Similar
| Rules for the use of gas in terms of ensuring safety when using ...… | Rules for the use of gas in terms of ensuring safety when using ...… | ||
| The rules for using Internet Banking for individuals apply from 1This document (hereinafter referred to as the Rules) governs the procedure for using the Internet banking of Baltiyskiy… | Rules for the use of gas in terms of ensuring safety when using ...On measures to ensure safety in the use and maintenance of in-house and in-house gas equipment | ||
| Rules for the technical operation of systems and structures of public water supply and sewerageThe purpose of these Rules is to create conditions for providing consumers with good-quality drinking water, as one of the factors ... | Rules for the technical operation of systems and structures of communal ...The purpose of these Rules is to create conditions for providing consumers with good-quality drinking water, as one of the factors ... | ||
| Comprehensive Development Program for Communal Infrastructure Systems…The goal of the Program is to ensure the sustainable and efficient functioning of communal infrastructure systems and communal… | Rules for the use of premises, maintenance of the common property of an apartment buildingRules of residence and internal regulations (hereinafter referred to as the "Rules") in apartment buildings. Violation of these Rules may result in... | ||
| Rules for working with personal data information systemsAll users, upon obtaining primary access to information system resources (hereinafter referred to as IS), are required to familiarize themselves with the requirements ... | Rules for the use of gas at homeApproved by order in "Rosstroygazifikatsiya" under the Council of Ministers of the Russian Federation No. 86-p dated 26. 04. 90 | ||
| Decree of the head of the administration (governor) of the Krasnodar Territory ...Krasnodar Territory in addressing issues of local importance to ensure the development of communal infrastructure, to ensure the implementation of… | Rules for the use of gas at homeThe rules are obligatory for officials of departments and organizations responsible for the safe operation of the gas facilities of residential ... | ||
| Rules for the use of public water supply and sewerageNote. In some cases, at the suggestion of Vodokanal and special permission | Rules for using the classroom by studentsRequirements for the computer science classroom as a basis for the successful implementation of the educational program | ||
| Rules for the use of gas at homeMonitor the intersections of internal gas pipelines and building elements of buildings, | Rules for the use of office equipment and PCThe job description defines the job duties, powers and responsibilities, as well as the working conditions of the chief accountant ... |
Calculation of dimensions and volume
To accurately determine the internal space of the tank, a specially developed formula for calculating the volume of a septic tank is used. But it implies a large number of complex meanings and is difficult for private practical application. In practice, the volume of a septic tank for a private house is calculated using a simpler formula. Number of people X 200 liters of sewage per person X 3 days (waste processing time) / 1000 = volume in cubic meters.

To serve 4 people, a septic tank with a volume of 2.4 cubic meters is required.
Most often there are 4 people in a family. Consider the option with the calculation of the volume for this number of family members.
4x200x3/1000=2.4 cu. m. A septic tank for 5 people will require a volume of 3 cubic meters. m. The volume calculated by this formula for 6 people is 3.6 cubic meters. m. For 20 people, the calculated figure is 12 cubic meters. m.
When calculating the “number of people” parameter, it is better to take it “with a margin” in order to take into account the load when visiting guests and other unforeseen situations. The daily rate can be increased if there are small children, pets. This indicator also increases if you use a large number of different household appliances with water consumption (washing machine).
As mentioned above, there are laboratory calculations that are given for factory septic tanks. According to these data, it is possible to carry out calculations in situations with containers made independently.
So, with a septic tank in three sections:
- for two people, a useful volume of 1.5 cubic meters is required. m.;
- for three or four people - 2 cubic meters. m.;
- for five or six people - 3 cubic meters. m.;
- for eight people - 4 cubic meters. m.;
- for ten people - 5 cubic meters. m.;
- for twenty people - 10 cubic meters. m.
Concrete rings are the main building material in the arrangement of a septic tank. And the key calculation is the determination of the amount of these materials. Most often, 3 reinforced concrete rings with a diameter of 1.5 m and a height of 0.9 m are enough. More than 5 rings are not used per septic tank.
