The battery does not heat in a private house
The reason that the batteries in a private house do not heat up can be a number of factors. We can only consider the question in a general way. There are various reasons and they are not always obvious. Sometimes such a trifle as a faulty faucet or a clogged chimney can become a stumbling block. Despite this, there are no hopeless situations, the main thing is to determine the reason why the battery in a private house does not heat up, the rest is a matter of technology.
Insufficient boiler power
If the batteries in a private house do not heat well, then one of the reasons may lie in the heating boiler. In your house, with almost 100% probability, it can be argued that the heating circuit is autonomous. So, there is a boiler. It could be:
Why do batteries in a private house not heat well? The reason may be incorrectly selected boiler power. That is, it lacks a resource to heat the required amount of liquid. The first call to the fact that the power is selected incorrectly is the constant operation of the heater, without shutdowns.
Although in this case the heat exchangers will heat up a little, but. And if the water in them is completely cold, it means that the boiler has broken down or cannot turn on. Modern units have a requirement for a minimum pressure in the system. If this requirement is not met, then it will not turn on. In addition, there is an automation and security system.
Take, for example, a gas boiler. It has a sensor that controls that all gases go into the chimney. It is possible that the chimney or some smoke exhaust pipe is clogged. In any case, the sensor will send a command to the control unit and it will not allow the boiler to turn on.
Problems with the batteries themselves
Batteries do not heat in a private house, what should I do? If no problems were found with the boiler and it is working correctly, then the reason why the batteries are cold must be sought in the circuit itself. Possible options:
- airing;
- pollution;
- insufficient pressure;
- incorrect piping;
- incorrect connection of heat exchangers.
If the batteries are cold, then you need to check all of the above factors. We have already written in more detail about what to do if the batteries do not heat up. The specificity of a private house is that all characteristics can be controlled independently.
Then make sure that there is no dirt in the pipes and heat exchangers. How to do it? You will have to drain water from cold batteries in a private house. What to do is known, it is necessary to unscrew one end (lower) in the battery and substitute a larger vessel. If black water flows, then there is nothing to think about - this is pollution. It is necessary to flush the circuit to clean water. Sometimes a thick slurry flows out of the radiators along with the water. This is dirt, collected in abundant quantities.
What other reasons could there be why cold batteries are in a private house? If the problem is not in the air or pollution, then the circulation is disturbed. This may be due to low blood pressure. In general, in an autonomous circuit, the coolant pressure does not exceed two atmospheres. If you have new batteries, then look at their passport. In modern heat exchangers, the requirements for working pressure are higher than in Soviet models
Pay attention to it
Violation of the circulation of the coolant
Separately, we consider a violation of the circulation of the coolant due to improper piping and piping of heat exchangers, as a result of which the batteries are cold. In your home, you are free to choose the method of piping. It could be:
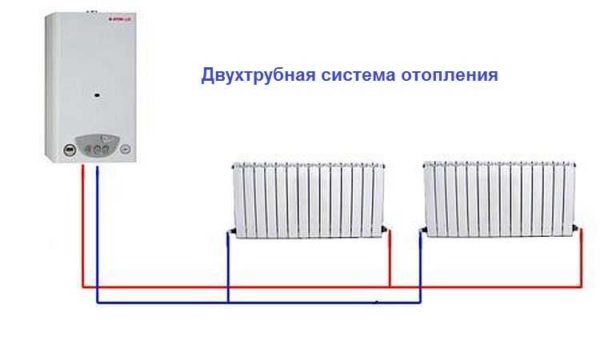
- two-pipe heating system;
- single pipe heating system.
