;
3. With an outer size of 530 mm to 1420 mm - to pipes with a large diameter. They are used in the laying of main oil and gas pipelines.
What are the GOSTs for steel pipes
The list of technical indicators of any type of steel pipe directly depends on which manufacturing method was used. All this is determined with the help of GOSTs, knowledge of which, at least, will make it possible to take into account recommendations for the operation of a certain type of pipe.
Currently, the following regulatory documents for the production of steel pipes are most often used:
GOST 30732-2006. It was adopted in 2006: its provisions relate to pipes and fittings made of steel coated with a heat-insulating layer.
Steel products, where polyurethane foam thermal insulation and a polyethylene sheath are used, or a protective steel coating, are used in cases where it is necessary to lay underground heating networks. The coolant temperature should not exceed 140 degrees (increase to 150 degrees is allowed only for a short time). In this case, the pressure in the system should not exceed 1.6 MPa. GOST 2591-2006 (88).
GOST, designed for hot-rolled steel, was adopted in 2006, although some sources allow the use of the old GOST - 2591-81. The document contains information regarding square steel products, for the manufacture of which the "hot" method was used. This GOST applies to all products with side sizes from 6 to 200 mm.
Larger square pipes are produced if the manufacturer and the customer draw up a separate contract. GOST 9567-75. It stipulates precision pipes made of steel, for which high precision manufacturing. A distinction is made between cold-formed and hot-rolled galvanized or chrome-plated precision tubes.
The machine-building industry especially needs the products of this increased GOST. GOST 52079-2003. This document specifies the standards for longitudinally welded and spiral welded pipes made of steel with a diameter of 114 - 1420 mm. From such overall products, main gas pipelines, pipelines through which oil and oil products are transported are equipped.
GOST 52079-2003 indicates that only products that do not have corrosive activity can be transferred through these pipes. With the help of steel pipes with large diameters, it is possible to transport substances with a pressure of up to 9.8 MPa. For the environment, a temperature minimum of -60 degrees is set.
At the same time, it is important to know that officially GOST 52079-2003 is no longer valid: from January 1, 2015, a new GOST 31447-2012.GOST 12336-66 is in effect. Its provisions apply to closed products of a profile type, with a section in the form of a square or rectangle.
Starting from January 1, 1981, the powers of GOST 12336-66 were transferred to TU 14-2-361-79, but the relevance of its provisions has not been lost to this day. GOST 10705-91 (80).
Contains a list of technical conditions under which longitudinally welded steel pipes with a diameter of 10 to 630 mm are produced. For the production of pipes according to this GOST, carbon or low-alloy steel is used. These products are used in many areas, but the priority is the pipeline for pumping water.
The provisions of the standard do not apply to steel pipes from which electric heaters are made. GOST 10706 76 (91). Concerns electric-welded steel pipes of longitudinal type, which have a general purpose. As follows from this document, the diameter of this product is in the range from 426 to 1620 mm. GOST 10707 80.
Here are the standards according to which electric-welded cold-formed pipes are produced, having a different degree of accuracy: ordinary, increased and precision. The diameter of the products targeted for this document can be from 5 to 110 mm: in this case, unalloyed carbon steel is used. Sometimes electrically welded longitudinally welded products have references to GOST 10707 80 in the accompanying documentation: this is due to the fact that in 1991 it was decided to extend the validity of this document.
The main types of pipeline parts
| bends | plugs | ||
| transitions | fitting | ||
| tees | adapter rings |
There are industrial (technological) and main pipeline transport depending on the territorial location and purpose. Gas and oil pipelines that transport products from production sites to processing and consumption sites, namely to factories or seaports for subsequent unloading into tankers and further transportation, are classified as trunk pipeline transport. Finished oil products are sent from the refineries through the main product pipelines to the areas of consumption. On the territory of Russia, the total length of main pipelines is about 200,000 km, including various water barriers that they cross more than 5,000 times on their way.
More than a third of the pipelines of industrial enterprises are technological pipelines. Process pipelines transport liquid, steam, gas, which are considered raw materials, semi-finished products, finished products, production waste or products required for the correct flow of the technological process. In addition, these pipelines transport flammable and hazardous products at different temperatures and pressures.
Classification of technological pipelines occurs according to the following criteria:
Location: intershop, intrashop.
Laying method: aboveground, ground, underground.
Internal pressure: non-pressure (gravity), vacuum, low pressure, medium pressure, high pressure.
Temperature of the transported substance: cryogenic, cold, normal, warm, hot, superheated.