Do not forget about other elements in the independent arrangement of the system. These include:
- Reinforced concrete slab.
- Pipe for ventilation.
- Cement, sand, gravel.
When calculating the required volume of a septic tank, the formulas given above are used. In addition, it is necessary to know the volume of one ring in order to determine a sufficient number of rings in the container.
V=∏R2H=∏(d2/4) H, where:
- V is the volume of the cylinder;
- ∏ is Pi number (3.14);
- R is the radius of the base;
- d is the diameter of the base;
- H is the height.
Knowing the volume of the ring, it can be compared with the obtained figures for the required volume of a concrete septic tank. The volume of 1 ring (d=1.5 m; H=0.9 m) is approximately equal to 1.6 cubic meters. m. It turns out that for 4 family members in a house with all amenities (hot water supply, etc.), 2 rings will be needed to equip a septic tank.
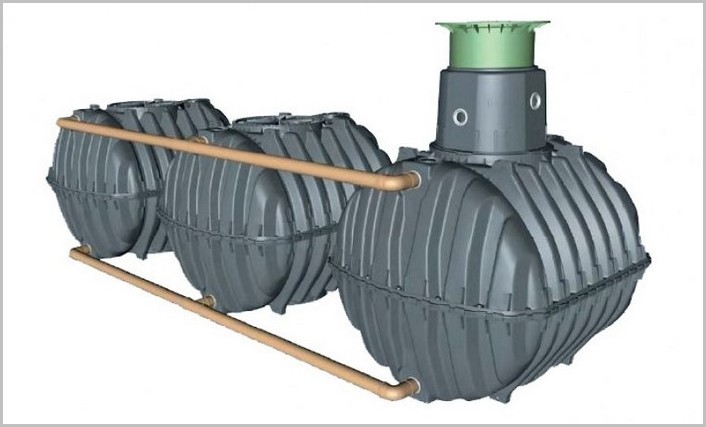
This amount will be enough for 5 people. Up to 10 people can be provided with one container of 3 rings. If you plan to stay from 10 to 20 people, you will need to equip a septic tank consisting of several containers, since more than 3 rings cannot be installed. In this case, it is better to take care of acquiring a factory model of sufficient volume.
The first rule in the construction of an autonomous sewage system is to correctly select pipes and a septic tank for wastewater treatment. When choosing pipes, general rules should be followed, while the selection of a septic tank is a more complex and voluminous task. Correct calculation of wastewater to determine the volume of the collection tank allows you to minimize the frequency of cleaning and reduce maintenance costs.
Some features of the installation of various types of septic tanks
Autonomous sewerage of a private house consists of 3 parts:
- Internal part - plumbing fixtures, connecting pipes;
- The outer part is a septic tank, storage or filtration well;
- A pipeline connecting the inside and outside of the sewer.
For the outer pipe leaving the house, it is most practical to use PVC, PP pipes. Its dimensions depend on the distance of the septic tank, and the diameter is not less than 100-110mm. Also, when laying them, it is necessary to observe a slope of 2-3 cm per 1 running meter.
Modern septic tanks are often equipped with pumping equipment. They are divided into gravity and forced pumping. In both cases, the power supply networks are buried in the ground, must be isolated from damage and protected by a corrugated channel or a polyethylene pipe with a diameter of 20 mm.
Septic tanks, in which the contact of wastewater with the soil is excluded, can be removed from a private house by only 3-5 meters.For sewer systems with soil post-treatment, there are a number of restrictions on the distance from objects on the site, depending on their design and filtration capacity.
Concrete septic tanks are arranged from several wells connected by connecting pipe cuts in their upper part for the outflow of clarified water. For this, standard concrete rings are used. Dimensions: diameter -1.5 m, height - 90 cm.

The performance of a septic tank is also determined based on the volume of salvo discharge of water. This characteristic indicates the volume of wastewater that the septic tank is able to take at a time, filtering them in its normal mode. Do-it-yourself concrete septic tanks in the country are capable of processing 1-5 cubic meters of wastewater per day, depending on the presence of a filtration system, the use of bacteriological additives and other catalysts for this process.
