Level detection
Before any work on the site, you should find out what is the depth of the water, this can be done independently, without even using special technical devices.
Observation
One way to find out the groundwater level in any area is to observe the vegetation. In particular, the grass is of interest, if it is green and juicy even during the dry periods of summer, then this indicates a high level. This is also indicated by a foggy haze over the site.
Another thing is plants that grow well on the site, if they are moisture-loving and at the same time grow violently, then this speaks for itself.
Examples of such indicator plants include:
- Reeds - occurrence from 1 to 3 meters.
- Wormwood - if it grows rapidly and occupies large areas - this indicates a groundwater level - 3-5 m.
- Nettle - water at a level of 2-3 meters.
- Currant, sea buckthorn, gooseberry - 1-2 meters.
- Willow loves water very much, so if it grows on the site, this indicates a level of less than 1 meter.
The easy way
The easiest way is to look at the depth of the well, if there is one on the site. The water level in it is the desired parameter. But this method, how to determine the level of groundwater on the site, can not always be applied.
Modern Method
Determining the groundwater level using this method will require some tools, namely:
- Garden drill from 2 m long, more is better.
- A long metal rod with a depth indication in centimeters.
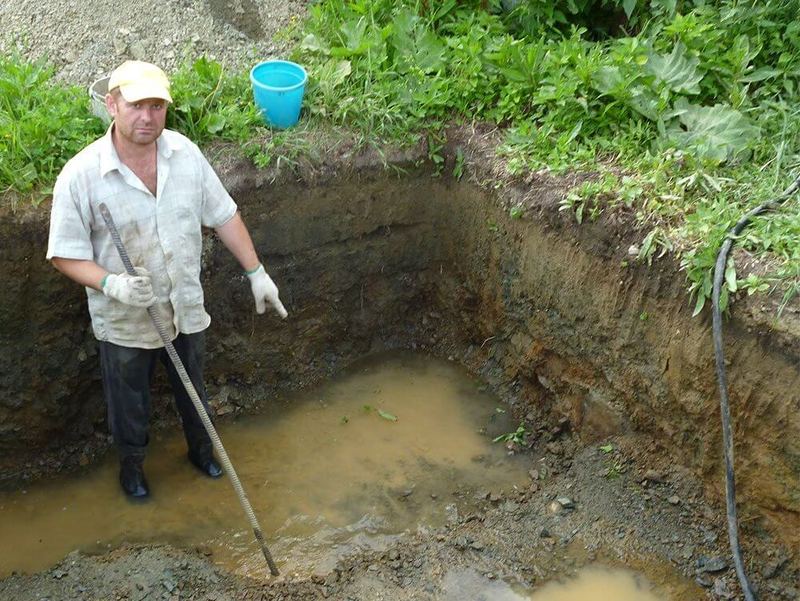
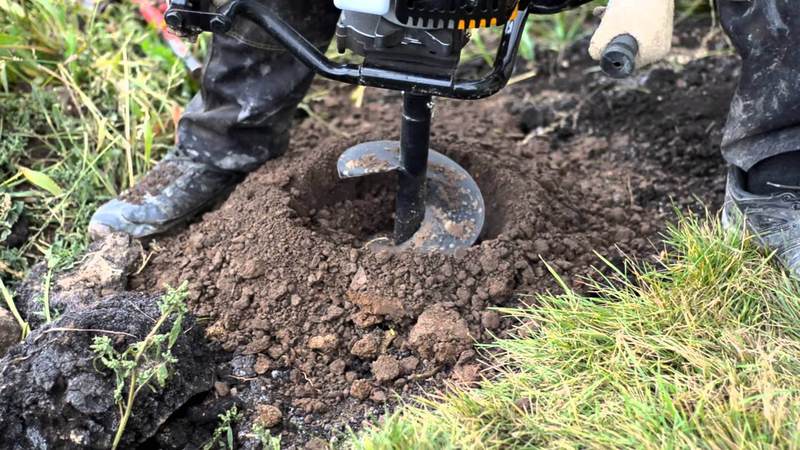
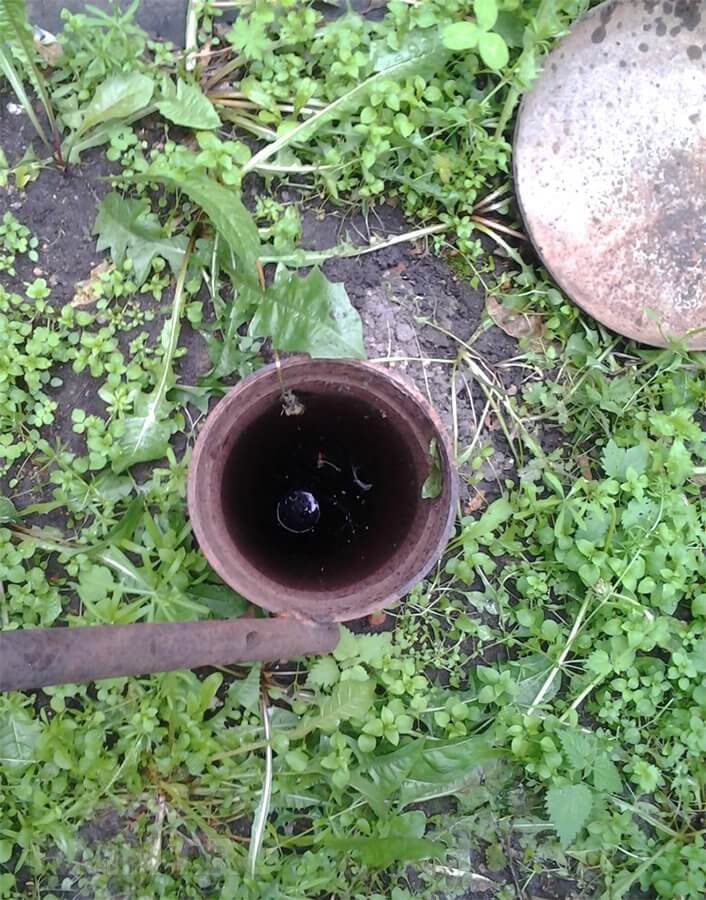
The work is extremely simple - you need to drill a hole to the maximum depth of the drill, preferably at 3-4 points on the site. Leave them for a day, during this period moisture will gather inside. All that remains is to lower the rod with marks into the holes, the wet mark will be the starting number, with which you need to make simple calculations in the future.