Aggressiveness of the transported substance: non-aggressive, slightly aggressive (low-aggressive), medium-aggressive, aggressive.
Transported substance: steam pipelines, water pipelines, oil pipelines, gas pipelines, oxygen pipelines, fuel oil pipelines, acetylene pipelines, oil pipelines, gasoline pipelines, acid pipelines, alkaline pipelines, ammonia pipelines, etc.
Material execution: steel, steel with internal or external coating, non-ferrous metals, cast iron, non-metallic materials.
Connection way: detachable, detachable.
The scope of connecting parts of pipelines is diverse: heavy chemical industry, petrochemical, gas; production of various specialized preparations; electric power industry (CHP and NPP); exploration, production, processing and storage of oil and gas, as well as other minerals; metallurgical and steel production; shipbuilding, automotive and food industries; civil engineering and utilities (district heating and water supply, water collection and hydropower facilities, distribution, irrigation systems, transport and pumping stations, wastewater treatment plants, water treatment and water treatment, control systems.)
Our plant manufactures pipeline parts from various steels: carbon, low-alloy, alloy steels, with increased corrosion and cold resistance, from non-metallic materials, as well as with various protective coatings.
Assortment of steel seamless pipes, according to GOST 8732-78 91
The production of hot-formed seamless steel pipes according to GOST 8732-78 (91) is characterized by long and complex processes. It is this factor that explains the rather high price of this product. The use of hot-formed and cold-rolled seamless pipes is suitable for extreme conditions, where the consequences can be the most serious if the slightest leak occurs.
The raw materials for the production of hot-formed pipes without seams are metal blanks: the piercing process and heating to high temperatures leads to the formation of hollow cylinders from them - sleeves. Initially, their irregular shape, due to the passage of the rollers, acquires even outlines. Segments 4-12.5 m long are cut from the sleeve (the length can be measured and unmeasured).
For steel hot-rolled according to GOST, a slight discrepancy in wall thickness is allowed. The same applies to deviations in diameter: the main thing is that these differences do not exceed special regulatory guidelines. The list of permissible diameter deviations according to GOST 8732-78 (91) is available in special documents.
6. Pipe fittings
Pipeline accessories
intended for
management of oil flows transported
through pipelines. According to the principle of action
fittings are divided into three classes: shut-off,
control and safety.
Shut-off valves (gate valves)
serves to completely cover the section
pipeline, regulatory
(pressure regulators)
- to change pressure or flow
pumped liquid, safety
(reverse and
safety valves) - to protect
pipelines and equipment for
exceeding the allowable pressure, and
also prevent reverse currents
liquids.
gate valves called
locking devices in which the passage
cross section is overlapped by translational
by moving the shutter in the direction
perpendicular to the direction of travel
oil. Structurally (Fig. 12.10) valve
is a solid cast or
welded body, equipped with two
branch pipes for connection to
pipeline (using flanges or
welding) and a spindle connected to a shut-off
element and controlled by
flywheel or special drive.
Spindle exit point
sealed with a gland
seals.
According to the design of the shutter
valves are divided into wedge and
parallel.
Valves on main oil pipelines
equipped with an electric drive (Fig. 12.11).
Pressure regulators
devices are called
employees for automatic maintenance
pressure at the required level. V
where supported
pressure - before or after the regulator -
distinguish between regulators of the type "to itself" and
"after myself".
|
|
|
|
Rice. 12.11. Flanged steel gate valve 1 — |
|
|
Rice. |
Safety
valves called
devices to prevent
pressure in the pipeline in excess of the set
quantities. Used in oil pipelines
small and full-lift safety
closed type valves
the principle of discharging part of the liquid from a place
increased pressure in
special prefabricated manifold (Fig.
12.12).
check valve called
anti-reverse device
movement of the medium in the pipeline.At
valves are used for pumping oil
reverse rotary - with a shutter,
rotating relative to the horizontal
axes (Fig. 12.13).
Armature of main oil pipelines
designed for a working pressure of 6.4 MPa.