Septic tanks manufactured by specialized companies, such as Topas, Septic-Tank, Tver, Termit, are designed for a much larger volume of volley discharges of wastewater, followed by their filtration up to 98%. For example, an inexpensive household septic tank Topas-6, with its low power of only 1.5 kW, is able to process up to 1.5 cubic meters. meters of wastewater per day, and provide a full-fledged sewage system for 6 people. However, there are complex local treatment systems that can process up to 3500 cubic meters. meters of wastewater per day, designed for a significantly larger number of people.

Whatever your choice of a septic tank for a summer cottage, its calculation is an engineering task, for the competent execution of which you need enough knowledge and initial data. Nowadays, all this information can be obtained on specialized websites of companies, departments and specialized portals and forums. Only after that, the calculation and installation of a septic tank for the whole family can be done at your summer cottage with your own hands!
Owners of private houses that are not connected to centralized sewer networks (CS) naturally face the problem of disposal of domestic wastewater. And most of these private homeowners resort to the option of installing a septic tank, which makes it necessary to solve the calculation problem for the construction or selection of ready-made autonomous treatment facilities.
It must be understood that the diversion and disposal of wastewater is clearly regulated by the regulatory documentation of the Russian Federation, non-compliance with which leads to negative consequences both for the ecosystem and for the responsibility of those responsible. Therefore, when calculating a septic tank for the needs of home ownership, they rely on a number of standards and rules, in particular:
- SNiP 2.04.03-85 “Sewerage. External networks and facilities”, regulating the sanitary protection zones around small treatment facilities, as well as adjusting the active volumes of installations.
- SNiP 2.04.01-85 "Internal water supply and sewerage" or their updated version SP30.13330.2012, to determine the flow rates.
- Manual for the design of engineering systems MDS 40-2.200, which provides the main regulatory calculations for the calculation of septic tanks and their auxiliary structures (drainage wells, filtration fields, etc.).
1.1 Reception chamber
Sharp fluctuations in flow and quantity
sewage pollution make it difficult for them
cleaning. To average consumption and
amount of contaminants used
receiving chamber. Receiving size
camera is taken in accordance with
tab. 5.1.
4.1.2 Grids
Screens are installed on all treatment plants
structures, regardless of how
wastewater goes to treatment
structures - by gravity or after
pumping station with grids.
The type of gratings is determined depending on
from the performance of the treatment plant
and the amount of waste removed from
gratings. With more than
0.1 m3/day provided
mechanized cleaning of gratings, with
less waste - manual.
With mechanized gratings,
provide for the installation of crushers
for shredding waste and feeding
crushed mass into wastewater before
gratings or direct them for joint
treatment with sludge from sewage treatment plants.
For low and medium performance
treatment plant use grate-crushers.
When calculating lattices, they are determined
dimensions and pressure losses arising
when sewage passes through them.
The dimensions of the gratings are determined by the flow
wastewater, according to the accepted width of the gaps
between the bars of the lattice and the width
rods, as well as the average speed
passing water through the grate.
The speed of movement of wastewater in the gaps
gratings at maximum inflow
to be accepted: for mechanized
gratings - 0.8 ... 1 m / s; for grate crushers
– 1.2 m/s.
The calculation of lattices begins with the selection
live section of the inlet channel in front of
lattice chamber. Channels and trays should
calculated on the maximum second
flow qmax,cwith a coefficient of 1.4. Travel speed
waste liquid in the channel should be
not less than 0.7 m/s and not more than 1.2…1.4 m/s.
The total width of the grating is determined by
formula:
Bp = S(n – 1) + bn, m,
(16)
where S is the thickness of the rods.