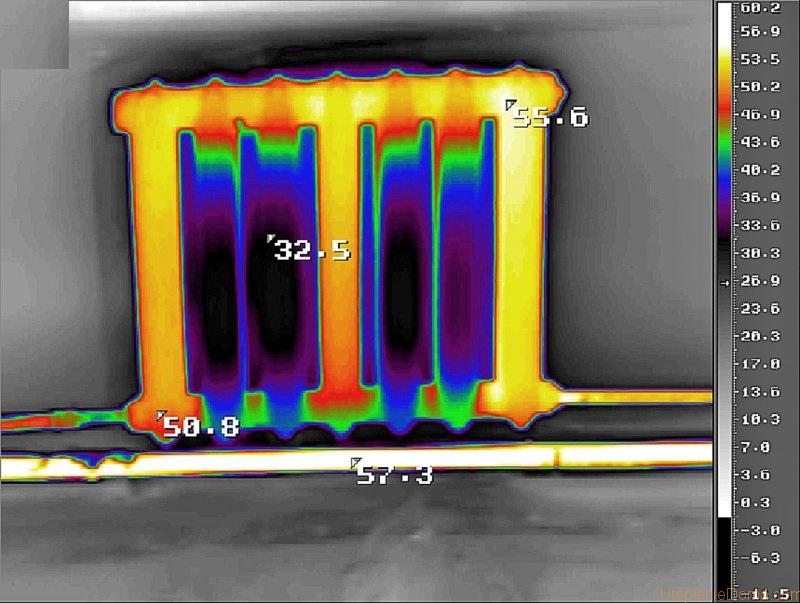
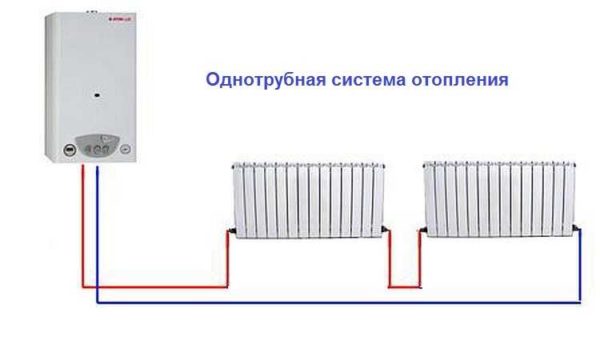
It so happened that earlier many preferred a single-pipe heating system, aka Leningradka. It was believed that it was simpler and cheaper, but in fact it is not.In addition, in this scheme it is very difficult to regulate the temperature of the heat exchangers as they are remote from the boiler room. The farther from the boiler, the more sections should be. Therefore, it is not uncommon that the last battery in a private house does not heat up. The coolant flows through one pipe. In such a scheme, there is no return.
It turns out that water enters the heat exchanger, cools down there and is again involved in the general flow. Accordingly, after each radiator, the total flow becomes colder. The difference increases with distance from the heating element. As a result, water can come to the extreme heat exchanger almost cold.
In a two-pipe system, tying errors can be made:
- improperly installed shutoff valves;
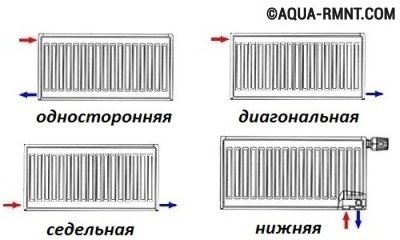
- incorrect connection of the heat exchanger (there are three types: side, bottom, diagonal);
- incorrectly selected diameter of the branches.
What types of heating systems are
In order to understand how to connect a heating radiator, you need to be clearly aware of which system it will be integrated into. Even if all the work will be carried out by craftsmen from a specialized company, the owner of the house still needs to know what heating scheme will be implemented in his home.
Single pipe heating
It is based on the supply of water to radiators installed in a multi-storey building (usually in high-rise buildings). Such a connection of a heating radiator is the simplest.
However, with the availability of installation, such a scheme has one serious drawback - it is impossible to regulate the heat supply. Such a system does not provide for any special devices. Therefore, heat transfer corresponds to the design norm laid down by the project.
Two-pipe heating
Considering the options for connecting heating radiators, it is naturally worth paying attention to a two-pipe heating system. Its operation is based on the supply of hot coolant through one pipe, and the removal of chilled water in the opposite direction through the second pipe.
Here parallel connection of heating devices is realized. The advantage of this connection is the uniform heating of all batteries. In addition, the intensity of heat transfer can be adjusted by a valve that is mounted in front of the radiator.
Important! Proper connection of heating radiators implies compliance with the requirements of the main regulatory document - SNiP 3.05.01-85
What is a heating system return?
Knowing the elementary principles of a heating device, it is quite simple to answer the question of what a return is - this is a pipeline through which the carrier leaving the heat transfer devices is directed to the boiler equipment for subsequent heating.
At least two pipes for connection are built into almost any heating device, and with a two-pipe system, the return and supply circuits have a clear distinction (separate collectors). With a single-pipe connection method, the devices are connected in series with each other, so the supply pipe is connected to the first battery from the boiler in the circuit, and the return pipe is the one coming out of the last one. When using the popular "Leningrad", the return line should be considered the pipeline section after all the heaters in the circuit.