- Pit depth 200 cm.
- The rod became wet at around 20 cm.
- Result = 200 - 20 = 180 cm.
The level should be checked 2-3 days in a row, if the measurements remain the same, then this is the desired parameter.
What is UGV
The groundwater level is the depth at which a layer of permeable rock is completely saturated with water. GWL fluctuates regularly, as the amount of moisture changes in the upper layers of the soil. During long dry periods, it evaporates, and when the snow melts, or during the rainy season, it quickly accumulates.
As a result, the groundwater level rises or falls. Moreover, these waters reach their maximum level during the rapid melting of snow, rainy autumn, when due to cool weather, moisture almost does not evaporate, unlike summer, when rains alternate with hot days.
Determination of GWL is required in different cases
If we are talking about construction or planting fruit trees, then it is important to know to what underground level the groundwater rises when the soil is most saturated with moisture and how to deal with groundwater on the site
In the case of arranging a well, other information is required - it is necessary to determine to what minimum the level drops, so that in dry times you will not be left without water in the source.
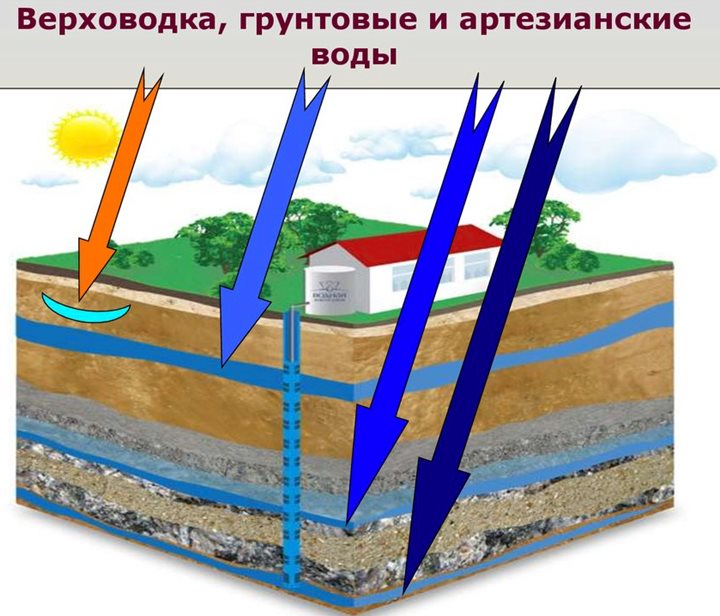
The groundwater level is very dependent on the climate and geological features of the area. In the southern regions it is much lower than in the northern ones. There are different types of groundwater:
- Upper water - the depth of occurrence is from 1.5 to 2.5 m, in dry weather they can dry out.
- Non-pressure - a layer formed above the first waterproof layer of different rocks.
- Artesian - are located in the thickness of the soil between two impermeable mountain strata.
Why do we need information about the GWL on the site
Data on the depth of water is very important for the owner of the land, if it is planned to build some buildings, plant shrubs and trees. He must know how to lower the groundwater level on the site.
Building
The choice of foundation, the depth of its occurrence, the option of waterproofing, as well as the principles of arranging drainage depend on the level of groundwater.An improperly laid foundation will quickly collapse due to too uneven subsidence on the ground, which is strongly eroded when the upper waters rise. This will lead to the destruction of the entire structure.
The high level of groundwater makes it impossible to build a cellar or basement, an inspection hole for a car in a garage, since the building is threatened with flooding in autumn and spring. Therefore, it is impossible to do without lowering and diverting the water level. Waterproofing and drainage, which can protect the structure, require quite a lot of money and do not provide a guarantee.
Gardening and horticulture
Waterlogging is very detrimental to the root system of fruit shrubs and trees. Before laying out a garden, you need to make sure that at the maximum rise the water is located at a depth of more than 1.5 m.
Flooding by spring floods also has a bad effect on the cultivation of various cultivated plants in the beds. Therefore, it is necessary to lower the level of groundwater here.
Water supply
The possibility of installing a water source on the site for household needs and drinking, as well as the choice between a well and a well, completely depends on the level at which the water-bearing layer lies.