The most used rods
rectangular section with rounded
corners measuring 860 mm,
i.e. S = 0.008,b is the width of the gaps between
rods 16 mm \u003d 0.016 m; n is the number of lattice gaps, determined
according to the formula
,
(17)
where H is the water depth in the channel before
grate when skipping the estimated flow
(without k=1.4),Vp- speed of movement of wastewater; k3- coefficient taking into account constraint
rake flow sections: with mechanized
cleaning 1.05, with manual cleaning - 1.1 ... 1.2.
The total construction length of the grating
is determined by the formula
L = 1 + P + 2, (18)
where 1- the length of the broadening in front of the grating, m,
determined by the formula
1=1.37(Bp – BTo),
(19)
where Bp– lattice chamber width, m; BTois the width of the supply channel, m;
P– working length
gratings, is adopted constructively
equal to 1.5 m;
2is the length of the broadening after the grating,
m, defined as
2= 0,51. (20)
The total construction height of the channel in
place of installation of gratings, N, m:
H = h1 +h2 +hp,
(21)
where h1- depth
water in the channel in front of the grate when passing
design flow сk=1.4,
m;h2– excess
sides of the chamber above the water level, should
be at least 0.3 m; hp- pressure loss in the grate, determined by
according to the formula
(22)
where g is the acceleration of a free
fall; k- coefficient
increase in head loss due to
clogging, equal to 3; - coefficient of resistance, depending
on the shape of the rods and determined by
formula
(23)
where is the coefficient,
determined by the shape of the rods, equal to
for rectangular 2.42, for rectangular
with rounded edges 1.83, for round
1.72,– angle of inclination
grids to flow.
The amount of waste removed from the grate
Wotb, m3/day,
is determined by the formula:
(24)
where
= 8 l/(personyear)
- the amount of waste per
one resident, removed from the bars from
gap width 16 ... 20 mm; - reduced number of inhabitants by weighted
substances.
Waste humidity is 80%,
density - 750 kg / m3.
For crushing waste in the grate building
hammer crushers are installed
type D-3, D-3a, performance
0.3…1.0 t/h. The work of crushers is periodic.
Crushed waste transported
the flow of water from the technical water supply,
allowed to be directed to the sewer canal
water in front of the grates or pump
in digesters. Consumption of water supplied
to the crusher, is taken at the rate of 40 m3 per 1 ton of waste.
The project must include a diagram
grid nodes and a schematic representation
crushers. Main technical
characteristics of screens and crushers
are given in table. 17.1, 17.5.
After determining the number of employees
gratings must be provided
installation of backup grids according to
tab.22.
flow volume
The small amount of waste water, diluted with eight or ten times the amount of groundwater, creates extremely poor conditions for the biological treatment process and, in addition, leads to very significant costs due to a significant increase in the required force and energy consumption of air compressors. These are the two main problems that stand in the way of the operation of wastewater treatment plants.
Then the treated effluents are fed from the secondary clarifiers into two contact tanks measuring 15 L x 15 W x 3.6 H (meters) with a usable volume of 810 m3, where they are disinfected with chlorine. Silt is removed by hydrostatic pressure.
The actual amount of effluent fed to the treatment plant is almost impossible to accurately determine, due to the significant dilution of wastewater with groundwater in the collector and transport network. The volume of the mixture of groundwater and runoff can be measured in a measuring channel, but this does not allow the amount of runoff to be determined. Therefore, the volume of wastewater is estimated based on the standards for wastewater production by households, industrial enterprises and budgetary organizations. This calculated volume is then corrected for the total incoming dilute effluent measured in the canal and the dilution factor. Estimated data for past periods on effluents processed in the period from 2001 to 2003 inclusive are presented in Table 2.5.
It is also necessary to take into account deviations in the volume of river flow over time (periods of high and low waters) - global cyclic variations in flow with periods from 2 to 3, from 5 to 7, from 11 to 13 and from 22 to 28 years and a steady decrease in the amount of water in land waters. It has been noted that in recent decades the level of the World Ocean has risen by an average of 1.2 mm per year, which is equivalent to the loss of land annually 430 km3 of water. The reasons for this are deforestation, drainage of swamps, a decrease in precipitation on land, plowing of steppes, underground mining, etc. Consequently, under the influence of human activity, there is a steady decrease in the amount of water in land reservoirs, that is, the depletion of fresh water resources.