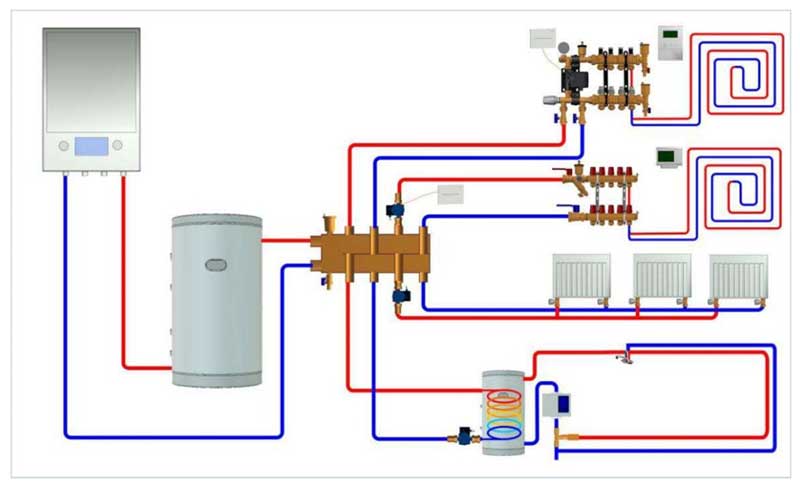
Rice. 2 Multi-circuit heating scheme for a cottage - an example
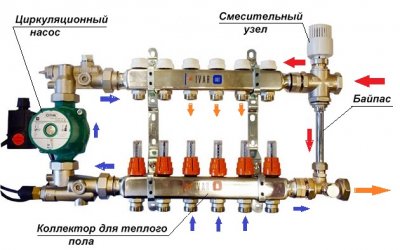
Bypass selection for heating
- It is recommended to shunt the radiator in a one-pipe system with a jumper in the form of a pipe section between the inlet and outlet to the radiator.
- The central heating pump, installed vertically on the boiler supply, is shunted by an automatic bypass with a differential (ball) valve on the supply pipe. The main manufacturer of differential valves is Invena (Poland).
- TsN, installed horizontally on the return line, is shunted with a bypass with a ball valve or with a check petal valve.
approximate cost
Approximate price of the device elements:
- differential (ball) valve 1 + 14 ″ Invena ZZ-10-025 - 500 rubles;
- horizontal petal valve Itap 1 + 14 ″ - 825 rubles;
- ball valve 1+14″ — 950 rub.
What you need for efficient battery life
An efficient heating system can save you money on fuel bills. Therefore, when designing it, decisions should be made carefully. After all, sometimes the advice of a neighbor in the country or a friend who recommends such a system as his is not at all suitable.
Sometimes there is no time to deal with these issues. In this case, it is better to turn to professionals who have been working in this field for more than 5 years and have grateful reviews.
Proper connection is guaranteed to ensure comfortable living in the house of all family members. After all, when choosing a scheme, you need to take into account a number of features of your home
Having decided to deal with the connection of heating radiators on your own, you need to take into account that the following indicators have a direct impact on their effectiveness:
- size and thermal power of heating devices;
- their location in the room;
- connection method.
The choice of heating appliances strikes the imagination of an inexperienced consumer. Among the offers are wall radiators made of various materials, floor and baseboard convectors. All of them have a different shape, size, level of heat transfer, type of connection. These characteristics must be taken into account when installing heating devices in the system.
Among the models of heating devices on the market, it is better to choose, focusing on the material and heat output indicated by the manufacturer
For each room, the number of radiators and their size will be different. It all depends on the area of the room, the level of insulation of the external walls of the building, the connection scheme, the heat output indicated by the manufacturer in the product passport.
Battery locations - under the window, between windows located at a fairly long distance from each other, along a blank wall or in the corner of a room, in the hallway, pantry, bathroom, in the entrances of apartment buildings.