Local water supply, sewerage
The depth of the cesspool, as well as the possibility of arranging and locating a filter well or trenches, filtration fields, according to sanitary standards, directly depend on the GWL.
Inspection of vegetation on the site
An experienced gardener at a glance at the site can determine whether there is groundwater near the surface of the earth.
If the site is already planted, then pay attention to the presence and condition of mature trees. Large apple trees, for example, will not be able to survive with surface water, they will simply “choke”
If the land allotment is still empty, the following list of “settlers” should alert you:
- cattail (distance from the surface to the water is less than 1 m);
- reeds, horsetail, willow, alder, meadowsweet (from 1.5 to 3 m);
- wormwood, licorice (up to 5 m).
Also, the fact that water is close can also be indicated by plants that are tilted to one side, but growing not next to each other. However, it can also be a sign of strong winds, so you should not focus only on this sign.
Groundwater protection
The geological situation in any area changes over time, and if the GWL began to rise (which can happen even on solid rocky soils), several methods can be applied to help facilitate groundwater drainage:
- Make a "living fence" of trees or tall shrubs on the site. Trees should have a high and wide crown so that moisture evaporates faster. Of shrubs and low trees, wild rose hips, willow, hawthorn, spirea, elder or sea buckthorn are excellent;
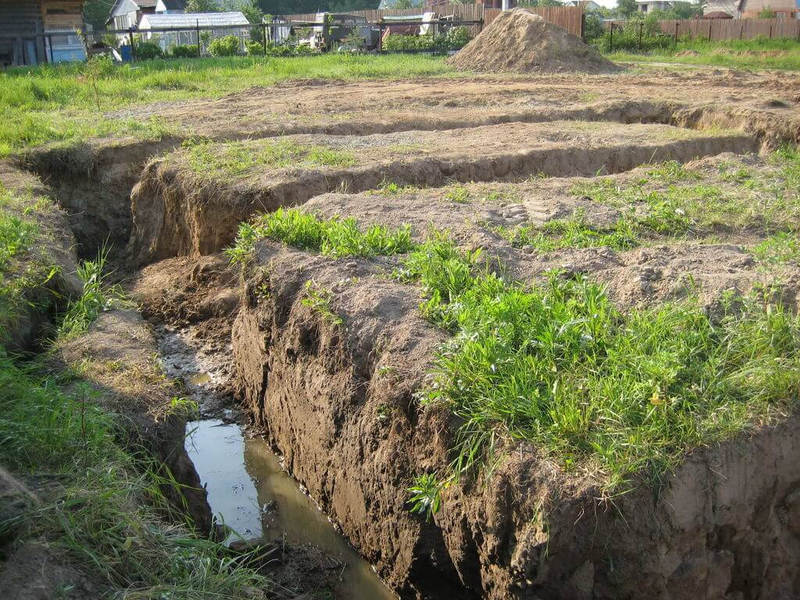
- Open drainage system pipeless ditches ≥ 0.7 m deep, the bottom of which is covered with sand, compacted and covered with a layer of rubble. Such drainage drains groundwater all year round, but it must be done taking into account the slope of the area several times a year to clean it from debris and siltation;
- Closed drainage systems, even deep ones, look like the same trenches, but deepened to 1,502 meters and covered with geotextile after laying a sand and gravel cushion. Perforated pipes (preferably plastic) are laid in the trenches;
- A drainage well is dug at the lowest point of the site, drainage ditches (trenches) are brought to it;
- Another way of dewatering is wellpoint equipment. This is an industrial product, which is a pipe with a needle filter, pumps and a vacuum manifold;
- The forced pumping system for excess deeper groundwater includes several deep wells, the location of which is calculated according to the conditions of the site.The system has a group of centrifugal water pumps that pump groundwater to the surface with their subsequent discharge into a drainage well (item No. 4) or a drainage system (item No. 2,3).
- Vacuum dewatering equipment is usually used when soil permeability is low. The device consists of a group of tanks in which low pressure is created, and due to the difference in pressure, water rises from the drainage system into these tanks.

https://youtube.com/watch?v=Y0OPmAChOJk
It is necessary to pump out layers of groundwater in compliance with measures to protect sources of drinking water: a caisson is installed in wells from concrete or asbestos-cement rings, external and internal waterproofing of the walls of the structure is equipped in wells. For example, the installation of concrete rings should be accompanied by their coating with hot bitumen or tar.

Conclusions: based on the existing technologies for determining the GWL on the site, building a house with a depth of water layers ≤ 2.5 meters, even on a layer of hard rocky rocks, is not recommended. Otherwise, it is necessary to build an extensive drainage system with water diversion outside the site, as well as to ensure the constant year-round performance of this system.
Other ways to determine
One of the easiest ways is to contact the land management service, where they can provide specific data, or at least topographic maps, by which you can determine the highs and lows. By the way, in this regard, you can make independent observations. Take a look around and evaluate whether the area is on a hill or in a lowland. The lower the level, the more likely it is that groundwater will be close.

In the case when there is a well nearby, then the level can approximately be estimated from it. To do this, just look into the middle, lower the measuring cord to the water mirror, then measure the distance. But the value will be approximate if the source is filled with an underground river, which can slightly raise this value due to the current. Also, this will not talk about the saturation of the soil specifically in your area.