The amount of sediment formed during the treatment of effluents with iron sulphate is 20-25% of the initial volume of the effluent. The sludge may have toxic properties due to the presence of an entrained part of the wastewater with residual cyanides.
Such a retrofit would reduce the amount of groundwater entering the sewerage system, and therefore reduce the volume of water entering the treatment plant and reduce the required feed force and the required compressor power. Replacing old, damaged pipes will also reduce the cost of materials and labor required for maintenance and reduce some of the damage caused by overflowing sewage during heavy rains. It is assumed that about 50% of reinforced concrete pipes will be reused.
The book contains environmental characteristics of the components of technological solutions, basic compositions of solutions and electrolytes for metal surface treatment. The characteristics of flushing systems are given, rational methods of flushing and regulation of water consumption are described. The variants of layouts of electroplating lines and electroplating shop, the volumes and contamination of wash and waste water, as well as technological schemes for the treatment of acid-alkaline and chromium-containing wastewater, technological schemes for the purification of waste technological solutions and electrolytes, as well as comparative characteristics of cleaning methods are given. On the example of a specific electroplating shop, the multivariance of both electroplating production in terms of the volume and composition of wastewater, and ways of organizing wastewater treatment systems is shown, and the principles of adapting electroplating production and various wastewater treatment systems are given.Methods for the regeneration of spent electrolytes and schemes for the recovery of waste solutions, as well as methods for the disposal of galvanic sludge are described. The main directions of creation of ecologically safe electroplating production are determined.
Calculation of material balance for sand traps
Wastewater at the facilities of the 1st stage of the VOC is fed to horizontal sand traps, with rectilinear water movement, with a flow rate of 80,000 m3/day.
According to passport data, we accept the cleaning efficiency for each pollutant: COD - 0%, BOD - 0%, suspended solids - 40%, ammonium nitrogen - 0%, nitrite nitrogen - 0%, nitrate nitrogen - 0%, phosphates - 0%, iron - 0%, oil products - 0%, phenols - 0%, surfactants - 0%, nonionic surfactants - 0%, heavy metals - 0%.
Knowing the initial concentration of pollutants, the cleaning efficiency for each substance and the efficiency formula, we find the final concentration of pollutants:
, (2.2)
Where Cn — initial concentration of the ith component, mg/l;
Ei — purification efficiency for each substance;
WITHTo — final concentration of the ith component, mg/l.
The final concentration of pollutants is determined by the formula:
, (2.3)
where Cin — initial concentration i — of that pollutant, mg/l;
WITHik — final concentration i — of that pollutant, mg/l;
E - cleaning efficiency,%.
Substituting the concentration values from Table 2.1 and the specified cleaning efficiency into formula (2.2), we obtain the values of the final concentrations after wastewater treatment in sand traps:
COD CTo = (1 — 0/100)*152 = 152,00
BOD CTo = (1 — 0/100)*81 = 81,00
suspended solids CTo = (1 — 40/100)*85 = 51,00
ammonium nitrogen CTo = (1 — 0/100)*4,2 = 4,20
nitrogen nitrite CTo = (1 — 0/100)*0,054 = 0,054
nitrogen nitrate CTo = (1 — 0/100)*0,94 = 0,94
phosphates CTo = (1 — 0/100)*0,32 = 0,32
iron CTo = (1 — 0/100)*0,15 = 0,15
oil products CTo = (1 — 0/100)*0,3 = 0,3
phenols CTo = (1 — 0/100)*0,0092 = 0,0092
APAV CTo = (1 — 0/100)*0,4 = 0,4
non-ionic surfactants CTo = (1 — 0/100)*0,55 = 0,55
heavy metals CTo = (1 — 0/100)*0,005 = 0,005
Mass flow M, t/day for i - that component is calculated by the formula:
Mi = Ci *Vi * 10-6, (2.4)
where Ci — concentration of the ith pollutant, mg/l;
Vi — volumetric water consumption, m3/day.