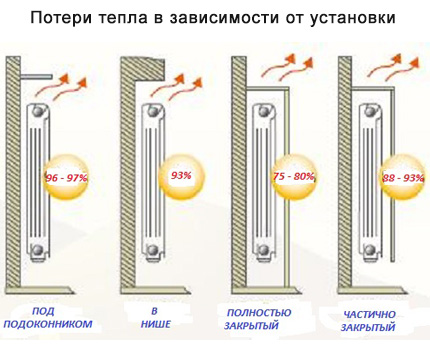
Depending on the place and method of installation of the heater, there will be different heat losses. The most unfortunate option - the radiator is completely closed by the screen
It is recommended to install a heat-reflecting screen between the wall and the heater. It can be made with your own hands, using for this one of the materials that reflect heat - penofol, isospan or another foil analogue. Also, you should follow these basic rules for installing the battery under the window:
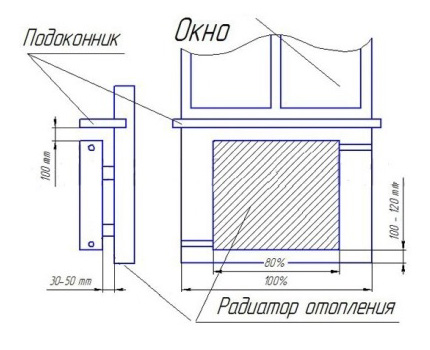
- all radiators in one room are located on the same level;
- convector fins in vertical position;
- the center of the heating equipment coincides with the center of the window or is 2 cm to the right (to the left);
- the length of the battery is not less than 75% of the length of the window itself;
- the distance to the window sill is at least 5 cm, to the floor - not less than 6 cm. The optimal distance is 10-12 cm.
The level of heat transfer from appliances and heat loss depends on the correct connection of radiators to the heating system in the house.
Having observed the basic norms for the placement of radiators, it is possible to prevent the penetration of cold into the room through the window as much as possible.
It happens that the owner of the dwelling is guided by the advice of a friend, but the result is not at all what was expected. Everything is done like his, but the batteries do not want to heat up. This means that the chosen connection scheme did not fit specifically for this house, the area of \u200b\u200bthe premises, the thermal power of the heating devices were not taken into account, or annoying errors were made during installation.
Types of heating systems
The amount of heat that a heating radiator will radiate depends not least on the type of heating system and the type of connection chosen. To choose the best option, you must first understand what kind of heating systems are and how they differ.
Single pipe
A single-pipe heating system is the most economical option in terms of installation costs.Therefore, it is this type of wiring that is preferred in multi-storey buildings, although in private such a system is far from uncommon. With such a scheme, the radiators are connected in series to the line and the coolant first passes through one heating part, then enters the second one, and so on. The output of the last radiator is connected to the input of the heating boiler or to the riser in high-rise buildings.
Example of a one-pipe system
The disadvantage of this wiring method is the impossibility of adjusting the heat transfer of radiators. By installing a regulator on any of the radiators, you will regulate the rest of the system. The second significant drawback is the different temperature of the coolant on different radiators. Those that are closer to the boiler heat up very well, those that are further away become colder. This is a consequence of the series connection of heating radiators.
Two-pipe wiring
A two-pipe heating system is distinguished by the fact that it has two pipelines - supply and return. Each radiator is connected to both, that is, it turns out that all radiators are connected to the system in parallel. This is good in that a coolant of the same temperature enters the inlet of each of them. The second positive point is that you can install a thermostat on each of the radiators and use it to change the amount of heat that it emits.
The disadvantage of such a system is that the number of pipes when distributing the system is almost twice as large. But the system can be easily balanced.
Multi-storey building heating system
The heating system of a multi-storey building is quite complex and its implementation is a very responsible event, the result of which will affect all the people in the building.
There are several schemes for heating multi-storey buildings, each of which has both its pros and cons:
- The single-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building is vertical - a reliable system, which makes it popular. In addition, its implementation requires less material costs, ease of installation, parts can be unified. Among the shortcomings, one can be noted, in the heating season there are periods when the air temperature outside rises, which means that less coolant enters the radiators (due to their overlap) and it leaves the system uncooled.
- The two-pipe heating system of a multi-storey building is vertical - this system allows you to directly save heat. If necessary, the thermostat closes, and the coolant will continue to flow into unregulated risers, which are located on the building's stairwells. Due to the fact that with such a scheme gravitational pressure arises in the riser, heating is often organized using the lower gasket of the distribution line.
- The two-pipe horizontal system is the most optimal both in terms of hydrodynamic and thermal performance. This system can be used in houses of various heights. Such a system allows you to effectively save heat, and is also less vulnerable even in cases that were not taken into account by the project. The only drawback is the high cost.