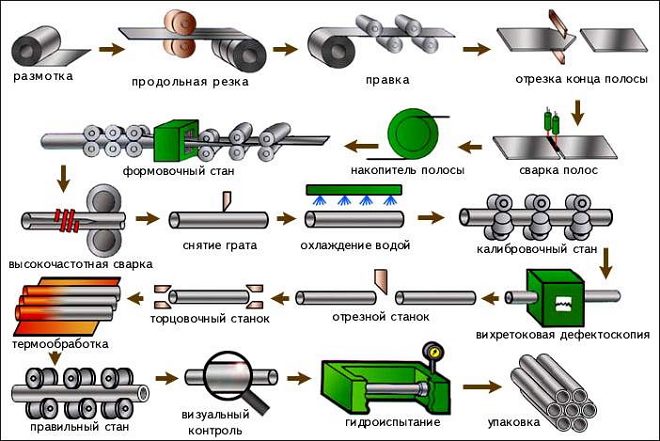
Production technology
The technological process by which electric-welded pipes are made consists of a number of operations. It is quite complex, laborious and time consuming. In order for the electric-welded pipe to acquire its finished form, it is rolled up from a strip (strip), which was previously made by cold or hot deformation.
For the manufacture of high-quality and reliable pipes of different diameters, radio frequency welding is mainly used, which, among other things, makes it possible to perform the metal joining process at a fairly high speed. With this method of welding, high voltage currents are passed through a pre-rolled workpiece, which contribute to the rapid heating of its edges. In order for a reliable weld to form in place of the heated and melted edges of the workpiece, they are pressed against each other under high pressure. In order to obtain a billet for an electric-welded pipe of the required diameter from a steel strip (strip), special swaging mills are used.
This technology, which is used at specialized enterprises to produce longitudinal and spiral-seam electric-welded steel pipes, allows not only to obtain high-quality and reliable products at the output, but also to provide them with an attractive appearance (the weld on such products is almost imperceptible).
Technological process of production of welded pipes
Other types of GOSTs for steel pipes
Normative documents also apply to other types of products and operations related to steel pipes.
The list of GOSTs that regulate the methods and procedures for installation using steel pipes, as well as various fasteners and connecting elements for them:
Welding. GOST 16037-80 - contains a list of requirements for welding steel pipes. There is also a setting for the main structural elements, typical sizes of welded joints with other elements (this does not apply to electric welds that are on the steel pipes themselves).
GOST 6996-66 - it regulates the strength characteristics of all metal joints. Fittings. This term generally refers to all piping parts of a connection. GOST 8966-75 describes how metal straight couplings are produced, with the help of which steel pipelines are created.
They can be galvanized, having a cylindrical thread at the ends: with their help it is allowed to mount pipelines for transporting non-aggressive media with temperatures up to 175 degrees, at a pressure of not more than 1.6 MPa. GOST 8967-75 refers to the production of galvanized or simple nipples, which have a cylindrical thread: they most often connect water pipes or gas systems. The diameters of the nipples are from 8 to 100 mm, with the galvanized models having the designation "C".
GOST 8968-75 determines the technical characteristics of a lock nut with or without an anti-corrosion coating: they are screwed on top of the main nuts. To prevent self-unraveling. Mass production is focused on locknuts with a diameter of 8-50 mm: larger sizes are produced only on individual orders.
According to GOST 8969-75, the production of spurs is regulated: this fitting is characterized by a thread at the end, which can have a different length. With their help, fixed connections of pipelines are organized, and their strength is almost the same as that of welded ones. Clamps. They are used to fasten pipelines to horizontal sections.
The clamps are in the form of metal U-shaped brackets, on which there are bolts for screwing.Steel pipelines can sometimes be fastened with plastic clamps, however, the strength of the connection in this case is reduced. In addition to clamps, pipelines can also be equipped with brackets, brackets, linings, hangers.
Moreover, the task of the fasteners is not only to securely fix the pipes: they absorb vibration well and slightly prevent thermal expansion. GOST 24137-80 concerns metal clamps for steel pipes with a diameter of 15-240 mm
When creating a fastener, it is important to consider that the distance between the clamps on a horizontal base should be no less than 0.75 mm, on a vertical one - 1-1.5 mm
https://youtube.com/watch?v=z4AjL8HmOcwrel%3D0%26controls%3D0%26showinfo%3D0
- ru-stroyka.com
- www.ktzholding.com
- tubespec.com
Steel precision pipes according to GOST 9567-75
This group of products is controlled by a separate GOST, since their manufacture requires compliance with increased accuracy and special measures.
These types of metal pipes are classified depending on the wall thickness and method of production:
With extra thin walls. The diameter here has a ratio with a wall thickness above 40, with a thickness of less than 0.5 mm. With thin walls.
For the first indicator, a level of 40 and below is set, with a wall thickness of less than 1.5 mm. With thick walls. The first ratio is from 6 to 12.5. Particularly thick walls. The ratio is less than 6.