The mass consumption of pollutants before cleaning will be equal, t/day:
COD Mn = 152,00*80000*10-6 = 12,16
BOD Mn = 81,00*80000*10-6 = 6,48
suspended solids Mn = 85*80000*10-6 = 6,80
ammonium nitrogen Mn = 4,2*80000*10-6 = 0,33
nitrogen nitrite Mn = 0,054*80000*10-6 = 0,004
nitrogen nitrate Mn = 0,94*80000*10-6 = 0,07
phosphates Mn = 0,32*80000*10-6 = 0,025
iron Mn = 0,15*80000*10-6 = 0,013
oil products Mn = 0,3*80000*10-6 = 0,024
phenols Mn = 0,0092*80000*10-6 = 0,00073
APAV Mn = 0,4*80000*10-6 = 0,032
NSAV Mn = 0,55*80000*10-6 = 0,04
heavy metals Mn = 0,005*80000*10-6 = 0,0004
The total mass flow rate of pollutants entering the treatment is Mn = 25.98 t/day.
In sand traps, wastewater is cleaned from suspended solids, therefore, the mass flow rate of suspended solids after treatment is calculated using formula (2.4) and will be equal to:
MIN VK = 51 * 80000 * 10-6 = 4.08 t/day
The total mass flow rate of pollutants after sand traps is М = 25.98 – 4.08 = 21.90 t/day.
The calculation results are summarized in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1 - Results of calculating the material balance for the sand trap
|
Indicators of the composition of wastewater |
Before cleaning |
Cleaning efficiency,% |
After cleaning |
||
|
Concentration of contaminants in wastewater, mg/l |
Mass flow, t/day |
Concentration of contaminants in wastewater, mg/l |
Mass flow, t/day |
||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
COD |
152,00 |
12,16 |
152,00 |
12,16 |
|
|
BOD |
81,00 |
6,48 |
81,00 |
6,48 |
|
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
Weighed- substances |
85 |
6,80 |
40 |
51 |
4,08 |
|
ammon nitrogen. |
4,20 |
0,33 |
4,20 |
0,33 |
|
|
nitrogen nitrite |
0,054 |
0,004 |
0,054 |
0,004 |
|
|
nitrogen nitrate |
0,94 |
0,07 |
0,94 |
0,07 |
|
|
phosphates |
0,32 |
0,025 |
0,32 |
0,025 |
|
|
iron |
0,15 |
0,013 |
0,15 |
0,013 |
|
|
oil products |
0,30 |
0,024 |
0,30 |
0,024 |
|
|
phenols |
0,0092 |
0,00073 |
0,0092 |
0,00073 |
|
|
AS |
0,40 |
0,032 |
0,40 |
0,032 |
|
|
nonionic surfactants |
0,55 |
0,04 |
0,55 |
0,04 |
|
|
heavy metals |
0,005 |
0,0004 |
0,005 |
0,0004 |
|
|
Total |
25,98 |
21,90 |
The mass of the sediment of the i-th component Moci , t/day removed from wastewater in sand traps:
Moci =Min — Mik (2.5)
Mass of sediment of suspended solids Mos.vv , t/day removed from waste water in sand traps:
Mos.vv = 6.80- 4.08 = 2.72 t/day
Humidity sediment in the sand trap is W = 65%. Therefore, the amount of moisture in the sediment of the i -th component Vwater.os. i , m3/day, calculated by the formula:
Vwater.os. i = Moci *W(2.6)
Substituting the values, we determine the amount of moisture in the sediment of suspended solids Vwater.os.vv , m3/day:
Vwater.os.vv = 2.72 * 0.65 = 1.77 t/day
Waste water volume flow after sand trap V1, m3day, therefore, will be equal to:
V1 = V - Vwater.os.vv (2.7)
V1 = 80000 - 1.77 = 79998.23 m3/day
How to choose the right volume of a septic tank
In order to choose a worthy sump, it is necessary to carry out calculations of its parameters and try to purchase a fairly compact and convenient model for giving.