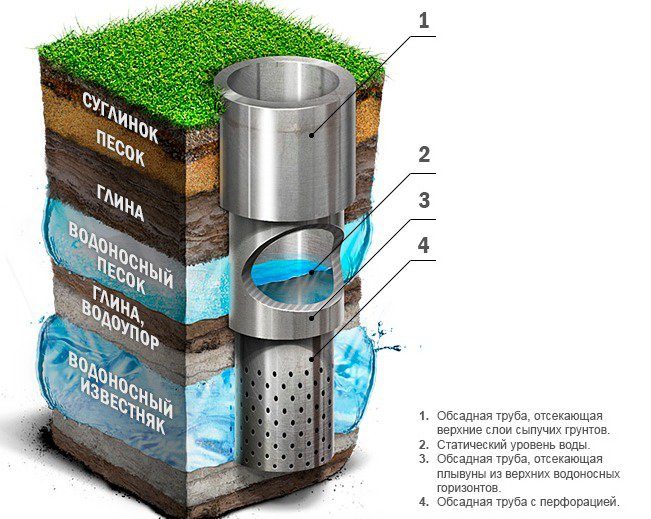
water wells
Wells for water.
To take water from horizons located close to the earth's surface, they dig an open mine working - a pit, it is called a well.
Wood is no longer used for fastening walls: reinforced concrete rings with a diameter of 1-1.5 m have replaced oak and larch crowns from use. To get to drinking water, you need a pit up to 15 m deep.
Water intake tunneling technology:
- Choose a place under the well, lay the first ring on it.
- Excavate the soil inside the contour until the top of the concrete element is level with the soil.
- Install the second cylinder on the dug-in block, repeat the operation. Dig in subsequent links in the same order.
- Pump out the water that has appeared with a submersible pump and continue installing the rings until the intended level of the aquifer is reached.
- Attach a cap to the well shaft. The structure consists of the last concrete element, which does not need to be buried, and the first ring in the ground.
- Dig around the mouth of the pit with a ditch 60 cm wide to a depth of 1 m, fill with clay and tamp. Pour a sandy blind area over the clay castle.
- Close the cap with a lid to prevent debris from getting inside the water intake.
If it was not possible to reach the interstratal horizon, then it is possible to use well water as drinking water after filtration and boiling. The main advantage of the well is the accumulation of moisture, which reduces the dependence of the flow rate on precipitation. The supply of water in the amount of 2-3 m³ is constantly present in the source.
Flaws
It is possible to build a concrete water source on any land plot owned by a citizen, without issuing permits. The technology for erecting a water intake is simple and available for independent execution.
The disadvantages of arranging a well include:
- the complexity of earthworks;
- the threat of being left without water during dry periods;
- the need to isolate the joints to prevent the top water from getting inside the well;
- obligatory periodic cleaning of the filtration layer at the bottom of the mine.
It is impossible to build a drinking water intake in wetlands and areas flooded during the flood period. This option carries the risk of bacteria entering the water source.
Artesian well
Scheme of an artesian well.
The name of this type of workings comes from the French language - from the place where the first flowing well was drilled: the province of Artois. The large length of the shaft and the solid rocks of the soil crossed on the way to the aquifer require the use of powerful drilling rigs - the auger method will not work.
The construction of the working is preceded by the stage of documentation. Drilling an artesian well is not a licensed activity, but in order to use water from it, many permits and approvals must be issued, including obtaining a license for subsoil use. The process is long and costly.
The main stages: agreement on the location of the site and well, geological survey project, registration of a license for exploration, drilling, drawing up a report and putting reserves on the state balance sheet.
Artesian wells are divided into 4 types:
- A double-cased development - a perforated pipe is mounted in the lower part of the column in the aquifer and a pump is placed in it, the other half is installed on top, reaching the limestone layer. Through the holes in the lower link, water enters the pipe and is pumped out at the mouth with a pump. Used when reservoir pressure is low.
- A water well with a transition is arranged with a variable geological section. 3 casing pipes are mounted - large diameter in the upper part, medium - in stones and sands, small - directly in the productive layer. Used for good water supply.
- The well is classical - with one casing pipe for normal conditions.
- A barrel with a conductor - from 2 casings: in the upper and lower parts.
Drilling technology is complex. The construction of an artesian water intake is carried out by specialized organizations.
Advantages
Advantages of an artesian well.
The main advantages of an artesian well are the remoteness of the water intake from the surface and the occurrence of water in porous limestone, excluding the presence of mechanical impurities in the liquid. This allows you to pump out an underground resource without installing a strainer at the bottom.
As a result, other advantages of artesian wells appear:
- ecological purity of water;
- independence from climatic and weather conditions;
- uninterrupted water supply: groundwater reserves are confirmed by geological surveys.
The source remains inexhaustible for ≥50 years. In this case, you do not need to spend money on periodic filter cleaning: there is none.
Flaws
Associated with costs at the stage of organization of construction and drilling of deep workings. The duration of the period from designing to obtaining a passport for an artesian well is 2 years.
It will not be possible to build a water intake in a limited area: the minimum area for a drilling rig is 6x9 m. The water contains mineral formations acquired during filtration through the soil, and is hard.
How to independently determine the level of groundwater on the site in bookmarks 10
The level of groundwater is a very important factor in the first place when building a house
You should definitely pay attention to this indicator when choosing the type of foundation, planning the arrangement of the basement and basement. The groundwater level, abbreviated GWL, is also important for gardeners
So how do you determine the level of groundwater?