All precision tubes are seamless, with high isotropic stiffness. This makes it possible to organize various systems of increased accuracy and complexity even from thin-walled steel products in accordance with GOST 9567-75. The surface of such a pipe can be galvanized or phosphoric coated with oil.
Seamless pipes
A distinctive feature of seamless pipes is the integrity of their structure. They are divided into cold and hot deformed. Cold-formed are produced on the basis of GOST 8734-75 and 8733-74.
They may have an outer diameter and wall thickness of 5-250 mm and 0.3-24 mm, respectively. Such products are characterized by precise geometric dimensions and high surface finish. Most often they are used in the refrigeration industry, automotive and aircraft industries, as well as in the laying of pipelines.
Hot-formed pipes are produced on the basis of GOST 8732-78 and 8731-74. Their outer diameter and wall thickness can vary between 28-530 mm and 2.5-75 mm, respectively.
Such products have a higher rigidity compared to cold-formed ones and are poorly bent. Externally, hot-formed pipes have a rough surface. Most often they are used in mechanical engineering, oil and chemical industries, as well as for the construction of pipelines with high design pressure.
Seamless pipes are characterized by the absence of any joints
Steel electric-welded pipes with straight seams assortment, according to GOST 10705-91
The list of technical conditions according to which straight-seam electric-welded pipes are made of steel contains GOST 10705-91.
Among the most important provisions of this document are the following:
- The size of the allowable curvature is indicated within 1.5 mm / linear meter for products that have undergone heat treatment, and 2 mm / linear meter for non-passed ones. If the customer wants it, in the first case, the parameter can be reduced to 1 mm, in the second - to 1.5 mm. If the pipe is subjected to heat treatment, then, with the appropriate recommendation of the customer, a special protective atmosphere can be created for this procedure. the edges of a straight-seam electric-welded tube, according to GOST 10707-91, are cut off in compliance with an angle of 90 degrees, followed by cleaning of all irregularities and defects that have arisen.
Gas and oil pipelines made of steel used in industry are subject to a separate GOST.
As already mentioned, GOST 52079-2003 concerns electric-welded steel products with a straight seam having a large diameter. In addition, a variety of welded and seamless steel pipes used by the motorbike industry belongs to a special category. Any section of these products should not have a curvature of more than 1.5 mm. Regulatory document 12132-66 authorizes the manufacture of products with an exceptionally high or increased degree of accuracy.
Pipe measuring systems
There is one feature in indicating the parameters of the most popular water and gas pipes for domestic needs. When constructing water pipelines with their use, individual elements are most often connected using the threaded method.
To do this, a thread is applied to the outer surface of the pipes. Given that this parameter is important when assembling the system, it is indicated by the manufacturer. In this case, the thread diameter is always smaller than the outer diameter of the pipe.
To date, when describing the parameters of pipes, two measurement systems are used: imperial and metric. In the first, all parameters are indicated in inches. It is used only in relation to water and gas pipes and fittings for them.
In the metric system, all parameters are indicated in millimeters, centimeters or meters. Sometimes, when joining pipes of different types, it is necessary to recalculate their dimensions from one system to another. For this, special tables are used, given in GOST 6357-81.
Physicochemical characteristics
The change in state during heating or cooling of dielectrics characterizes their physical and chemical properties, as well as chemically active substances under the action of moisture, mechanical loads, etc. Undesirable, and sometimes emergency consequences in the operation of electrical installations can cause extreme heating of the electrical insulating material. An example of this is a fire, a short circuit, electric shock to people. This places high demands on dielectrics in terms of their heat resistance.
Heat resistance is the ability of a dielectric to withstand a given operating temperature for a long time without a noticeable change in its electrical insulating qualities. It distinguishes seven classes of electrical insulating materials used at temperatures of 90, 105, 120, 130, 155, 180, more than 18-0 ° C. A number of materials (asbestos, ceramic materials, mica, etc.) due to their structure have high heat resistance. Fibrous materials - from silk, cotton, cellulose, etc. in order to increase the heat resistance, they are impregnated with special substances.
Some dielectrics can melt when heated, such as mica, paraffin, and also soften - resins, bitumens, or even catch fire (there is an outbreak of vapors of electrical insulating liquids at certain temperatures): cable oil, transformer, synthetic electrical insulating liquids.
Cooling of dielectrics leads to a loss of elasticity, as well as to the appearance of cracks, etc. Each material from this is characterized by cold resistance. Cold resistance is the ability of a dielectric to retain its basic properties when cooled. For example, the cold resistance of a solid dielectric is taken to be such a temperature (below 0°C) at which its mechanical destruction begins.