Example. The required volume of a septic tank based on the number of residents of private ownership:
- Less than three people -1.3 cubic meters;
- 3 - 5 people - 2.5 cubic meters;
- 6-10 hours - 10 cubic meters.
Example.You have installed a water meter, which means that the amount of daily water consumed will decrease, because a person will start saving.
Calculation of the volume of a septic tank for a family of four permanent residents
For example, we will consider the calculation of the required capacity of a septic tank for a family of four. It is worth noting that it is produced for permanent residents in the country or in the house.
The first thing we do is calculate the three-day water consumption of one person. Why is that? The answer is simple: the time for water to settle in a septic tank is 2-3 days, and how much water is processed in a septic tank. The maximum volume of consumption in this case is calculated by the formula:
Q is the optimal volume of water consumption by one family member.
To make accurate calculations, you need to find out what technical means this inhabitant of the house uses. For calculation, we take the minimum indicator of water consumption per person per day - 150 liters.
Example. The picture of daily water consumption may look like this:
- For 4 minutes of taking a shower - 40 cubes;
- Average shower or bath is 7-15 minutes;
- Bidet or toilet bowl - 8 l;
- Bidet - an average of 5 minutes;
- Take a bath or jacuzzi once - 110 l;
- One washing machine - about 70 liters;
- Dishwasher - 15 l.
Calculation of the use of a shower or bath for 1 person:
(150 + 10 x 7 + 8 x 5 + 110) = 370 cubes per day
The calculation of a septic tank for a family of 4 assumes: the number of people (4) x 200 l x 3 days / 1000 = cubic meters. As a result, we get 2.4 cubic meters.
The calculation of a septic tank for a family of 5 assumes: the number of people (5) x 200 l x 3 days / 1000 = cubic meters. The result is 3 cubic meters. That is, for a family of five, in which each member will consume 200 liters of water for three days, a septic tank will be enough, the volume of which will not exceed 3 cubic meters.
But all these are the minimum indicators of the volume of the treatment plant according to a simple formula. In order to calculate the maximum required volume of a septic tank that your family will need, just together 200 liters per day per person, calculate 300 liters per day. It is not easy for one person to spend more than 300 liters per day, even taking into account the use of a bath, shower, toilet, washing machine and dishwasher.
Be sure to note that the required volume of the cleaning station may fluctuate. It can be influenced by the requirements of each family member, the arrival of guests to your house, who will spend water just like you, as well as the frequency of the family's arrival. If you regularly live in the country for three summer months, then you should take a larger volume of the septic tank than the result of this formula, since you need to additionally take into account the watering of the garden and flowers.
That is, if in total your family consumes up to 5 cubic meters of water per day, a single-chamber septic tank will be enough for you. If more than 5 cubic meters, then it will be necessary to install a local treatment device with two or three chambers in order to speed up the processing of sewage.
Therefore, soberly assess the needs of your family, correctly calculate the required volume of a purifying septic tank using the above formulas specifically for your case, taking into account your required water discharge rate.
Volume calculation
The volume of the cesspool is an important parameter on which the efficiency of the sewer system and the frequency of drain cleaning depend. It is calculated based on the number of people living in the house. If we are talking about a country option, then the arithmetic mean of the people staying in the building is taken. For example, 4 people live in a year-round cottage: 3 adults and 1 child.
Expert advice:
As a standard, 0.5 cubic meters of waste is accepted per 1 adult, half less for a child. If any devices that consume water are connected to the drain, they are also taken into account.In our example, they are not connected.
It turns out that 3 * 0.5 + 0.25 = 1.75 cubic meters of wastewater will merge into the cesspool per day. The resulting value is always rounded up. This will help prevent overfilling of the tanks, if necessary, select the appropriate volume of the finished container. In our case, the value of 2 cubic meters is taken.