There are three types of groundwater:
- Artesian waters. The lowest and cleanest layer, during construction, usually does not cause any trouble, as it is located at a great depth.
- Unpressurised waters. Soil, located above the artesian, on a waterproof layer. Can be formed in case of filtration of surface water, the level depends on precipitation. The depth of this layer does not change, since there is no pressure, hence the name.
- Verkhovodka. The depth of this layer is only a few meters; during drought and severe frosts in winter, it can disappear altogether. Basically, perched water appears on loamy or clayey areas, and is usually absent on slopes.
Important! The groundwater level should be measured in autumn or spring, immediately after snow melts and heavy rains. In winter, in frosts, the water level underground will be minimal and you will not get an accurate picture
As in summer, after prolonged heat and drought. As experienced builders say, it is better to prepare for the worst and measure the really highest level of groundwater in your area during a period when there is a lot of precipitation.
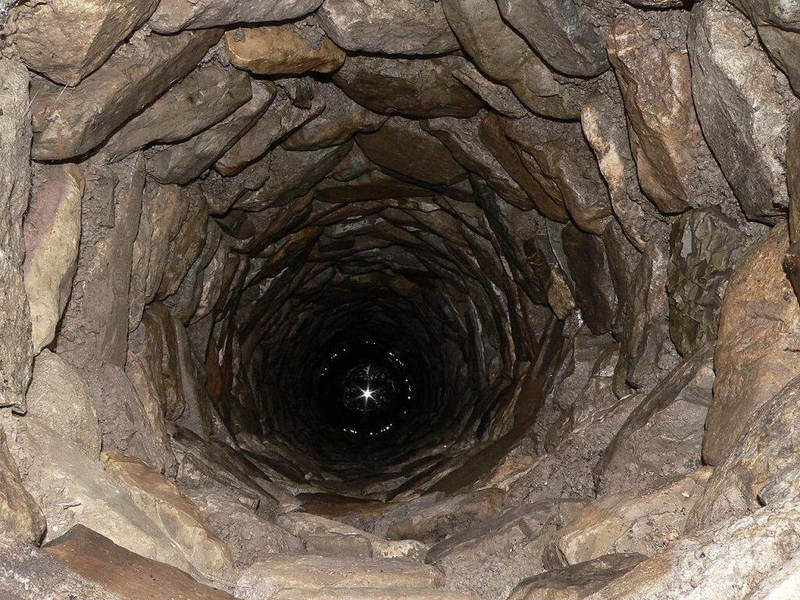
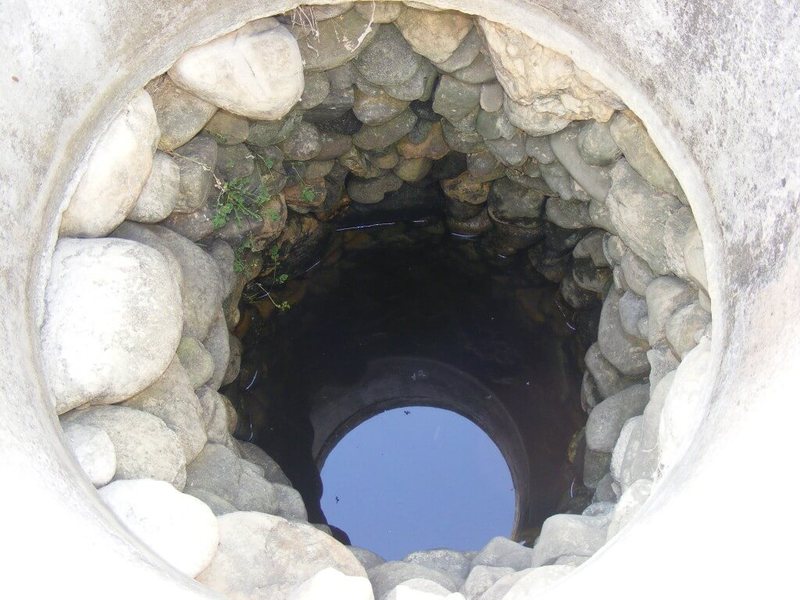
A simple, but at the same time quite reliable way to determine how deep the groundwater lies is to use a well. Look at these two pictures and you will immediately understand where the groundwater has gone deep and where it is closer to the surface. For accuracy, you can measure the depth to the surface of the water in the well using a coil of rope, a construction tape measure and weight, it's simple. It is best to inspect several nearby wells, walk around the neighbors, study the water level for several days.
If there are simply no wells in your and neighboring areas, well, it is advisable to use a construction drill. Several wells should be drilled at once with a depth of at least two or three meters along the perimeter of the future construction site and garden
Pay special attention to low-lying areas, because it is there that the groundwater layer usually rises the highest.
The wells will also have to be monitored for several days to find out whether the waters have risen, how high, how their level changes. The wells remained empty - calm down, build calmly, most likely, groundwater will not interfere with you while living in a new house.
Experienced summer residents who are accustomed to trusting popular, proven signs often do not need to look into a well or drill wells to find out how deep the groundwater is. Plants available on the site can tell about this. If you have cattail growing, then it is no more than a meter to groundwater, reeds - up to three meters, licorice - from one and a half to five meters, and if wormwood - from three to five meters.