Before proceeding with installation work, it is necessary to design heating. As a rule, the design of the heating system of a multi-storey building is carried out at the design stage of the house itself. In the process of designing the heating system, calculations are made, and a multi-storey heating scheme is developed up to the location of pipes and heating devices. At the end of the work on the project, it goes through the stage of coordination and approval in state authorities.
As soon as the project is approved and all the necessary decisions are received, the stage of selection of equipment and materials, their purchase, and their delivery to the facility begins. At the facility, a team of installers is already starting installation work.
Our installers perform all work in compliance with all standards, as well as in strict accordance with the project documentation. At the final stage, the heating system of a multi-storey building is pressure tested and commissioning is carried out.
The heating system of a multi-storey building is of particular interest; it can be considered using the example of a standard five-story building. It is necessary to find out how heating and hot water supply functions in such a house.
Heating scheme for a two-story house.
The five-story house implies central heating. the house has a heating main input, there are water valves, there may be several heating units.
In most homes, the heating unit is locked, which is done to achieve security. Despite the fact that all this may seem very complicated, the heating system can be described in accessible words. The easiest way is to take a five-story building as an example.
The house heating scheme is as follows. Mud collectors are located after the water valves (there can be one mud collector). If the heating system is open, then after the mud collectors, through the tie-ins, there are valves that stand from processing and supply. The heating system is made in such a way that water, depending on the circumstances, could not be taken from the back of the house or from the supply. The thing is that the central heating system of an apartment building operates on water that is overheated, the water is supplied from the boiler house or from the CHP, its pressure is from 6 to 10 Kgf, and the water temperature reaches 1500 ° C. Water is in a liquid state even in very cold weather due to increased pressure, so it does not boil in the pipeline to form steam.
When the temperature is so high, the DHW is turned on from the back of the building, where the water temperature does not exceed 700 ° C. If the coolant temperature is low (this happens in spring and autumn), then this temperature cannot be sufficient for the normal functioning of the hot water supply, then the water for the hot water supply comes from the supply to the building.
Now you can disassemble the open heating system of such a house (this is called an open water intake), this scheme is one of the most common.
Heating scheme of a multi-storey building
Owning an apartment in the city is a luxury item. It is also comfort and coziness for its owners, since a city apartment is the most common place for living among modern citizens. It should be noted that an important role in creating a comfortable environment in such an apartment is a good heating system.
The heating scheme of a multi-storey building is a very important detail for any person.
In modern life, such a scheme has many design differences from conventional heating methods. Therefore, heating schemes for a three-story house and more guarantee effective heating of the walls even in the most unpredictable weather.
The principle of operation of the elevator unit
Heating boiler connection diagram.
Water that comes in and has high temperatures enters the elevator unit. It functions on the principle of an injector, only instead of air it uses water. A coolant with high pressure and temperature passes through the elevator nozzle, then the water from the return flows to the recirculation in the heating system. Thus, the temperature of the mixed water flow is obtained as it is in the batteries, and as for the excess water that has arrived, but has already cooled down, they go into the return line. According to experts, it is this heating system that is the most effective.
The heating unit has valves for heating an apartment building (the scheme can be different, only the entrance can be used). Such a system is possible when a collector is installed, it has several valves. And at the entrance to the house, the location of the heat meter is possible, it can be on the house or on a separate entrance.
Coolant circulation methods
As you know, water, and usually it is poured into the heating system, can circulate by force or naturally. The first option involves the use of a special water pump that pushes water through the system. Naturally, this element is included in the overall heating circuit. And it is installed in most cases either near the heating boiler, or is already its structural element.
The system with natural circulation is very relevant in places where there are frequent power outages. The circuit does not provide for a pump, and the heating boiler itself is non-volatile. Water moves through the system due to the fact that a cold coolant is displaced by a heated column of water. How the connection of radiators will be implemented under such circumstances depends on many factors, including the need to take into account the peculiarities of the passage of the heating main and its length.
So, let's look at these options in more detail.
Method number 1 - one-way connection
Such a battery connection involves the installation of a supply pipe (supply) and a discharge pipe (return) to the same section of the radiator:
Thus, uniform heating of all sections of each individual battery is ensured. A one-way heating system is a rational solution in one-story houses if it is planned to install radiators with a large number of sections (about 15). However, if the accordion has more sections, then there will be significant heat loss, which means it is worth considering another connection option.