The volume of the tank should be 3 times the daily amount of waste. Therefore, 3*2=6. The optimal volume of the tank for a family of three adults and one child will be 6 cubic meters.
For the equipment of the sewer system of a country house, a different scheme is used. Most often, large families do not live in the country, but they come for a few days to relax, harvest or clean the garden. You can not make calculations, but simply equip the drain, the capacity of which will be within 1-2 cubic meters.
Why calculate volume:
- This is necessary for the selection of an appropriate design of the cesspool. There are two types of drains: open and closed. Open ones are easier to arrange and maintain, but are only suitable for processing wastewater up to 1 cubic meter. Closed ones are more practical, because they are able to absorb more waste and are environmentally safer;
- If it is incorrect to calculate the volume of wastewater at an open tank, then it will cope with its work much more slowly than it should. In addition, effluent will contaminate soils and groundwater.
When calculating the required volume, it is necessary to additionally take into account the level of groundwater. In areas where they are close to the surface of the earth, the pit may overflow due to their increase.
2. Calculation of the averager for costs
For calculation
cost averaging required
schedule of wastewater inflow during
shifts or days (in the task). Wherein
wastewater inflow regime according to
concentrations are assumed to be uniform.
Pumping out wastewater from the equalizer is also
uniform. 
For instance:
Admission Schedule
sewage during the shift is presented
in figure 1:
Figure 1 - Graph
wastewater inflows during
shifts.
For determining
averager volume, we calculate the average
flow rate (in %) to be pumped out
averaging pump:
Compiling an hourly
schedule of inflow and pumping of sewage
(Table 2.2):
table
2.2 - Schedule of inflow and pumping of waste
waters
|
Clock |
Admission |
pumping out |
Remainder |
Dynamics |
New |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
1 |
10 |
12,5 |
— 2,5 |
-2,5 |
+5 |
|
2 |
10 |
12,5 |
— 2,5 |
-5,0 |
+2,5 |
|
3 |
10 |
12,5 |
— 2,5 |
-7,5 |
|
|
4 |
20 |
12,5 |
+7,5 |
+7,5 |
|
|
5 |
20 |
12,5 |
+7,5 |
+7,5 |
+15,0 |
|
6 |
10 |
12,5 |
— 2,5 |
+5,0 |
+12,5 |
|
7 |
10 |
12,5 |
— 2,5 |
+2,5 |
+10,0 |
|
8 |
10 |
12,5 |
— 2,5 |
+7,5 |
|
|
Total |
100 |
100 |
Column 2 indicates
% of expenses in accordance with the hourly
schedule of wastewater inflow into
averager; in column 3 - indicate%
wastewater pumping from the equalizer; v
column 3 - the value obtained by the difference
between the values in columns 2 and 3; v
column 5 - the value of the first hour
duplicated from column 4, second and
subsequent values are
summing subsequent values,
for example for the second hour: (first
value from column 5) + (second value
from column 4), etc.
Next, you need
find the smallest value in a column
5 and mark it as "0" in column 6 (in
in this example, it happens on the third
hour). Next to find the value
the fourth hour, add to the value
third hour value from column 4 for
the fourth hour (i.e. to 0+7.5=7.5), etc. bye
all values of column 6 will not be filled.
Averaging volume
defined as the maximum value
in column 6, i.e. for this case 15%.
With a changeable water flow Q=100
m³/shift minimum required volume
the averager will be 15 m³. With considering
reserve 10%, the volume of the averager will be
16.5 m³.
After defining
the required volume of the equalizer
select its dimensions taking into account the height
sides 0.5 m. Number of equalizer sections
at least 2 and both are working. accepted
2 sections with a size of 2.4x2.4m2,
2 m high; the working volume of each is 8.64 m3.
In the averaging, as a rule, it is used
the following equipment:
– submersible pumps
for uniform pumping of wastewater;
- agitators for
mixing wastewater (if necessary)
averaging and over concentrations);
- bubbling system
compressed air (for agitation
falling sediment).
Averager calculation
on expenses, except for the tabular form, can
be made in the form of an integral
graphics.