Willows, currants, alder, meadowsweet grow well in wet areas.
If several trees on the site have a slope in one direction - this is also a sign of a high level of the aquifer, you need to pay attention to this
In areas with high groundwater, fogs are not uncommon in the evenings, even if there is no reservoir nearby. Close groundwater may also be indicated by frequent dew in the morning. In wet areas, there are also usually many small flies and mosquitoes, but there are no mouse holes and anthills.
There is also such an old, fairly reliable and proven over the years method for determining GWL. You need to take a very fresh egg, preferably just laid. The top layer is removed from the ground, a piece of wool is placed, an egg is placed on top of it, and then everything is covered with a clay pot. After they fall asleep with previously cleaned earth. The very next day, the pot is torn off and lifted. If the wool has become wet, and the egg is dry, the groundwater is deep.If everything is dry, there is no water at all. But if dew has formed on the egg, you have groundwater close to the surface.
Do not believe folk methods and want to get the most accurate indicators of the level of groundwater and the condition of the site in general? Order geological surveys, contact professionals.
Methods of determination
In many villages and towns, pumps and wells are still used. To extract this water, the depth of occurrence is checked. Professional workers who have special technical devices, for example, a surveyor, will help to learn it, without which this work will be carried out many times longer and harder.
Ordinary local residents can do this without the help of professionals - on their own. There are several simple ways to check the depth of groundwater.
Plants
Our beloved flora is a good way to find out if there is water nearby. To begin with, you should carefully look around, see the area for the presence of plants, determine their type. For example, reeds growing on the site indicate that the depth here is from 1 to 3 meters, cattail - 1 meter, wormwood - 3-5, and licorice - no more than 5.
If the water is not so deep, then the grass will be very bright and saturated in color, and if it is deep, vice versa. The soil filled with moisture and precipitation can be recognized by currants growing on it, other plants and berries. Many also estimate the humidity from the trees growing nearby. If more than three trees are tilted to one side, then we can safely say that there is a high aquifer under them.
Vine
It's never a failing way. A vine is a branch with a fork at the end. In a place where there is water, it will definitely tremble. Many prefer a wire arrow to the vine.
Ring
A simple and uncomplicated device is the so-called ring. You can get this device: for this you need 4 nails of 200 mm each, a battery designed for a flashlight, a wire, a voltmeter. On top of the desired area, it is necessary to hammer 2 nails with a certain interval. Next, attach the battery. This is done using wire.
Not forgetting the nails, two more are driven in, to which a voltmeter is subsequently attached. In an area with groundwater, the electrical conductivity will increase. In addition to the above, there are many other methods of determination. But these are the most economical.
You can also use a method that helps solve this problem by examining the nearby area, namely: inspect for the presence of wells. Every well has a concrete footprint at the bottom, and every villager has a drill at home. So, at the bottom of the well, you can create a well using this drill, and then observe how long the water will begin to ooze.
Rising water levels indicate that the level of this groundwater increases after rainy weather. If there is no water, then there will be no problems during construction and should not be.
We dive
The main difficulty in the development of the oceans is pressure: for every 10 m of depth, it increases by one more atmosphere. When the count reaches thousands of meters and hundreds of atmospheres, everything changes. Liquids flow differently, gases behave unusually... Devices capable of withstanding these conditions remain a piece product, and even the most modern submarines are not designed for such pressure. The maximum diving depth of the latest nuclear submarines of project 955 "Borey" is only 480 m.
Divers descending hundreds of meters are respectfully called aquanauts, comparing them with space explorers. But the abyss of the seas is in its own way more dangerous than the cosmic vacuum. If it happens that the crew working on the ISS will be able to transfer to the docked spacecraft and in a few hours will be on the surface of the Earth. This path is closed to divers: it may take weeks to evacuate from the depths.And this term cannot be reduced under any circumstances.
However, there is an alternative way to the depth. Instead of creating more and more durable hulls, you can send there ... live divers. The pressure record endured by the testers in the laboratory is almost twice the capacity of the submarines. There is nothing incredible here: the cells of all living organisms are filled with the same water, which freely transfers pressure in all directions.
The cells do not resist the water column, like the solid hulls of submarines, they compensate for the external pressure with the internal one. No wonder the inhabitants of the "black smokers", including roundworms and shrimps, feel great at many kilometers deep of the ocean floor. Some types of bacteria tolerate well even thousands of atmospheres. Man is no exception here - with the only difference that he needs air.
Technologies
The first flight of the Seraph electric air taxi: video
Groundwater control

If it so happened that the situation in your area has changed dramatically and for some reason groundwater has begun to rise closer to the surface, there are several ways to help partially alleviate the situation:
- Organizing a hedge. To do this, you need to choose plants that are very fond of moisture and have a wide crown, which will contribute to a sufficient level of evaporation. For example, you can use wild rose, hawthorn, spirea, willow, sea buckthorn, elderberry. By organizing a small garden, you can significantly reduce the level of flooding.