Many electrical installations operate outdoors, and their electrical insulating materials are subsequently exposed to moisture. Yes, and depending on the environment and in closed electrical installations, the specifics of the technological process, electrical equipment is also exposed to moisture. First of all, its electrical insulating properties are worsened by the penetration of water into the dielectric, since water is undoubtedly a conductor of electric current. To absorb moisture from the environment is characterized by the ability of a dielectric - moisture absorption. Moisture absorption is also determined empirically: a dielectric sample is kept in distilled water for 24 hours at a temperature of usually 20 ° C; and there are other ways to determine moisture absorption.
Solid dielectrics are also characterized by the wettability of their surface by water, since the presence of water reduces the specific surface electrical resistance of the dielectric. The wetting angle is used to judge wettability.The larger the contact angle, the lower the wettability of the dielectric and the better its electrical insulating properties. electrical insulating materials intended for operation in a chemically active (aggressive) environment must withstand the action of alkalis and acids. Such properties are defined in much the same way as moisture absorption.
Most of the many electrical insulating materials are used, in addition to their intended purpose, also to protect metal conductors from corrosion. With the rapid development of nuclear power engineering and space technology, more and more high demands are placed on the radiation resistance of dielectrics.
Viscosity is also characterized by liquid dielectrics, it is determined by the time the liquid flows out of a vessel that has a strictly defined opening and shape.
In the manufacture of devices, electrical machines and other electrical equipment, repair or installation of electrical installations, it is often necessary to process electrical insulating materials by mechanical means, such as drilling, cutting, grinding, etc.
From this it is important to know the mechanical properties of dielectrics, such as hardness, tensile strength, etc., and it is equally important to know the properties of dielectrics to dissolve in solvents and varnishes, to stick together. Extreme properties are especially common in connection with the introduction of new, progressive methods of assembling electrical apparatus, machines and electrical work.
Pipe diameters
In addition to the wall thickness, several different diameters are used to describe the dimensions of the cross-section of pipes:
The inner diameter is always indicated in millimeters; Nominal diameter is a dimensionless quantity. It is similar to the inner diameter, but may not match it in size. In fact, the conditional passage is the value of the average inner diameter of the pipes rounded up or down.
Its value is important when making calculations for the entire liquid, steam or gas supply system. The convenience of this parameter becomes apparent in practical application.
In this case, to assemble a guaranteed working system, pipes and fittings with the same nominal bore are selected; The outer diameter is the main overall size of the pipes.
Water and gas pipes are the most common material for assembling domestic plumbing systems.
6. Gaseous dielectrics
Benefits
gases before other types
electrical insulating materials are:
high specific electric
resistance, small tangent
dielectric losses; small, close
unity dielectric permittivity.
The most valuable property of gases
is their ability to restore
electrical strength after discharge.
Except air as electric
insulation is widely used two- and
triatomic gases - nitrogen, hydrogen,
carbon dioxide. Electrical strength
these gases are rare under normal conditions
differ from each other and can
be taken with sufficient accuracy
equal to the strength of air. Table
3.5.1 shows the ratio of electrical
strength of some gases, including
high-strength, Epr g to electric
air strength, which is taken as
unit. Points are given in the same table.
boiling gases at normal pressure.
Table 3.5.1
|
Gas |
Density kg/m3 |
temperature |
^tf |
|
Nitrogen |
1,25 |
-196 |
1,0 |
|
Hexafluoride |
6,70 |
-64 |
2,3 |
|
dichlorofluoromethane |
6,33* |
-30 |
2,4 |
|
Trifluoromethylpentaftorsulfur |
— |
-20,4 |
3,05 |
the best
according to the requirements for gases used
in electrical insulating structures,
satisfies SF6 and freon. Hexafluoroethane
cannot be used at high
pressures due to low critical
parameters.
Conclusion
The most popular for domestic use are water and gas pipes.Knowing their basic parameters, as well as the features of metric and inch products and the differences between them, both types of materials can be used for plumbing or heating systems.
Although the market is currently flooded with a huge number of different polymer pipes, this does not affect the popularity of steel products, which, as before, remain indispensable in a number of construction, industrial and domestic areas of life. Pipes made of steel, especially galvanized steel, are characterized by significant durability, strength and ease of installation, and their assortments are oriented to GOSTs for 2003 and 2006 (certain standards have been transferred from the second half of the 20th century).