Method number 2 - bottom and saddle connection
Actual in those systems where the heating pipeline is hidden under the floor. In this case, both the coolant inlet pipe and the outlet pipe are mounted to the lower branch pipes of the opposite sections. In such a connection of batteries, the "weak" point is low efficiency, since in percentage terms, heat loss can reach 15%. Logically, the radiators heat up unevenly in the upper part.
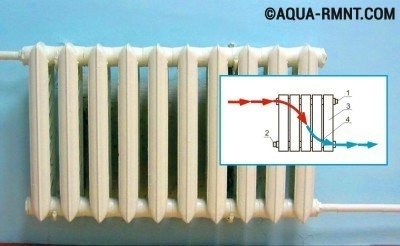
Method number 3 - cross (diagonal) connection
This option is designed to connect batteries with a large number of sections to the heating system. Thanks to a special design, the coolant is evenly distributed inside the radiator, which ensures maximum heat transfer.
The answer to the question of how to properly connect the heating battery in such a situation is extremely simple: the supply is from above, the return is from below, but from different sides. With a diagonal connection of radiators, heat loss does not exceed 2%.
We tried to reveal the topic of possible schemes for connecting heating radiators in as much detail as possible. We hope you will be able to evaluate all the pros and cons of each of the described options, and choose the most relevant in your particular case.
Varieties of bypasses
There are several types of bypasses for use in heating systems.
Unregulated
It is carried out in the form of a bypass jumper. There is no shut-off and control valve (faucet or check valve) on the jumper.
Operating principle
- Part of the hot HP that has passed through the bypass is mixed with the flow at the battery outlet and increases the temperature of the HP entering the next battery.
- When the heater fails, the HP flow bypasses the battery, while maintaining circulation.
Peculiarities
- With vertical wiring, the bypass diameter is one step smaller than the diameter of the supply pipes.
- With horizontal wiring, the bypass in diameter coincides with the supply pipe, and the diameter of the outlets up the battery is one step smaller (the heated HP tends upwards).
- Install as close as possible to the battery (next to the shut-off valves).
Manually controlled: what is it
For manual regulation of the HP flow through the bypass, either a ball valve is installed on it to shut off, or a three-way valve is installed at the intersection of the bypass and the supply pipe to the radiator.
Operating principle
The three-way valve has three positions:
- closes the bypass and directs the entire HP flow to the radiator;
- blocks the supply to the radiator and opens the bypass for the HP flow (position for repair or replacement of the radiator);
- opens both ways for the HP: to the battery and along the bypass.
Peculiarities
- A tap on the bypass next to the battery is usually installed in order to close the jumper with a poorly heating radiator. But such a solution is technically illiterate - the flow through the bypass is approximately equal to the flow through one section of the radiator, so there will be no significant increase in battery temperature.
- In a private house, a ball valve is installed in parallel with the central heating on the return pipe. The valve is closed when the pump is running, and is opened manually when the pump fails or when it is replaced to restore circulation.
Attention! In an apartment building with a one-pipe system, it is forbidden to install a tap on the radiator bypass. It can lead to disruption of circulation and low temperature of the coolant entering neighboring apartments.
Automatic as it works with a pump
It is installed in parallel with the central heating. A non-return valve is mounted on the shunt pipe to automatically restore circulation through the bypass when the central pump is stopped.
Operating principle
A bypass with a differential (ball) valve is installed in parallel with the central heating on a vertical pipe for supplying coolant from the boiler.
When the pump is running, part of the flow presses the rubber ball against the funnel and closes the HP passage through the shunt pipeline.
When the pump is turned off, the ball rises under the pressure of the HP flow through the supply pipe and opens the passage for the HP bypass.
A bypass with a flap check valve is installed parallel to the pump on a horizontal return pipe (in a gravity system). The shutter (petal) of the valve is pressed against the seal under the action of the flow from the pump, closing the bypass. When the pump stops, the petal moves away from the seal (opens) under the action of the hydraulic return pressure, restoring circulation.
Important! It is required to periodically check the operation of the check valve so that it does not become clogged with deposits and dirt. The check valve is usually mounted on the main pipe (supply or return)
Branches from the main pipe to the central valve are made two sizes smaller in diameter
The check valve is usually mounted on the main pipe (supply or return). Branches from the main pipe to the central valve are made two sizes smaller in diameter.