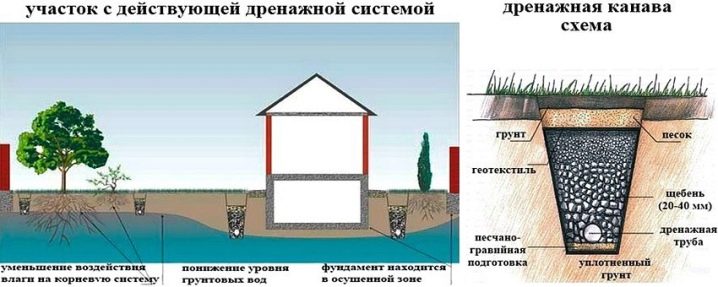
- Open drainage system Open drainage system. A trench is dug around the perimeter of the site. Its depth must be at least 70 cm. In some cases, you will need to go deeper. Everything will depend on what level the top water is at. The bottom is rammed and covered with sand, which is also well compacted. Its layer should reach at least 10 cm. Small gravel is laid in the same layer. Excess moisture will go into this drain. You can take it out as far as possible from the territory. The disadvantage of this solution is the need for constant cleaning of the channels so that they do not become swamped.
- Closed drainage system. The trenches are prepared in the same way as described for the previous case, but it will take up to 1.5–2 m to go deeper. Geotextiles are laid on the sand and gravel cushion. Holes are made in a plastic or other pipe with a diameter of 200 mm or more to make it perforated. The pipes are lowered into the trench and again covered with geotextile. From above, everything is covered with soil.
- The well will help to some extent to solve the difficulty. To do this, it will be necessary to select the lowest point on the site and dig a well of the maximum possible depth. All water will be collected there.
- Wellpoint installation Well filter installation. It is a commercial product. This is a pipe with a wellpoint at the end. It is connected to a vacuum manifold and a pump. Water is pumped out automatically.
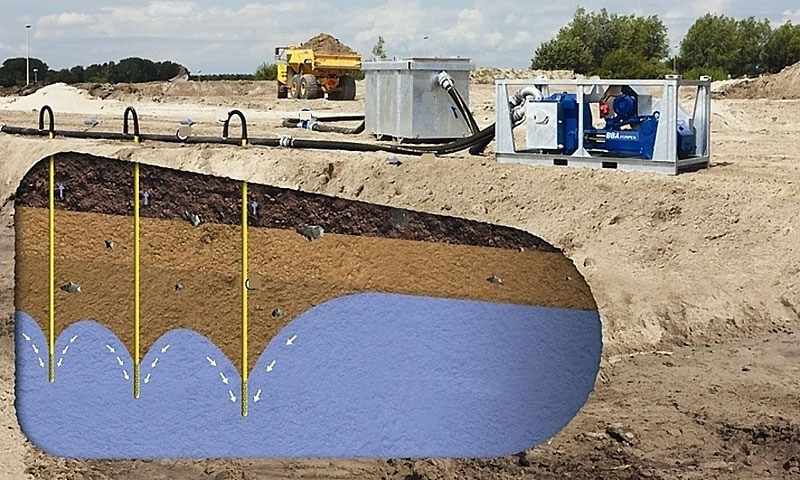
- Forced release. For these purposes, several wells are drilled in certain places to the aquifer. Centrifugal pumps are installed in the middle, which pump liquid to the surface. Then it is discharged into the sewer or drainage system.
- Vacuum installation. It is used in cases where the permeability of the soil is low. Tanks are installed on the surface. A rarefied pressure is created in them, which causes the water to rise in them. Withdrawal is carried out as in the previous case.
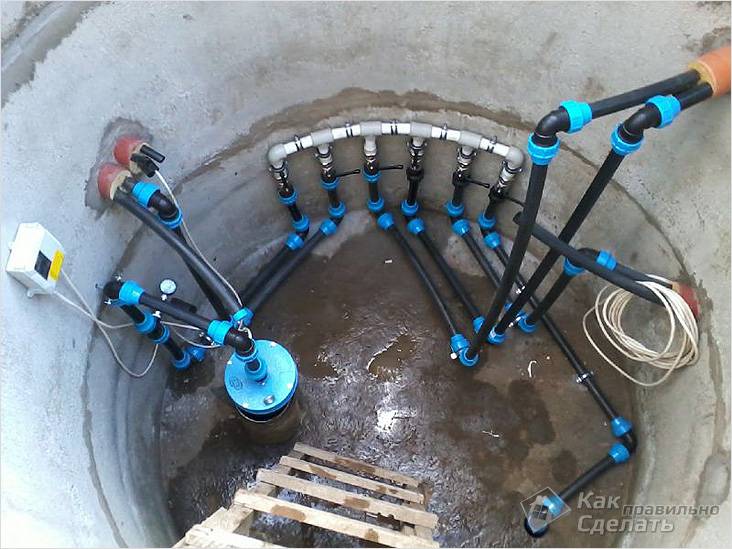

When raising groundwater, it is important to take care to protect sources of clean drinking water. For wells, a caisson installation is used
Land works are being carried out to the lower level of the water-resistant layer.A design is installed that will cut off the ingress of unwanted liquid inside. For wells, the method of external and internal waterproofing is used. A trench is dug around the perimeter and the rings are processed with a special compound.
Now you know the main methods using which you can roughly determine the level of groundwater. If they are at a depth of less than 2.5 meters, then construction on such a site is undesirable.
Level detection
Before any work on the site, you should find out what is the depth of the water, this can be done independently, without even using special technical devices.
Observation
One way to find out the groundwater level in any area is to observe the vegetation. In particular, the grass is of interest, if it is green and juicy even during the dry periods of summer, then this indicates a high level. This is also indicated by a foggy haze over the site.
Another thing is plants that grow well on the site, if they are moisture-loving and at the same time grow violently, then this speaks for itself.
Examples of such indicator plants include:
- Reeds - occurrence from 1 to 3 meters.
- Wormwood - if it grows rapidly and occupies large areas - this indicates a groundwater level - 3-5 m.
- Nettle - water at a level of 2-3 meters.
- Currant, sea buckthorn, gooseberry - 1-2 meters.
- Willow loves water very much, so if it grows on the site, this indicates a level of less than 1 meter.

The easy way
The easiest way is to look at the depth of the well, if there is one on the site. The water level in it is the desired parameter. But this method, how to determine the level of groundwater on the site, can not always be applied.
Modern Method
Determining the groundwater level using this method will require some tools, namely:
- Garden drill from 2 m long, more is better.
- A long metal rod with a depth indication in centimeters.
The work is extremely simple - you need to drill a hole to the maximum depth of the drill, preferably at 3-4 points on the site. Leave them for a day, during this period moisture will gather inside. All that remains is to lower the rod with marks into the holes, the wet mark will be the starting number, with which you need to make simple calculations in the future.

Algorithm:
- Pit depth 200 cm.
- The rod became wet at around 20 cm.
- Result = 200 - 20 = 180 cm.
The level should be checked 2-3 days in a row, if the measurements remain the same, then this is the desired parameter.
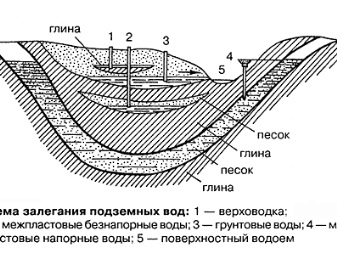
Features and types of GW
The thickness of their reservoir is relatively small, and the depth is usually no more than 3 meters. The layers are separated by a stone layer.
At the moment, there are several types of groundwater.
- Upper waters. This species is usually found at shallow depths, and it is able to disappear in very cold or very hot weather, that is, it changes throughout the year.
- Non-pressure layer of water. This water layer depends on the precipitation. It can be both high and low. The depth does not change, there is no pressure. They are able to slow down construction work, they depend on each other directly.
- Artesian ground currents. They are located between water-resistant soil layers.
Second sandy horizon
Alluvial soils, consisting of a mixture of sand and water-resistant clays, can serve as a substrate for the upper layer of groundwater. Usually this layer is not thick and has low water permeability.
The main water exchange with the upper layer occurs through fracture zones and faults with a predominance of fine sands. The filtering capabilities of such a layer are limited and depend on its thickness and composition. Therefore, testing the water from it in the Vodokanal laboratory is mandatory.
The water in the layer can be backed up, that is, it is under pressure in it, which is due to the excess of neighboring levels above the intake point on the site.
The amount of groundwater that can be supplied by the second layer is from 7 to 30 meters. Moreover, the more water is taken from a greater depth, the more likely it is that there will be sufficiently clean drinking life-giving moisture in the well, which is quite suitable for use in the country after boiling.
It is even possible to drill to such a depth manually, and the option of a well flowing with water supported by the internal pressure of the aquifer is not ruled out. The choice is yours, but professionals will do it better.
A typical representative of water intake devices on such aquifers is a well - a well or a trunk of medium diameters (108 - 168 mm). Such water intakes in the country are subject to licensing and must be under constant state control.
Drilling method
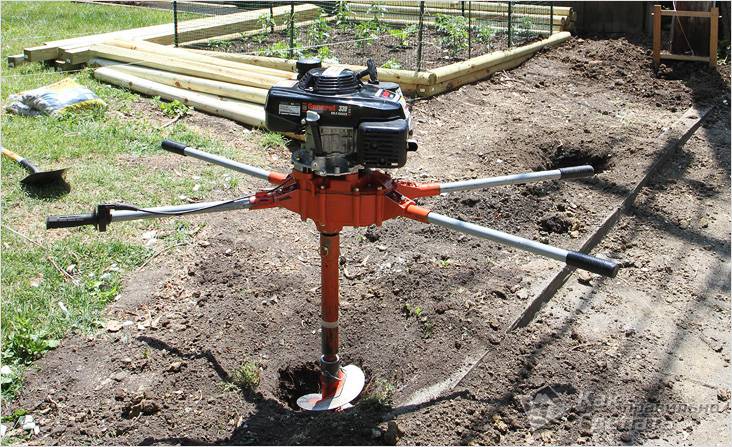

One of the modern and simple ways to determine the level of occurrence of perched water is carried out using a conventional hand drill. The fact is that if the reservoir is deeper than 2 meters, then there is nothing to worry about and you can safely carry out construction. A garden drill machine perfectly breaks through such a distance. For work you will need:
- spoon drill;
- metal or other straight rod;
- roulette.
With everything you need, a small well is drilled
It is important to go deeper than 2 meters. When performing work, it will be necessary to remove the soil in a timely manner so that it does not crumble
After reaching the required depth, cover the hole and leave it in this state for a day. The rod is marked with a tape measure. You can choose the step that is convenient for you personally. It sinks to the bottom, is removed and a visual assessment of the liquid is made. These actions should be repeated for several days. If the indicators do not change, then the value can be considered constant.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=6fEh5sKPTp8